Abstract
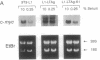
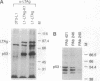
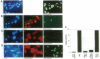
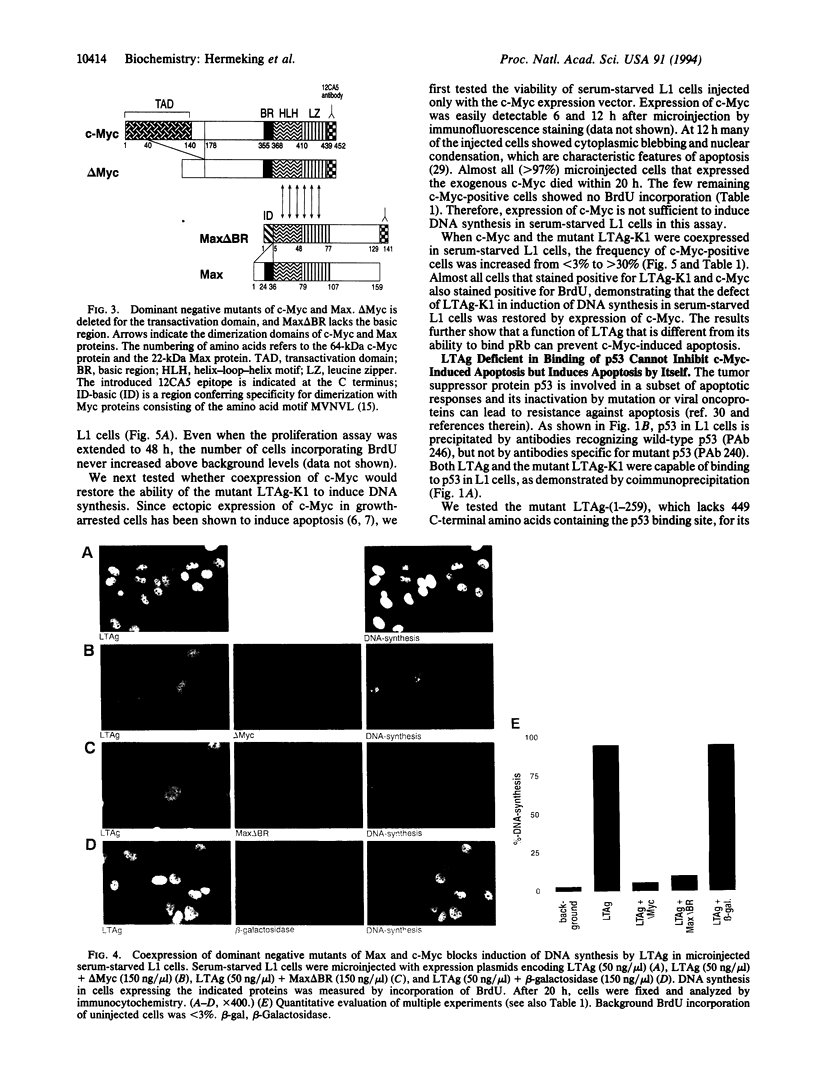
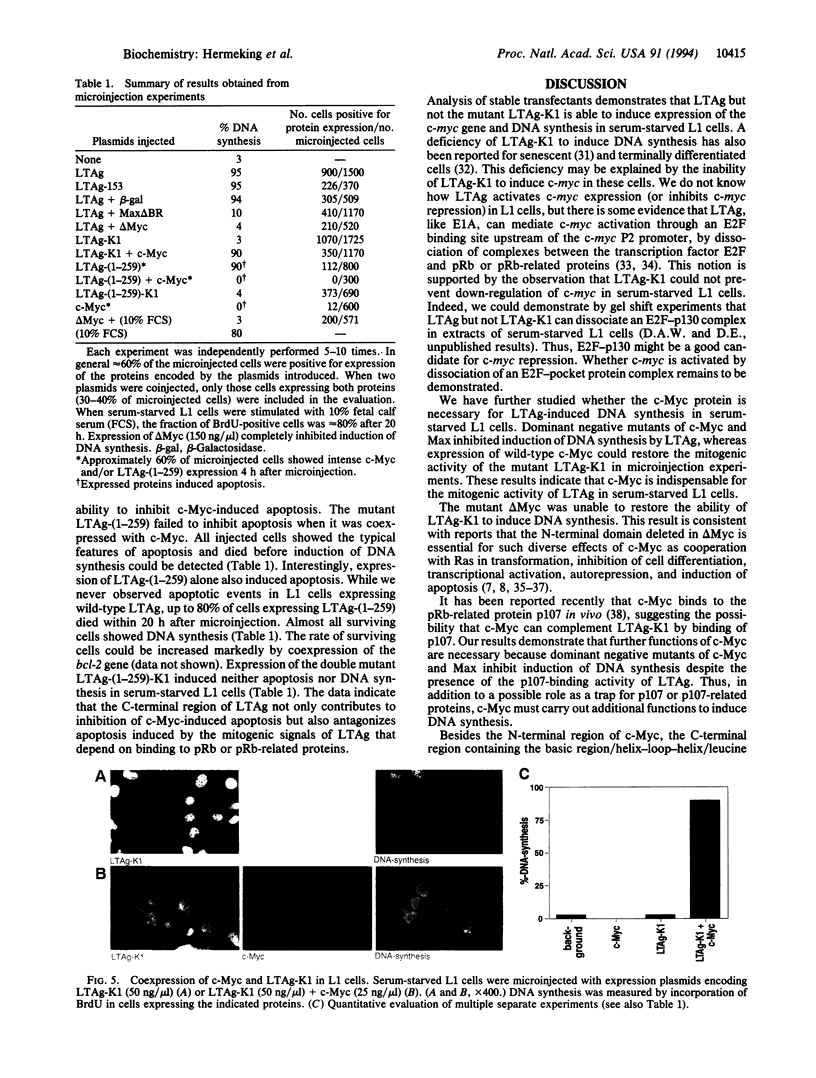
Stably transfected NIH 3T3-L1 mouse fibroblasts (L1 cells) expressing the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen (LTAg) maintain c-myc expression and proliferation in low serum, whereas cells expressing the mutant form LTAg-K1, defective in binding of the retinoblastoma suppressor gene product pRb, showed reduced levels of c-myc RNA and only background levels of DNA synthesis in low serum. The role of the c-Myc protein in LTAg-induced DNA synthesis was studied in microinjection experiments. Expression of LTAg induced cellular DNA synthesis in > 95% of microinjected serum-starved L1 cells, whereas the mutant LTAg-K1 could not induce DNA synthesis. Coexpression of dominant negative c-Myc or Max mutants with LTAg inhibited DNA synthesis, indicating that functional c-Myc is necessary for induction of DNA synthesis by LTAg. Expression of c-Myc induced programmed cell death (apoptosis) in serum-starved L1 cells. Coexpression of c-Myc with LTAg-K1 restored induction of DNA synthesis without apoptosis. Expression of a truncated LTAg, LTAg-(1-259), defective in binding of the tumor suppressor gene product p53, failed to prevent c-Myc-induced apoptosis. The data indicate that c-Myc can restore the ability of LTAg-K1 to induce DNA synthesis and that LTAg-K1 prevents c-Myc-induced apoptosis in serum-starved L1 cells by its interaction with p53.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati B., Brooks M. W., Levy N., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Oncogenic activity of the c-Myc protein requires dimerization with Max. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90663-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. The c-Myc protein induces cell cycle progression and apoptosis through dimerization with Max. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5083–5087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askew D. S., Ashmun R. A., Simmons B. C., Cleveland J. L. Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Kretzner L., Eisenman R. N. Mad: a heterodimeric partner for Max that antagonizes Myc transcriptional activity. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billaud M., Isselbacher K. J., Bernards R. A dominant-negative mutant of Max that inhibits sequence-specific DNA binding by Myc proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2739–2743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Pepperkok R., Wang F. B., Giordano T. J., McAllister W. T., Ansorge W., Bujard H. Regulated expression of foreign genes in mammalian cells under the control of coliphage T3 RNA polymerase and lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5400–5404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickmanns A., Zeitvogel A., Simmersbach F., Weber R., Arthur A. K., Dehde S., Wildeman A. G., Fanning E. The kinetics of simian virus 40-induced progression of quiescent cells into S phase depend on four independent functions of large T antigen. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5496–5508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5496-5508.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbelstein M., Arthur A. K., Dehde S., van Zee K., Dickmanns A., Fanning E. Intracistronic complementation reveals a new function of SV40 T antigen that co-operates with Rb and p53 binding to stimulate DNA synthesis in quiescent cells. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):837–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schirm S., Bishop J. M. The MYC protein activates transcription of the alpha-prothymosin gene. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Knippers R. Structure and function of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:55–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O. Enforced expression of the c-myc oncogene inhibits cell differentiation by precluding entry into a distinct predifferentiation state in G0/G1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1614–1624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Ahrens B. SV40 early mutants that are defective for viral DNA synthesis but competent for transformation of cultured rat and simian cells. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):78–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Meuth M. An established pre-adipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. Cell. 1974 Oct;3(2):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Bhatia K., Magrath I. T., Dang C. V., Dalla-Favera R. Binding and suppression of the Myc transcriptional activation domain by p107. Science. 1994 Apr 8;264(5156):251–254. doi: 10.1126/science.8146655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Schneider J. W., Condorelli G., Kaushal S., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Interaction of myogenic factors and the retinoblastoma protein mediates muscle cell commitment and differentiation. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):309–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90110-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R., Schwab G., Wickstrom E., Loke S. L., Pluznik D. H., Watt R., Neckers L. M. A c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits entry into S phase but not progress from G0 to G1. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):445–449. doi: 10.1038/328445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermeking H., Eick D. Mediation of c-Myc-induced apoptosis by p53. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2091–2093. doi: 10.1126/science.8091232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Smith A. E. In vitro mutagenesis of a putative DNA binding domain of SV40 large-T. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):109–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Dang C. V. An amino-terminal c-myc domain required for neoplastic transformation activates transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5914–5920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E., Jacks T., Housman D. E. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):957–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90719-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur H., Walter G. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the carboxy terminus of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):483–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.483-491.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Bossone S. A., Patel A. J. myc function and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:809–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moberg K. H., Logan T. J., Tyndall W. A., Hall D. J. Three distinct elements within the murine c-myc promoter are required for transcription. Oncogene. 1992 Mar;7(3):411–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee B., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A. Myc family oncoproteins function through a common pathway to transform normal cells in culture: cross-interference by Max and trans-acting dominant mutants. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1480–1492. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn L. J., Brooks M. W., Laufer E. M., Littlewood T. D., Morgenstern J. P., Evan G. I., Lee W. M., Land H. Domains of human c-myc protein required for autosuppression and cooperation with ras oncogenes are overlapping. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4961–4966. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto K., Howard T., Ogryzko V., Xu N. Z., Corsico C. C., Jones D. H., Howard B. Relative mitogenic activities of wild-type and retinoblastoma binding-defective SV40 T antigens in serum-deprived and senescent human diploid fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1887–1893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalmeier K., Synovzik H., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L., Lipp M. Nuclear factor E2F mediates basic transcription and trans-activation by E1a of the human MYC promoter. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):527–536. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Fey G., Graessmann A. Biological activity of purified simian virus 40 T antigen proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1279–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis: cell death under homeostatic control. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1987;11:3–10. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-72558-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.444-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos A. S., Gyuris J., Brent R. Mxi1, a protein that specifically interacts with Max to bind Myc-Max recognition sites. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90662-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]