Significance
The efficient translation of the vast majority of eukaryotic mRNAs requires the presence of a poly(A) tail. Although the poly(A) tail was originally thought of as a stable modification, it is now clear that it is much more dynamic. Poly(A) tails can be shortened by deadenylases, leading to mRNA decay or translational repression. The short poly(A) tails of translationally inactive mRNAs can also be reextended by cytoplasmic noncanonical poly(A) polymerases, activating their translation. This mechanism of translational control is found predominantly in metazoan oocytes and neurons and is mediated by germ-line development defective (GLD)-2. Here, we report the molecular mechanism with which Caenorhabditis elegans GLD-2 is activated by GLD-3, a homologue of Bicaudal-C, and identify the unusual substrate specificity of this class of noncanonical poly(A) polymerases.
Keywords: posttranscriptional regulation, cytoplasmic poly(A)-polymerase, noncanonical poly(A)-polymerase, germ-line maturation, cytoplasmic polyadenylation
Abstract
The Caenorhabditis elegans germ-line development defective (GLD)-2–GLD-3 complex up-regulates the expression of genes required for meiotic progression. GLD-2–GLD-3 acts by extending the short poly(A) tail of germ-line–specific mRNAs, switching them from a dormant state into a translationally active state. GLD-2 is a cytoplasmic noncanonical poly(A) polymerase that lacks the RNA-binding domain typical of the canonical nuclear poly(A)-polymerase Pap1. The activity of C. elegans GLD-2 in vivo and in vitro depends on its association with the multi-K homology (KH) domain-containing protein, GLD-3, a homolog of Bicaudal-C. We have identified a minimal polyadenylation complex that includes the conserved nucleotidyl-transferase core of GLD-2 and the N-terminal domain of GLD-3, and determined its structure at 2.3-Å resolution. The structure shows that the N-terminal domain of GLD-3 does not fold into the predicted KH domain but wraps around the catalytic domain of GLD-2. The picture that emerges from the structural and biochemical data are that GLD-3 activates GLD-2 both indirectly by stabilizing the enzyme and directly by contributing positively charged residues near the RNA-binding cleft. The RNA-binding cleft of GLD-2 has distinct structural features compared with the poly(A)-polymerases Pap1 and Trf4. Consistently, GLD-2 has distinct biochemical properties: It displays unusual specificity in vitro for single-stranded RNAs with at least one adenosine at the 3′ end. GLD-2 thus appears to have evolved specialized nucleotidyl-transferase properties that match the 3′ end features of dormant cytoplasmic mRNAs.
The poly(A) tail is a major regulatory determinant of eukaryotic gene expression. This string of nontemplated adenosines is added to the 3′ end of the vast majority of eukaryotic mRNAs upon transcription termination by the canonical nuclear poly(A) polymerase (Pap1) (reviewed in ref. 1) The presence of an intact poly(A) tail is required for nuclear export and for cytoplasmic translation (reviewed in ref. 2). Conversely, shortening of the poly(A) tail is connected to translational repression and mRNA decay (reviewed in refs. 3–5) In metazoans, the short poly(A) tail of translationally repressed mRNAs can also be reextended by cytoplasmic noncanonical poly(A) polymerases, initiating the synthesis of the corresponding gene products (reviewed in ref. 1). This mechanism of translational regulation allows rapid protein production in physiological contexts where transcription is silenced (e.g., in oocytes and early embryos) or at a significant physical distance from the translation machinery (e.g., in neuronal dendrites) (reviewed in refs. 6–9).
The cytoplasmic poly(A) polymerase germ-line development defective 2 (GLD-2) was originally discovered in a screen for Caenorhabditis elegans mutants causing ectopic germ-line proliferation (10) and has since been studied in several vertebrate and invertebrate model organisms (9, 11–16). In the hermaphrodite germ line of this nematode, GLD-2 is envisioned to activate the translation of a set of mRNAs required for the transition from mitosis to meiosis and has been shown to promote mRNA stability (10, 17). In Drosophila, Xenopus, and mice, GLD-2 orthologs are involved in the translation of maternal mRNAs during oocyte maturation and egg activation (11, 13, 15, 18). GLD-2 is highly expressed in the hippocampus in mammals, and in Drosophila, it activates the translation of dormant synaptic mRNAs and the formation of long-term memory (13, 19, 20). In mammals and Drosophila, GLD-2 orthologs have also been shown to add an adenosine tail to the 3′ end of microRNAs (21–23). No ortholog of GLD-2 exists in yeast. However, related noncanonical nucleotidyl transferases are present in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae nucleus (Trf4/Trf5) and in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe cytoplasm (Cid1), where they extend the 3′ end of RNAs, prompting their degradation (reviewed in refs. 24–26).
Canonical and noncanonical nucleotidyl transferases contain a similar enzymatic core composed of the catalytic and the so-called central domains, which act in concert to transfer the incoming nucleotide to the 3′ end of an RNA substrate (reviewed in ref. 25). Canonical nucleotidyl transferases, like yeast Pap1, also contain an RNA recognition motif (RRM) that is key for RNA binding and activity (27, 28), but no such domain is present in the sequence of GLD-2, Trf4/Trf5, or Cid1. Different nucleotidyl transferases vary in the selection of the incoming nucleotide (ATP in the case of Pap1, GLD-2, and Trf4/Trf5, and UTP in the case of Cid1) and in the number of consecutive reactions they perform on a given substrate (reviewed in refs. 24–26). C. elegans GLD-2 has weak activity in isolation, but is converted into an active poly(A) polymerase upon binding to GLD-3, a nematode protein with similarity to Bicaudal-C (Bic-C) (10, 29). In addition to GLD-3, several other GLD-2–interacting proteins have been identified in various species (e.g., CPEB, RNP-8, Rbm9, Musashi, and Ago-1) and typically contain domains found in RNA-binding proteins (11, 30–32). In the case of GLD-3, the GLD-2–binding region features a pattern of hydrophobic residues that matches the signature sequence of K homology (KH) domains (33, 34). These observations have lead to the concept that GLD-2–binding partners might endow the noncanonical poly(A) polymerase with an RNA-binding fold in the context of the heterodimer (10). The conundrum, however, is that the closest homolog of GLD-2, Cid1, is an efficient nucleotidyl transferase even in the absence of additional proteins. To obtain insights into how GLD-2 functions at the molecular level, we set out to dissect the molecular mechanisms with which GLD-3 stimulates the poly(A)-polymerase activity of GLD-2.
Results and Discussion
Identification of a Minimal poly(A) Polymerase Core of C. elegans GLD-2–GLD-3.
