Abstract
The objective of this study was to investigate the impacts of the Deepwater Horizon (DWH) oil discharge at the seafloor as recorded in bottom sediments of the DeSoto Canyon region in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Through a close coupling of sedimentological, geochemical, and biological approaches, multiple independent lines of evidence from 11 sites sampled in November/December 2010 revealed that the upper ~1 cm depth interval is distinct from underlying sediments and results indicate that particles originated at the sea surface. Consistent dissimilarities in grain size over the surficial ~1 cm of sediments correspond to excess 234Th depths, which indicates a lack of vertical mixing (bioturbation), suggesting the entire layer was deposited within a 4–5 month period. Further, a time series from four deep-sea sites sampled up to three additional times over the following two years revealed that excess 234Th depths, accumulation rates, and 234Th inventories decreased rapidly, within a few to several months after initial coring. The interpretation of a rapid sedimentation pulse is corroborated by stratification in solid phase Mn, which is linked to diagenesis and redox change, and the dramatic decrease in benthic formanifera density that was recorded in surficial sediments. Results are consistent with a brief depositional pulse that was also reported in previous studies of sediments, and marine snow formation in surface waters closer to the wellhead during the summer and fall of 2010. Although sediment input from the Mississippi River and advective transport may influence sedimentation on the seafloor in the DeSoto Canyon region, we conclude based on multidisciplinary evidence that the sedimentation pulse in late 2010 is the product of marine snow formation and is likely linked to the DWH discharge.
Introduction
The 2010 Deepwater Horizon (DWH) blowout event discharged >600 million L of oil and large quantities of natural gas (e.g., methane, ethane, butane, propane) into NE Gulf of Mexico (GoM) waters over an ~3-month period [1–4]. In addition, almost 7 million L of chemical dispersants were injected into the deep-sea environment for the first time at such a great depth (~1500 m) [5–7]. It is estimated that at least 60% of the oil released reached the sea surface where it was subjected to a variety of processes including biotic and abiotic reactions, cleanup activities, transport out of the study area or to nearby beaches by physical processes, evaporation, and settling to the sea floor [5, 7, 8]. The remaining ~40% of the oil and an unknown quantity of the deep injected dispersants never reached the surface and remain unaccounted for [5, 9].
An oil slick was detected in open marine and coastal surface waters from Louisiana to Florida, including the DeSoto Canyon region (Fig 1) [10, 11]. Subsurface hydrocarbon-rich plumes were initially detected to the southwest of the wellhead at depths between ~1000 and 1200 m, with a more diffuse plume identified between ~50 and 500 m [1, 4, 6, 9, 12]. Later, subsurface plumes were identified between ~1000 and 1400 m, and ~400 m to the northeast of the wellhead, in the DeSoto Canyon region [13].
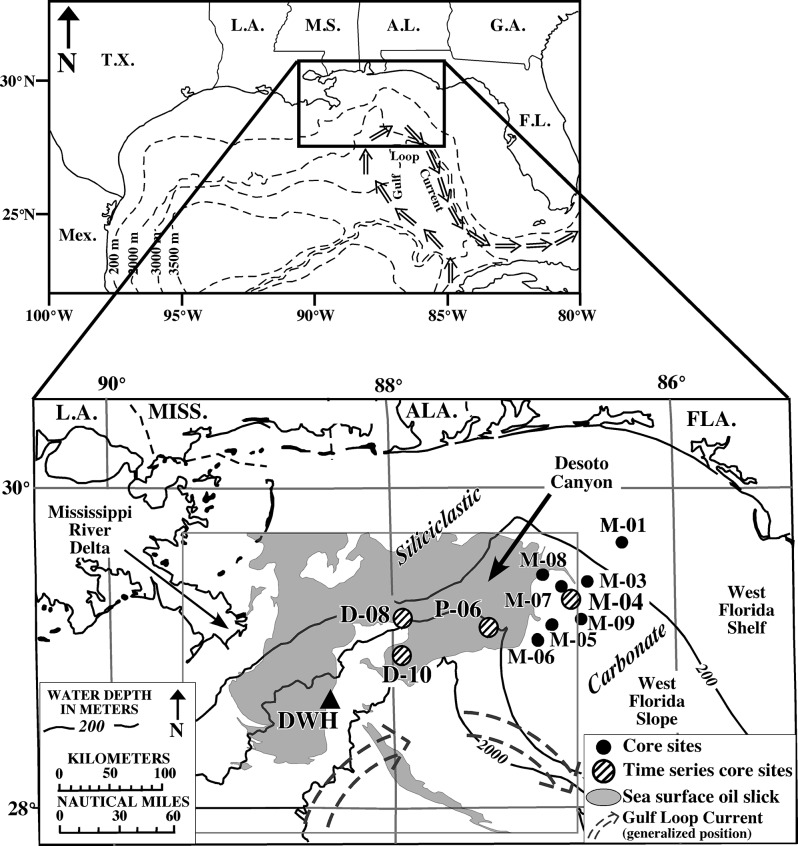
Fig 1. Study area map.
Location map of the northeastern Gulf of Mexico showing core sites discussed here in proximity to the DWH wellhead, Desoto Canyon, the Mississippi River, and the extent of the sea surface oil slick (gray shading) mapped by Garcia-Pineda [11].
An unusually large marine snow event was documented in oil contaminated surface waters following the blowout [14]. The marine snow may have formed from extracellular polysaccharides and other exudates produced by phytoplankton and/or bacterioplankton in response to exposure from surfaced oil [15, 16]. Originally thought to have formed in situ in direct response to the oil [14], the marine snow was no longer present in surface waters by the end of June 2010, likely due to rapid sedimentation to depth [15]. It was reported that as the marine snow attracted particulates on the sea surface and in the water column, it lost buoyancy and rapidly sank in what was termed a “dirty blizzard” [13, 17], potentially creating a sedimentation pulse on the sea floor [16–19]. The wide range in particle size and density within the marine snow was attributed to the heterogeneous nature of the particles. Approximately 60% of the marine snow particles fell between diatom and coccolithophore densities [14]. Calculated settling rates [14] suggest it took particles a few days to several weeks to reach the seafloor for the depth range of cores collected in this study. Sea floor sediment traps continued to accumulate an abnormally large amount of marine snow throughout the Fall 2010. A sediment trap deployed by Passow (Pers. Comm., 2013) ~120 m above the seafloor (~1400 m depth) in the vicinity of the DWH wellhead, began collecting samples in late August of 2010. The first cup (collecting until mid September, 2010) was described as “overflowing”, with more than 1.5 g/m2/d on average during the 3-week period. Sedimentation rates in September and early October of 2010 were 2–5 times higher than those observed one year later (U. Passow, Pers. Comm., 2013).
Previous marine snow investigations have documented that once the rapidly sinking marine snow reaches the sea floor, it may cover and suffocate benthic communities, potentially causing temporary anoxic bottom conditions [20–22]. Although little is known about marine snow formation at depth, it was suggested that marine snow may have formed within subsurface plumes as well [7, 14, 23].
Deep GoM sediment impacts following the DWH event have not been well documented, but a 3.8–5 cm-thick reddish-brown surface layer within 10 km of the DWH wellhead was interpreted as freshly sedimented material in response to the “dirty blizzard” [16, 17, 19]. The primary objective of this study was to investigate the impacts of the DWH discharge as recorded in bottom sediments from the DeSoto Canyon area approximately 20–100 nautical miles east/northeast of the DWH wellhead. Specific questions addressed include: 1) Did the event directly or indirectly alter the temporal and/or spatial sediment distribution patterns in the study area, and if so, how? 2) What is the sedimentary signature of the event, and how is it manifested in bottom sediments? and 3) What is the long-term preservation potential of the event signature in the sedimentary record?
Setting
The study area is located along the NW Florida outer continental shelf and slope, to the east of the DWH wellhead, in ~100 m to >1500 m water depths (Fig 1). The most conspicuous physiographic feature in the study area is the DeSoto Canyon, an S-shaped submarine canyon located ~100 km south of the Florida panhandle. The canyon exhibits both erosional and depositional features and is constrained by at least five salt domes [24].
Bottom sediments surrounding the DeSoto Canyon are complex in both texture and composition, reflecting the different sedimentologic regimes to the west and east. To the west, sedimentation is dictated by the Mississippi River and the input of siliciclastics into the NE GoM. Bottom sediments are dominated by quartz sand on the shelf forming the “MAFLA” (Mississippi-Alabama-Florida) Sand Sheet [25, 26]. Slope sediments are siliciclastic-rich silts and clays, with pelagic carbonate oozes making up a larger fraction in deeper regions [27]. To the east, sedimentation is dictated by biogenic carbonate production forming the West Florida Sand Sheet on the mid-outer shelf, grading down slope into the finer-grained West Florida Lime Mud [26]. Sediment accumulation rates calculated from 14C dates range from ~17 cm/ky northwest of DeSoto Canyon [28] to ~10 cm/ky to the southeast [28, 29]. These are linear accumulation rates (LAR), which do not account for down-core compaction. A mass accumulation rate (MAR) of 0.05 g/cm2/yr was determined by 210Pb methods for a single core in the DeSoto Canyon region at ~1850 m water depth [30].
Typically, the highest proportion of carbonate in bottom sediments, frequently in excess of 75%, occurs on the west Florida shelf, and carbonate content decreases from ~60% at the shelf-slope break to ~25% at the base of slope [27]. To the west of the canyon, the carbonate content exhibits an opposing pattern with a basin-ward increase, likely reflecting a seaward decrease in Mississippi River influence and corresponding increase in pelagic carbonate deposition [27]. Particulate organic carbon (POC) for one core in the DeSoto Canyon region at ~1850 m water depth ranged from ~0.67%–1.17% for the upper 18.5 cm of the core [30]. Clay mineral assemblages in bottom sediments are also complex. In general, smectite is the dominant clay mineral west of the canyon, due to input from the Mississippi River, while kaolinite is dominant east of the canyon reflecting input from the Apalachicola River [27, 31, 32]. The differences in sediment types/sources on either side of Desoto Canyon makes this an ideal region to investigate if the DWH event altered natural sedimentation patterns/processes; as any alteration should be readily visible as a change in the relative abundance of the two sediment types.
