Abstract
Malawi adopted the Option B+ strategy in 2011. Its success in reducing MTCT depends on coverage and timing of HIV testing. We assessed HIV status ascertainment and its predictors during pregnancy. HIV status ascertainment was 82.3% (95%-CI 80.2–85.9) in the pre-Option B+ period and 85.7% (95%-CI 83.4–88.0) in the Option B+ period. Higher HIV ascertainment was independently associated with higher age, attending ANC more than once, and registration in 2010. The observed high variability of HIV ascertainment between sites (50.6%–97.7%) and over time suggests that HIV test kits shortages and insufficient numbers of staff posed major barriers to reducing MTCT.
Keywords: PMTCT, HIV testing, antenatal care, supplies, Malawi
Background
UNAIDS and other agencies have called for the virtual elimination of mother-to-child transmission (EMTCT) of HIV. The 2011 global EMTCT plan (1) established strategies for accomplishing this goal, and requires that 90% of all HIV-positive women have access to ART, so that new infections can be reduced to <5%. But in many African countries, far fewer than 90% of pregnant women are tested for HIV. In Malawi, just over 70% of pregnant women had their HIV status ascertained during antenatal care in 2010 (2). Many women are tested for the first time during pregnancy, and HIV testing rates vary substantially between settings (3).
Until August 2011, pregnant HIV-positive women in Malawi were managed under the 2006 World Health Organisation prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) guidelines. These guidelines recommended women with a CD4 count ≥350 cells/µl, and women in WHO stage 1 and 2 to start on antiretroviral prophylaxis in the third trimester (28 weeks). Lifelong ART was only recommended for women with a CD4 cell count <350 cells/µl and those in WHO stage 3 or 4.
In September 2011, Malawi was the first country to introduce the Option B+ strategy, which calls for lifelong ART for all pregnant and breastfeeding women, irrespective of CD4 count and clinical status (4). Option B+ is intended to streamline access to treatment and care for HIV-positive women, but its success depends on testing a sufficient percentage of pregnant women. We sought to determine the coverage, timing and predictors of HIV testing among pregnant Malawian women who attended antenatal care.
Methods
The PMTCT service cascade starts at the antenatal care (ANC) clinic, which is usually part of an integrated maternal and child health (MCH) service. Upon registration at the clinic, a woman’s baseline data, including age, parity, gravidity, gestational age, treatment history, preventive medicines (i.e. tetanus vaccine and malaria prophylaxis), and previous HIV test results are recorded in paper-based registers. Follow-up data are recorded at every visit thereafter, and include HIV testing status, preventive medications, and body weight. Each woman is followed for 6 months from registration, after which ANC outcomes are determined. During this follow-up period the woman is expected to make at least four scheduled visits. ART data are collected in paper-based registers at smaller health facilities, while facilities with more than 2500 patients use an electronic medical records system (EMR) (5).
Our primary measure was HIV ascertainment among pregnant women who attended ANC between January 1, 2010 and March 31, 2014 in Southern and Central Malawi. We included all sites that had an EMR ART system in April 2011, the time when data entry started. Women were classified as HIV negative if their records included a negative HIV test within the last three months before the antenatal visit. They were classified HIV positive if their record showed a positive HIV test, or if there was written evidence that they were on ART. Secondary outcomes were gestational age at the first ANC visit, percentage of women tested for HIV during the first trimester among all women who attended antenatal care, and percentage of HIV-positive women among all women whose HIV status had been ascertained. We analysed individual records of HIV tests extracted from the paper-based ANC registers for the pre Option B+ period (January 1, 2010 until June 30, 2011) and aggregated facility data for the whole time period (January 1, 2010 until March 2014).
We entered the individual-level ANC records into an electronic database. We calculated, by facility, the percentage of women whose HIV status had been ascertained, and combined the results in a random-effect meta-analysis. Among women whose HIV status was unknown at ANC initiation, we calculated, for each facility, the percentage that was given rapid HIV tests. The percentage of women tested at clinics with at least 10 ANC attendees was calculated for each week. We used univariable and multivariable random-effects logistic regression models to identify demographic and facility-level characteristics associated with ascertaining HIV status. We considered the following variables: age (<20, 20–34, and ≥35 years); parity (0, 1, >1); gestational age at first ANC visit (first trimester versus thereafter); number of ANC visits (1, >1); and, year of ANC registration (2010, 2011). We also included facility-level characteristics: facility location (urban, rural); zone (Central-East, Central-West, South-East, South-West); type of facility (health centre, Christian Health Association of Malawi [CHAM] hospital, district hospital, central hospital); and, the mean number of women registered at ANC per month (<300 women, ≥300 women). We did a complete case analysis and an analysis with multiple imputations. Missing data concerning gestational age, HIV ascertainment, parity and age were imputed using multiple imputation with chained equations (6). We imputed values dependent upon on HIV ascertainment, parity category, gestational age category, as well as the other predictor variables from the multivariable analysis. We created 15 imputed datasets and combined results using Rubin’s rule (7).