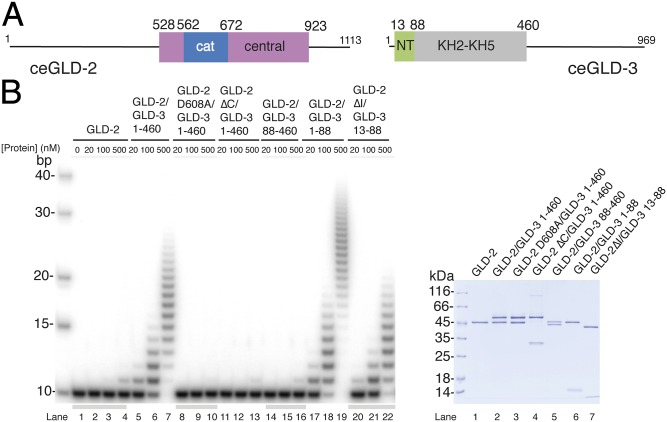
In C. elegans (C.e.) GLD-2 (1,113 residues), N- and C-terminal low-complexity sequences flank the catalytic and central domains of the nucleotidyl-transferase region (10) (Fig. 1A). C.e. GLD-3 (969 residues) is predicted to contain 5 KH domains followed by a C-terminal low-complexity sequence (29, 33, 34). In a previous study, we have shown that a proteolytically resistant core of GLD-3 folds into a compact globular unit formed by the KH2–KH5 domains (residues 110–460) and a C-terminal segment of the putative KH1 domain (residues 88–110) (33, 34) (Fig. 1A). An N-terminal segment of the putative KH1 domain (residues 33–81) has been shown to interact with the GLD-2 nucleotidyl-transferase region by yeast two-hybrid assays (29, 33, 34). To map the minimal interacting regions experimentally, we purified two different complexes consisting of either GLD-2528–1042 and GLD-31–460 (as described in ref. 34) or GLD-2528–808 and GLD-31–106 and subjected them to limited proteolysis experiments with different proteases (elastase and GluC). Using mass spectrometry and sequence analyses, we mapped the domain boundaries of a smaller core complex to GLD-2528–923 and GLD-31–88, and also identified the presence of proteolytically sensitive regions at GLD-3 residues 1–12 and at GLD-2 residues 814–856 (Fig. S1A). These residues of GLD-2 correspond to an insertion that is present in C. elegans but not in other species (see below).
Fig. 1.
Poly(A)-polymerase core of the GLD-2–GLD-3 complex. (A) Schematic domain organization of C.e. GLD-2 and GLD-3. Folded domains are shown in rectangles and low-complexity sequences as lines. The portions of the molecule included in the structure reported in this work are in blue and pink [for the catalytic (cat) and central domains of GLD-2] and in green (the N-terminal NT domain of GLD-3). In gray is the folded region formed by the KH2-KH5 domains (34). (B) Poly(A)-polymerase assays with different C.e GLD-2 and GLD-3 protein fragments and mutants. In the assay, 20, 100, or 500 nM for proteins were incubated with 100 nM 5′-32P-labeled A10 RNA and 0.5 mM ATP. Reactions were run on a 10% polyacrylamide/7 M urea gel and visualized by phosphorimaging. The purified proteins used in the assay are shown at Right in a Coomassie-stained 12% SDS/PAGE gel.
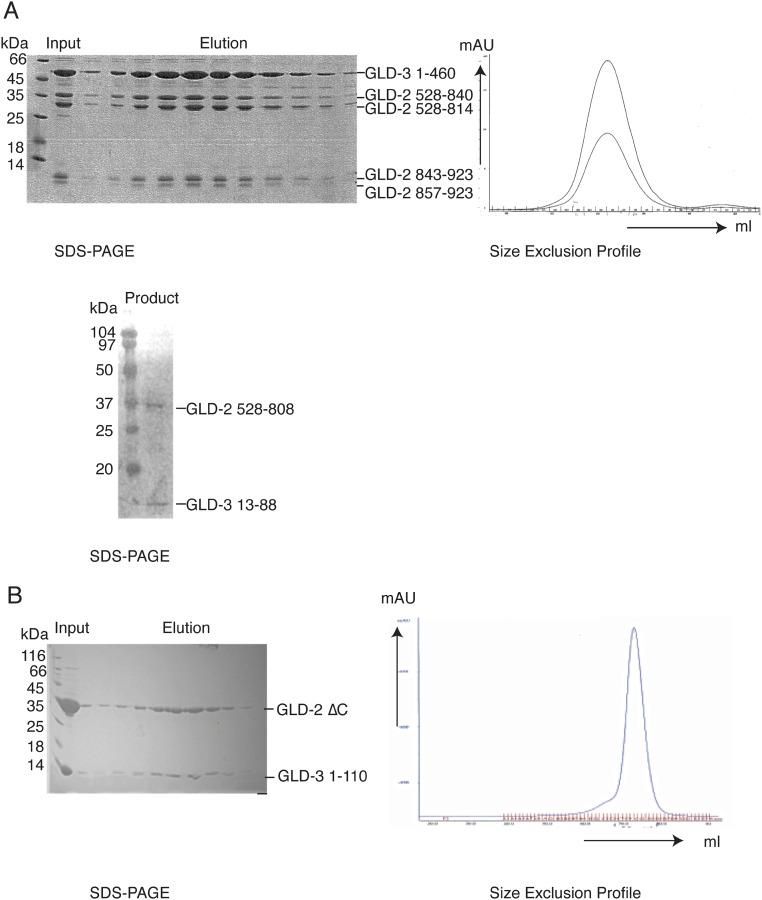
Fig. S1.
Biochemical characterization of the GLD-2–GLD-3 core complex. (A) Preparative and analytical limited proteolysis experiments. (Upper) Three milligrams of purified GLD-2528–1042–GLD-31–460 (34) was incubated with 90 μg of Elastase for 30 min on ice. The reaction was stopped by adding 1:10 (vol/vol) AEBSF (150 mM) and loaded on a gel filtration column (Superdex 200; GE Healthcare). Using mass spectrometry and N-terminal sequencing analyzes, we mapped the domain boundaries of GLD-2528–1042 to a smaller core domain, GLD-2528–923, whereas GLD-31–460 was not affected by elastase. The chromatography profile is shown at Right, and the Coomassie-stained 15% SDS/PAGE is shown at Left. (Lower) Ten microliters of purified GLD-2528–808–GLD-31–106 (1 mg/mL) was incubated with 3 μL of GluC (0.1 mg/mL) and incubated for 30 min on ice. The reaction was stopped by the addition of 5 μL of SDS loading dye. For this complex, we identified proteolytically sensitive regions at GLD-3 residues 1–12 and 89–106 (34), whereas GLD-2528–808 was not affected by GluC. Shown is the Coomassie-stained 15% SDS/PAGE of the complex after proteolysis. (B) Purification of GLD-2ΔC–GLD-31–110. The protein complex was expressed and purified as described in the method section. The Coomassie-stained 15% SDS/PAGE of the protein complex after size exclusion is shown at Left. The respective size exclusion profile is shown at Right (blue line: UV280).