Methods
Sample collection
Multicores were collected from seventeen sites in the DeSoto Canyon region of the NE Gulf of Mexico (GoM) during November/December 2010, using a MC-800 Multicorer capable of collecting up to eight, 10-cm diameter by 70 cm-long cores per deployment with minimal disturbance to the sediment-water interface (Fig 1). Eleven of these cores, collected 20–100 nautical miles (NM) northeast of the DWH wellhead from 100 m to >1500 m water depths, were chosen for detailed analyses based on the following criteria: 1) no visible evidence of a break in sediment deposition, 2) well preserved sediment-water interface, 3) no visible evidence of sediment mixing, 4) no evidence of gravity flow deposition, 5) representative coverage of different water depths (including the depths of the two documented subsurface plumes at ~400 m and 1000–1400 m), and 6) representative coverage of both the siliciclastic–dominated and carbonate–dominated sediment regimes west and east of DeSoto Canyon, respectively. Four of the eleven sites (M-04, P-06, D-08, D-10) were reoccupied and cored up to three more times over the following two years to obtain a temporal perspective, and are referred to here as ‘time series’ sites (Fig 1). No permissions were required for collection of cores at any sites and this study did not involve endangered or protected species.
One core per deployment was split longitudinally, photographed, and described visually. For select cores, the entire core half was x-rayed to ensure stratigraphic integrity and to detect subtle sedimentary structures. One core per deployment was extruded at 2–5 mm intervals for sediment texture/composition and geochronological analyses. The 2 mm sampling interval was focused on the surficial 2–10 cm (based on visual descriptions), which represents most recent deposition, and would ensure the greatest possible resolution of recently impacted sediments. A calibrated threaded rod attached to a tight fitting plunger was used to extrude the core vertically upward through a flat acrylic surface, where the sample was carefully extracted from the top. Once extruded, samples were weighed immediately to provide the wet weight required for determining pore water content. Each sample was then freeze-dried and weighed for dry weight to calculate dry bulk density.
Sediment texture and composition
Sediment texture/composition analyses were conducted on all cores collected in November/December 2010, and included grain size, calcium carbonate content (%CaCO3), and total organic matter (%TOM). Grain size was determined by wet sieving the sample through a 63 μm screen. The fine-size (<63 μm) fraction was analyzed by pipette [33] to measure %silt/%clay. The sand-size (>63 μm) fraction was volumetrically too small to analyze further and is reported here as %sand. Carbonate content was determined by the acid leaching method according to Milliman [34]. Total organic matter (TOM) was determined by loss on ignition (LOI) at 550°C for at least 2.5 hours [35].
Additional compositional analyses were performed on a subset of the time series cores collected in November/December 2010, using a variety of techniques including microscopic (digital and SEM), energy dispersive x-ray (EDS), core-scanning x-ray fluorescence (XRF) and x-ray diffraction (XRD). Microscopic analysis was performed using a digital microscope (Dino-Lite) at magnifications ranging from 70x to 220x, and by Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) at magnifications ranging from 2kx to 8kx. The latter was conducted on a Hitachi S-3500N SEM at the University of South Florida College of Marine Science, St. Petersburg, FL. Select grains identified under the SEM, were analyzed by EDS to determine the elemental composition.
Entire core elemental compositions were determined for all four 2010 time series cores at the mm-scale by XRF core scanning at the NIOZ (Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research) laboratory using standard optimized settings [36]. This technique provides a rapid, non-destructive means to analyze sediment cores at high-resolution for elemental composition. Analysis was performed on an Avaatec XRF Core-Scanner with a 1mm by 1cm wide slit window at 1mm step resolution. Whole sediment cores were covered with a thin film transparent to X-rays to prevent sediment sticking to the device and prevent the core from drying out. The analysis chamber was flushed with He to provide accurate measurement of light elements.
Select cores/samples were analyzed by XRD to determine mineralogical content. Samples were analyzed on a Bruker D-8 Advanced system using cobalt radiation at the University of Georgia Department of Geology.
Microbial community structure
Based on radiocarbon evidence and proximity to the wellhead, microbial community structure was examined on 2010 time series core D-10 using next generation sequencing. Total genomic DNA was extracted from 0.5 g of sediment from each core section using a MoBio PowerSoil DNA extraction kit according to the manufacturer’s protocol (MoBio Laboratories, Carlsbad, CA). DNA concentration was determined using a Quant-IT kit (Life Technologies, Grand Isle, NY). DNA was sent to the Institute for Genomics and Systems Biology Next Generation Sequencing Core facility at Argonne National Laboratory for SSU rRNA gene sequencing. Sequencing reactions were conducted on an Illumina MiSeq platform in a 151x151x12 bp run using sequencing primers and procedures that were previously described [37]. The resulting sequences were processed using QIIME v.1.7 [38]. Briefly, reads were demultiplexed using QIIME default paramaters (reads were truncated if 3 consecutive bases had a phred score less than 3, only reads >114 bases were retained). Sequences that were less than 60% similarity to any sequence in the GreenGenes database (v.13-5) [39] were discarded. Operational taxonomic units (OTU) were defined at 97% similarity using UCLUST [40], and only OTUs that represented more than 0.005% of the total reads were considered [41]. Putative taxonomy was assigned to representative reads using RDP classifier [42, 43] at 50% confidence and all reads assigned to the sequences from predominant photosynthetic microbial groups, cyanobacteria and phytoplankton chloroplasts were extracted. Samples were grouped based on sediment depth (0–2 cm, > 2 cm depth intervals) and the relative abundance of phototroph sequences was transformed to meet assumptions of normality. A Welch’s t test was used to compare the two groups.
Natural abundance radiocarbon
Subsamples of 2010 time series cores P-06 and D-08 and D-10 were prepared for Δ14C analysis at the National High Magnetic Laboratory at Florida State University. Dried sediment was acid treated in 10% HCl to remove carbonates then combusted and purified to CO2 following the methods of Choi and Wang [44]. The break seal tubes for Δ14C analysis were sent to National Ocean Sciences Accelerator Mass Spectrometry Facility (NOSAMS) where they were converted to graphite targets and analyzed by accelerator mass spectrometry [45]. Values are reported in the Δ14C notation according to Stuiver and Polach [46].
Benthic foraminifera
Subsamples of 2010 time series cores P-06 and D-08 were freeze-dried, weighed and washed with a sodium hexametaphosphate solution through a 63-μm sieve to disaggregate the clay particles from foraminifera tests. The >63-μm fraction was dried, weighed again, and stored at room temperature. All benthic foraminifera were picked from the samples, identified, and counted. Foraminifera assemblage density values were reported in individuals per unit volume (indiv./cm3) [47]. The values were normalized to the known wet volume of each sample based on the diameter of the core tube (10 cm) and the height of each sample (2 or 5 mm).
Biomarkers
Biomarkers were analyzed using a modified EPA method [48] for the analysis of biomarkers. Freeze-dried samples were extracted (at 100°C, 1500 psi, 9:1v:v dichloromethane: methanol) using an ASE system (Dionex 200). Previous to extraction, samples were spiked with d50-Tetracosane. Activated copper (40 mesh, 99.9%, Sigma-Aldrich, USA) was added and lipid extracts were clean using solid-phase extraction (SPE) with silica/cyanopropyl glass columns (SiO2/C3-CN, 1 g/0.5 g, 6 mL) made at the USFCMS-PL. Silica gel (high purity grade, 100–200 mesh, pore size 30A, Sigma Aldrich, USA) was combusted (450°C for 4h) and deactivated (2%) previous to column preparation for SPE. Biomarkers were collected using hexane (100%). All solvents used were the highest purity available. Two blanks were included in each set of samples (15–18 samples) to ensure no contamination during sample preparation. Biomarkers were quantified using GC/MS/MS multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) on a Varian 320 triple quadrupole MS. Splitless injections of 1μL of the sample were conducted. We used a RXi5sil column (30 m x 0.25 mm x 0.25 μm) with a GC oven temperature programming of 80°C held for 1 min, then increased to 200°C at a rate of 40°C/min, to 250°C at 5°C/min, to 300°C at 2°C/min, to 320°C at 10°C/min, and held for 2 min. The GC was operated in constant-flow mode (1ml/min) with an inlet temperature of 275°C and a transfer line temperature of 320°C. Ion source temperature was 180°C and source electron energy was 70eV. Argon at a pressure of 1 millitorr was used as a collision gas. We targeted biomarker compounds (hopanes, steranes, diasteranes) as conservative tracers for crude oil [49, 50]. Total concentration of biomarkers was calculated using the response factor by comparison with a known standard mixture (Calibration mix, Chiron, S-4436-10-IO) and the internal standard (d4-cholestane). When no commercial reference standard was available, compounds were quantified using the response factor for the nearest available homologue in the same compound class. Concentrations were corrected for the recovery of the surrogate standard (d50-Tetracosane). Recoveries from spiked samples included with each batch were generally within 60–80%. Replicate analyses were performed on selected samples and relative standard deviations (RSDs) of replicates (N = 4) for biomarker analysis were between 4% and 22%. Total biomarker concentration is expressed as sediment dry weight.
Short-lived radioisotopes
Short-lived radioisotope analyses were conducted on all cores collected at the eleven sites and throughout the two-year time series. Samples were analyzed by gamma spectrometry on Series HPGe (High-Purity Germanium) Coaxial Planar Photon Detectors for total 210Pb (46.5Kev), 214Pb (295 Kev and 351 Kev), 214Bi (609Kev), 137Cs (661Kev), 7Be (447 Kev), and 234Th (63 Kev) activities. Data were corrected for counting time and detector efficiency, as well as for the fraction of the total radioisotope measured yielding activity in dpm/g (disintegrations per minute per gram).
