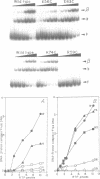
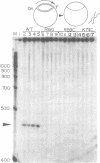
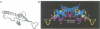
Abstract
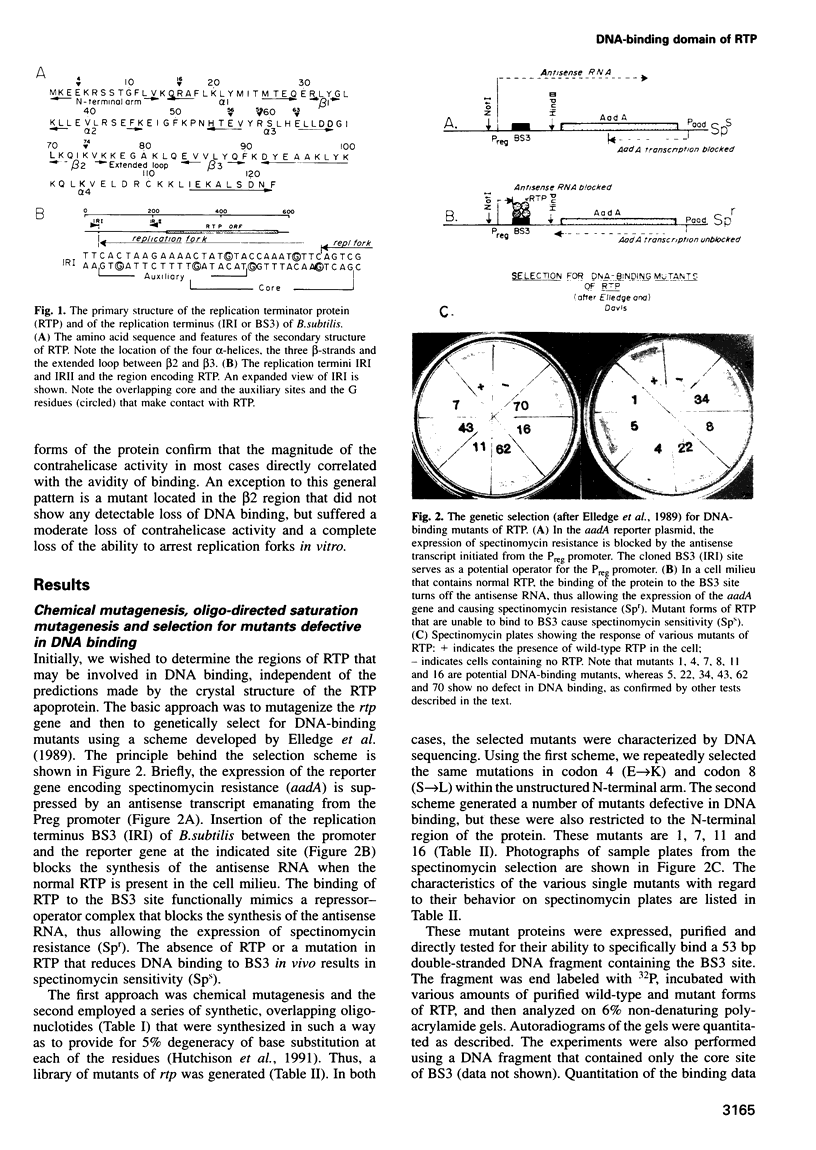
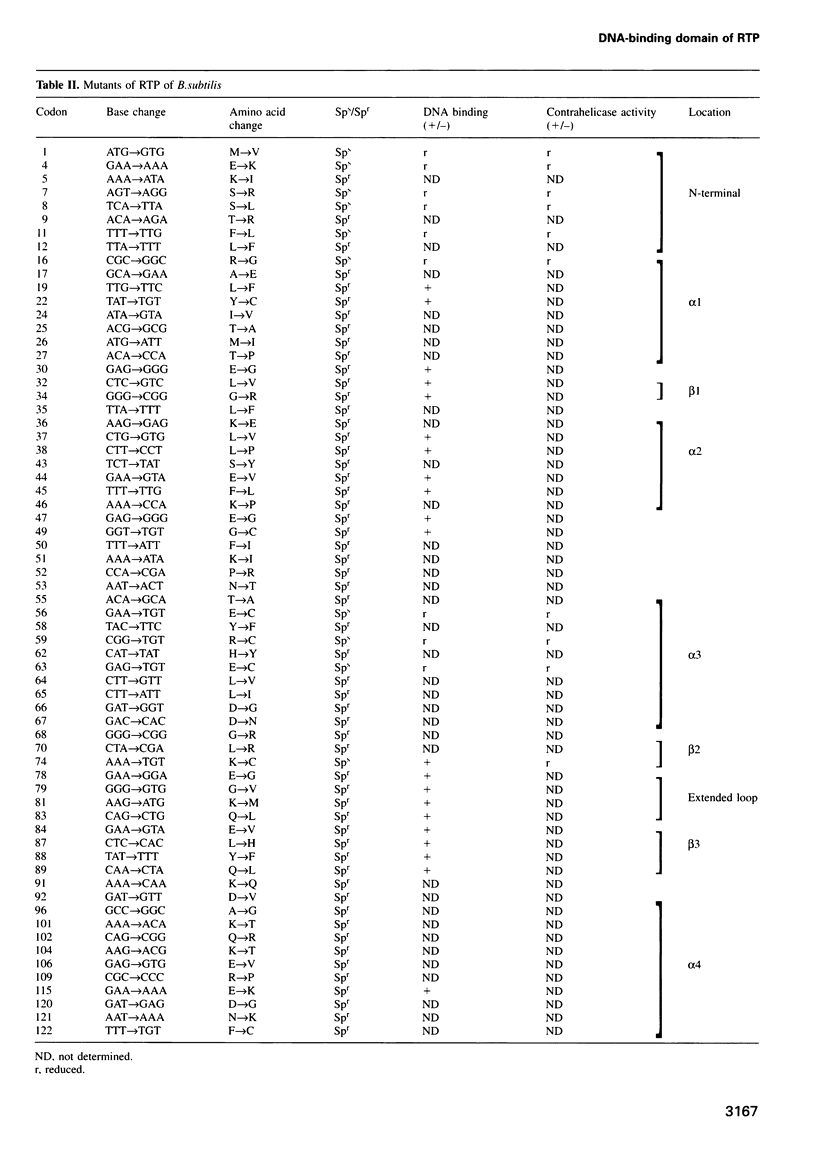
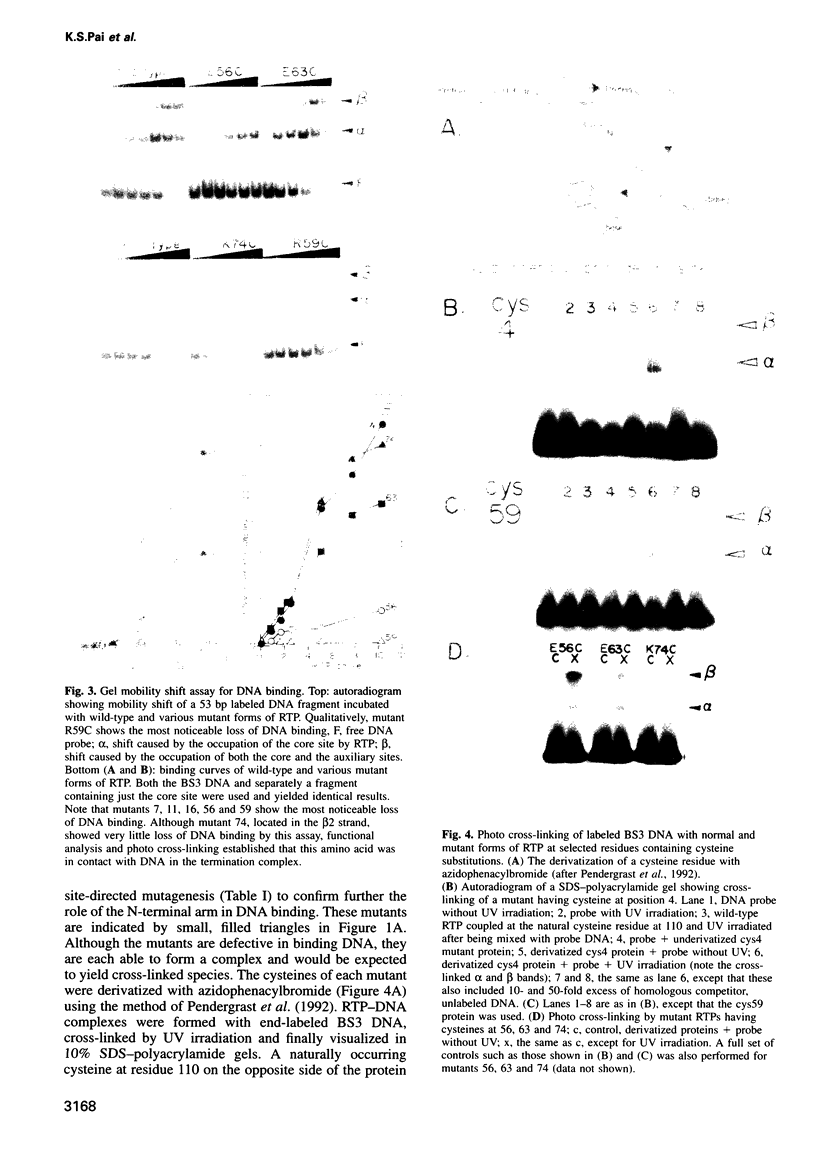
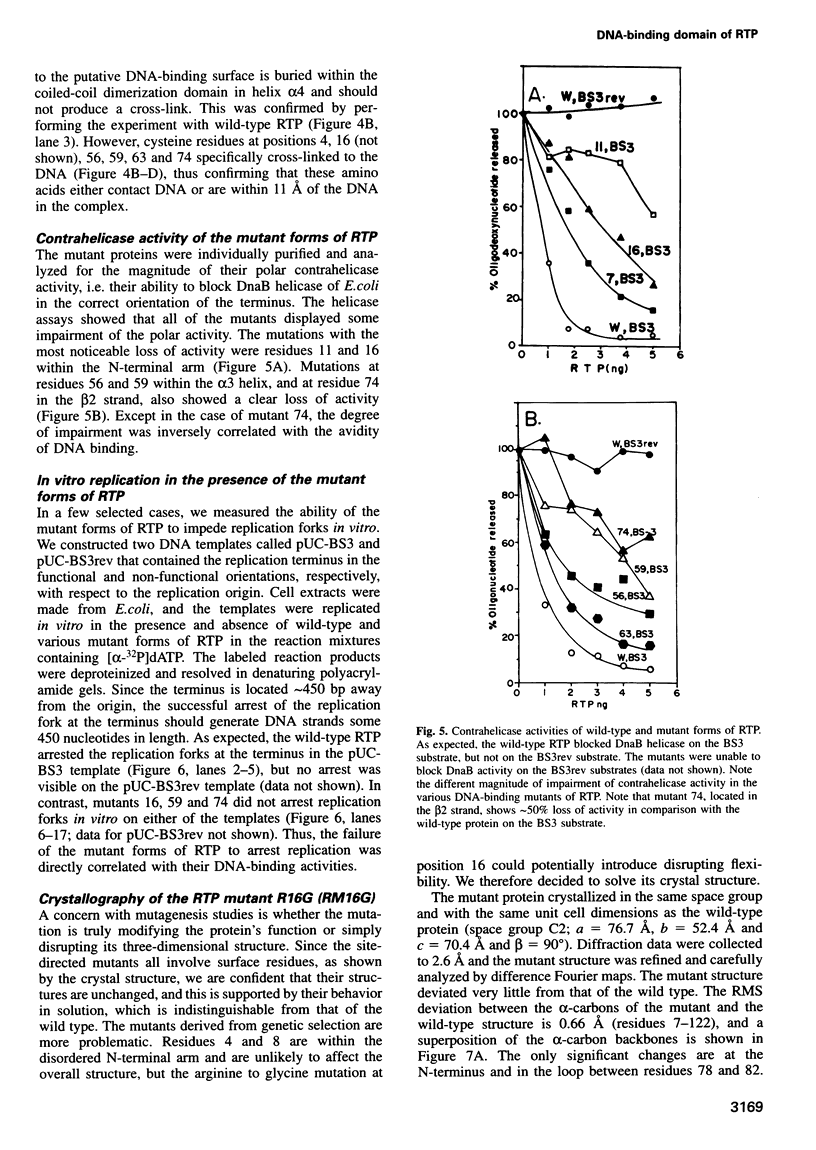
The replication terminator protein (RTP) of Bacillus subtilis impedes replication fork movement in a polar mode upon binding as two interacting dimers to each of the replication termini. The mode of interaction of RTP with the terminus DNA is of considerable mechanistic significance because the DNA-protein complex not only localizes the helicase-blocking activity to the terminus, but also generates functional asymmetry from structurally symmetric protein dimers. The functional asymmetry is manifested in the polar impedance of replication fork movement. Although the crystal structure of the apoprotein has been solved, hitherto there was no direct evidence as to which parts of RTP were in contact with the replication terminus. Here we have used a variety of approaches, including saturation mutagenesis, genetic selection for DNA-binding mutants, photo cross-linking, biochemical and functional characterizations of the mutant proteins, and X-ray crystallography, to identify the regions of RTP that are either in direct contact with or are located within 11 angstroms of the replication terminus. The data show that the unstructured N-terminal arm, the alpha3 helix and the beta2 strand are involved in DNA binding. The mapping of amino acids of RTP in contact with DNA, confirms a 'winged helix' DNA-binding motif.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastia D., Germino J., Crosa J. H., Ram J. The nucleotide sequence surrounding the replication terminus of R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2095–2099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussiere D. E., Bastia D., White S. W. Crystal structure of the replication terminator protein from B. subtilis at 2.6 A. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):651–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90519-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrigan C. M., Pack R. A., Smith M. T., Wake R. G. Normal terC-region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome acts in a polar manner to arrest the clockwise replication fork. J Mol Biol. 1991 Nov 20;222(2):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90206-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark K. L., Halay E. D., Lai E., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):412–420. doi: 10.1038/364412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Ebright Y. W., Pendergrast P. S., Gunasekera A. Conversion of a helix-turn-helix motif sequence-specific DNA binding protein into a site-specific DNA cleavage agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2882–2886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Sugiono P., Guarente L., Davis R. W. Genetic selection for genes encoding sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3689–3693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh R. H., Ottleben G., Rüterjans H., Schnarr M., Boelens R., Kaptein R. Solution structure of the LexA repressor DNA binding domain determined by 1H NMR spectroscopy. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):3936–3944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06709.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiasa H., Marians K. J. Differential inhibition of the DNA translocation and DNA unwinding activities of DNA helicases by the Escherichia coli Tus protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11379–11385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Tecklenburg M. L., Pelletier A. J., Kuempel P. L. tus, the trans-acting gene required for termination of DNA replication in Escherichia coli, encodes a DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1593–1597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Swanstrom R., Loeb D. D. Complete mutagenesis of protein coding domains. Methods Enzymol. 1991;202:356–390. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)02019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul S., Mohanty B. K., Sahoo T., Patel I., Khan S. A., Bastia D. The replication terminator protein of the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis functions as a polar contrahelicase in gram-negative Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11143–11147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatri G. S., MacAllister T., Sista P. R., Bastia D. The replication terminator protein of E. coli is a DNA sequence-specific contra-helicase. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Helinski D. R. Activity of the replication terminus of plasmid R6K in hybrid replicons in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 25;124(3):425–441. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley D. B., Smith M. T., Lewis P. J., Wake R. G. Protein-nucleoside contacts in the interaction between the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis and the DNA terminator. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(4):771–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. H., Kornberg A., Hidaka M., Kobayashi T., Horiuchi T. Escherichia coli replication termination protein impedes the action of helicases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9104–9108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Ralston G. B., Christopherson R. I., Wake R. G. Identification of the replication terminator protein binding sites in the terminus region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome and stoichiometry of the binding. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90147-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Smith M. T., Wake R. G. A protein involved in termination of chromosome replication in Bacillus subtilis binds specifically to the terC site. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3564–3567. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3564-3567.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Wake R. G. DNA and protein sequence conservation at the replication terminus in Bacillus subtilis 168 and W23. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1402–1408. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1402-1408.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louarn J., Patte J., Louarn J. M. Evidence for a fixed termination site of chromosome replication in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):295–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manna A. C., Pai K. S., Bussiere D. E., White S. W., Bastia D. The dimer-dimer interaction surface of the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis and termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 16;93(8):3253–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarelli J. M., Ermácora M. R., Fox R. O., Grindley N. D. Mapping interactions between the catalytic domain of resolvase and its DNA substrate using cysteine-coupled EDTA-iron. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 30;32(12):2979–2986. doi: 10.1021/bi00063a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta P. P., Bussiere D. E., Hoffman D. W., Bastia D., White S. W. Crystallization and preliminary structural analysis of the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18885–18889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Krovatin W., Jeffrey A., Sauer R. T. The N-terminal arms of lambda repressor wrap around the operator DNA. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):441–443. doi: 10.1038/298441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan C. Q., Feng J. A., Finkel S. E., Landgraf R., Sigman D., Johnson R. C. Structure of the Escherichia coli Fis-DNA complex probed by protein conjugated with 1,10-phenanthroline copper(I) complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1721–1725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergrast P. S., Chen Y., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Determination of the orientation of a DNA binding motif in a protein-DNA complex by photocrosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10287–10291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., Finch J. T., Graziano V., Lee P. L., Sweet R. M. Crystal structure of globular domain of histone H5 and its implications for nucleosome binding. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):219–223. doi: 10.1038/362219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Echevarría M. J., Giménez-Gallego G., Sabariegos-Jareño R., Díaz-Orejas R. Kid, a small protein of the parD stability system of plasmid R1, is an inhibitor of DNA replication acting at the initiation of DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1995 Apr 7;247(4):568–577. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo T., Mohanty B. K., Lobert M., Manna A. C., Bastia D. The contrahelicase activities of the replication terminator proteins of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis are helicase-specific and impede both helicase translocation and authentic DNA unwinding. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 8;270(49):29138–29144. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.49.29138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo T., Mohanty B. K., Patel I., Bastia D. Termination of DNA replication in vitro: requirement for stereospecific interaction between two dimers of the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis and with the terminator site to elicit polar contrahelicase and fork impedance. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 1;14(3):619–628. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07038.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang Z., Isaac V. E., Li H., Patel L., Catron K. M., Curran T., Montelione G. T., Abate C. Design of a "minimAl" homeodomain: the N-terminal arm modulates DNA binding affinity and stabilizes homeodomain structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8373–8377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sista P. R., Mukherjee S., Patel P., Khatri G. S., Bastia D. A host-encoded DNA-binding protein promotes termination of plasmid replication at a sequence-specific replication terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3026–3030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. T., Wake R. G. Definition and polarity of action of DNA replication terminators in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):648–657. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swindells M. B. Identification of a common fold in the replication terminator protein suggests a possible mode for DNA binding. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Aug;20(8):300–302. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. W., Appelt K., Wilson K. S., Tanaka I. A protein structural motif that bends DNA. Proteins. 1989;5(4):281–288. doi: 10.1002/prot.340050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Nash H. A. The interaction of E. coli IHF protein with its specific binding sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90801-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P. A., Wake R. G. The Bacillus subtilis replication terminator system functions in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jul 22;240(4):275–280. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]