We tested the activity of the complex in in vitro polyadenylation assays by using a 10-mer poly(A) RNA substrate. When in isolation, the activity of GLD-2528–923 (hereafter defined as GLD-2) was negligible (Fig. 1B, lanes 2–4). Addition of GLD-31–460 resulted in robust polyadenylation (Fig. 1B, lanes 5–7). As control, the GLD-2–GLD-31–460 activity was abrogated by introducing a single substitution of one of the aspartic acids in the catalytic site of GLD-2 (Asp608Ala) (Fig. 1B, lanes 8–10). Deletion of residues 815–923 in the central domain (GLD-2ΔC) did not impair the interaction with GLD-3 (Fig. S1B) but impaired the polyadenylation properties of the complex (Fig. 1B, lanes 11–13). Incubating GLD-2 with a GLD-3 protein consisting only of the N-terminal GLD-2–interacting region (GLD-31–88) was sufficient to restore robust polyadenylation (Fig. 1B, lanes 17–19). Consistently, a GLD-3 protein where the N-terminal GLD-2–interacting region had been deleted (GLD-388–460) was unable to increase polyadenylation above the level detected for GLD-2 in isolation (Fig. 1B, lanes 14–16). We concluded that GLD-2–GLD-31–88 is a catalytically active core of the polyadenylation complex.
Attempts to crystallize the GLD-2–GLD-31–88 complex failed. To obtain crystals, we trimmed the proteolytically sensitive regions further and formed a complex between GLD-313–88 (hereby defined as GLD-3NT) and a GLD-2 protein where the insertion between residues 813–846 had been deleted (GLD-2ΔI). This complex was capable of polyadenylation activity, albeit to a slighly lower extent than GLD-2–GLD-31–460 (Fig. 1B, lanes 20–22). The structure of GLD-2ΔI–GLD-3NT was solved by using selenomethionine-based single anomalous dispersion (SAD) and refined at 2.3-Å resolution to Rfree of 23.0%, R factor of 18.7%, and good stereochemistry (Table S1). The final model includes residues 546–923 of GLD-2ΔI (with the exception of disordered loops between residues 766 and 773, 804 and 812, 847 and 854, and 876 and 881), residues 25–88 of GLD-3NT, and a chloride ion.
Table S1.
Data collection and refinement statistic
| Data collection | |
| Spacegroup | P212121 |
| Cell constants, Å | a = 50.99, b = 89.68,c = 95.25,α = β = γ = 90° |
| Wavelength, Å | 0.97975 |
| Resolution (last shell), Å | 50.0–2.28 (2.42–2.28) |
| No. of unique reflections | 37155 (5515) |
| No. of total reflections | 284963 (41350) |
| Completeness, % | 98.4 (90.6) |
| Redundancy | 7.7 (7.5) |
| Rmeas, % | 13.4 (73.1) |
| I/Iσ | 13.36 (3.03) |
| Refinement | |
| Resolution, Å | 47.3–2.28 |
| Rwork/Rfree, % | 18.7/23.0 |
| Residues modeled ceGLD-2 | 546–765, 774–803, 855–875, 882–923 |
| Residues modeled ceGLD-3 | 25–88 |
| Total no. of waters | 115 |
| Total no. of heteroatoms | 1 |
| Rms deviations | |
| Bond lengths, Å | 0.003 |
| Bond angles, ° | 0.753 |
| Dihedral angles, ° | 14.37 |
| Average B factors, Å2 | 44.2 |
| Ramachandran plot | |
| Residues in most favored region, % | 95.9 |
| Additionally allowed, % | 3.8 |
| Generously allowed or not allowed, % | 0.3 |
Numbers in parentheses correspond to the last shell.
GLD-2 Features Large Insertions in the poly(A) Polymerase Core.
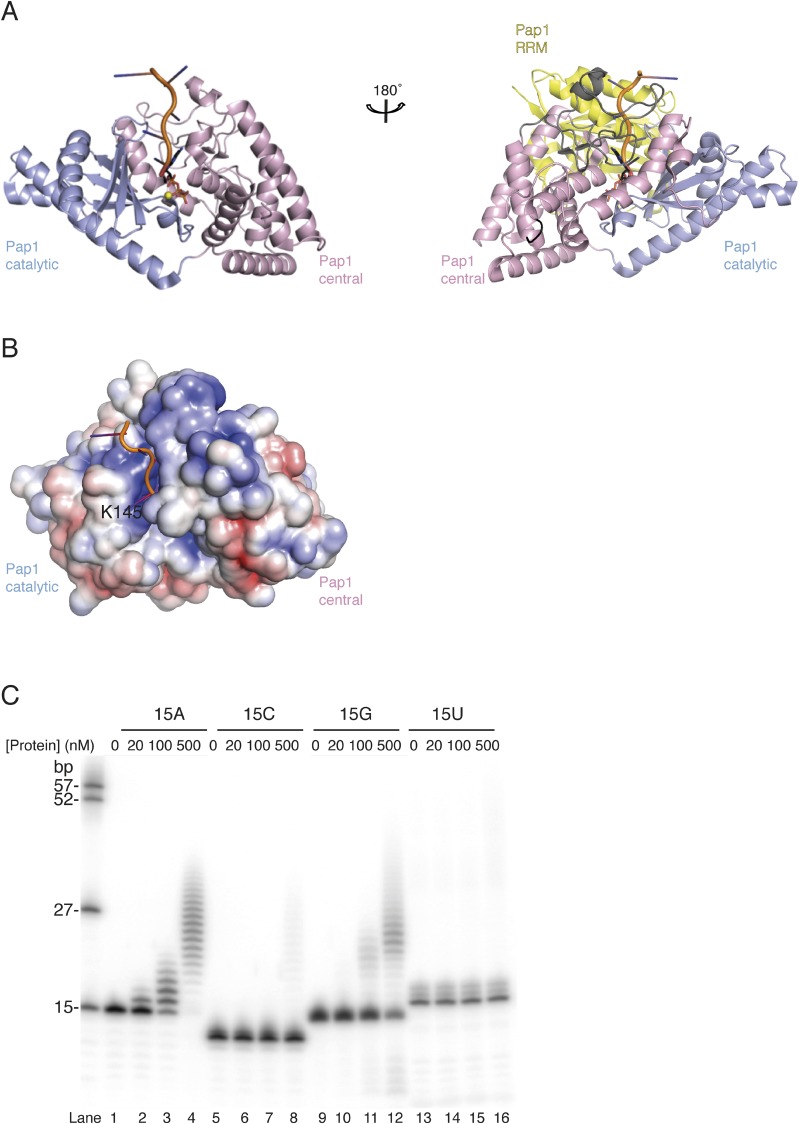
The structure of GLD-2ΔI shows the characteristic architecture of an RNA-dependent nucleotidyl transferase (Fig. 2A) (25, 28). Briefly, the catalytic domain is centered at a five-stranded β-sheet flanked by two α-helices (α2 and α3). Helix α4 connects the catalytic domain to the central domain. The central domain is an α-helical bundle formed by two noncontiguous stretches (helix α1 and helices α5–α8, Figs. 1A and 2A). The two domains of GLD-2ΔI are separated by a pronounced cleft. The sidewalls of the cleft are lined by the β-sheet of the catalytic domain and by helices α5-α6 of the central domain, whereas helix α4 lines the bottom. The cleft harbors the active site: Strands β2 and β5 of the catalytic domain provide the three conserved aspartic acids that mediate the chemical reaction characteristic of nucleotidyl transferases (25, 35) (Fig. 2A).