Detector efficiencies were all <3% of the activities measured, determined by similar methods to Kitto [51]. The IAEA-447 organic standard, which has a similar density to the sediment analyzed in this study, was analyzed using varying weights (1g, 3g, 5g, 7g, 9g, 12g, 15g, 17g, 20g, 30g, 40g and 50g) as a proxy for geometry. A calibration template was produced relating the counts measured to the known activity of the standard for the range of sample weights. By using the calibration template for various weights, self-absorption of the sample is included in the detector efficiency calculations [52]. The Cutshall method [53] was used on select sediment samples, and results show that the self-absorption and variability is negligible and within detection error. The activity of the 214Pb (295 Kev), 214Pb (351 Kev), and 214Bi (609 Kev) were averaged as a proxy for the 226Ra activity of the sample or the supported 210Pb that is produced in situ. The supported 210Pb was subtracted from the total 210Pb to determine the unsupported (i.e., excess) 210Pb, which is used for dating within the last ~100 years [54]. 137Cs is a thermonuclear byproduct and represents the height of nuclear bomb testing in the early-mid 1960s [55], or other thermonuclear incidents [56]. 7Be has a short half-life (~53 days) and is an indicator of recent sediment deposition. 234Th has a half-life of ~24 days and is usually only detectable at the sediment surface. Supported 234Th was determined by reanalysis of the same sample >120 (~5 half-lives) days after core collection (i.e., all excess 234Th decayed). The supported 234Th was subtracted from the total 234Th to determine the unsupported (i.e., excess) 234Th. Activities of excess 234Th were corrected for activity decayed between the time of core collection and sample analysis and are termed “Decay Corrected 234Th”. Although excess 234Th is typically used as in indicator of surface mixing (e.g., bioturbation) [30, 57, 58], it has been used as a geochronological tool where sediments are unmixed [59].
In order to assign specific ages to sedimentary layers down core, excess 210Pb data were run through the CIC (Constant Initial Concentration) and CRS (Constant Rate of Supply) models, the latter of which is appropriate under conditions of varying accumulation rates [60, 61]. Activity values vs. depth down core were plotted for each core, and model results applied to assign a date to each individual sample. Mass accumulation rates (MAR) were calculated for each data point (i.e., “date”), thereby giving MAR over the past ~100 years. The use of mass accumulation rates corrects for differential sediment compaction down core, thereby enabling a direct comparison of excess 210Pb accumulation rates throughout the core (i.e., over the last ~100 years). Mass accumulation rates were calculated as follows:
Recognizing that excess 234Th profiles may represent deposition and not bioturbation, excess 234Th-based MAR were calculated from CIC and CRS model results in the same fashion as excess 210Pb, as well as by simply dividing the depth of the excess 234Th penetration by 120 days (~5 half lives) to acquire LAR. MAR were then calculated according to the same equation as described above.
Sediment inventories of excess 234Th were calculated according to the method described in Baskaran and Santschi [62] following the equation:
Where I is the excess 234Th inventory (dpm/cm2), p i is the dry bulk density (g/cm3), A i is the activity of excess 234Th (dpm/g) of sample I, and z i is the thickness of sample i in cm. All excess 234Th inventories were decay corrected to the date of collection. Sediment inventories are independent of excess 234Th depth and therefore not impacted by bioturbation.
Results
With the exception of the shallowest core at ~100 m (M-01), the surficial ~1–10 cm of all cores collected were brown in color, overlying a massive light tan unit (Figs 2–4). The surface discoloration was typically thicker and better defined with increasing water depth. In most cores the medium to dark brown layer contained one or more ≤1 cm-thick dark brown-black bands that correspond with Mn spikes in XRF data (discussed below). Core photographs and x-radiographs show little in the way of sedimentary structures, although sand-sized biogenic particles (planktonic foraminifera and/or pteropods) were occasionally visible.
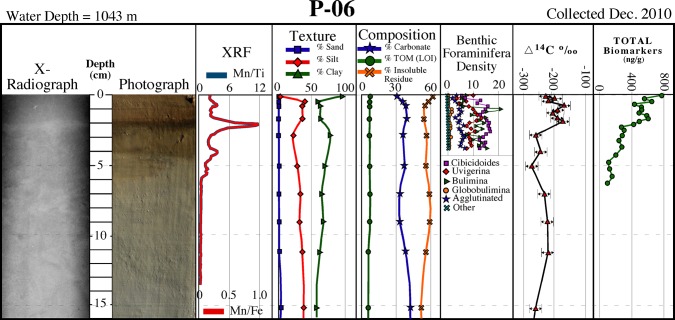
Fig 2. Core P-06 description.
Description of core P–06 collected in December 2010 showing a surficial brown layer containing multiple dark brown-black bands corresponding to Mn spikes, and distinct sediment texture/composition, benthic foraminifera density, natural abundance radiocarbon (∆14C), and biomarkers over the surficial ~1 cm (see Fig 1 for location).
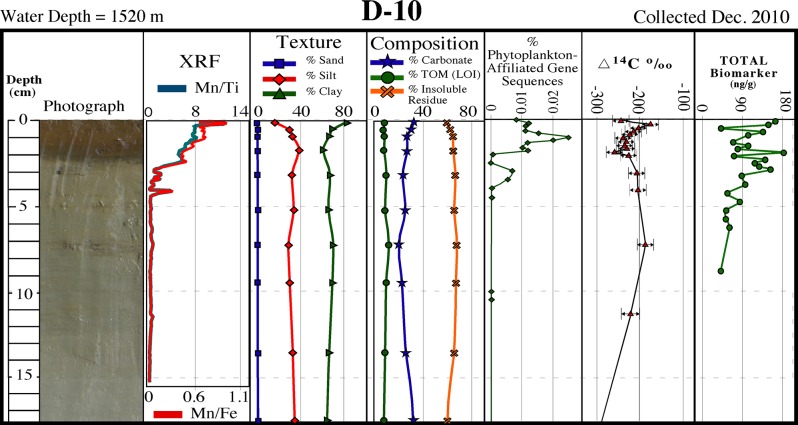
Fig 4. Core D-10 description.
Description of core D–10 collected in December 2010 showing a surficial brown layer containing dark brown-black bands corresponding to Mn spikes, and a distinct sediment texture/composition, phytoplankton-affiliated gene sequences, natural abundance radiocarbon (∆14C), and biomarkers over the surficial ~1 cm (see Fig 1 for location).
Sediment texture and composition
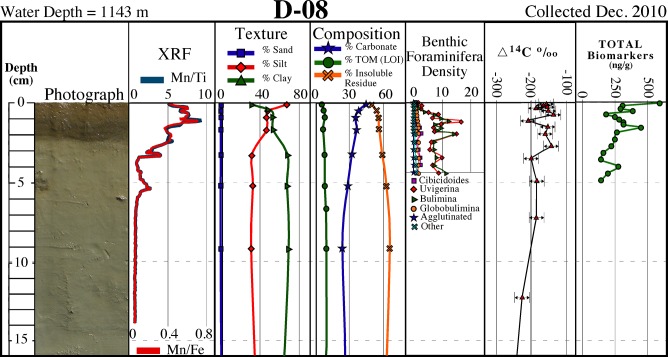
Texturally, the grain size of all 2010 cores tends to become finer with increasing water depth as expected, and with few exceptions tends to fine-upward over the ~1 cm-thick surficial layers (Figs 2–4; Table 1). For cores collected in water depths of ≤600 m, the fining-upward unit is often manifested as a decrease in sand-sized sediments, whereas for sites in >1000 m depths it is often represented as an increase in clay-sized sediments. Carbonate content tends to increase slightly over the surface layer in cores collected in ≥600 m water depths (Figs 2–4; Table 1 ). Both deep (>1000 m) sites on the siliciclastic-dominated west side of DeSoto Canyon (D-08 and D-10) recorded slight increases in carbonate content. Total organic matter (TOM) ranges from ~3% to ~12% with the highest percentages occurring in sediments from the deepest sites (Figs 2–4; Table 1). Down-core TOM percentages exhibit little variability (Figs 2–4; Table 1).
Table 1. Sediment texture and composition data at 2 mm intervals to excess 234Th depth, as well as average and ranges below excess 234Th depths to depths of excess 210Pb (~100 yrs).
