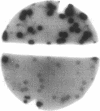
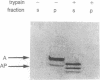
Abstract
We have investigated the topology of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor expressed in Escherichia coli, using the genetic method described by Beckwith and coworkers. We found that fusions with alkaline phosphatase beyond a certain point on the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor sequence were assembled into the bacterial membrane with the same topology as the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor in the mammalian membrane. The pattern that might have been expected on the basis of the topology of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor in mammalian membranes was not reflected in the levels of alkaline phosphatase activity of the fusions occurring between the N-terminal region and positions close to the second external domain. Our data suggest that the correct positioning of the N terminus of the receptor depends on the presence of its C-terminal portions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd D., Beckwith J. The role of charged amino acids in the localization of secreted and membrane proteins. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90378-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Traxler B., Beckwith J. Analysis of the topology of a membrane protein by using a minimum number of alkaline phosphatase fusions. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(2):553–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.2.553-556.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury A., Persic L., Werge T., Cattaneo A. Use of living columns to select specific phage antibodies. Biotechnology (N Y) 1993 Dec;11(13):1565–1569. doi: 10.1038/nbt1293-1565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breyer R. M., Strosberg A. D., Guillet J. G. Mutational analysis of ligand binding activity of beta 2 adrenergic receptor expressed in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2679–2684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07453.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. The yeast alpha-factor receptor: structural properties deduced from the sequence of the STE2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8463–8475. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calamia J., Manoil C. Membrane protein spanning segments as export signals. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 5;224(3):539–543. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90542-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calamia J., Manoil C. lac permease of Escherichia coli: topology and sequence elements promoting membrane insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4937–4941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbit A., Ronco J., Michel V., Werts C., Hofnung M. Permissive sites and topology of an outer membrane protein with a reporter epitope. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):262–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.262-275.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbey R. E. Positively charged residues are important determinants of membrane protein topology. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90047-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman A. I., Beckwith J. Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase fails to acquire disulfide bonds when retained in the cytoplasm. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7719–7722. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7719-7722.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman A. I., Beckwith J. Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase fails to acquire disulfide bonds when retained in the cytoplasm. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7719–7722. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7719-7722.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Bouvier M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The multiple membrane spanning topography of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Localization of the sites of binding, glycosylation, and regulatory phosphorylation by limited proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14282–14288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. A family of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2657–2664. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrmann M., Boyd D., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of membrane protein topology by a sandwich gene fusion approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7574–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Selzer E., Marullo S., Schütz W., Strosberg A. D. Expression of two human beta-adrenergic receptors in Escherichia coli: functional interaction with two forms of the stimulatory G protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8548–8552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Matteoni R., Bianchi E., Testa L., Marazziti D., Rossi N., Tocchini-Valentini G. Replica filter assay of human beta-adrenergic receptors expressed in E.coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 14;173(2):680–688. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez C., Devedjian J. C. A plasmid facilitating in vitro construction of phoA gene fusions in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3999–3999. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- High S., Flint N., Dobberstein B. Requirements for the membrane insertion of signal-anchor type proteins. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):25–34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins? Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Dixon R. A., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Sigal I. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. I., Kuhn A., Dalbey R. E. Distinct domains of an oligotopic membrane protein are Sec-dependent and Sec-independent for membrane insertion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):938–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J., Beckwith J. Alkaline phosphatase fusions: sensors of subcellular location. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):515–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.515-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marullo S., Delavier-Klutchko C., Eshdat Y., Strosberg A. D., Emorine L. Human beta 2-adrenergic receptors expressed in Escherichia coli membranes retain their pharmacological properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern K., Ehrmann M., Beckwith J. Decoding signals for membrane protein assembly using alkaline phosphatase fusions. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2773–2782. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Inouye H., Oliver D., Beckwith J. Mutations that alter the signal sequence of alkaline phosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.366-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I., von Heijne G. Fine-tuning the topology of a polytopic membrane protein: role of positively and negatively charged amino acids. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1135–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90390-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Millan J. L., Boyd D., Dalbey R., Wickner W., Beckwith J. Use of phoA fusions to study the topology of the Escherichia coli inner membrane protein leader peptidase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5536–5541. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5536-5541.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traxler B., Lee C., Boyd D., Beckwith J. The dynamics of assembly of a cytoplasmic membrane protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5339–5345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Lipfert L., Malbon C. C., Bahouth S. Site-directed anti-peptide antibodies define the topography of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14424–14431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Membrane protein structure prediction. Hydrophobicity analysis and the positive-inside rule. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90934-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]