Fig. 2.
Structure of the GLD-2–GLD-3 core complex. (A) The structure of GLD-2ΔI–GLD-3NT is shown in cartoon representation, colored as in the schematics in Fig. 1A. The N- and C-terminal residues and the α-helices of GLD-2 are indicated. Disordered regions are shown with dotted lines. The region deleted for crystallization (residues 813–846) resides in the disordered loop region between α-helices 7 and 8. In stick representations are the three active-site aspartic acids and the Glu875 residue identified in the C. elegans gld-2 mutant allele h292 (42). The chloride ion is shown as a black sphere. This and all structure figures were made with the PyMOL program (57). (B) Upper shows a cartoon representation of GLD-2ΔI–GLD-3NT, oriented with a 180° rotation around a vertical axis with respect to the view in A. The N- and C-terminal residues and the α-helices of GLD-3 are labeled. The α6-α7 and α7-α8 insertions of the central domain are highlighted in black and gray, respectively. Center and Lower show the structures of Cid1 [PDB ID code 4E80 (39); UTP molecule shown as stick representation] and Trf4-Air2 [PDB ID code 3NYB (37); Air2 in yellow, Zn ions shown as gray spheres] with the same color coding and in the same orientation as GLD-2ΔI–GLD-3NT in Upper, after optimal superposition. N- and C-terminal residues are labeled. Disordered loop regions are highlighted with dotted lines.
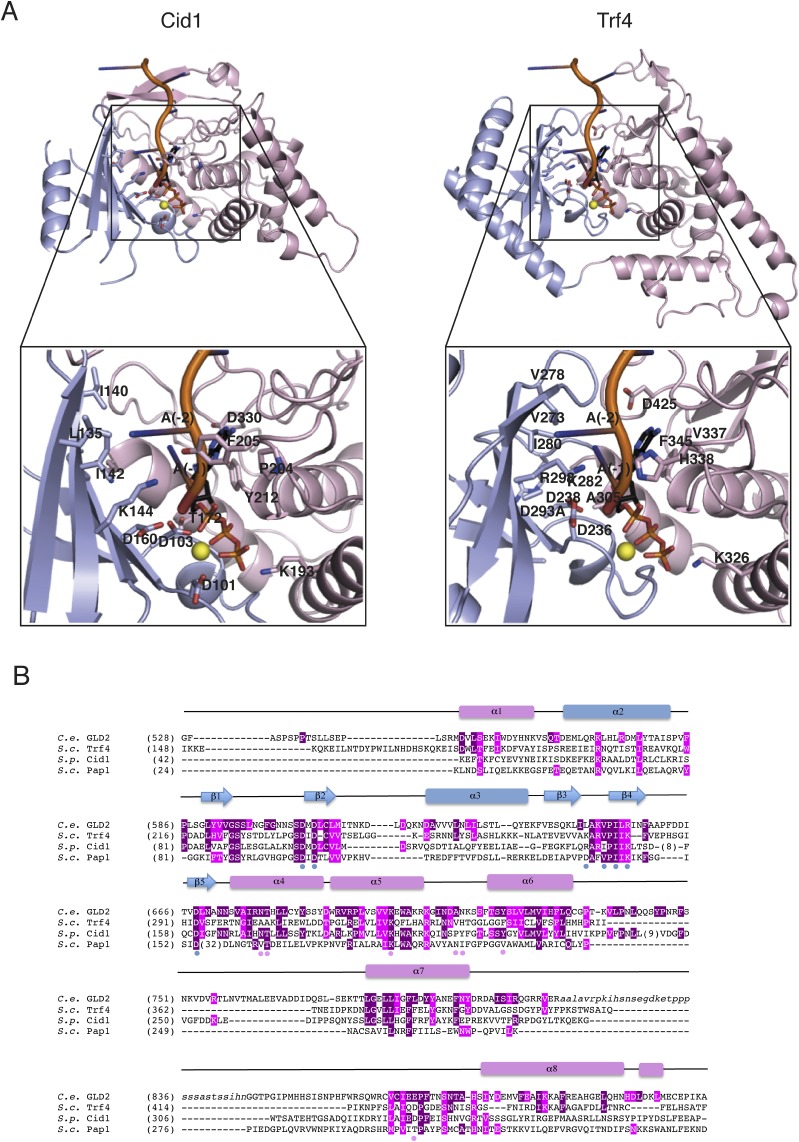
Comparisons with previously determined structures in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) using the program Dali (36) shows that GLD-2ΔI resembles most closely the S. pombe poly(U)-polymerase Cid1 [root mean square deviation (rmsd) of 1.7 Å over 75% of all Cα atoms; 30% sequence identity] and to a lesser extent the S. cerevisiae poly(A)-polymerase Trf4 (rmsd of 3.0 Å over 70% of all Cα atoms; 21% sequence identity) (37–40). All three noncanonical nucleotidyl transferases were crystallized in the absence of RNA and show a similar open conformation of the catalytic and central domains (Fig. 2B). In the structure of the canonical poly(A)-polymerase Pap1 determined with ATP and an A5 RNA, the interdomain cleft closes upon substrate binding (27) (Fig. S2A).
Fig. S2.
Closed conformations of nucleotidyl transferases. (A) Cartoon representation of substrate bound Pap1 in closed conformation (27). The molecules are shown in the same orientation as the view in Fig. 2A (Left) and 2B (Right). The loop regions between helices α6-α7 and α7-α8 are colored in black and gray, according to Fig. 2B (Right). Colors according to Fig. 2, with the RRM domain in yellow. RNA and ATP molecules are shown as cartoon and stick representations, respectively. The magnesium ion is shown as yellow sphere. RRM domain was removed for clarity in the left molecule. (B) Surface representation of Pap1 (without RRM domain), colored according to electrostatic surface potential over the range from −5 kT/e (red) to +5 kT/e (blue). The molecule is shown in the same view as in Fig. 4A. The conserved residue K145 near the active site (R655 in GLD-2) is annotated. (C) Polyadenylation assay with different protein concentrations (0, 20, 100, 500 nM) in the presence of 5′-32P-labeled 15mer poly(A), (C), (G), and (U) homopolymeric RNA substrates (100 nM).