| Site ID | Top Depth (cm) | Bottom Depth (cm) | % Gravel | % Sand | % Silt | % Clay | % Carbonate | % TOM (LOI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 11.4 | 73.4 | 15.3 | 77.2 | 3.8 | |
| M-01 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 19.6 | 67.2 | 13.2 | 76.1 | 3.4 |
| 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 19.5 | 77.3 | 3.1 | 76.4 | 3.2 | |
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 20.7 | 67.6 | 11.7 | 76.1 | 3.4 | |
| 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 17.0 | 68.8 | 14.2 | 76.4 | 3.1 | |
| Average | 2.0 | 11.5 | 0.1 | 19.5 | 71.1 | 9.3 | 75.1 | 3.6 |
| Range | 2.0 | 11.5 | 0.0–0.4 | 16.3–24.6 | 67.8–75.5 | 4.5–14.2 | 74.4–75.9 | 3.1–4.1 |
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 7.2 | 18.4 | 74.4 | 62.7 | 6.1 | |
| M-03 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 4.8 | 66.3 | 28.8 | 64.2 | 5.0 |
| 0.4 | 0.6 | 2.2 | 11.1 | 64.8 | 21.9 | 61.6 | 6.8 | |
| Average | 0.6 | 15.5 | 0.2 | 9.4 | 60.0 | 30.5 | 62.3 | 5.1 |
| Range | 0.6 | 15.5 | 0.0–0.6 | 3.0–15.7 | 49.9–79.4 | 12.2–40.0 | 58.5–65.3 | 3.2–6.4 |
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 5.8 | 57.5 | 36.7 | 54.2 | 6.5 | |
| M-04 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 7.8 | 67.3 | 24.9 | *NA | *NA |
| 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 13.9 | 64.2 | 21.9 | 59.1 | 6.6 | |
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 9.2 | 59.0 | 31.8 | *NA | *NA | |
| 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 5.5 | 65.4 | 29.1 | 54.7 | 6.8 | |
| 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 9.2 | 62.7 | 28.1 | 54.9 | 6.4 | |
| Average | 1.2 | 16.5 | 0.0 | 20.4 | 49.9 | 29.7 | 57.4 | 6.4 |
| Range | 1.2 | 16.5 | 0.0–0.0 | 11.8–28.1 | 42.7–58.7 | 24.6–36.2 | 54.3–61.9 | 5.1–7.6 |
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 46.0 | 53.3 | 54.1 | 6.7 | |
| M-05 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 38.8 | 60.6 | 42.6 | 8.4 |
| 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 3.1 | 45.0 | 51.9 | 46.2 | 7.4 | |
| Average | 0.6 | 9.5 | 0.0 | 7.8 | 48.2 | 44.0 | 46.9 | 7.7 |
| Range | 0.6 | 9.5 | 0.0–0.0 | 3.5–11.4 | 36.4–74.9 | 18.5–58.8 | 43.6–50.5 | 6.2–9.1 |
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 49.3 | 50.1 | 55.0 | 4.7 | |
| M-06 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 58.7 | 40.4 | 52.2 | 6.2 |
| 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 15.8 | 81.7 | 46.3 | 7.9 | |
| Average | 0.6 | 10.5 | 0.0 | 4.1 | 45.1 | 50.8 | 44.9 | 7.0 |
| Range | 0.6 | 10.5 | 0.0–0.1 | 1.6–9.1 | 37.0–65.3 | 29.6–60.1 | 40.5–50.3 | 5.6–9.1 |
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 16.4 | 44.9 | 38.7 | 62.2 | 5.4 | |
| M-07 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 23.2 | 48.5 | 28.3 | 66.5 | 4.6 |
| 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 30.6 | 46.0 | 23.4 | 65.0 | 5.1 | |
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 30.1 | 44.5 | 25.4 | 68.6 | 4.3 | |
| 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 33.8 | 44.6 | 21.6 | 69.6 | 4.2 | |
| Average | 1.0 | 15.5 | 0.0 | 26.9 | 45.0 | 28.1 | 64.1 | 4.7 |
| Range | 1.0 | 15.5 | 0.0–0.1 | 13.1–42.5 | 34.9–56.4 | 13.3–36.1 | 60.1–67.5 | 4.4–4.9 |
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 49.8 | 30.7 | 19.5 | 73.2 | 3.7 | |
| M-08 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 47.5 | 35.3 | 17.2 | 73.3 | 4.8 |
| 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 51.4 | 36.9 | 11.7 | 72.4 | 6.4 | |
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 53.3 | 31.1 | 15.6 | 74.6 | 5.0 | |
| Average | 0.8 | 17.5 | 0.1 | 45.0 | 34.6 | 20.2 | 71.0 | 5.0 |
| Range | 0.8 | 17.5 | 0.0–0.8 | 29.8–65.9 | 27.1–49.8 | 5.0–30.2 | 51.9–79.0 | 2.9–8.1 |
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 60.0 | 37.4 | 59.7 | 6.0 | |
| M-09 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 4.8 | 72.1 | 23.1 | *NA | *NA |
| 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 7.9 | 61.7 | 30.4 | *NA | *NA | |
| Average | 0.6 | 16.5 | 0.0 | 11.4 | 48.4 | 40.2 | 54.9 | 6.0 |
| Range | 0.6 | 16.5 | 0.0–0.2 | 6.0–18.9 | 39.0–65.0 | 25.0–48.5 | 53.1–57.8 | 5.5–6.9 |
*NA–Not Analyzed
Microscopic analyses for three 2010 time series sites (D–08, D–10, P–06) using both the digital microscope (70x-200x) and SEM (2kx-8kx magnification) show that sediments consist predominantly of unidentifiable, amorphous aggregates with trace amounts of identifiable siliciclastic grains and biogenic carbonates. SEM analysis showed biogenic material to consist predominantly of coccolithophore plates, which appeared to be more common near the sediment surface. Otherwise, no discernible difference(s) were evident between the surface and underlying layers in the three cores analyzed.
Elemental composition, determined by SEM/EDS and Scanning XRF, yielded similar results in that, with few exceptions, no discernable differences were evident between the surface and underlying layers. EDS data showed surficial and underlying sediments from all 2010 cores analyzed (D–08, D–10, P–06) to consist dominantly of Si, O, Al, and Ca with subordinate amounts of C, Mg and K. Scanning XRF data for the same three cores showed no appreciable differences in lithogenic elements (Ti, Al, Fe, Si) and/or biogenic elements (Ca, Si) between the surface and underlying layers. An exception is Mn, which substantially increased in the surficial ~1–10 cm brown layer, and consistently exhibited pronounced spikes correlating to the ≤1 cm-thick darkest brown-black bands that occur within this interval (Figs 2–4).
XRD results showed a detrital silicate and biogenic carbonate mineral assemblage considered typical for the NE GoM. Dominant clay minerals include smectite and kaolinite, as expected. No discernable variations in mineralogical composition over the surficial layer, as compared to down-core, was evident.
Natural abundance radiocarbon
Natural abundance radiocarbon, analyzed on 2010 time series cores P-06, D-08 and D-10 (Figs 2–4), exhibited a reproducibility of ±6.5‰ based on 17 replicate samples. We hypothesized that if significant quantities of petroleum-based carbon had been input to surface layers, then surficial sediments would be depleted in 14C relative to underlying sediments, as observed at sites P-06 and D-10, the sites closest to the DWH wellhead (Fig 1). Most petro-carbon depletion was to the south and west of the wellhead, although some migrated to the northeast also [63]. Consistent with our observations, Chanton et al. [63], and Valentine et al. [23], observed that petro-carbon deposition was mainly within the 0–1 cm surface interval of sediments.
Microbial community structure
Microbial communities were characterized using next generation sequencing of SSU rRNA gene sequences. Overall, communities were dominated by members of the prokaryotic phyla Proteobacteria, Planctomycetes, Chloroflexi, and Thaumarchaeota. These phyla were observed at high relative abundance in all cores sampled in the northern Gulf and likely represent the core community observed in sediments of this region. Since chloroplasts of eukaryotes also contain rRNA genes, eukaryotic algae may also be detected in our dataset. Unlike other microbial groups mentioned above, sequences affiliated photosynthetic microbial groups, Cyanobacteria (Synechococcus) and chloroplasts of marine diatoms, were significantly enriched by one order of magnitude (p < 0.00008) in surficial (0–2 cm depth) sediments compared to underlying sections (Fig 4). The relative abundances of these planktonic phototroph sequences reached a maximum at ~1 cm sediment depth. Sequences related to the Bacillariophyta comprised the majority of detected phytoplankton chloroplast sequences (> 98%).
Benthic foraminifera
A decline in benthic foraminiferal density was evident in all 2010 time series cores analyzed. This decline is represented by a continuous decrease below down-core means of 80–93% in assemblage density (all genera, infaunal and epifaunal) and benthic foraminiferal accumulation rate (BFAR) in the surficial ~1 cm in cores P-06 and D-08 (Figs 2 and 3).
Fig 3. Core D-08 description.
Description of core D–08 collected in December 2010 showing a surficial brown layer containing dark brown-black bands corresponding to Mn spikes, and distinct sediment texture/composition, benthic foraminifera density, natural abundance radiocarbon (∆14C), and biomarkers over the surficial ~1 cm (see Fig 1 for location).
Biomarkers
All 2010 time series cores analyzed for total biomarkers showed elevated concentrations over the surface ~1 cm (Figs 2–4). A comparison of the ~1 cm thick surface interval to underlying sediments indicated an increase in the concentration of total biomarkers in the surface sediment layer by 26% in D-10, 37% in D-08, and 72% in P-06.
Short-lived radioisotopes
Excess 210Pb and 234Th were detected in almost all cores. When detected, 137Cs and 7Be levels were exceptionally low, which is consistent with other reports [30], and will not be discussed here. Excess 210Pb was detected in all eleven November/December 2010 cores to depths ranging from ~10–19 cm. Mass accumulation rates over the past ~100 years ranged from 0.05–0.16 g/cm2/yr (Table 2), which is consistent with rates previously reported for the NE GoM [30]. Excess 234Th was detected in all November/December 2010 cores, except for Core M-01, collected at the shallowest depth of 100 m (Fig 1). Excess 234Th depths ranged from 0.4 to 1.2 cm (Table 2). Excess 234Th-based MAR calculated by the CRS model are reported here (because they are the most conservative) and range from 0.48 to 2.40 g/cm2/yr ( Table 2). Sediment inventories of excess 234Th ranged from 0.37 to 2.72 dpm/cm2 (Table 2).