We used the aggregated facility-level data to compare the proportion of women with ascertained HIV status during the pre-Option B+ and the Option B+ period.
The National Health Sciences Research Committee granted ethical approval for the study (approval number 962). All data analyses were done with STATA software (Version 13.1, Stata Corporation,USA).
Results
100,515 women from 19 sites were included in the individual-level data analysis and 194,345 women from the same sites were included in the aggregated data analysis. There were 13 district hospitals, 3 CHAM hospitals, 2 central hospitals and 1 health centre. 5 of the 19 sites were located in urban areas while other 5 sites served more than 300 new ANC women every month. 5 sites were located in the central west zone, 4 in the central east zone, 6 in the south east zone and 4 in the south west zone.
Individual-level data
The characteristics of these women are shown in Table 1. Only few women (5,641; 5.6%) made their first antenatal visit in the first trimester (range between facilities 1.6% to 14.7%). We had missing data of 5,370 (5.3%) women on HIV ascertainment, 10,254 (10.2%) on gestational age at first ANC visit and 3,319 (3.3%) on parity.
Table 1.
Patients and facility characteristics associated with HIV status ascertainment among pregnant women attending antenatal care in selected health facilities in Malawi
| No. of women |
Women with ascertained HIV status |
Imputed |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Adjusted | |||||||
| N | % | OR | 95% CI | P-value | OR | 95% CI | P-value | |
| Clinic burden | ||||||||
| ≤300women/month | 50,252 | 87.4 | 1 | <0.001 | 1 | 0.928 | ||
| >300 women/month | 50,263 | 77.2 | 0.45 | 0.43–0.47 | 0.78 | 0.21–2.91 | ||
| Facility type | ||||||||
| Health center | 7,470 | 50.6 | 1 | <0.001 | 1 | 0.155 | ||
| CHAM hospital | 10,738 | 82.2 | 2.94 | 2.72–3.19 | 1.44 | 0.12–16.86 | ||
| District hospital | 75,062 | 84.4 | 2.69 | 2.54–2.85 | 2.39 | 0.26–22.19 | ||
| Central hospital | 7,245 | 92.7 | 11.25 | 9.66–13.11 | 8.61 | 0.61–121.43 | ||
| Gestational age at 1st visit | ||||||||
| ≤12 weeks | 5,641 | 80.7 | 1 | 0.481 | 1 | 0.605 | ||
| >12 weeks | 84,620 | 81.1 | 1.03 | 0.95–1.12 | 0.98 | 0.89–1.07 | ||
| Unknown | 10,254 | 92.6 | ||||||
| Parity | ||||||||
| Never given birth | 26,195 | 81.9 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.825 | |||
| 1 birth | 21,911 | 82.2 | 1.00 | 0. 94–1.05 | 1.00 | 0.93–1.07 | ||
| >1 births | 49,090 | 83.1 | 1.06 | 1.01–1.11 | 0.98 | 0.92–1.05 | ||
| Unknown | 3,319 | 74.5 | ||||||
| Age (years) | ||||||||
| <20 | 19,219 | 81.2 | 1 | <0.001 | 1 | 0.005 | ||
| 20–35 | 69,371 | 83.0 | 1.15 | 1.10–1.21 | 1.10 | 1.03–1.17 | ||
| >35 | 7,278 | 84.4 | 1.21 | 1.12–1.32 | 1.15 | 1.04–1.28 | ||
| Unknown | 4,647 | 73.6 | ||||||
| Registration year | ||||||||
| 2011 | 65,084 | 77.2 | 1 | <0.001 | 1 | <0.001 | ||
| 2010 | 35,431 | 85.1 | 1.67 | 1.61–1.73 | 1.77 | 1.70–1.85 | ||
| Facility location | ||||||||
| Rural | 34,983 | 84.0 | 1 | 0.516 | 1 | 0.745 | ||
| Urban | 65,532 | 79.0 | 1 | 0.99–1.02 | 0.77 | 0.17–3.60 | ||
| Health Area Zone | ||||||||
| Central East | 15,922 | 87.1 | 1 | <0.001 | 1 | 0.947 | ||
| Central West | 38,465 | 86.3 | 0.89 | 0.83–0.95 | 0.99 | 0.28–3.48 | ||
| South East | 29,301 | 82.3 | 0.54 | 0.50–0.57 | 1.34 | 0.34–5.36 | ||
| South West | 16,827 | 68.7 | 0.46 | 0.43–0.50 | 0.95 | 0.26–3.46 | ||
| No of ANC visits | ||||||||
| 1 ANC visit | 27,164 | 71.1 | 1 | <0.001 | 1 | <0.001 | ||
| >1 ANC visits | 73,351 | 86.4 | 2.38 | 2.29–2.47 | 2.65 | 2.54–2.77 | ||
CHAM: Christian Health Association of Malawi; OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; n: number of participants; ANC: antenatal care
Adjusted for all variables shown in the table above.