The major differences in the structures of different nucleotidyl transferases lie in the central domain (Fig. 2B and Fig. S3). GLD-2 features particularly long and convoluted segments in the linkers connecting helix α6 to α7 and helix α7 to α8 (Fig. 2B, Upper). The α7-α8 linker spans 90 residues (794–886), and includes the so-called nucleotide recognition motif (NRM, residues 871–881) and the C. elegans-specific insertion that was truncated in GLD-2ΔI. The α7-α8 loop interacts with helices α4 and α6 and contributes to line the entry of the interdomain cleft (suggesting the NRM and possibly part of the truncated insertion might contribute to substrate binding). The α6-α7 linker of GLD-2ΔI is 50 residues long (732–781). It zig-zags around helix α4 and contributes to form the binding site for GLD-3NT. In comparison, the α6-α7 and α7-α8 linkers of Trf4 are shorter and both form the binding site for the zinc knuckle protein Air2 (37). A remarkable difference between the two noncanonical poly(A) polymerases is that they recognize binding partners on diametrically opposite surfaces: Air2 binds exclusively at the central domain of Trf4 (37), whereas GLD-3 binds mainly at the catalytic domain of GLD-2 (Fig. 2B).
Fig. S3.
Structure-based sequence alignment of GLD-2 orthologs from C. elegans (C.e.), Homo sapiens (H.s.), Drosophila melanogaster (D.m.) and Xenopus laevis (X.l.) together with S. cerevisiae (S.c.) Trf4, S. pombe (S.p.) Cid1, and S.c. Pap1. The secondary structure elements of C.e. GLD-2 are shown above the sequence and colored according to Fig. 1A. Strictly and well conserved residues are highlighted in dark and light purple, respectively. GLD-3–interacting residues are indicated with green dots. Residues targeted for mutagenesis are shown with the substituted amino acid in red, below the sequences, or black, above the sequences. Active-site residues discussed in the text are indicated with an asterisk. Also indicated is the sequence corresponding to the nucleotide recognition motif (NRM; refs. 28 and 40).
The N Terminus of GLD-3 Wraps Around the GLD-2 poly(A)-Polymerase Domain.
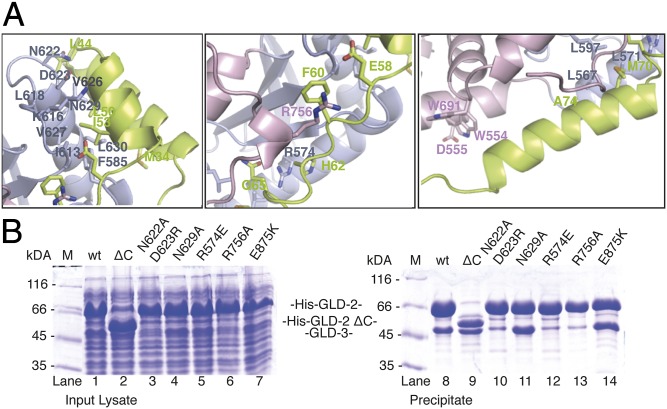
GLD-3NT folds into three helices (referred to as αA, αB, and αC) (Fig. 2A) and does not resemble a KH domain fold. GLD-3NT stretches on the surface of GLD-2, extending for more than 90 Å and burying a surface area of approximately 1,900 Å2 (calculated for GLD-2 by using the PISA program; refs. 27 and 41). Indeed, in isolation, GLD-3NT appears to be predominantely unstructured, as judged by circular dichroism on GLD-31–110 (Fig. S4A). The catalytic domain of GLD-2 mediates more than 70% of the total GLD-3–interaction surface. A helix-turn-helix formed by the αA and αB helices of GLD-3NT (residues 25–57) binds the GLD-2 catalytic domain at helix α3 and at the preceding loop (Fig. 3A, Left). Here, a hydrophobic surface of GLD-2 (Phe585, Ile613, Leu618, Val626, Val627, Leu630) recognizes apolar residues of GLD3. The interaction is reinforced by polar contacts (via GLD-2 Asn622, Asp623, Lys616, Asn629). GLD-3NT then continues with an extended segment (residue 58–66), which packs on the side of the GLD-2 β-sheet and wedges in between helix α4 and the α6-α7 insertion (Fig. 3A, Middle). Here, the interaction is dominated by two arginine residues of GLD-2 (Arg756 and Arg574). Finally, the last helix of GLD-3NT (residues 67–83) binds a composite surface of GLD-2 formed by the catalytic and central domains. The GLD-3 interaction is mediated both by hydrophobic contacts (with GLD-2 Leu567, Leu571, Leu597, Trp554, and Trp691) and polar contacts with GLD-2 Asp555 (Fig. 3A, Right). The portion of the central domain spanning the α7-α8 linker and helix α8 is not involved in GLD-3 binding, rationalizing why its deletion in the GLD-2ΔC mutant still supported the interaction (Fig. 3B, lanes 2 and 9 and Fig. S1B). GLD-3, which is highly conserved in all Caenorhabditis species (Fig. S4B), shares no obvious sequence similarity with other GLD-2–binding factors (e.g., CPEB, RNP-8, Rbm9, Musashi, and Ago1) (11, 30–32) and the similarity with Bic-C is too low to draw conclusions based on the GLD-3NT interactions. However, a subset of residues lining the GLD-3–binding surface of GLD-2 is conserved across species (Fig. 3A and Figs. S3 and S4C). GLD-2 orthologs might therefore use similar surface hotspots to mediate macromolecular interactions.
Fig. S4.