Table 2. Excess 234Th and excess 210Pb profile depths, MAR, and inventories.
| Site ID | Nov. 2010 | Dec. 2010 | Feb. 2011 | Sept 2011 | Aug. 2012 | Oct. 2012 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-08 | Depth (cm) | 1.2 | 0.4 | |||||
| 234Th | MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 2.00* | 0.40+ | |||||
| 1143 | Inventory (dpm/cm2) | 1.04* | 0.19+ | |||||
| 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 13.5 | ||||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.07 | |||||||
| D-10 | Depth (cm) | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |||
| 234Th | MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.60* | 0.48* | 0.25+ | 0.14+ | |||
| 1520 | Inventory (dpm/cm2) | 1.68* | 1.70* | 0.40+ | 0.26+ | |||
| 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 18.0 | ||||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.12 | |||||||
| P-06 | Depth (cm) | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | ||||
| 234Th | MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 1.35* | 0.35+ | 0.66+ | ||||
| 1043 | Inventory (dpm/cm2) | 1.06* | 0.06+ | 0.35+ | ||||
| 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 16.0 | ||||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.06 | |||||||
| M-04 | 234Th | Depth (cm) | 1.2 | 0.4 | ||||
| 234Th | MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 1.76* | 0.20+ | |||||
| 400 | Inventory (dpm/cm2) | 1.34* | 0.44+ | |||||
| 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 16.0 | ||||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.07 | |||||||
| M-01 | 234Th | Not Detected | ||||||
| 100 | 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 10.0 | |||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.16 | |||||||
| M-03 | Depth (cm) | 0.6 | ||||||
| 234Th | MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 1.09* | ||||||
| 300 | Inventory (dpm/cm2) | 1.89* | ||||||
| 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 16.0 | ||||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.07 | |||||||
| M-05 | Depth (cm) | 0.6 | ||||||
| 234Th | MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 1.17* | ||||||
| 500 | Inventory (dpm/cm2) | 1.01* | ||||||
| 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 9.0 | ||||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.08 | |||||||
| M-06 | Depth (cm) | 0.6 | ||||||
| 34Th | MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 2.4* | ||||||
| 600 | Inventory (dpm/cm2) | 0.59* | ||||||
| 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 10.0 | ||||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.05 | |||||||
| M-07 | Depth (cm) | 1.0 | ||||||
| 234Th | MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 1.34* | ||||||
| 400 | Inventory (dpm/cm2) | 1.24* | ||||||
| 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 15.0 | ||||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.07 | |||||||
| M-08 | Depth (cm) | 0.8 | ||||||
| 234Th | MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 1.58* | ||||||
| 400 | Inventory (dpm/cm2) | 2.72* | ||||||
| 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 18.0 | ||||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.15 | |||||||
| M-09 | Depth (cm) | 0.6 | ||||||
| 234Th | MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.74* | ||||||
| 400 | Inventory (dpm/cm2) | 0.37* | ||||||
| 210Pb | Depth (cm) | 16.5 | ||||||
| MAR (g/cm2/yr) | 0.07 |
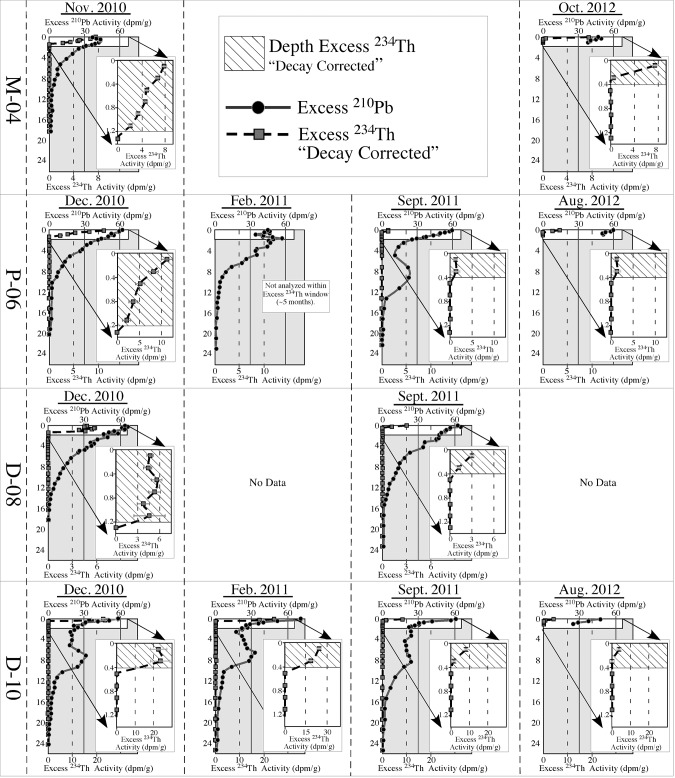
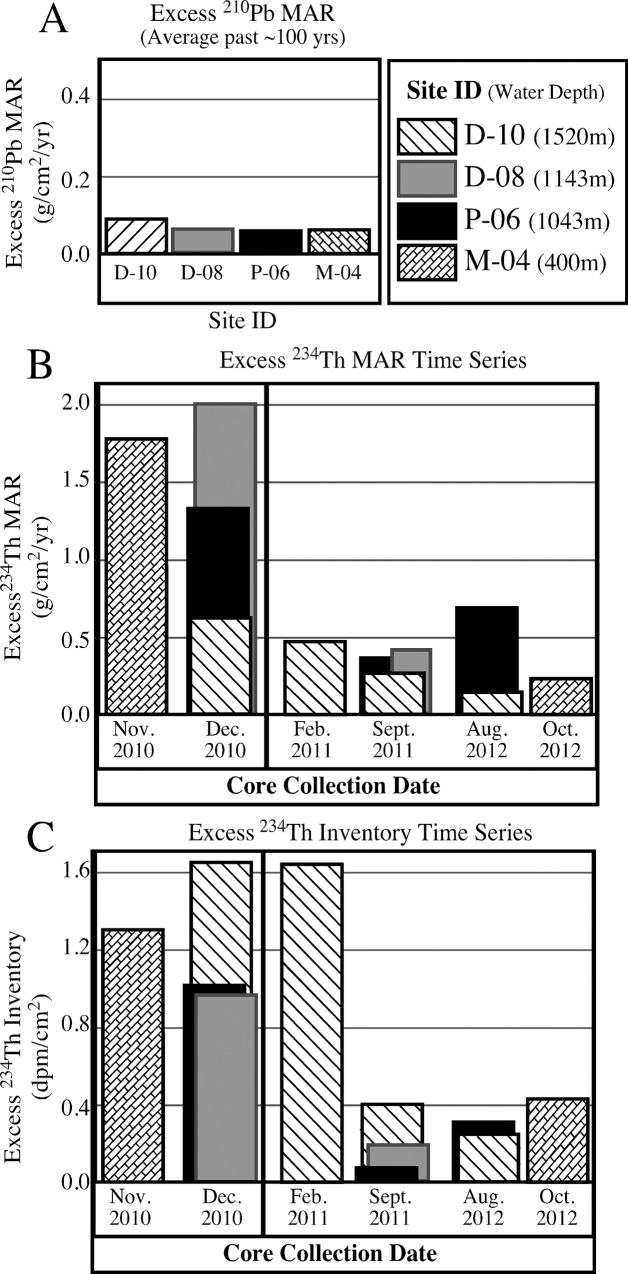
Excess 210Pb and 234Th was detected in all cores collected from the four time series sites (M-04, D-08, D-10, P-06) over the entire two-year period (Table 2). Excess 234Th profile depths, MAR, and inventories are all highest in cores collected in late 2010/early 2011, after which they decreased rapidly (within a few to several months) and then remain relatively stable over the following ~2 years (Figs 5 and 6; Table 2 ). Excess 234Th inventories and MAR were categorized by their core collection date. Late 2010/early 2011 inventories and MAR were compared to late 2011 and 2012 inventories and MAR with a student’s T test and differences between the two time periods were highly significant, p = 0.007 for MAR and p = 0.0018 for inventories (Table 3).
Fig 5. Excess 210Pb and 234Th profiles for time series sites.
Excess 210Pb and excess 234Th profiles for time series cores collected at site M-04 in November 2010 and October 2012, and sites P–06, D–08, and D–10 collected in December 2010, February 2011, September 2011 and August 2012. Profiles are expanded to show the decrease in decay-corrected excess 234Th activities and excess 234Th depths following initial coring in December 2010 (see Fig 1 for core site locations).
Fig 6. Mass accumulation rates (MAR) and 234Th inventories for time series sites.
Graphs showing (A) average MAR over the past ~100 years calculated using excess 210Pb, (B) MAR of the four time series sites from November 2010 to October 2012 calculated using excess 234Th, (C) excess 234Th inventories of the four time series sites from November 2010 to October 2012.
Table 3. Results of T–test using Excess 234Th MAR and Inventories from *Late 2010/Early 2011 time period and +Late 2011/2012 time period.
| * Late 2010/ Early 2011 MAR | +Late 2011/2012 MAR | * Late 2010/ Early 2011 Inventory | +Late 2011/2012 Inventory | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.76 | 0.40 | 1.34 | 0.19 | |
| 1.09 | 0.25 | 1.89 | 0.40 | |
| 1.17 | 0.35 | 1.01 | 0.06 | |
| 2.40 | 0.14 | 0.59 | 0.26 | |
| 1.34 | 0.66 | 1.24 | 0.35 | |
| 1.58 | 0.20 | 2.72 | 0.44 | |
| 0.74 | 0.37 | |||
| 2.00 | 1.04 | |||
| 0.60 | 1.68 | |||
| 1.30 | 1.06 | |||
| 0.48 | 1.70 | |||
| Average | 1.31 | 0.33 | 1.34 | 0.28 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.59 | 0.19 | 0.66 | 0.14 |
| Standard Error | 0.18 | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.06 |
| n | 11 | 6 | 11 | 6 |
| P Value | 0.0070 | 0.0018 | ||
Discussion
Multiple independent lines of sedimentological, geochronological, geochemical, and biological evidence point to a rapid, but short-lived sedimentation event from surface waters to the deep sea floor of the NE Gulf of Mexico (GoM) in late 2010 that was coincident with the formation of oil slicks and marine snow formation from the DWH discharge [16, 23, 63]. A radionuclide distribution time series from sites occupied multiple times between 2010 and 2012 indicates greater excess 234Th depths, MAR and inventories in late 2010/early 2011 relative to later collection periods (Figs 5 and 6). Consistent dissimilarities in grain size and natural abundance radiocarbon over the surficial ~1 cm of sediments relative to underlying sediments are consistent with a lack of downward mixing of the surface ~1 cm into underlying, relatively homogeneous sediments by bioturbation, or other processes. Stratification in the form of speciation of metals, specifically solid phase Mn, provides evidence for redox change in sediments that is consistent with elevated sedimentation rates [64]. Total biomarker concentrations in sediments were also elevated above baseline levels (Figs 3 and 4). A dramatic decrease in benthic foraminifera density in surficial sediments coincided with the lack of bioturbation, apparent elevated mass accumulation rates and total biomarker concentrations (Figs 3 and 4). Lastly, a substantial enrichment in SSU rRNA gene sequences derived from photosynthetic organisms (phytoplankton chloroplasts) that normally occupy the sea surface mixed layer were detected in the top ~2 cm of deep-sea sediment cores, which is consistent with the hypothesis of a depositional event directly after the Deepwater Horizon (DWH) discharge (Fig 4). Both the microbial community structure (relative abundance of phytoplankton-affiliated gene sequences) and hydrocarbon chemistry (recalcitrant biomarkers) suggest input/deposition of material from surface waters was recorded in surficial sediments of cores collected in December, 2010.
