Abstract
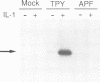
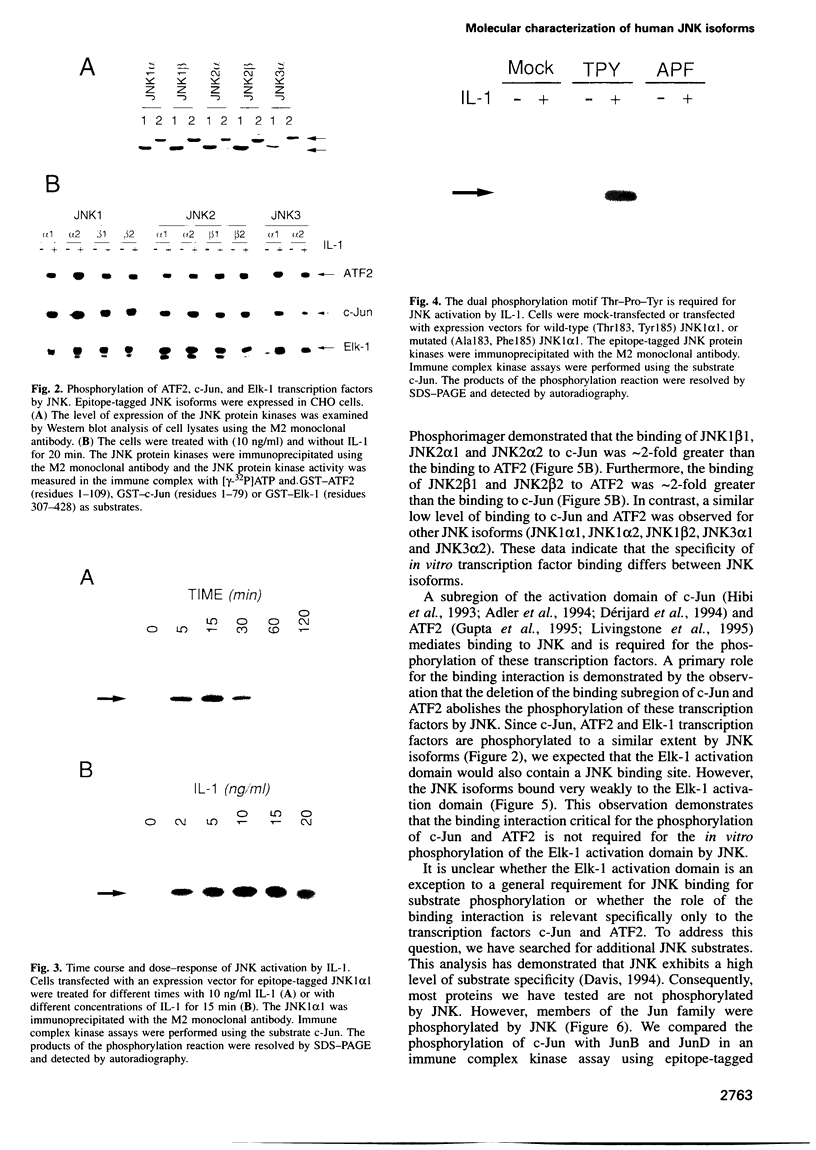
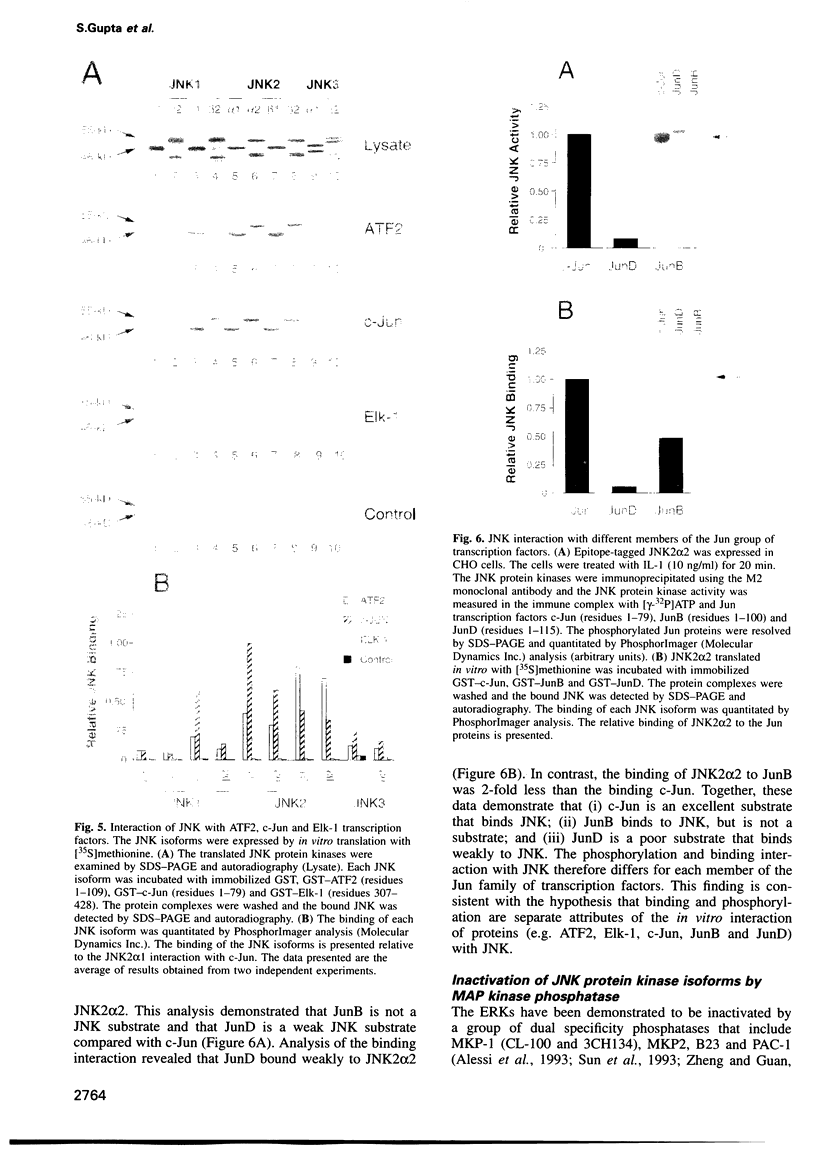
The JNK protein kinase is a member of the MAP kinase group that is activated in response to dual phosphorylation on threonine and tyrosine. Ten JNK isoforms were identified in human brain by molecular cloning. These protein kinases correspond to alternatively spliced isoforms derived from the JNK1, JNK2 and JNK3 genes. The protein kinase activity of these JNK isoforms was measured using the transcription factors ATF2, Elk-1 and members of the Jun family as substrates. Treatment of cells with interleukin-1 (IL-1) caused activation of the JNK isoforms. This activation was blocked by expression of the MAP kinase phosphatase MKP-1. Comparison of the binding activity of the JNK isoforms demonstrated that the JNK proteins differ in their interaction with ATF2, Elk-1 and Jun transcription factors. Individual members of the JNK group may therefore selectively target specific transcription factors in vivo.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler V., Franklin C. C., Kraft A. S. Phorbol esters stimulate the phosphorylation of c-Jun but not v-Jun: regulation by the N-terminal delta domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5341–5345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler V., Polotskaya A., Wagner F., Kraft A. S. Affinity-purified c-Jun amino-terminal protein kinase requires serine/threonine phosphorylation for activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17001–17005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler V., Unlap T., Kraft A. S. A peptide encoding the c-Jun delta domain inhibits the activity of a c-jun amino-terminal protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11186–11191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagrodia S., Dérijard B., Davis R. J., Cerione R. A. Cdc42 and PAK-mediated signaling leads to Jun kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 24;270(47):27995–27998. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.47.27995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles C. H., Abler A. S., Lau L. F. cDNA sequence of a growth factor-inducible immediate early gene and characterization of its encoded protein. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Angel P., Karin M. Jun-B differs in its biological properties from, and is a negative regulator of, c-Jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90754-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coso O. A., Chiariello M., Yu J. C., Teramoto H., Crespo P., Xu N., Miki T., Gutkind J. S. The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Abate C., Baker S., Kerppola T., Xanthoudakis S. The regulation of c-fos: too much is never enough. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1993;28:271–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. MAPKs: new JNK expands the group. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Nov;19(11):470–473. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T., Karin M. JunB differs from c-Jun in its DNA-binding and dimerization domains, and represses c-Jun by formation of inactive heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):479–490. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T., Karin M. c-Fos transcriptional activity stimulated by H-Ras-activated protein kinase distinct from JNK and ERK. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):171–175. doi: 10.1038/371171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Raingeaud J., Barrett T., Wu I. H., Han J., Ulevitch R. J., Davis R. J. Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.7839144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin C. C., Sanchez V., Wagner F., Woodgett J. R., Kraft A. S. Phorbol ester-induced amino-terminal phosphorylation of human JUN but not JUNB regulates transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7247–7251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Strahl T., Shaw P. E. Activation of ternary complex factor Elk-1 by stress-activated protein kinases. Curr Biol. 1995 Oct 1;5(10):1191–1200. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Campbell D., Dérijard B., Davis R. J. Transcription factor ATF2 regulation by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Science. 1995 Jan 20;267(5196):389–393. doi: 10.1126/science.7824938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Seth A., Davis R. J. Transactivation of gene expression by Myc is inhibited by mutation at the phosphorylation sites Thr-58 and Ser-62. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3216–3220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Lin A., Smeal T., Minden A., Karin M. Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2135–2148. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S. I., Ryseck R. P., Mechta F., Bravo R., Yaniv M. Characterization of junD: a new member of the jun proto-oncogene family. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1433–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Both Jun and Fos contribute to transcription activation by the heterodimer. Oncogene. 1990 Jan;5(1):39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi T., Bottaro D. P., Michieli P., Kelley C. A., Aaronson S. A. A novel dual specificity phosphatase induced by serum stimulation and heat shock. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29897–29902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallunki T., Su B., Tsigelny I., Sluss H. K., Dérijard B., Moore G., Davis R., Karin M. JNK2 contains a specificity-determining region responsible for efficient c-Jun binding and phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):2996–3007. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.2996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyse S. M., Emslie E. A. Oxidative stress and heat shock induce a human gene encoding a protein-tyrosine phosphatase. Nature. 1992 Oct 15;359(6396):644–647. doi: 10.1038/359644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Minden A., Martinetto H., Claret F. X., Lange-Carter C., Mercurio F., Johnson G. L., Karin M. Identification of a dual specificity kinase that activates the Jun kinases and p38-Mpk2. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):286–290. doi: 10.1126/science.7716521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Gorospe M., Yang C., Holbrook N. J. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase during the cellular response to genotoxic stress. Inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activity and AP-1-dependent gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 14;270(15):8377–8380. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.15.8377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone C., Patel G., Jones N. ATF-2 contains a phosphorylation-dependent transcriptional activation domain. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 18;14(8):1785–1797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07167.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., Claret F. X., Abo A., Karin M. Selective activation of the JNK signaling cascade and c-Jun transcriptional activity by the small GTPases Rac and Cdc42Hs. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1147–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., McMahon M., Lange-Carter C., Dérijard B., Davis R. J., Johnson G. L., Karin M. Differential activation of ERK and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinases by Raf-1 and MEKK. Science. 1994 Dec 9;266(5191):1719–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.7992057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra-Press A., Rim C. S., Yao H., Roberson M. S., Stork P. J. A novel mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase. Structure, expression, and regulation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14587–14596. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. F., Ashworth A., Hall A. An essential role for Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 GTPases in cell cycle progression through G1. Science. 1995 Sep 1;269(5228):1270–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.7652575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfarr C. M., Mechta F., Spyrou G., Lallemand D., Carillo S., Yaniv M. Mouse JunD negatively regulates fibroblast growth and antagonizes transformation by ras. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):747–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90513-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raingeaud J., Gupta S., Rogers J. S., Dickens M., Han J., Ulevitch R. J., Davis R. J. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7420–7426. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohan P. J., Davis P., Moskaluk C. A., Kearns M., Krutzsch H., Siebenlist U., Kelly K. PAC-1: a mitogen-induced nuclear protein tyrosine phosphatase. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1763–1766. doi: 10.1126/science.7681221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M., Lange-Carter C. A., Johnson G. L. Direct interaction between Ras and the kinase domain of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MEKK1). J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):11757–11760. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.11757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütte J., Minna J. D., Birrer M. J. Deregulated expression of human c-jun transforms primary rat embryo cells in cooperation with an activated c-Ha-ras gene and transforms rat-1a cells as a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2257–2261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütte J., Viallet J., Nau M., Segal S., Fedorko J., Minna J. jun-B inhibits and c-fos stimulates the transforming and trans-activating activities of c-jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90755-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Gonzalez F. A., Gupta S., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Signal transduction within the nucleus by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24796–24804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluss H. K., Barrett T., Dérijard B., Davis R. J. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor mediated by JNK protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8376–8384. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D. A., Birrer M., Karin M. Oncogenic and transcriptional cooperation with Ha-Ras requires phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):494–496. doi: 10.1038/354494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Charles C. H., Lau L. F., Tonks N. K. MKP-1 (3CH134), an immediate early gene product, is a dual specificity phosphatase that dephosphorylates MAP kinase in vivo. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Tonks N. K., Bar-Sagi D. Inhibition of Ras-induced DNA synthesis by expression of the phosphatase MKP-1. Science. 1994 Oct 14;266(5183):285–288. doi: 10.1126/science.7939666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez I., Hughes R. T., Mayer B. J., Yee K., Woodgett J. R., Avruch J., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I. Role of SAPK/ERK kinase-1 in the stress-activated pathway regulating transcription factor c-Jun. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):794–798. doi: 10.1038/372794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J. jun: oncogene and transcription factor. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;55:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60466-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward Y., Gupta S., Jensen P., Wartmann M., Davis R. J., Kelly K. Control of MAP kinase activation by the mitogen-induced threonine/tyrosine phosphatase PAC1. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):651–654. doi: 10.1038/367651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmarsh A. J., Shore P., Sharrocks A. D., Davis R. J. Integration of MAP kinase signal transduction pathways at the serum response element. Science. 1995 Jul 21;269(5222):403–407. doi: 10.1126/science.7618106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan M., Dai T., Deak J. C., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I., Woodgett J. R., Templeton D. J. Activation of stress-activated protein kinase by MEKK1 phosphorylation of its activator SEK1. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):798–800. doi: 10.1038/372798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. F., Guan K. L. Dephosphorylation and inactivation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase by a mitogen-induced Thr/Tyr protein phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16116–16119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinck R., Cahill M. A., Kracht M., Sachsenmaier C., Hipskind R. A., Nordheim A. Protein synthesis inhibitors reveal differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and stress-activated protein kinase pathways that converge on Elk-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;15(9):4930–4938. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.9.4930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Wilhelm D., Herr I., Steffen A., Herrlich P., Angel P. ATF-2 is preferentially activated by stress-activated protein kinases to mediate c-jun induction in response to genotoxic agents. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 18;14(8):1798–1811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]