Sequence conservation of interface residues in GLD-2 and GLD-3. (A) Circular dichroism (CD) spectra obtained for 0.15 mg/mL GLD-31–110 (blue line) and 0.18 mg/mL GLD-388–460 (red line) in 20 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, and 10% glycerol at 20 °C from 250 to 190 nm by using a 1-mm cuvette. For GLD-31–110, the strong negative peak at 202 nm indicate the presence of a random coil structure, whereas for GLD-388–460, the spectra indicate the presence of a globular structure. (B) Structure-based sequence alignment of GLD-3NT from C. elegans, Caenorhabditis brenneri, Caenorhabditis briggsae, and Caenorhabditis remanei. The secondary structure elements of C.e. GLD-3NT are shown above the sequence and colored according to Fig. 1A. Strictly and well-conserved residues are highlighted in dark and light purple, respectively. GLD-2-interacting residues are indicated with blue or pink dots, for highlighting interaction with the catalytic or central domain of GLD-2, respectively. Residues targeted for mutagenesis are shown with the substituted amino acid in black, above the sequences. (C, Left) Structure-based sequence alignment of GLD-2 from C. elegans (C.e.), H. sapiens (H.s.), D. melanogaster (D.m.), and X. laevis (X.l.) adapted from Fig. S3. The secondary structure elements of C.e. GLD-2 are shown above the sequence and colored according to Fig. 1A. Strictly and well conserved residues are highlighted in dark and light purple, respectively. Low conserved residues are highlighted in light pink. GLD-3–interacting residues are indicated with green dots. Active-site residues discussed in the text are indicated with an asterisk. (Right) Cartoon representation of the GLD-2–GLD-3 heterodimer in the same orientation as in Fig. 2B. Conserved interface residues in GLD-2 highlighted in the sequence alignment are annotated and shown as sticks.
Fig. 3.
Hydrophobic and polar interactions anchor GLD-3 on the GLD-2 surface. (A) Three zoom-in views showing a representative set of interactions between GLD-2ΔI and GLD-3NT. The molecules are oriented as in Fig. 2B. (B) Coomassie-stained 12% SDS/PAGE of His-pulldown experiments of coexpressed wild-type (wt) and mutant GLD-2528–923 with GLD-31–460. Proteins were coexpressed in 4 mL of TB overnight at 20 °C. Pull-down assays were carried out by using a Tecan robot, using 50 μL of total lysate and 200 μL of Ni-NTA resin, and a buffer containing 250 mM NaCl. Total lysate control is shown at Left; pulled-down protein precipitate is shown at Right.
The interpretation of previous yeast-two hybrid results (33) in light of these structural data suggests that the helix-turn-helix of GLD-3NT is essential for GLD-2 binding. Based on the structural analysis, we engineered specific mutations in GLD-2 and tested their ability to interact with GLD-31–460 in coexpression and pull-down assays. Binding was impaired with the GLD-2 N622A and D623R mutant, which is expected to affect the interaction with the turn between the GLD-3 helices αA and αB (Fig. 3B, lanes 3 and 10). Interfering with a single polar contact between GLD-2 (N629A) and GLD-3 helix αA did not noticeably affect complex formation (Fig. 3B, lanes 4 and 11). The helix-turn-helix of GLD-3NT is, however, not sufficient for the interaction, because mutations of GLD-2 (either R574E or R756A) predicted to destabilize binding to the extended segment of GLD-3NT impaired complex formation (Fig. 3B, lanes 5 and 12 and lanes 6 and 13). As a note, Arg574 and Arg756 are much better conserved than Asn629 in GLD-2 orthologs and are not present in Trf4. Finally, we tested the effect of the E875K substitution on complex formation. This substitution was originally identified in the C. elegans mutant gld-2(h292) to result in the failure of normal gametes formation and ectopic proliferation in the proximal germ line (42). In the mutant, the interaction with GLD-3 was reduced, although the protein levels were comparable to those of the wild type (10). However, this conserved residue (Fig. S3) points inside the interdomain cleft and is far from GLD-3NT (Fig. 2A). Consistently, the pull-down assays showed that GLD-2 E875K was able to coprecipitate GLD-31–460 (Fig. 3B, lanes 7 and 14).
GLD-3 Contributes Both Directly and Indirectly to the Enzymatic Activity of GLD-2.
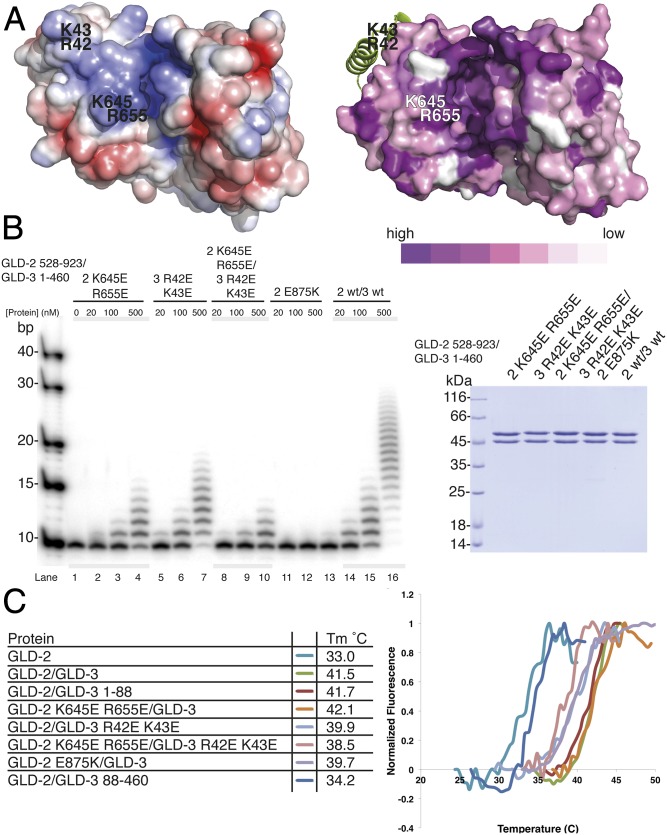
The finding that GLD-3NT is positioned on the outer surface of GLD-2 and is far from the active site (Figs. 2A and 3A) raises the question of how it boosts the poly(A)-polymerase activity. In the case of the canonical poly(A)-polymerase Pap1, RNA binds at a positively charged surface that spans from the RRM domain (at the entrance of the cleft) to the active site (27) (Fig. S2 A and B). When analyzing the surface properties of GLD-2ΔI–GLD-3NT based on electrostatic potential and evolutionary conservation (Fig. 4A), we noticed that the conserved positively charged surface of the active site is extended at the entrance of the cleft, with residues from GLD-2 (Lys645 and Arg655) and from the helix-turn-helix of GLD-3NT (Arg42 and Lys43). We purified recombinant GLD-2–GLD-31–460 mutant complexes with reverse-charged substitutions at these residues and tested them in polyadenylation assays (Fig. 4B).
Fig. 4.
Molecular basis for the stimulation of GLD-2 activity by GLD-3. (A) Structure of GLD-2ΔI–GLD-3NT shown in surface representation; colored at Left according to electrostatic surface potential over the range from −5 kT/e (red) to +5 kT/e (blue) and at Right according to evolutionary conservation, from dark violet (conserved) to white (variable). The surface conservation was calculated with the ConSurf Server (58) by using the alignment of the four GLD-2 orthologs in Fig. 2C. For clarity, GLD-3 is shown in a ribbon representation in green. Residues targeted for mutagenesis are indicated. (B, Left) Polyadenylation assay of GLD-2–GLD-3 wild type (wt) and mutants (0, 20, 100, 500 nM) in the presence of a 5′-32P-labeled 10-mer poly(A) RNA substrate (100 nM). (B, Right) Coomassie-stained 12% SDS/PAGE of GLD-2–GLD-3 protein complexes used for polyadenylation assays. (C) Protein stability of different GLD-2–GLD-3 complexes as determined by thermofluor experiments. Proteins were assayed in the presence of 150 mM NaCl and 10% glycerol. The table at Left shows the melting temperature (Tm), and Right shows the corresponding normalized curves.