Sedimentological, biological and chemical evidence are consistent with the rapid deposition of a layer corresponding to the depth of excess 234Th. In the absence of downward mixing, we hypothesize that the observed excess 234Th profiles reflect deposition, and that the entire 0.4–1.2 cm thick surface layer was deposited rapidly, within a period of 4–5 months. A central issue that must be addressed is that although the down-core excess 234Th profiles are consistent with decay profiles, bioturbation could produce similar distributions [65, 66]. Little information is available on bioturbation in shelf and slope sediments of the Gulf of Mexico. Polychaetes (38%) and amphipods (21%) comprised the majority of the macrofaunal (primary bioturbators) standing stock along the north-central and northeastern GoM slope previous to the DWH event [67]. Anecdotally, during foraminiferal identification [68], there were no visible skeletal remains of polychaete or amphipod taxa in the surface 50 mm of the D-08 and P-06 cores collected in December 2010 and February 2011. Bioturbation depths reported for deep-sea sediments in the GoM at sites near our study area (1.75 to 3.25 cm) are larger than the maximum excess 234Th depths (1.2 cm) observed in this study [30]. However, the variation in excess 234Th inventory is consistent with increased sediment deposition in 2010 and early 2011, and cannot be explained by variations in bioturbation. Bioturbation could increase the excess 234Th depth, but would not affect the excess 234Th inventory.
At steady state, excess 234Th inventories should be directly proportional to sediment accumulation rates. Under steady state conditions, the flux of excess 234Th to the seafloor (J in dpm cm-2 y-1) is directly proportional to the inventory of excess 234Th in seafloor sediments (I in dpm cm-2) multiplied by the decay constant (in y-1):
The summed decay rate of excess 234Th in the sediments is equal to the decay constant (λ) multiplied by the excess 234Th inventory (I) in sediments. At steady state (constant inventory) this decay rate is balanced by the input of new excess 234Th. As 234Th is highly particle reactive, excess 234Th input should be directly proportional to the sediment accumulation rate, and the input rate of excess 234Th should balance the decay rate. Since the decay rate is directly proportional to the inventory, so is the input rate and thus the sediment accumulation rate, assuming relatively steady state conditions on the time scale of the life of the tracer, which is several months.
Our results demonstrate that excess 234Th inventories decreased by a factor of 4–5 from late 2010 to late 2011 and 2012. Thus we assert that sediment accumulation rates follow the same trend. Excess 234Th inventories are independent of bioturbation, which would merely redistribute excess 234Th, not change the quantity of it. Over time, we observe the excess 234Th inventory decrease, which is consistent with decreasing rates of excess 234Th input via decreased sedimentation rates. Excess 234Th-derived sediment mass accumulation rates were at least 4 times higher in late 2010 (0.48 to 2.40 g.cm-2y-1), as compared to 2011 and 2012 (0.14 to 0.66 g cm-2y-1) (Figs 5 and 6).
The dramatic decline in excess 234Th depth, mass accumulation rates (MAR), and excess 234Th inventories (which is independent of bioturbation) in our time series results (Figs 5 and 6; Table 2) are consistent with the occurrence of a brief, but rapid depositional event in summer/fall 2010 after the DWH discharge. These results indicate that the depositional event quickly subsided in 2011, and sedimentation remained relatively constant over the subsequent two years (Figs 5 and 6). The depositional pulse was detected in continental slope sediments between ~300 m and ~1500 m both to the east and west of DeSoto Canyon. The 100 m site (M-01) revealed no indication of a distinct surface layer and no excess 234Th signal. Although excess 234Th-derived MAR for the surface layer are considerably higher than average rates calculated for the previous ~100 years using excess 210Pb (Table 2), rates determined using these different methods cannot be directly compared due to the differences in time scales involved [69, 70].
In contrast to surface sediment layers characterized in previous work conducted closer to the wellhead [17, 19], the distinct color change in the surface layer (<1–10 cm) of this study is not a reflection of the sedimentology or petroleum input, but reflects diagenetic processes that are consistent with a rapid depositional event. The ≤1 cm-thick dark brown-black color bands within the surficial brown layer represent spikes in manganese (Mn) oxides, as indicated by enrichments of Mn relative to titanium (Ti) and iron (Fe) in XRF core scans (Figs 3 and 4). Manganese oxide enrichments are commonly observed in pelagic surface sediments due to redox-related cycling of Mn in association with organic matter diagenesis. Below the oxygen penetration depth in the sediment column, Mn oxides are utilized as electron acceptors in ongoing organic matter remineralization [71]. This process releases dissolved Mn2+ into pore waters, which then diffuses vertically upwards and reprecipitates as Mn oxides upon contact with dissolved oxygen. In pore waters, such Mn cycling results in a single, well-defined peak of Mn oxide close to the oxygen penetration depth [72]. However, most cores analyzed in this study show multiple Mn peaks in the upper sediments, suggesting a pulsing of sediment input. Multiple Mn peaks in sediment cores have been interpreted to indicate vertical shifts in the oxygen penetration depth [73, 74], which causes the active Mn peak to shift vertically, leaving a relict peak at the former position. Bulk Mn sampled at mm-scale resolution, digested in strong acid, and measured by ICP-MS by Hastings [64] corroborates the multiple Mn peaks we observe and the rapid shoaling of the Mn oxide peak.
Depositional mechanisms
Our observations are consistent with a depositional pulse driven by the formation and rapid settling of the large marine snow particles, as documented in overlying surface waters of the northern GoM during early summer 2010 [14]. Elevated hopane concentrations in sediments [23, 75], depletion in natural abundance radiocarbon [63], and the detection of oil-associated marine snow [16], is consistent with the incorporation of DWH oil in marine snow particles and their rapid sedimentation to the deep NE GoM. Specifically, hopanes, steranes, and diasteranes, which are widely used for oil fingerprinting, detected in the surface sediment pulse layer of cores used in this study, indicated the presence of DWH oil. Sediments below the surface layer and from a control site (all depth intervals) showed no match with DWH oil [75]. Following the DWH event, marine snow aggregates over a wide range of size classes formed in surface oil slicks and possibly in subsurface oil plumes [7, 14]. Once buoyancy was lost, the marine snow rapidly settled to the sea floor. The detection of gene sequences affiliated with planktonic diatoms originating from sea surface habitats in the surficial sediment layer (Fig 4), as well as larger concentrations of petrogenic hydrocarbons (Figs 3 and 4), is consistent with rapid settling of sea-surface material to the sea floor. Upon reaching the sea floor, organic matter was respired, creating reducing conditions in the sediments [64], thus apparently inhibiting bioturbation and facilitating the preservation of the sediment pulse layer. The relatively consistent siliciclastic and biogenic sedimentary components in surface sediments suggests that sediment sources did not noticeably change, but the depositional mechanism created a much higher flux rate of the natural particles in the water column to the sea floor, as supported by sediment trap observations by Passow (Pers. Comm, 2013). The slight increase in carbonate content and coccolithophores observed in some surface sediments is consistent with the observed increase in the clay-size fraction of the surface interval in some deeper cores.
Although our findings are consistent with a documented marine snow event, alternative depositional mechanisms must be considered. For example, the intentional discharge of Mississippi River water to repel oiled waters from coastal regions [76] would be expected to increase siliciclastic input/deposition. The unusually high seasonal runoff may also have increased siliciclastic input/deposition. An increase in bio-mineral (i.e., carbonate and/or siliceous) production due to nutrient input from increased Mississippi River discharge may also have occurred. However, no significant increase in siliciclastic composition was detected. In fact, the only systematic variation in sediment composition was a subtle increase in calcium carbonate content in the two deep cores (D-08 and D-10) west of DeSoto Canyon, which is where increased siliciclastic input would be most expected. In addition, with one exception (core P-06), cores collected to the east of DeSoto Canyon, a carbonate province generally believed to receive little input from Mississippi River sediments, recorded the pulse with no increase in siliciclastic input. Additionally, Mississippi River discharge could not explain the elevated hopane, sterane, and diasterane concentrations [23, 75] and depletion in natural abundance radiocarbon [63] in NE GoM surface sediments that are indicative of petroleum hydrocarbon input. Thus, although input from the Mississippi River may have played a role, our evidence supports marine snow as the primary depositional mechanism.
Advective, or lateral sediment transport is another possibility, and is not uncommon in deep-sea settings [77], including the NE GoM [78]. Advection could explain the variations in excess 234Th inventories in our two-year time series due to sediment focusing. However, our observations of organisms and chemicals transferred from the sea-surface to surficial sediments (phytoplankton gene sequences and biomarkers) and the consistency in sediment source cannot be explained by an advective transport mechanism. Though advective transport undoubtedly plays a role in depositional patterns of the NE GoM and should continue to be investigated, our results are more consistent with a sedimentation pulse originating from the sea surface.