HIV status was ascertained for 82,714 (82.3%) of women, but this percentage varied widely across sites, from 50.6% to 97.7%. In eight (42.1%) of the 19 facilities at least 90% of women had their HIV status ascertained during pregnancy. Most of the women (70,879; 85.7%) whose HIV status was ascertained had no previous valid HIV test result at the start of ANC and thus took a rapid HIV test, but the percentage ranged from 55.0% to 99.0% between facilities. Among women with known HIV status, 12.8% (10,596 out of 82,714) were HIV-positive; this percentage varied from 1.4% to 19.5% between facilities.
Table 1 shows the predictors of HIV ascertainment of the imputed analyses. In the unadjusted analysis, the likelihood of ascertained HIV status increased with age, parity and the number of ANC visits. There was no difference between women who started ANC during the first trimester and those who started later. Women who were registered in 2011 were less likely to have ascertained HIV status. Health facilities in urban areas, that were health centres, located in southern zones, and that had ≥300 women registered per month were less likely to have high ascertained levels than health facilities in rural areas, located in central zones, that were not health centres, and that served <300 women per month. In multivariable analyses age, registration year, and number of ANC visits remained independently associated with HIV ascertainment.
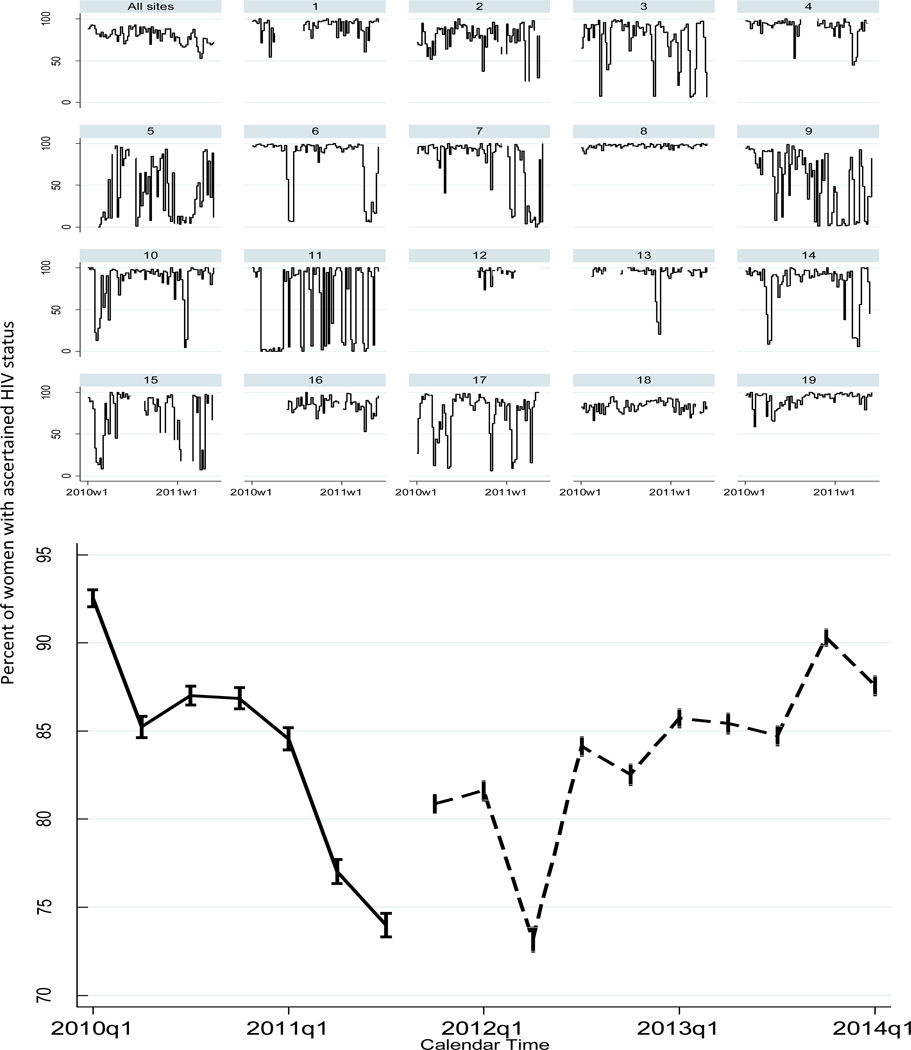
Figure 1 top panel shows weekly percentages of women whose HIV status was unknown at their first ANC visit, and who were subsequently tested during pregnancy. The proportion of women tested during pregnancy declined over time. In many facilities testing rates fluctuated widely, and there were often weeks in which almost no women were tested. In only one site was HIV testing coverage >90% throughout the whole period examined.