Complexes containing either the GLD-2 K645E,R655E or the GLD-3 R42E,K43E mutants showed decreased activity with respect to the wild-type sample (Fig. 4B, lanes 2–4, 5–7, and 14–16, respectively). Combining both sets of protein mutants had an additive effect on the extent of polyadenylation (Fig. 4B, lanes 8–10), but did not significantly decrease the stability of the complex, as assessed by measuring the corresponding melting temperatures using thermofluor assays (Fig. 4C). We concluded that GLD-3 has a direct effect on GLD-2 poly(A)-polymerase activity, probably by contributing to RNA binding at the entry of the active site cleft. However, we found that the melting temperatures of GLD-2 either in isolation (Tm 33 °C) and or supplemented with GLD-388–460 (Tm 34.2 °C) were markedly lower than when in the presence of GLD-31–460 or GLD-3NT (Tm > 41 °C) (Fig. 4C). Thus, GLD-3 also appears to have an indirect effect in stabilizing the fold of GLD-2. In the structure, GLD-3 covers hydrophobic surface patches of GLD-2, shielding them from solvent. With hindsight, the finding that GLD-2 in isolation is capable of adding only a few adenosines (10, 23, 43) (Fig. 1B) might be explained by the rapid inactivation of the protein in the time and conditions of the assays.
Specific Substrate-Binding Properties of the GLD-2 Active Site.
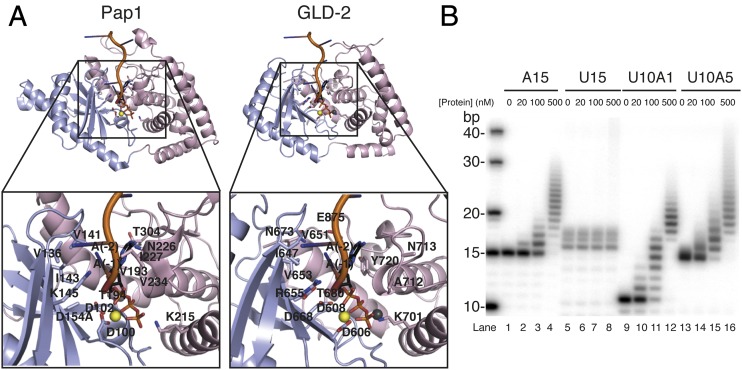
The most severe effect on the polyadenylation properties of GLD-2–GLD-31–460 was obtained with the reverse-charged substitution of Glu875 corresponding to gld-2(h292) (42). The Glu875Lys mutation did not destabilize the GLD-2–GLD-31–460 complex in thermofluor assays (Tm ∼ 40 °C; Fig. 4C), yet it essentially abolished enzymatic activity (Fig. 4B, lanes 11–13). Because Glu875 points into the interdomain cleft, we superposed the catalytic and central domains of GLD-2 separately to the equivalent domains of Pap1 in the ATP-A5–bound structure (27) and compared the residues in the active site (Fig. 5A).
Fig. 5.
Idiosyncratic biochemical and structural features of the GLD-2 poly(A)-polymerase site. (A) Cartoon representations of Pap1 (Left; PDB ID code 2Q66; ref. 27) and GLD-2ΔI–GLD-3NT (Right; GLD-3 not displayed, RNA and ATP molecules are modeled according to the superposition with Pap1; ref. 27) after optimal, separate superposition of the catalytic and central domains. The zoom-in views show residues outlined in the text involved in interaction with the RNA and ATP molecules as seen in Pap1 and at the same or similar position in GLD-3–complexed GLD-2. Molecules are rotated by 20° around a horizontal axis with respect to the view in Fig. 2A and colored accordingly. The RNA and ATP molecules are shown as cartoon and stick representations, and the magnesium and chloride ions are shown as yellow and gray spheres, respectively. (B) Polyadenylation assay of GLD-2–GLD-3 wild type (0, 20, 100, 500 nM) in the presence of 5′-32P-labeled poly(U):poly(A) heterooligomers (100 nM).
The structural analysis shows that the chloride ion in the GLD-2ΔI–GLD-3NT structure occupies the position between the β- and γ-phosphates of ATP. Functionally important residues are present at conserved positions, including those expected to mediate electrostatic and polar interactions with the magnesium ions and with the phosphate and ribose moieties of the nucleotides, and those expected to mediate hydrophobic interactions with the bases (Fig. 5A and Fig. S5). In the case of Cid1, the specificity for UTP depends on His336 (38, 40, 44, 45). In the case of Pap1, the base of ATP is recognized indirectly by stacking interactions with the base of the nucleotide at the 3′ end of the RNA substrate (nucleotide −1) (27). With the possible exception of Pap1 Asn226, no other polar residue of the canonical poly(A) polymerase approaches the pyrimidines of ATP and nucleotide −1 (27). In GLD-2, however, this site is lined by several polar residues that are strictly conserved across species (Figs. S3 and S4). In particular, Glu875 from the NRM segment is expected to approach both adenines and is flanked by Asn673 from helix α4 (Fig. 5A), suggesting an involvement in substrate binding and specificity. Therefore, we assessed the substrate specificity of GLD-2 in polyadenylation assays by using different homopolymeric substrates in vitro. We found that GLD-2–GLD-31–460 is highly selective for a poly(A) RNA substrate and does not polyadenylate poly(U) or poly(C) RNAs (Fig. 5B and Fig. S2C). Remarkably, addition of a single adenine nucleotide at the 3′ end of a poly(U) RNA was sufficient to restore GLD-2–mediated polyadenylation (Fig. 5B).
Fig. S5.
Structural features of the Cid1 and Trf4 poly(A)-polymerase active site. (A) Cartoon representations of Cid1 (PDB ID code 4E80; ref. 39) and Trf4 (PDB ID code 3NYB; ref. 37; Air2 not displayed) after optimal, separate superposition of the catalytic and central domains on Pap1. The RNA and ATP molecules are modeled according to the superposition with Pap1 (27).The zoom-in views show residues outlined in the text involved in interaction with the RNA and ATP molecules as seen in yeast Pap1 and at the same or similar position in Cid1 and Trf4. Molecules are shown in the same orientation as in Fig. 5A and colored accordingly. The RNA and ATP molecules are shown as cartoon and stick representations; the magnesium ion is shown as a yellow sphere. (B) Structure-based sequence alignment of C. elegans (C.e.) GLD-2 with S. cerevisiae (S.c.) Trf4, S. pombe (S.p.) Cid1, and S.c. Pap1 adapted from Fig. 3. The secondary structure elements of C.e. GLD-2 are shown above the sequence and colored according to Fig. 1A. Strictly and well-conserved residues based on Fig. 3 are highlighted in dark and light purple, respectively. Substrate interacting residues from Pap1 catalytic and central domains, as highlighted in Fig. 5, are indicated with blue and pink dots, respectively.
