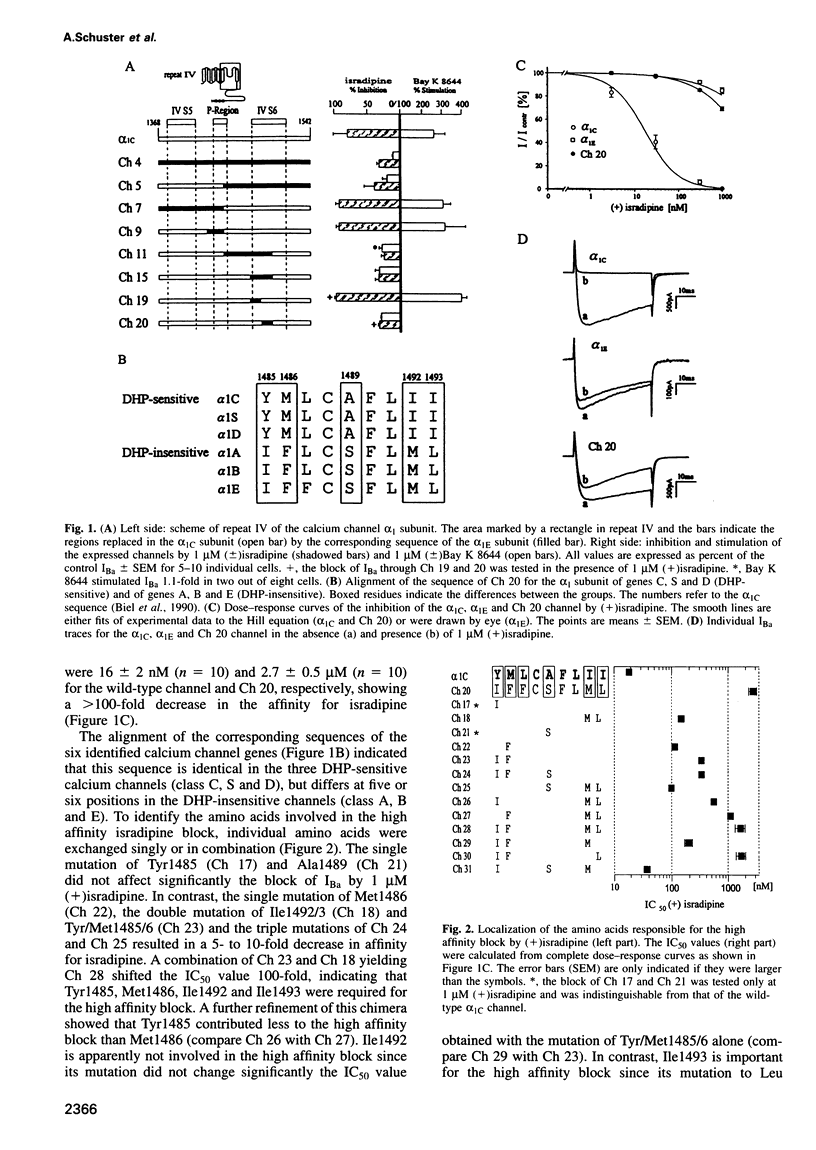
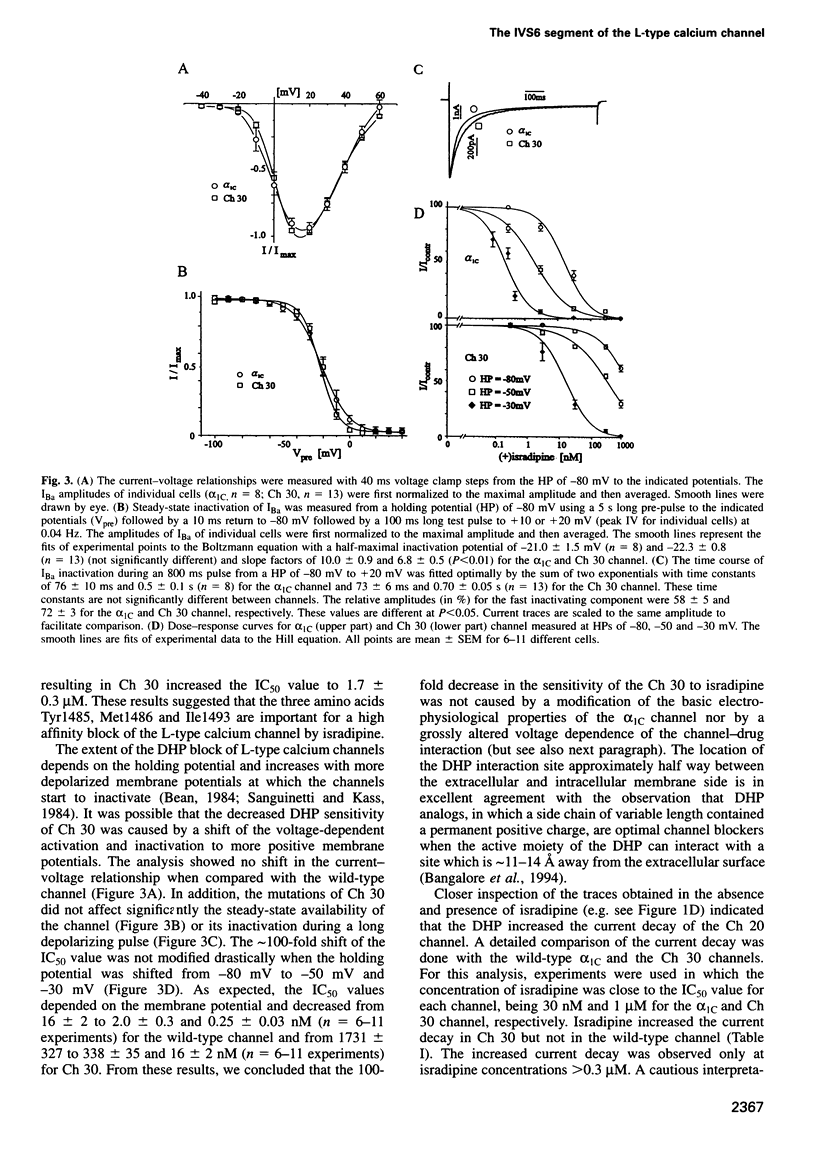
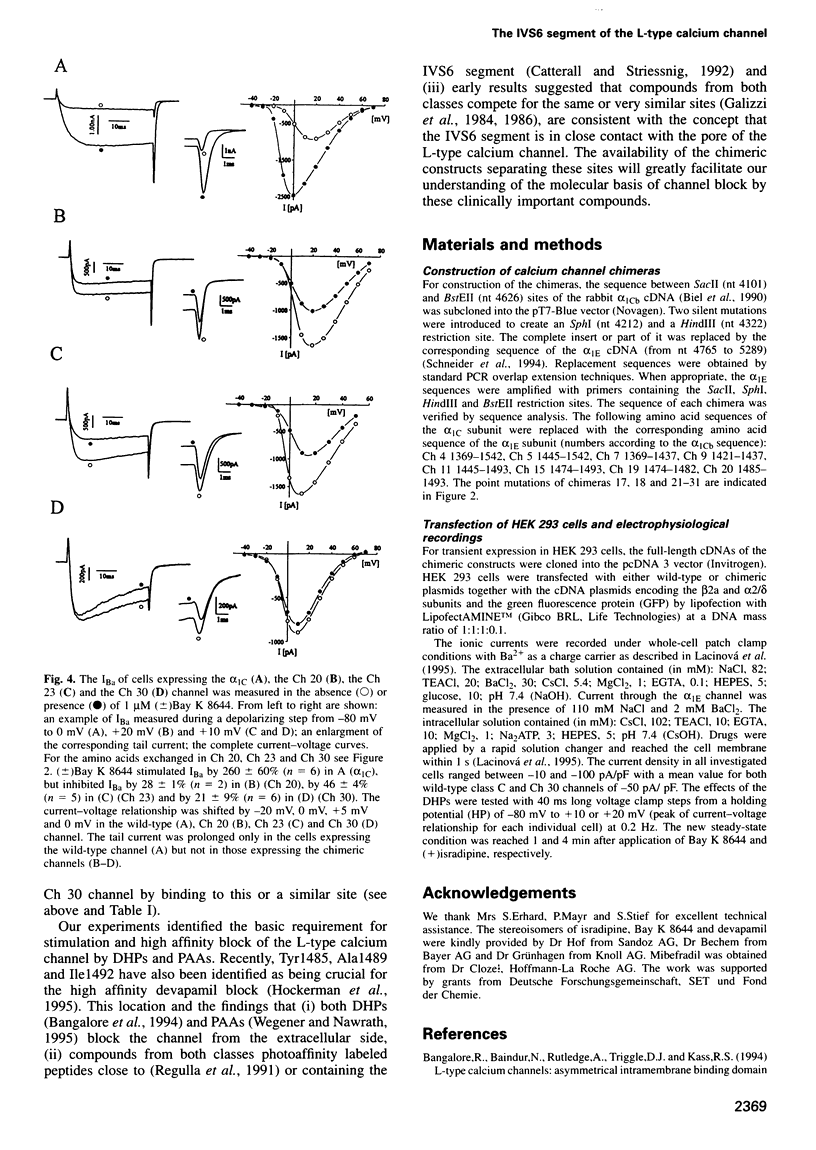
Abstract
The current through the L-type calcium channel is inhibited and stimulated by distinct dihydropyridines at very low concentrations. The molecular determinants for the high affinity block and stimulation were investigated using chimeras between the class C and E calcium channels. Mutation of three amino acids in the last putative transmembrane segment (IVS6) of the alpha1C subunit decreased the affinity for (+)isradipine 100-fold without significantly affecting the basic properties of the expressed channel. Mutation of two of these three amino acids completely abolished the stimulatory effect of the calcium channel agonist Bay K 8644. These mutations only slightly affected the blocking efficacy of mibefradil and the phenylalkylamine devapamil. Three distinct but adjacently located amino acids mediated the high affinity block by devapamil. These results suggest that the IVS6 segment of the alpha1C subunit is critical for the high affinity interaction between the L-type calcium channel and the calcium channel agonist Bay K 8644 and the two antagonists isradipine and devapamil.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangalore R., Baindur N., Rutledge A., Triggle D. J., Kass R. S. L-type calcium channels: asymmetrical intramembrane binding domain revealed by variable length, permanently charged 1,4-dihydropyridines. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Oct;46(4):660–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Nitrendipine block of cardiac calcium channels: high-affinity binding to the inactivated state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6388–6392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechem M., Hoffmann H. The molecular mode of action of the Ca agonist (-) BAY K 8644 on the cardiac Ca channel. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Aug;424(3-4):343–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00384362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Tsien R. W. Voltage-dependent blockade of diverse types of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes by the Ca2+ channel antagonist mibefradil (Ro 40-5967). Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Sep;48(3):540–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biel M., Ruth P., Bosse E., Hullin R., Stühmer W., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Primary structure and functional expression of a high voltage activated calcium channel from rabbit lung. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81205-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Striessnig J. Receptor sites for Ca2+ channel antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jun;13(6):256–262. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90079-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Characterization and photoaffinity labeling of receptor sites for the Ca2+ channel inhibitors d-cis-diltiazem, (+/-)-bepridil, desmethoxyverapamil, and (+)-PN 200-110 in skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. [3H] verapamil binding sites in skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hering S., Hughes A. D., Timin E. N., Bolton T. B. Modulation of calcium channels in arterial smooth muscle cells by dihydropyridine enantiomers. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Mar;101(3):393–410. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockerman G. H., Johnson B. D., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Molecular determinants of high affinity phenylalkylamine block of L-type calcium channels. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 22;270(38):22119–22122. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.38.22119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Biel M., Flockerzi V. Molecular basis for Ca2+ channel diversity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:399–418. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalasz H., Watanabe T., Yabana H., Itagaki K., Naito K., Nakayama H., Schwartz A., Vaghy P. L. Identification of 1,4-dihydropyridine binding domains within the primary structure of the alpha 1 subunit of the skeletal muscle L-type calcium channel. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 27;331(1-2):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80321-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacinová L., Welling A., Bosse E., Ruth P., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Interaction of Ro 40-5967 and verapamil with the stably expressed alpha 1-subunit of the cardiac L-type calcium channel. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jul;274(1):54–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrke G., Zong X. G., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. The Ca(++)-channel blocker Ro 40-5967 blocks differently T-type and L-type Ca++ channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Dec;271(3):1483–1488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama H., Taki M., Striessnig J., Glossmann H., Catterall W. A., Kanaoka Y. Identification of 1,4-dihydropyridine binding regions within the alpha 1 subunit of skeletal muscle Ca2+ channels by photoaffinity labeling with diazipine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9203–9207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Long-opening mode of gating of neuronal calcium channels and its promotion by the dihydropyridine calcium agonist Bay K 8644. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2178–2182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regulla S., Schneider T., Nastainczyk W., Meyer H. E., Hofmann F. Identification of the site of interaction of the dihydropyridine channel blockers nitrendipine and azidopine with the calcium-channel alpha 1 subunit. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):45–49. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07919.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):569–574. doi: 10.1038/301569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Kass R. S. Voltage-dependent block of calcium channel current in the calf cardiac Purkinje fiber by dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists. Circ Res. 1984 Sep;55(3):336–348. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.3.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T., Wei X., Olcese R., Costantin J. L., Neely A., Palade P., Perez-Reyes E., Qin N., Zhou J., Crawford G. D. Molecular analysis and functional expression of the human type E neuronal Ca2+ channel alpha 1 subunit. Receptors Channels. 1994;2(4):255–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D., Biel M., Lotan I., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F., Dascal N. The roles of the subunits in the function of the calcium channel. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1553–1557. doi: 10.1126/science.1716787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striessnig J., Murphy B. J., Catterall W. A. Dihydropyridine receptor of L-type Ca2+ channels: identification of binding domains for [3H](+)-PN200-110 and [3H]azidopine within the alpha 1 subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10769–10773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang S., Yatani A., Bahinski A., Mori Y., Schwartz A. Molecular localization of regions in the L-type calcium channel critical for dihydropyridine action. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):1013–1021. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90215-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Ellinor P. T., Horne W. A. Molecular diversity of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Sep;12(9):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90595-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener J. W., Nawrath H. Extracellular site of action of phenylalkylamines on L-type calcium current in rat ventricular myocytes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995 Sep;352(3):322–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00168564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X. Y., Perez-Reyes E., Lacerda A. E., Schuster G., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Heterologous regulation of the cardiac Ca2+ channel alpha 1 subunit by skeletal muscle beta and gamma subunits. Implications for the structure of cardiac L-type Ca2+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21943–21947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling A., Bosse E., Cavalié A., Bottlender R., Ludwig A., Nastainczyk W., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Stable co-expression of calcium channel alpha 1, beta and alpha 2/delta subunits in a somatic cell line. J Physiol. 1993 Nov;471:749–765. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zong X., Schreieck J., Mehrke G., Welling A., Schuster A., Bosse E., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. On the regulation of the expressed L-type calcium channel by cAMP-dependent phosphorylation. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Jul;430(3):340–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00373908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