Conclusions
A depositional pulse was recorded in bottom sediments in the DeSoto Canyon region of the NE Gulf of Mexico during late summer and fall of 2010, as a ~1 cm-thick sedimentary layer extending up to 100 nautical miles northeast of the DWH wellhead in water depths ranging from ~300 to ~1500 m. The sediment pulse layer was detected in two diverse sedimentological regimes, exhibited sedimentary properties distinctly different from underlying sediments, and included components originating from the sea surface. The depositional mechanism is interpreted to be an extensive marine snow event that was observed in surface waters over the study area during the summer of 2010. Independent studies have linked the marine snow event with the 2010 DWH blowout. Sediments below the surface pulse layer are generally homogeneous and contain no evidence of previous similar depositional events, which suggests that either this was a unique occurrence, or that deposits resulting from such events have not been preserved in the sedimentary record. Continued study will help to determine if/how this depositional event will eventually be recorded in bottom sediments in the NE GoM.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to dedicate this work to Benjamin (Ben) P. Flower, who passed away in July 2012. Without Ben’s foresight, scientific acuity, and immense amount of work, this project would not have been possible. We wish to thank Tony Greco and Dominika Wojcieszek, College of Marine Science, University of South Florida, for help with SEM/EDS analysis. Thanks also to Paul Schroeder, University of Georgia Department of Geology for X-ray Diffraction (XRD) analysis. Thanks to Samantha Bosman at Florida State University and NOSAMS at Woods Hole, MA for radiocarbon sample processing and analysis. Special thanks go to Rineke Gieles and the NIOZ (Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research) for help with XRF and Color Scanning analysis. We thank Tessa Hill for her valuable review comments. We also wish to thank Eckerd College students Alexandra Valente, Aya Matsunaga, Henry Ashworth, Nichole Clark, and Kacie Hill for their dedication and hard work. Data pertaining to this study can be accessed at the GRIIDC website: https://data.gulfresearchinitiative.org/.
Data Availability
(https://data.gulfresearchinitiative.org) (https://data.gulfresearchinitiative.org/data/Y1.x031.000:0001) (https://data.gulfresearchinitiative.org/data/Y1.x031.000:0002) (https://data.gulfresearchinitiative.org/data/Y1.x031.000:0003).
Funding Statement
Funding was provided by the Gulf of Mexico Research Initiative (http://gulfresearchinitiative.org) through the Florida Institute of Oceanography (http://www.fio.usf.edu), Center for Integrated Modeling and Analysis of Gulf Ecosystems (http://www.marine.usf.edu/c-image/), and Deepsea to Coast Connectivity in the Eastern Gulf of Mexico (http://deep-c.org) consortia. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Environchron provided support in the form of salaries for authors C.W.H., but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the ‘author contributions’ section.
References
- 1. Camilli R, Reddy CM, Yoerger DR, Van Mooy BAS, Jakuba MV, Kinsey JC, et al. (2010) Tracking hydrocarbon plume transport and biodegradation at Deepwater Horizon. Science 330: 201–204. 10.1126/science.1195223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Graham WM, Condon RH, Carmichael RH, D’Ambra I, Patterson, Linn LJ, et al. (2010) Oil Carbon entered the coastal planktonic food web during the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ. Res. Lett. 5: 045301. [Google Scholar]
- 3. Valentine DL, Kesser JD, Redmond MC, Mendes SD, Heintz MB, Farwell C, et al. (2010) Propane respiration jump-starts microbial response to Deep Oil spill. Science 330: 208–211. 10.1126/science.1196830 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Joye SB, MacDonald IR, Leifer I, Asper V, (2011) Magnitude and oxidation potential of hydrocarbon gases released from the BP oil well blowout. Nat. Geosci. 4: 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- 5. Thibodeaux LJ, Valsaraj KT, John VT, Papadopoulos KD, Pratt LR, Pesika NS, et al. (2011) Marine oil fate: knowledge gaps, basic research, and development needs; a perspective based on the Deepwater Horizon spill. Environ. Eng. Sci. 28: 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- 6. Barron MG, (2012) Ecological impacts of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill: implications for immunotoxicity. Toxicol. Pathol. 40: 315–20. 10.1177/0192623311428474 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Ziervogel K, Mckay L, Rhodes B, Osburn CL, Dickson-Brown J, Arnosti C, et al. (2012) Microbial activities and dissolved organic matter dynamics in oil-contaminated surface seawater from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill site. PLOS ONE 7(4): e34816 10.1371/journal.pone.0034816 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Lubchenco J, McNutt MK, Dreyfus G, Murawski SA, Kennedy DM, Anastas PT, et al. (2012) Science in support of the Deepwater Horizon response. PNAS 109(50): 20212–20221. 10.1073/pnas.1204729109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ryerson TB, Camilli R, Kessler JD, Kujawinski EB, Reddy CM, Valentine DL, et al. (2011) Chemical data quantify Deepwater horizon hydrocarbon flow rate and the environmental distribution. PNAS 109(50): 20246–20253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Dietrich JC, (2012) Surface trajectories of oil transport along the northern coastline of the Gulf of Mexico. Continental Shelf Research 41: 17–47. [Google Scholar]
- 11. Garcia-Pineda O, MacDonald I, Hu C, Svejkovsky J, Hess M, Dukhovskay D, et al. (2013) Detection of floating oil anomalies from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill with synthetic aperture radar. Oceanography 26: 124–137. [Google Scholar]
- 12. Spier C, Stringfellow WT, Hazen TC, Conrad M, (2013) Distribution of hydrocarbons released during the 2010, MC252 oil spill in the deep offshore waters. Environ. Pollut. 173: 224–230. 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.10.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hollander, DJ, Flower, BP, Larson, R, Brooks, G, Romero, I, Zinzola, N, et al. (2012) Deposition, distribution and fate of Macondo oil in the sediments of the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. 2012 Ocean Sciences Meeting. Feb 23 2012.
- 14. Passow U, Ziervogel K, Aper V, Diercks A, (2012) Marine snow formation in the aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Res. Lett. 7: 035301. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dell’Amore, C, Sept 23, 2010. "Sea Snot" Explosion Caused by Gulf Oil Spill? National Geographic News. http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2010/09/100916-sea-snot-gulf-bp-oil-spill-marine-snow-science-environment/
- 16.Passow, U, (2014) Formation of rapidly–sinking, oil-associated marine snow. Deep-Sea Research-II. 10.1016/j.dsr2.2014.10.001. [DOI]
- 17. Joye SB, Teske AP, Kostka JE, (2014) Microbial dynamics following the Macondo oil well blowout across Gulf of Mexico environments. BioScience 64: 766–777. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brooks, GR, Larson, RA, Hollander, D, Flower, B, Hastings, D, Valenete, A, et al. (2012) Rapid increase in sediment accumulation rate and shift in sedimentary regime in the NE Gulf of Mexico following the 2010 BP blowout, Poster presentation, AGU/ASLO Ocean Sciences meeting, Feb. 2012, Salt Lake City, UT.
