Abstract
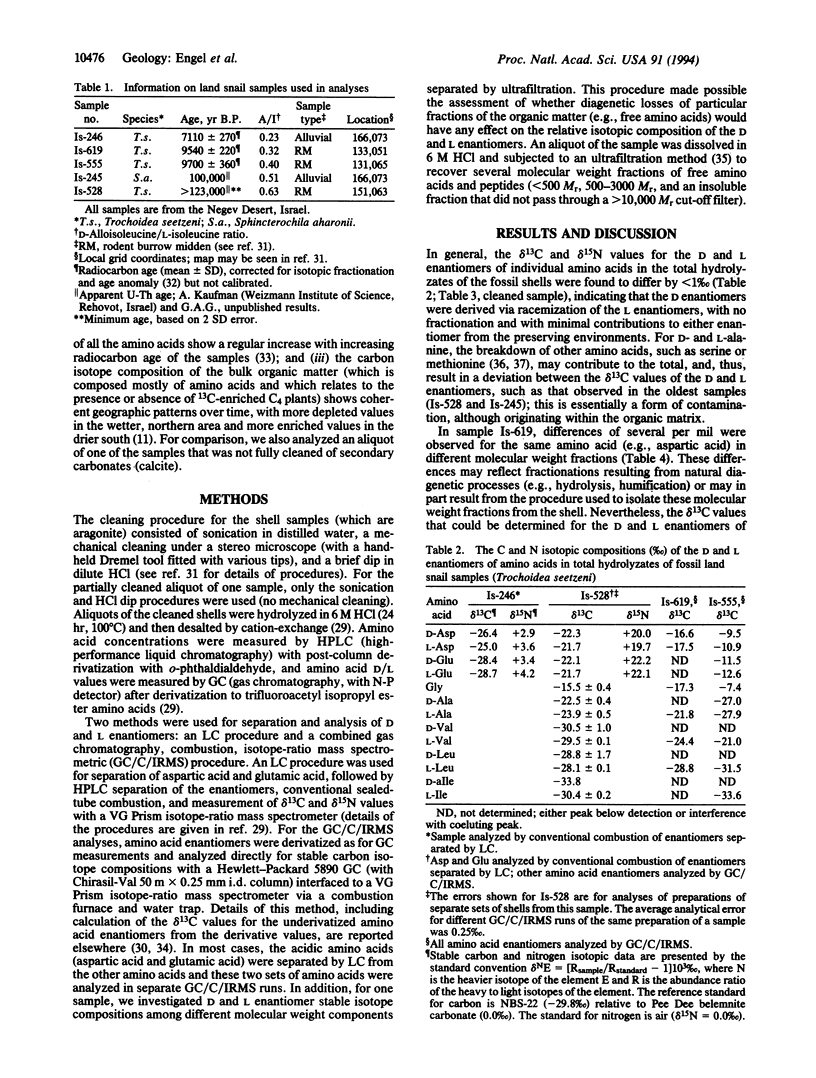
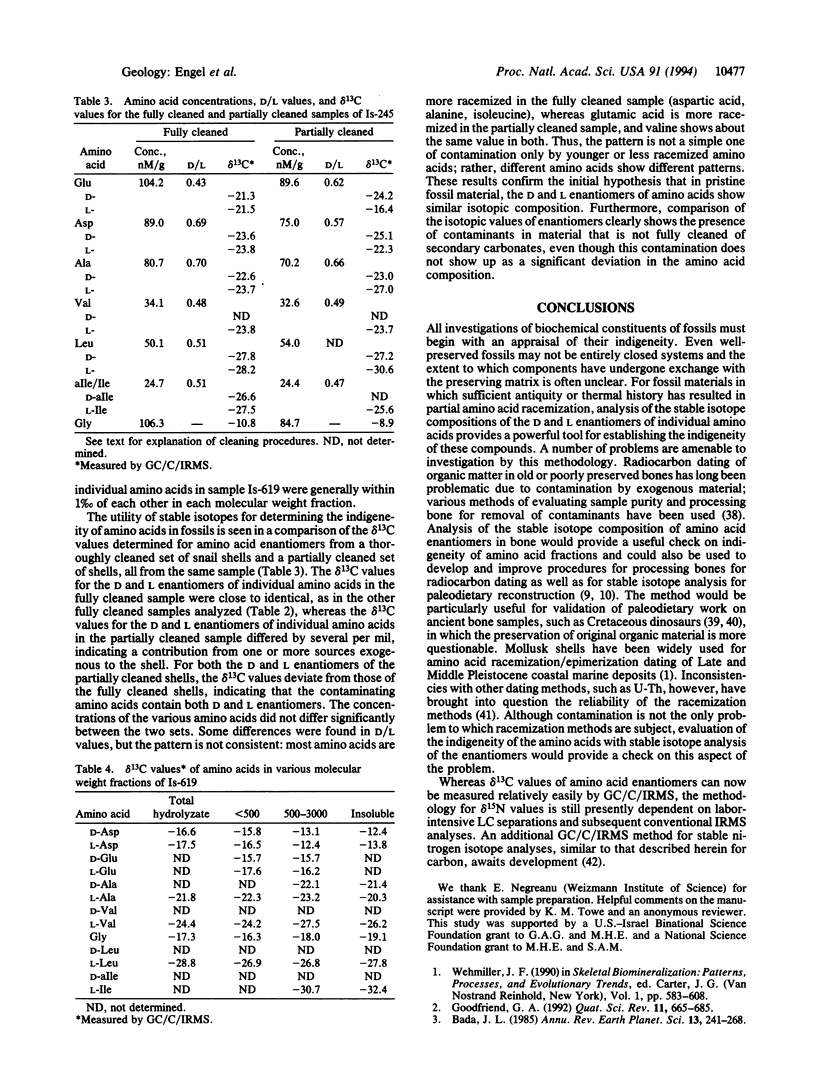
Comparison of the delta 13C values of D and L enantiomers of individual amino acids was used to evaluate the presence of amino acid contaminants in Quaternary land snails. Measurements of delta 13C values of amino acid D and L enantiomers determined by combined gas chromatography, combustion, isotope-ratio mass spectrometry are reported. Conventional combustion techniques, following separation of aspartic acid and glutamic acid enantiomers by liquid chromatography, were also used to determine delta 13C as well as delta 15N values. Thoroughly cleaned samples ranging in age from 7000 to > 100,000 yr B.P. are shown to have analytically identical delta 13C values for the D and L enantiomers of each amino acid, thus confirming that the amino acids are indigenous to the shells, even in Pleistocene samples. On the other hand, partially cleaned material shows divergence of isotopic values, thus indicating the presence of amino acid contaminants and emphasizing the importance of proper cleaning procedures. This approach provides a powerful method for assessing the indigeneity of amino acids in fossils.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Merritt D. A., Hayes J. M. Nitrogen isotopic analyses by isotope-ratio-monitoring gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 1994;5:387–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner S., Lowenstam H. A., Hood L. Characterization of 80-million-year-old mollusk shell proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2541–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



