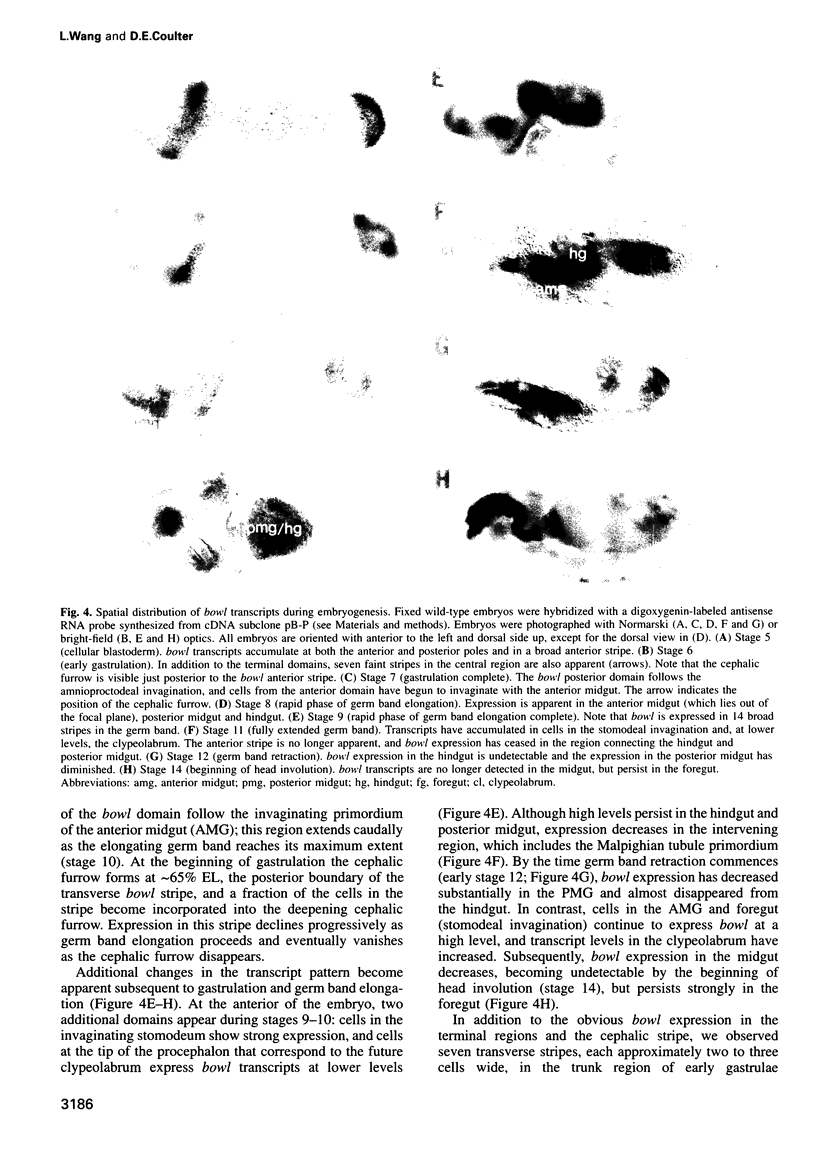
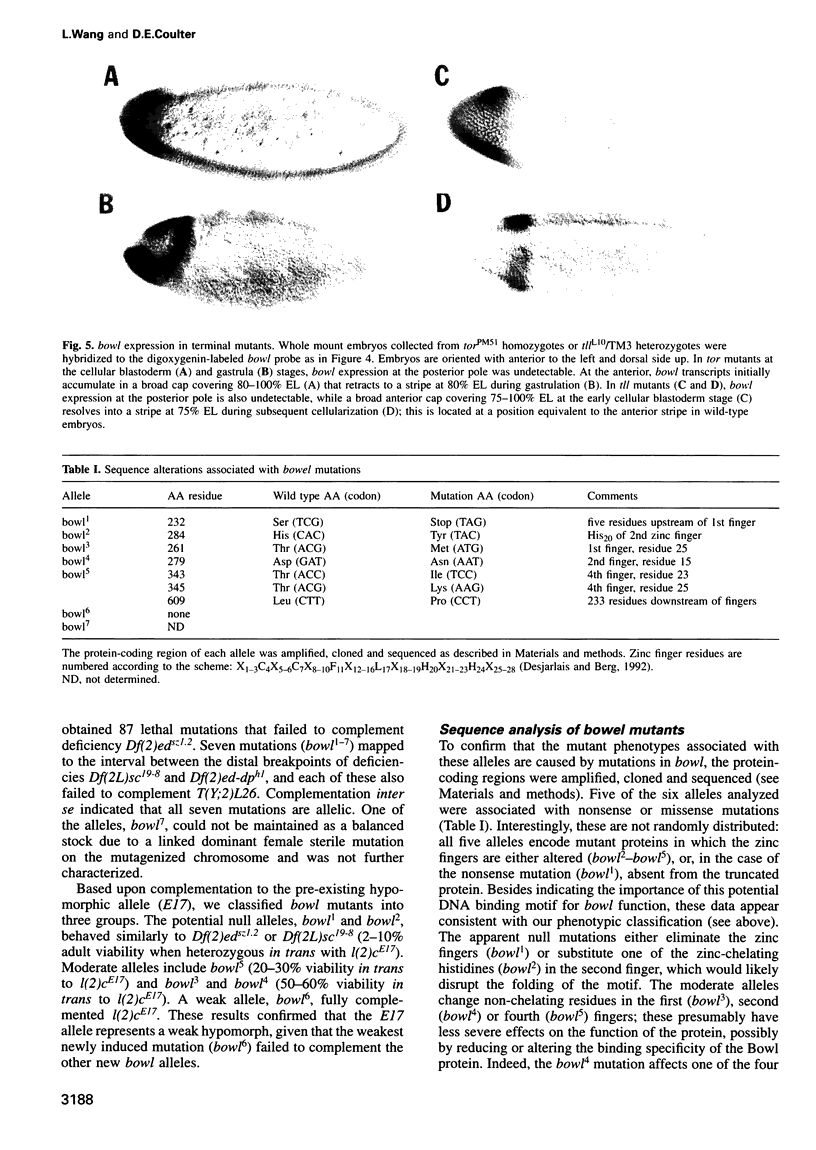
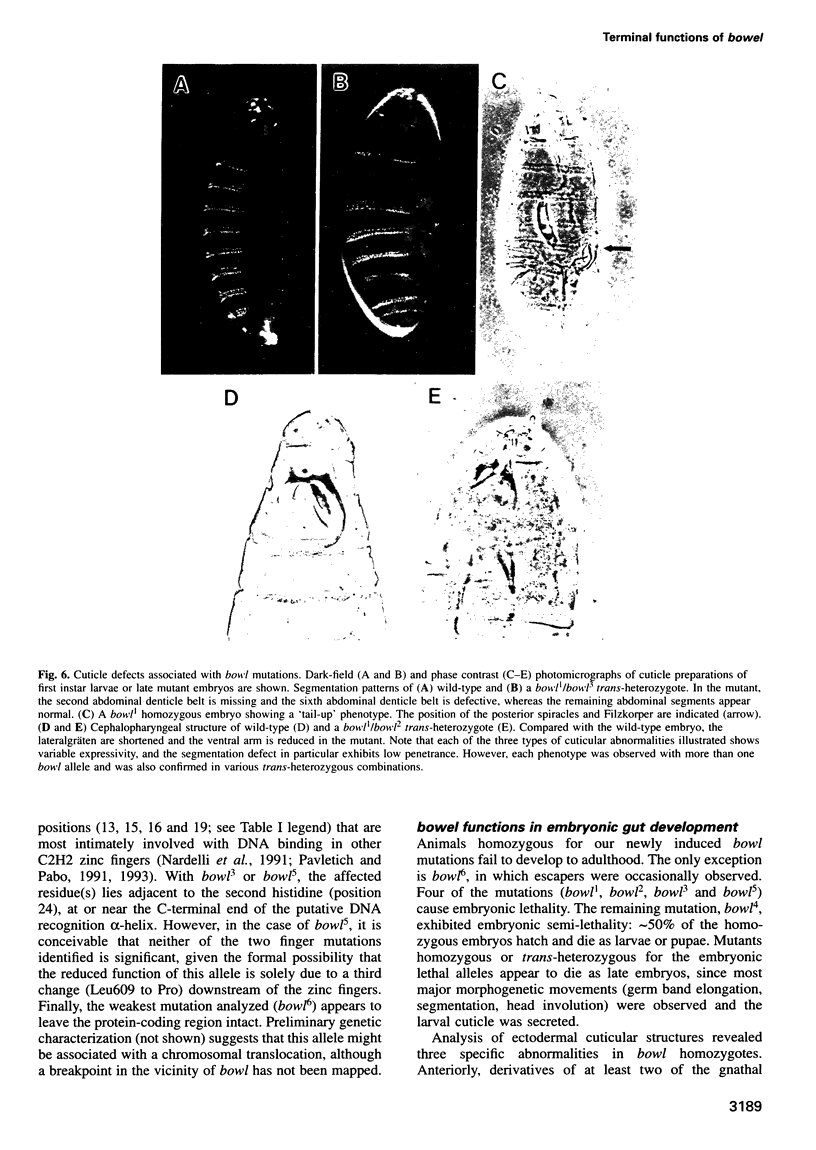
Abstract
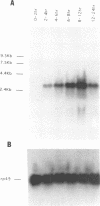
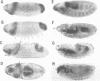
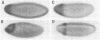
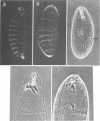
The terminal genes of Drosophila specify non-segmented regions of the larval body that are derived from the anterior and posterior regions of the early embryo. Terminal class genes include both maternal-effect loci (typified by the receptor tyrosine kinase torso) that encode components of a signal transduction cascade and zygotic genes (e.g. tailless and huckebein) that are transcribed at the poles of the embryo in response to the local activation of the pathway. We have characterized a zygotic gene, bowel, that was identified as a zinc finger homolog of the pair-rule segmentation gene odd-skipped. bowel transcripts are initially expressed at both poles of the blastoderm embryo and in a single cephalic stripe. This pattern depends upon torso and tailless activity, but is not affected in huckebein mutants. We isolated and sequenced five mutations that affect the bowel protein, including a nonsense mutation upstream of the zinc fingers and a missense mutation in a putative zinc-chelating residue. bowel mutants die as late embryos with defects in terminal derivatives including the hindgut and proventriculus. Our results indicate that the developmental roles of odd-skipped and bowel have diverged substantially, and that bowel represents a new member of the terminal hierarchy that acts downstream of tailless and mediates a subset of tailless functions in the posterior of the embryo.
Full text
PDF




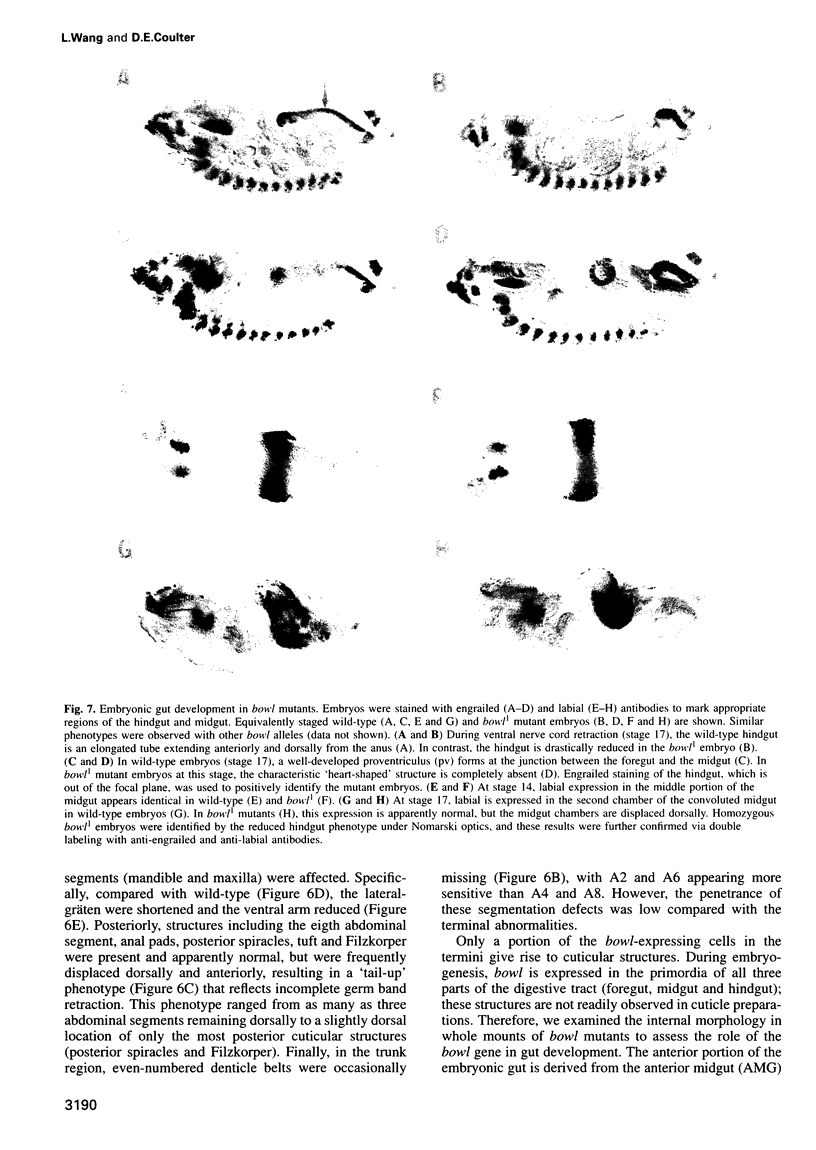






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambrosio L., Mahowald A. P., Perrimon N. Requirement of the Drosophila raf homologue for torso function. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):288–291. doi: 10.1038/342288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner S., Noll M. Network of interactions among pair-rule genes regulating paired expression during primordial segmentation of Drosophila. Mech Dev. 1990 Dec;33(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(90)90130-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brönner G., Chu-LaGraff Q., Doe C. Q., Cohen B., Weigel D., Taubert H., Jäckle H. Sp1/egr-like zinc-finger protein required for endoderm specification and germ-layer formation in Drosophila. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):664–668. doi: 10.1038/369664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J., Furriols M., McCormick C. A., Struhl G. Similarities between trunk and spätzle, putative extracellular ligands specifying body pattern in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1995 Oct 15;9(20):2539–2544. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.20.2539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J. Pattern formation under the control of the terminal system in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):621–628. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherbas L., Cherbas P. The arthropod initiator: the capsite consensus plays an important role in transcription. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;23(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(93)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. E., Swaykus E. A., Beran-Koehn M. A., Goldberg D., Wieschaus E., Schedl P. Molecular analysis of odd-skipped, a zinc finger encoding segmentation gene with a novel pair-rule expression pattern. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3795–3804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. E., Wieschaus E. Gene activities and segmental patterning in Drosophila: analysis of odd-skipped and pair-rule double mutants. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1812–1823. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjarlais J. R., Berg J. M. Redesigning the DNA-binding specificity of a zinc finger protein: a data base-guided approach. Proteins. 1992 Feb;12(2):101–104. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., O'Farrell P. H. Establishment and refinement of segmental pattern in the Drosophila embryo: spatial control of engrailed expression by pair-rule genes. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1212–1225. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diederich R. J., Merrill V. K., Pultz M. A., Kaufman T. C. Isolation, structure, and expression of labial, a homeotic gene of the Antennapedia Complex involved in Drosophila head development. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):399–414. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. B., Perrimon N. The torso pathway in Drosophila: lessons on receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and pattern formation. Dev Biol. 1994 Dec;166(2):380–395. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R., Perrimon N. The orthodenticle gene is regulated by bicoid and torso and specifies Drosophila head development. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):485–488. doi: 10.1038/346485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul U., Seifert E., Schuh R., Jäckle H. Analysis of Krüppel protein distribution during early Drosophila development reveals posttranscriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul U., Weigel D. Regulation of Krüppel expression in the anlage of the Malpighian tubules in the Drosophila embryo. Mech Dev. 1990 Dec;33(1):57–67. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(90)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossniklaus U., Pearson R. K., Gehring W. J. The Drosophila sloppy paired locus encodes two proteins involved in segmentation that show homology to mammalian transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):1030–1051. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutjahr T., Frei E., Noll M. Complex regulation of early paired expression: initial activation by gap genes and pattern modulation by pair-rule genes. Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):609–623. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliker A. J., Trusis-Coulter S. N. Analysis of the functional significance of linkage group conservation in Drosophila. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):233–244. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Pinchin S. M., Schedl P., Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Mirault M. E. Genetic and molecular analysis of the 87A7 and 87C1 heat-inducible loci of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1351–1358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90245-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kispert A., Herrmann B. G., Leptin M., Reuter R. Homologs of the mouse Brachyury gene are involved in the specification of posterior terminal structures in Drosophila, Tribolium, and Locusta. Genes Dev. 1994 Sep 15;8(18):2137–2150. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.18.2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingler M., Erdélyi M., Szabad J., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Function of torso in determining the terminal anlagen of the Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):275–277. doi: 10.1038/335275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg T., Sidén I., O'Farrell P., Simon M. The engrailed locus of Drosophila: in situ localization of transcripts reveals compartment-specific expression. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause H. M., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Expression, modification, and localization of the fushi tarazu protein in Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):1021–1036. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Chou T. B., Williams N. G., Roberts T., Perrimon N. Control of cell fate determination by p21ras/Ras1, an essential component of torso signaling in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):621–632. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney P. A., Lengyel J. A. The zygotic segmentation mutant tailless alters the blastoderm fate map of the Drosophila embryo. Dev Biol. 1987 Aug;122(2):464–470. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. R., Raibaud A., Ollo R. Terminal pattern elements in Drosophila embryo induced by the torso-like protein. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):741–745. doi: 10.1038/367741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen J. R., DiNardo S. Establishing parasegments in Drosophila embryos: roles of the odd-skipped and naked genes. Dev Biol. 1995 May;169(1):295–308. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel N. H., Martin-Blanco E., Coleman K. G., Poole S. J., Ellis M. C., Kornberg T. B., Goodman C. S. Expression of engrailed proteins in arthropods, annelids, and chordates. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):955–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90947-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a five-finger GLI-DNA complex: new perspectives on zinc fingers. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1701–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.8378770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignoni F., Baldarelli R. M., Steingrímsson E., Diaz R. J., Patapoutian A., Merriam J. R., Lengyel J. A. The Drosophila gene tailless is expressed at the embryonic termini and is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90249-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignoni F., Steingrímsson E., Lengyel J. A. bicoid and the terminal system activate tailless expression in the early Drosophila embryo. Development. 1992 May;115(1):239–251. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.1.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Kauvar L. M., Drees B., Kornberg T. The engrailed locus of Drosophila: structural analysis of an embryonic transcript. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter G., Szidonya J. Cytogenetic analysis of variegation suppressors and a dominant temperature-sensitive lethal in region 23-26 of chromosome 2L in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1983;88(4):277–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00292904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronchi E., Treisman J., Dostatni N., Struhl G., Desplan C. Down-regulation of the Drosophila morphogen bicoid by the torso receptor-mediated signal transduction cascade. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90425-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savant-Bhonsale S., Montell D. J. torso-like encodes the localized determinant of Drosophila terminal pattern formation. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2548–2555. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoller D. A., Petrov D., Hartl D. L. Characterization of bacteriophage P1 library containing inserts of Drosophila DNA of 75-100 kilobase pairs. Chromosoma. 1991 Sep;100(8):487–494. doi: 10.1007/BF00352199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger F., Stevens L. M., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The Drosophila gene torso encodes a putative receptor tyrosine kinase. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):478–483. doi: 10.1038/338478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90466-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steingrímsson E., Pignoni F., Liaw G. J., Lengyel J. A. Dual role of the Drosophila pattern gene tailless in embryonic termini. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):418–421. doi: 10.1126/science.1925599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strecker T. R., Halsell S. R., Fisher W. W., Lipshitz H. D. Reciprocal effects of hyper- and hypoactivity mutations in the Drosophila pattern gene torso. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1062–1066. doi: 10.1126/science.2922596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepass U., Hartenstein V. The development of cellular junctions in the Drosophila embryo. Dev Biol. 1994 Feb;161(2):563–596. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jürgens G., Klingler M., Jäckle H. Two gap genes mediate maternal terminal pattern information in Drosophila. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):495–498. doi: 10.1126/science.2158673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jürgens G., Küttner F., Seifert E., Jäckle H. The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):645–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]