Figure 1.
Upper Panel: Proportion of women with unknown HIV status tested at their first antenatal care visit (n=70,879/88,680* *11,835 women with previous HIV test result have been excluded from the denominator; w1= first week of the year. Lower Panel: Percentage of women with ascertained HIV status by quarter for pre-optionB+ (solid) and optionB+ (dash) periods. q1 = first quarter of the year (January-March
Aggregated-level data
Aggregated-level data show that HIV ascertainment did not improve in the Option B+ period: while it was 82.3% (95% CI 80.2 –85.9) in the pre Option B+ period, it was 85.7 (95% CI 83.4– 88.0) in the B+ period (Figure 1 lower panel.
Discussion
We found that EMTCT goal of ascertaining the HIV status of at least 90% of all pregnant women at ANC clinics was not reached in Malawi between 2010 and 2014. Over this period of 51 months the overall rate of HIV ascertainment was 84.8% and did not change significantly since the introduction of Option B+. Ascertainment rates varied widely between sites and fluctuated tremendously in sites over short time periods. Prior to Option B+ only 16% of facilities reached or exceeded the target of 90% of testing women with unknown status, but only one facility reached 90% every week. Women were more likely to have ascertained HIV status if they were older, registered in 2010 and if they made more than one antenatal visit.
Our data suggest that important barriers to achieving the EMTCT goal exist at the facility level. We observed sudden decreases over time in the number of women who received a new HIV test, and this is in line with previous findings that showed that temporary shortages of test kit supplies and staff interrupt regular testing of women for HIV during pregnancy (8–12). Unfortunately, adequate data about the availability of HIV test kits and staff during the period were not available.
Several studies have shown that social and individual factors are associated with low rates of HIV testing. Low uptake of HIV testing has been associated with single motherhood, low level of education, lower socio-economical class, late antenatal care attendance, and fewer ANC visits (3, 4, 13–17). We also found that women who had more than one ANC visit were more likely to have an ascertained HIV status than those who made a single visit, probably because multiple visits increased the chance to attend when materials and testing staff were available. Consistent with findings in the Malawi Demographic Health Survey of 2010, we found that women less younger than 20 were less likely to have known HIV status than older women (18).
The large number of participants, and the diverse group of facilities across the whole country of Malawi allowed us to examine many factors in parallel that can influence HIV ascertainment. Our study also has a number of limitations: If women registered more than once, we would have been unable to identify this. We lacked access to socio-economic information, while this can determine HIV testing status importantly. We had incomplete data on gestational age, age, parity and HIV testing, however similar results of the analysis with multiple imputations and the complete case analysis in multivariable modelling suggests that this did not affect outcomes importantly. We were also limited by our inability to determine why individual women were not tested. A Malawian study from 2005 showed that 4.5% of women refused pre-test counselling, saying they wanted to get their husband’s consent and then never coming back (19). We restricted our study to women who attended ANC in a health facility, since all but 3% of pregnant women attend antenatal care (18); an unknown proportion of women first present only in maternity or during delivery.
Conclusion
The current level of HIV testing uptake among pregnant women in Malawi is too low to reach the EMTCT targets and the millennium development goals, and this rate needs to be improved to attain the full benefits that the Option B+ strategy potentially offers. The reasons why some facilities consistently have high ascertainment rates must be determined by future research. Potential barriers such as HIV test kits shortages and an inadequate number of trained staff at clinics need to be tackled with high priority.