- 19.Ziervogel, K, Joye, SB, Arnosti, C, (2014) Microbial enzymatic activity and secondary production in sediments affected by the sedimentation pulse following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Deep-Sea Research-II. 10.1016/j.dsr2.2014.04.003. [DOI]
- 20. Penna N, Rinaldi A, Montanari G, Di Paolo A, Penna A, (1993) Mucilaginous masses in the Adriatic Sea in the summer of 1989. Water Res. 27: 1767–1771. [Google Scholar]
- 21. Herndl GJ, Arrieta JM, Stoderegger K, (1999) Interaction between specific hydrological and microbial activity leading to extensive mucilage formation in the northern Adriatic Sea. Ann 1st Super Sanita. 35 (3): 405–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Stachowitsch M, Fanuko N, Richter M, (1990) Mucus aggregates in the Adriatic Sea: an overview of stages and occurrence. Mar. Ecol. 11: 327–350. [Google Scholar]
- 23. Valentine DL, Fisher GB, Bagby SC, Nelson RK, Reddy CM, Sylva SP, et al. (2014) Fallout plume of submerged oil from Deepwater Horizon. PNAS 111(45): 15906–15911. 10.1073/pnas.1414873111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Harbison RN, (1968) Geology of De Soto Canyon. J. Geophys. Res. 73: 5175–5185. [Google Scholar]
- 25. Gould HR, Stewart RH, (1956) Continental terrace sediments in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Soc. Econ. Paleont. and Min. Sp. Pub 3: 2–19. [Google Scholar]
- 26. Doyle LJ, Sparks TN, (1980) Sediments of the Mississippi Alabama and Florida (MAFLA) continental shelf. Journ. Sed. Petrol. 50: 905–916. [Google Scholar]
- 27. Balsam WL, Beeson JP, (2003) Sea-floor sediment distribution in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep-Sea Res I. 50: 1421–1444. [Google Scholar]
- 28. Emiliani C, (1975) Paleoclimatological analysis of late Quaternary cores from the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Science 189: 1083–1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Nurnberg D, Ziegler M, Karas C, Tiedemann R, Schmidt MW, (2008) Interacting loop current variability and Mississippi river discharge over the past 400 kyr. Earth Planet. Sci. 272: 278–289. [Google Scholar]
- 30. Yeager KM, Stantschi PH, Rowe GT, (2004) Sediment accumulation and radionuclide inventories (239,240Pu, 210Pb and 234Th) in the northern Gulf of Mexico, as influenced by organic matter and macrofaunal density. Mar. Chem. 91: 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- 31. Griffin GM, (1962) Regional clay mineral facies. Products of weathering intensity and current distribution in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 73: 737–768. [Google Scholar]
- 32. Sionneau T, Bout-Roumazeilles V, Biscayne PE, Van Vilet-Lanoe B, Broy A, (2008) Clay mineral distributions in and around the Mississippi river watershed and northern Gulf of Mexico: source and transport patterns. Quat. Sci. Rev. 27: 1740–1751. [Google Scholar]
- 33. Folk RL, (1965) Petrology of sedimentary rocks Hemphillis, Austin, Texas. [Google Scholar]
- 34. Milliman JD, (1974) Marine Carbonates. Springer-Verlag, New York. [Google Scholar]
- 35. Dean WE, (1974) Determination of carbonate and organic material in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: comparison with other methods. Journ. of Sed. Petrol. 44m: 242–248. [Google Scholar]
- 36. Tjallingii R, Röhl U, Kölling M, Bickert T, (2007) Influence of the water content on X-ray fluorescence core scanning measurements in soft marine sediments. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems (G-cubed). 8: 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 37. Caporaso J, Lauber CL, Walters W, Berg-Lyons D, Huntley J, Fierer N, et al. (2012) Ultra-high-throughput Microbial Community Analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq Platforms. The ISME Journal 6 (8): 1621–1624. 10.1038/ismej.2012.8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Caporaso J, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman F, Costello EK, et al. (2010) QIIME Allows Analysis of High-Throughput Community Sequencing Data. Nature Publishing Group 7 (5): 335–336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, et al. , (2006) Greengenes, a Chimera-checked 16S rRNA Gene Database and Workbench Compatible with ARB. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 72 (7): 5069–5072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Edgar RC, (2010) Search and Clustering Orders of Magnitude Faster Than BLAST. Bioinformatics. 26 (19): 2460–2461. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, et al. (2013) Quality-filtering Vastly Improves Diversity Estimates from Illumina Amplicon Sequencing. Nat Meth 10 (1): 57–59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J., Chai B, Farris RJ, et al. , (2009). The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 37 (Supp. 1): D141–D145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR, (2007) Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 73(16):5261–5267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Choi Y, Wang Y, (2004) Dynamics of carbon sequestration in a coastal wetland using radiocarbon measurements. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 18, 10.1029/2004GB002261 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Vogel JS, Southon JR, Nelson DE, Brown TA, (1984) Performance of catalytically condensed carbon for use in accelerator mass spectrometry. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research. B5: 289–293. [Google Scholar]
- 46. Stuiver M, Polach HA, (1977) Reporting of 14C Data. Radiocarbon 19: 355–363 [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sen Gupta, BK, Lobegeier, MK, Smith, LE, (2009). Foraminiferal communities of bathyal hydrocarbon seeps, northern Gulf of Mexico: A taxonomic, ecologic, and geologic study. U.S. Dept. of the Interior, Minerals Management Service, Gulf of Mexico OCS Region, New Orleans, LA. OCS Study MMS 2009–013, 385.
- 48.8272 EM (2007) Parent and alkyl polycyclic aromatics in sediment pore water by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry in selected ion monitoring mode. 1–34.
- 49. Prince RC, Elmendorf DL, Lute JR, Hsu CS, Haith CE, Senius JD, et al. (1994) 17.alpha.(H)-21.beta.(H)-hopane as a conserved internal marker for estimating the biodegradation of crude oil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 28(1): 142–145. 10.1021/es00050a019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Aeppli C, Nelson RK, Radović JR, Carmichael CA, Valentine DL, Reddy CM, et al. (2014) Recalcitrance and degradation of petroleum biomarkers upon abiotic and biotic natural weathering of Deepwater Horizon oil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48: 6726–6734. 10.1021/es500825q [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Kitto ME, (1991) Determination of photon self-absorption corrections for soil samples. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 42: 835–839. [Google Scholar]
- 52. Hussain N, Kim G, Church TM, Carey W, (1996) A simplified technique for gamma-spectrometric analysis of 210Pb in sediment samples. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 47: 473–477. [Google Scholar]
- 53. Cutshall NH, Larsen IL, Olsen C.R. (1983) Direct analysis of 210Pb in sediment samples: self-absorption corrections. Nuclear Inst. and Meth. 206: 309–312. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Holmes, CW, (2001) Short-lived isotopes in sediments (a tool for assessing sedimentary dynamics). USGS open file report.
- 55. Olsson IU, (1986) Radiometric dating, in, Berglund B.E. (ed.) Handbook of Holocene palaeoecology and palaeohydrology: New York, John Wiley and Sons, 298–331. [Google Scholar]
- 56. Bonnet PJP, Appleby PG, (1991) Deposition and transport of radionuclides within an upland drainage basin in mid-Wales. Hydrobiologia. 214: 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- 57. Pope RH, Demaster JD, Smith CR, Seltmann H, (1996) Rapid bioturbation in equatorial Pacific sediments: evidence from excess 234Th measurements. Deep-Sea Research 43: 1339–1364. [Google Scholar]
- 58. Santschi PH, Guo L, Asbill S, Allison M, Kepple AB, Wen LS, (2001) Accumulation rates and sources of sediment and organic carbon on the Palos Verdes shelf based on radioisotopic tracers (137Cs, 239,240Pu, 210Pb 234Th 238U 14C). Mar. Chem. 73: 125–152. [Google Scholar]
- 59. McKee BA, Nittrouer CA, DeMaster DJ, (1983) Concepts of sediment deposition and accumulation applied to the continental shelf near the mouth of the Yangtze River. Geology 11: 631–633. [Google Scholar]
- 60. Appleby PG, Oldfield F, (1983) The assessment of 210Pb data from sites with varying sediment accumulation rates. Hydrobiologia 103: 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- 61. Binford MW, (1990) Calculation and uncertainty analysis of 210Pb dates for PIRLA project lake sediment cores. J. Paleolimnology 3: 253–267. [Google Scholar]
- 62. Baskaran M, Santschi PH, (2002) Particulate and dissolved 210Pb activities in the shelf and slope regions of the Gulf of Mexico waters. Continental Shelf Research 22: 1493–1510. [Google Scholar]
- 63. Chanton J, Zhao T, Rosenheim BE, Joye S, Bosman S, Brunner C, et al. (2015) Using natural abundance radiocarbon to trace the flux of petrocarbon to the seafloor following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Env. Sci and Tech. 49(2): 847–854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hastings DW, Schwing, PT, Brooks, GR, Larson, RA, Morford, JL, Roeder, T, et al. (2014) Changes in sediment redox conditions following the BP DWH blowout event. Deep-Sea Research-II. 10.1016/j.dsr2.2014.12.009. [DOI]
- 65. Crusius J, Kenna TC (2007) Ensuring confidence in radionuclide-based sediment chronologies and bioturbation rates. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Sci. 71: 537–544. [Google Scholar]
- 66. Alexander CR, Walsh JP, Orpin AR, (2010) Modern sediment dispersal and marine accumulation on the outer Poverty continental margin. Marine Geology. 270: 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Rowe GT, Kennicutt, MC II, eds. (2009) Northern Gulf of Mexico continental slope habitats and benthic ecology study: Final report. U.S. Dept. of the Interior, Minerals Management. Service, Gulf of Mexico OCS Region, New Orleans, LA. OCS Study MMS 2009–039. 456 pp.
- 68. Schwing PT, Romero IC, Brooks GR, Hastings DW, Larson RA, Hollander DJ, (2015). A Decline in Deep-Sea Benthic Foraminifera Following the Deepwater Horizon Event in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. PLOSone, 10(3): e0120565 10.1371/journal.pone.0120565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Sadler P, (1981) Sedimentation rates and the completeness of stratigraphic sections. Journal of Geology 89, 569–584. [Google Scholar]
- 70. Anders MH, Krueger SW, Sadler PM, (1987) A new look at sedimentation rates and the completeness of the stratigraphic record. Journal of Geology 95: 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- 71. Froelich PN, Klinkhammer GP, Bender ML, Luedtke NA, Heath GR, Cullen D, et al. , (1979) Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: sub-oxic diagenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 43: 1075–1090. [Google Scholar]
- 72. Burdige DJ, (1993) The biogeochemistry of manganese and iron reduction in marine sediments. Earth Sci. Rev. 35: 249–284. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Price, BA, (1998) Equatorial Pacific Sediments: A Chemical Approach to Ocean History, Ph. D. Diss., Scripps Inst. Oceanol., UCSD, 364 pp.
- 74. Finney BP, Lyle MW, Heath GR, (1988) Sedimentation at MANOP site H (eastern Equatorial Pacific) over the past 400,000 years: climatically induced redox variations and their effects on transition metal cycling. Paleoceanography 3:169–189. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Romero, IC, Schwing, PT, Brooks, GR, Larson, RA, Hastings, DW, Ellis, G, et al., (In Press). Hydrocarbons in deep-sea sediments following the 2010 Deepwater Horizon blowout in the northeast Gulf of Mexico. PLOSone, [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 76. Bianchi TS, Cook RL, Perdue EM, Kolic PE, Green N, Zhang Y, et al. , (2011) Impacts of diverted freshwater on dissolved organic matter and microbial communities in Barataria Bay, Louisiana, U.S.A. Marine Environmental Research 72: 248–257. 10.1016/j.marenvres.2011.09.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Gardner WD, Southard JB, Hollister CD, (1985) Sedimentation, resuspension and chemistry of particles in the northwest Atlantic. Marine Geology 65: 199–242. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Diercks, A, Asper, V, Passow, U, Ziervogel, K, Dike, C, (2013) Hydrography and its implication to resuspension of sediments in the northern Gulf of Mexico. 2013 MOSSFA Meeting. Oct.22–23, 2013, Tallahassee, FL.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
(https://data.gulfresearchinitiative.org) (https://data.gulfresearchinitiative.org/data/Y1.x031.000:0001) (https://data.gulfresearchinitiative.org/data/Y1.x031.000:0002) (https://data.gulfresearchinitiative.org/data/Y1.x031.000:0003).