Abstract
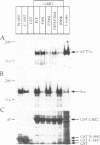
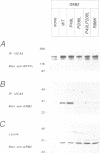
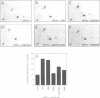
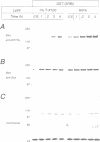
Receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase alpha (RPTPalpha), a transmembrane member of the extensive family of protein-tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs), is constitutively phosphorylated on Tyr789, a consensus binding site for the SH2 domain of the SH3-SH2-SH3 adaptor protein GRB2. We have previously shown that GRB2 binds to P.Tyr789 in vivo and in vitro via its SH2 domain. Here, we report that not only the GRB2 SH2 domain, but also the C-terminal SH3 domain is involved in binding to RPTPalpha in vitro and in vivo. Although the N-terminal SH3 domain of GRB2 is essential for binding to the Ras guanine nucleotide exchange factor Son of Sevenless (Sos), an RPTPalpha-GRB2-Sos complex could not be detected. The inclusion of peptides encompassing an hSos1 proline-rich motif in cell lysates resulted in enhanced binding of RPTPalpha to GRB2 in vitro, suggesting that steric hindrance prohibits formation of the RPTPalpha-GRB2-Sos complex. In vitro binding experiments indicated that the binding of GRB2 to Sos/dynamin and RPTPalpha was mutually exclusive. Analysis of in vitro binding kinetics coupled with results from transient co-transfections demonstrated that RPTPalpha is tightly bound to GRB2. The site of interaction of the C-terminal SH3 domain of GRB2 with RPTPalpha was mapped using deletion mutants to an 18-residue region in the N-terminal PTP domain. Arg469, within this region, was identified as one of the residues that is involved in the interaction with the C-terminal SH3 domain of GRB2. RPTPalpha residues 469-486 are localized close to the catalytic site cleft in the structure of the N-terminal PTP-domain, suggesting that interaction with the C-terminal SH3 domain may block access to the catalytic site, thus inhibiting RPTPalpha activity.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando A., Yonezawa K., Gout I., Nakata T., Ueda H., Hara K., Kitamura Y., Noda Y., Takenawa T., Hirokawa N. A complex of GRB2-dynamin binds to tyrosine-phosphorylated insulin receptor substrate-1 after insulin treatment. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3033–3038. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06602.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronheim A., Engelberg D., Li N., al-Alawi N., Schlessinger J., Karin M. Membrane targeting of the nucleotide exchange factor Sos is sufficient for activating the Ras signaling pathway. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):949–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autero M., Saharinen J., Pessa-Morikawa T., Soula-Rothhut M., Oetken C., Gassmann M., Bergman M., Alitalo K., Burn P., Gahmberg C. G. Tyrosine phosphorylation of CD45 phosphotyrosine phosphatase by p50csk kinase creates a binding site for p56lck tyrosine kinase and activates the phosphatase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1308–1321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barford D., Flint A. J., Tonks N. K. Crystal structure of human protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1397–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard P., Zhao Z., Banville D., Dumas F., Fischer E. H., Shen S. H. Phosphorylation and identification of a major tyrosine phosphorylation site in protein tyrosine phosphatase 1C. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19585–19589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady-Kalnay S. M., Flint A. J., Tonks N. K. Homophilic binding of PTP mu, a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase, can mediate cell-cell aggregation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):961–972. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90146-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. 1002 protein phosphatases? Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:463–493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. G., Stern M. J., Horvitz H. R. C. elegans cell-signalling gene sem-5 encodes a protein with SH2 and SH3 domains. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):340–344. doi: 10.1038/356340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cussac D., Frech M., Chardin P. Binding of the Grb2 SH2 domain to phosphotyrosine motifs does not change the affinity of its SH3 domains for Sos proline-rich motifs. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):4011–4021. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G., Regenass S., Sap J., Schlessinger J., Fischer E. H. Multiple forms of the human tyrosine phosphatase RPTP alpha. Isozymes and differences in glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10524–10528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Hui C. C., Pawson T. SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase as a target of protein-tyrosine kinases. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1607–1611. doi: 10.1126/science.8096088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Chen J. K., Yu H., Simon J. A., Schreiber S. L. Two binding orientations for peptides to the Src SH3 domain: development of a general model for SH3-ligand interactions. Science. 1994 Nov 18;266(5188):1241–1247. doi: 10.1126/science.7526465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E. H., Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: a diverse family of intracellular and transmembrane enzymes. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):401–406. doi: 10.1126/science.1650499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale N. W., Kaplan S., Lowenstein E. J., Schlessinger J., Bar-Sagi D. Grb2 mediates the EGF-dependent activation of guanine nucleotide exchange on Ras. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):88–92. doi: 10.1038/363088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garton A. J., Tonks N. K. PTP-PEST: a protein tyrosine phosphatase regulated by serine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3763–3771. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06687.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebbink M. F., Zondag G. C., Wubbolts R. W., Beijersbergen R. L., van Etten I., Moolenaar W. H. Cell-cell adhesion mediated by a receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16101–16104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gout I., Dhand R., Hiles I. D., Fry M. J., Panayotou G., Das P., Truong O., Totty N. F., Hsuan J., Booker G. W. The GTPase dynamin binds to and is activated by a subset of SH3 domains. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):25–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Issemann I., Sheer E. A versatile in vivo and in vitro eukaryotic expression vector for protein engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):369–369. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia Z., Barford D., Flint A. J., Tonks N. K. Structural basis for phosphotyrosine peptide recognition by protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Science. 1995 Jun 23;268(5218):1754–1758. doi: 10.1126/science.7540771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Feng G. S., Pawson T., Valius M. The 64-kDa protein that associates with the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta subunit via Tyr-1009 is the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6939–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger N. X., Streuli M., Saito H. Structural diversity and evolution of human receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatases. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3241–3252. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleider R. J., Freeman R. M., Jr, Neel B. G. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and growth factor receptor association of the human corkscrew homologue, SH-PTP2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13434–13438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Ladbury J. E., Mandiyan V., Zhou M., Schlessinger J. Independent binding of peptide ligands to the SH2 and SH3 domains of Grb2. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31653–31658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Nishimura R., Kashishian A., Batzer A. G., Kim W. J., Cooper J. A., Schlessinger J. A new function for a phosphotyrosine phosphatase: linking GRB2-Sos to a receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):509–517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim W. A., Richards F. M., Fox R. O. Structural determinants of peptide-binding orientation and of sequence specificity in SH3 domains. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):375–379. doi: 10.1038/372375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz U., Ravichandran K. S., Pei D., Walsh C. T., Burakoff S. J., Neel B. G. Lck-dependent tyrosyl phosphorylation of the phosphotyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP1 in murine T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1824–1834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein E. J., Daly R. J., Batzer A. G., Li W., Margolis B., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Skolnik E. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Schlessinger J. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90167-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maignan S., Guilloteau J. P., Fromage N., Arnoux B., Becquart J., Ducruix A. Crystal structure of the mammalian Grb2 adaptor. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):291–293. doi: 10.1126/science.7716522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. J., Cahir E. D., Thomas M. L. Identification of an additional member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family: evidence for alternative splicing in the tyrosine phosphatase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4444–4448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier J. P., Raabe T., Henkemeyer M., Dickson B., Mbamalu G., Margolis B., Schlessinger J., Hafen E., Pawson T. A Drosophila SH2-SH3 adaptor protein implicated in coupling the sevenless tyrosine kinase to an activator of Ras guanine nucleotide exchange, Sos. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90170-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peles E., Nativ M., Campbell P. L., Sakurai T., Martinez R., Lev S., Clary D. O., Schilling J., Barnea G., Plowman G. D. The carbonic anhydrase domain of receptor tyrosine phosphatase beta is a functional ligand for the axonal cell recognition molecule contactin. Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90312-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam L. A., Huff S. Y., Rabun K. M., Wei W., Park W., Broek D., Der C. J. Membrane-targeting potentiates guanine nucleotide exchange factor CDC25 and SOS1 activation of Ras transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8512–8516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran K. S., Lorenz U., Shoelson S. E., Burakoff S. J. Interaction of Shc with Grb2 regulates association of Grb2 with mSOS. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):593–600. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., D'Eustachio P., Givol D., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of a widely expressed receptor tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6112–6116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Jiang Y. P., Friedlander D., Grumet M., Schlessinger J. Receptor tyrosine phosphatase R-PTP-kappa mediates homophilic binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Tsai A. Y., Saito H. A family of receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatases in humans and Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8698–8702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su J., Batzer A., Sap J. Receptor tyrosine phosphatase R-PTP-alpha is tyrosine-phosphorylated and associated with the adaptor protein Grb2. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):18731–18734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy S., van der Geer P., Hunter T. The receptor-like protein-tyrosine phosphatase, RPTP alpha, is phosphorylated by protein kinase C on two serines close to the inner face of the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10587–10594. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W., Lammers R., Huang J., Ullrich A. Activation of a phosphotyrosine phosphatase by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1611–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.7681217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. M., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:101–120. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Pallen C. J. The receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase HPTP alpha has two active catalytic domains with distinct substrate specificities. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3231–3237. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye Z. S., Baltimore D. Binding of Vav to Grb2 through dimerization of Src homology 3 domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12629–12633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T., Ihle J. N. Association of hematopoietic cell phosphatase with c-Kit after stimulation with c-Kit ligand. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3350–3358. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Chen J. K., Feng S., Dalgarno D. C., Brauer A. W., Schreiber S. L. Structural basis for the binding of proline-rich peptides to SH3 domains. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):933–945. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog J., Pals C. E., Peppelenbosch M. P., Tertoolen L. G., de Laat S. W., Kruijer W. Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha activates pp60c-src and is involved in neuronal differentiation. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3789–3798. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog J., Sap J., Pals C. E., Schlessinger J., Kruijer W. Stimulation of receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase alpha activity and phosphorylation by phorbol ester. Cell Growth Differ. 1995 Mar;6(3):303–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
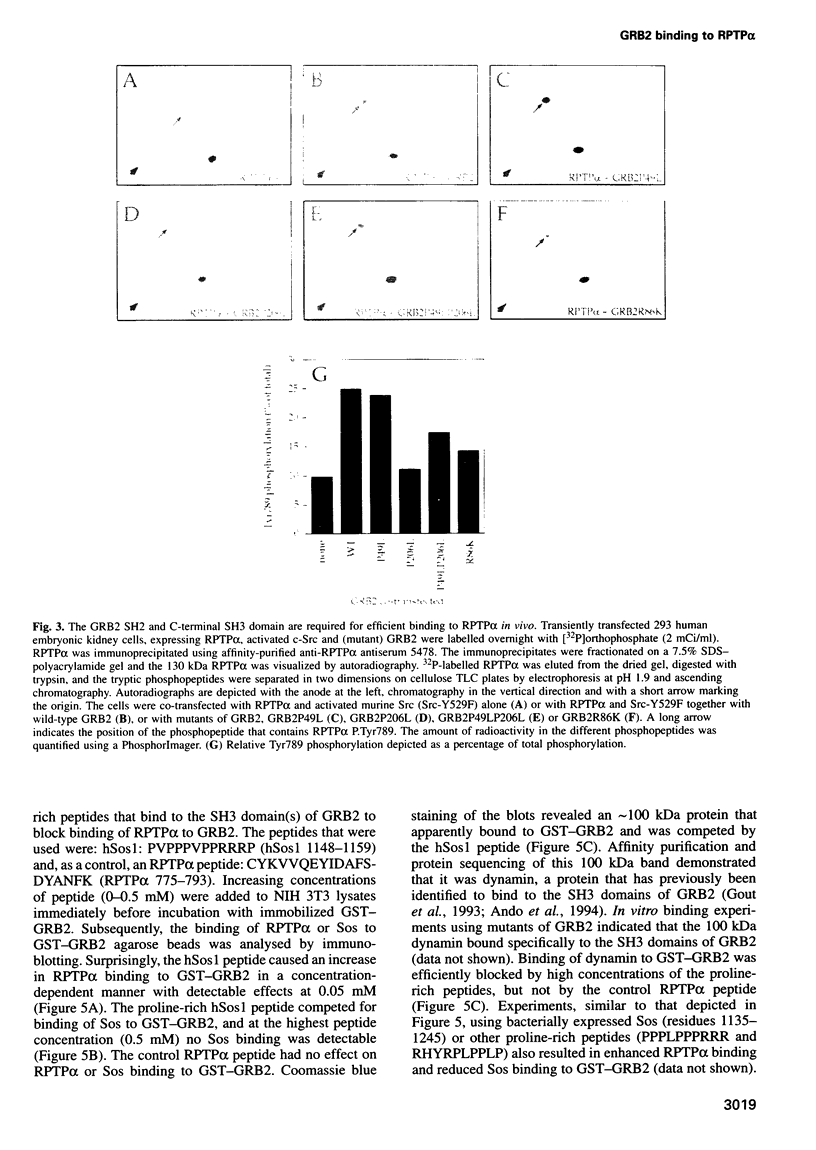
- den Hertog J., Tracy S., Hunter T. Phosphorylation of receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase alpha on Tyr789, a binding site for the SH3-SH2-SH3 adaptor protein GRB-2 in vivo. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3020–3032. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]