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank the following persons who did the data entry: Ashton Mwechumu, Salome Shaba, Bazaliel Nemoni, Clement Nthala, Dorren Makamba, Enock Chauwa, Gomezyani Nayasulu, Gladys Mpacha, Lyton Chimososla, Memory Dzonzi, Alinafe Chingwalu, Takondwa Zidana, Asemenye Nyasulu, Faith Phiri, Mafuno Midiani, Synos Nkhata, Nancy Maosa and Alinafe Kantambo. This work was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute for Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)[IeDEA Southern Africa grant number U01 AI0699 24], the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation [Global Health Grant number opp1090200] and the USAID-NIH initiative http://sites.nationalacademies.org/PGA/dsc/peerhealth/index.htm Partnership for Enhanced Engagement in Research (PEER) Health (NIH/PEER) grant number AID-OAA-A-11-00012.
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the sponsors. O.K. and J.E. were supported by a PROSPER fellowship grant to O.K. from the Swiss National Science Foundation (number 150934). The Malawi MOH HIV/ AIDS Program is funded by The Global Fund and the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR).
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: None to declare
References
- 1.Mahy M, Stover J, Kiragu K, et al. What will it take to achieve virtual elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV? An assessment of current progress and future needs. Sexually transmitted infections. 2010 Dec;86(Suppl 2):ii48–ii55. doi: 10.1136/sti.2010.045989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ministry of Health Government of M. Quarterly HIV Programme Report 2010. 2010. Mar, [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wettstein C, Mugglin C, Egger M, et al. Missed opportunities to prevent mother-to-child-transmission: systematic review and meta-analysis. Aids. 2012 Nov 28;26(18):2361–2373. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328359ab0c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schouten EJ, Jahn A, Midiani D, et al. Prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV and the health-related Millennium Development Goals: time for a public health approach. Lancet. 2011;378(9787):282–284. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Douglas GP, Gadabu OJ, Joukes S, et al. Using touchscreen electronic medical record systems to support and monitor national scale-up of antiretroviral therapy in Malawi. PLoS medicine. 2010;7(8) doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sterne JA, White IR, Carlin JB, et al. Multiple imputation for missing data in epidemiological and clinical research: potential and pitfalls. Bmj. 2009;338:b2393. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.D. R. Multiple imputation for nonresponse in surveys. Wiley; 1987. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Government of Malawi MoH. Quarterly HIV Programme Report. Lilongwe, Malawi; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Government of Malawi MoH. HIV Programme Quarterly Report. Lilongwe, Malawi; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ministry of Health Government of M. Quarterly HIV Program Report. 2010. Oct, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 11.MOH MG. Integrated HIV Program Quarterly Report. 2012. Jan-Mar [Google Scholar]
- 12.Government M. Integrated HIV program Quarterly Report. Lilongwe: 2013. Jan-Mar. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Larsson EC, Thorson AE, Pariyo G, et al. Missed Opportunities: barriers to HIV testing during pregnancy from a population based cohort study in rural Uganda. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e37590. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Peltzer K, Mlambo G, Phaweni K. Factors determining prenatal HIV testing for prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV in Mpumalanga, South Africa. AIDS and behavior. 2010 Oct;14(5):1115–1123. doi: 10.1007/s10461-009-9662-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hanh NT, Gammeltoft TM, Rasch V. Number and timing of antenatal HIV testing: evidence from a community-based study in Northern Vietnam. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:183. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Perez F, Zvandaziva C, Engelsmann B, Dabis F. Acceptability of routine HIV testing ("opt-out") in antenatal services in two rural districts of Zimbabwe. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2006 Apr 1;41(4):514–520. doi: 10.1097/01.qai.0000191285.70331.a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.WHO. Use of AntiretrovirAl DrUgs for treAting PregnAnt Women AnD Preventing Hiv infection in infAnts. 2012
- 18.Macro. NSONaI. Malawi Demographic and Health Survey 2010. Zomba, Malawi, and Calverton, Maryland, USA: 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Manzi M, Zachariah R, Teck R, et al. High acceptability of voluntary counselling and HIV-testing but unacceptable loss to follow up in a prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission programme in rural Malawi: scaling-up requires a different way of acting. Tropical medicine & international health : TM & IH. 2005 Dec;10(12):1242–1250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2005.01526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]