Conclusions
At the mechanistic level, GLD-3 increases the poly(A)-polymerase activity of GLD-2 and directs it to specific substrates (10, 33). Although it was expected that GLD-3 would provide an RNA-binding KH domain to boost the polyadenylation properties of this noncanonical poly(A) polymerase, the KH2–KH5 unit of GLD-3 has no detectable RNA-binding properties in vitro (34), and we now find the so-called KH1 domain does not adopt the structure of a KH fold: It wraps around the surface of the poly(A) polymerase rather than docking onto it as observed for the globular RRM of Pap1 (27, 46–48). The mechanism of GLD-3–mediated activation of GLD-2 is conceptually rather different, and involves a direct contribution of residues lining the RNA-binding site and an indirect contribution due to increased stability. In this context, the observation that the closely related nucleotidyl-transferase Cid1 is active without binding partners can be rationalized on the basis of its different surface properties (38–40, 49).
GLD-2 has distinct structural features in the active site and distinct biochemical properties, with specificity for an adenine at the 3′ end of the RNA substrate. This specificity is unusual, because Pap1 and Trf4 polyadenylate a relatively broad range of RNA substrates (27, 37, 50, 51). It is tempting to speculate that this property might be tailored to the majority of GLD-2 substrates, namely dormant mRNAs with shortened poly(A) tail at their 3′ end.
Experimental Procedures
Protein Expression and Purification.
C. elegans GLD-2 and GLD-3 proteins and mutants were subcloned in expression vectors with an N-terminal His-tag cleavable by tobacco etch virus (TEV) protease (SI Experimental Procedures). They were expressed (in isolation or as a complex) in Escherichia coli BL21 Gold pLyS cells (Stratagene) by using Terrific Broth (TB) medium and overnight induction at 18 °C. Expression of selenomethionine-derivatized proteins was carried out in minimal medium in the presence of 50 mg/L selenomethionine. All proteins were purified with a similar protocol (see SI Experimental Procedures for details). In short, cells were lysed in a buffer containing 500 mM NaCl and protease inhibitors (Roche), and the lysate was loaded on a Ni-NTA affinity column (His60; GE Healthcare). After elution and tag cleavage, the proteins were further purified by ion exchange chromatography (Q Sepharose; GE Healthcare) and size exclusion chromatography (Superdex; GE Healthcare). They were concentrated in 20 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, and 4 mM DTT. The stability of the purified samples was assessed by thermofluor experiments (SI Experimental Procedures). Coexpression and pull-down assays were carried out by using a Tecan robot, using 50 μL of total lysate and 200 μL of Ni-NTA resin, and a buffer containing 250 mM NaCl (SI Experimental Procedures).
Crystallization and Structure Determination.
Crystals of the selenomethionine-derivatized GLD-2ΔI–GLD-3NT grew at 20 °C in a sitting-drop vapor diffusion setup by using as reservoir solution 18% (vol/vol) PEG MME 550, 50 mM potassium nitrate, 60 mM magnesium nitrate, and 30 mM Hepes pH 7.0. Single crystals appeared in a few days. They were transferred to a cryoprotectant solution containing 15% (vol/vol) ethylene glycol and flash-cooled in liquid nitrogen. Single-anomalous diffraction data were collected at the beamline PXII at the Swiss Light Source (Switzerland) at 100K and processed with X-ray detector software (52). The crystals belong to an orthorhombic spacegroup with one molecule per asymmetric unit. The HKL2MAP program (53) located 11 of 14 selenium sites. The initial phases were calculated with PHENIX software (54). Model building was first carried out with PHENIX (54) and BUCCANEER (55). Further manual model building and iterative refinement were performed by using COOT (56) and PHENIX (54). Detailed data collection and refinement statistics are summarized in Table S1.
Polyadenylation Assays.
Polyadenylation assays were carried out in a 10-μL reaction volume containing 25 mM Tris pH 8.0, 20 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 10% (vol/vol) glycerol, 0.02% (vol/vol) Nonidet P-40, 1 mM DTT, and 0.05 mg/mL BSA. Final concentrations were either 20, 100, or 500 nM for proteins and 0.5 mM for ATP. Relevant 5′-32P-labeled RNA (synthetic oligos from biomers.net; γ-[32P]ATP 3000 Ci/mmol from PerkinElmer) was added to a final concentration of 100 nM to start the reaction. Reaction mixtures were incubated at 30 °C for 10 min and quenched by adding 10 μL of a buffer containing 50 mM EDTA, 0.1% SDS, and 2 mg/mL Proteinase K (New England Biolabs). Samples were incubated 10 min at 37 °C before diluting 1:3 in 95% (vol/vol) formamide, 10 mM EDTA, 0.1% bromophenol blue, 0.1% xylene cyanole, and loading 2 μL of each reaction on a 10% (wt/vol) polyacrylamide/7M urea gel. Gels were exposed overnight at −80 °C to Fuji image plates and visualized by using a Typhoon FLA 7000 phosphorimager (GE Healthcare).
SI Experimental Procedures
Expression Construct Design.
C.e. GLD-2 and C.e. GLD-3 constructs were PCR amplified from full-length DNA clones (primer sequences are available upon request). The PCR products of GLD-2 were inserted between the NcoI/NotI sites of pETM30 (EMBL vectors) resulting in an N-terminal GST-fusion tag. PCR products of GLD-3 were inserted between the NcoI/NotI sites of pET21 (Novagene). The loop truncated versions of GLD-2 (∆813–846), and additional mutants of both GLD-2 (D608A, E875K, K645ER655E, N622AD623R, N629A, R574E, R756A) and GLD-3 (R42EK43E) were prepared by overlapping PCR. All constructs were verified by DNA sequencing.
GLD-2 and GLD-3 Expression and Purification.
E. coli BL-21 Gold pLyS cells (Stratagene) were cotransformed with GLD-2 pETM30 and GLD-3 pET21 constructs and grown at 37 °C in TB medium containing the respective antibiotics until reaching an OD600 ∼ 0.8. The temperature was reduced to 18 °C, and protein expression was induced by addition of 1 mM isopropyl β-d-thiogalactoside (IPTG) at OD600 −1.2. Cells were harvested 16 h after induction by centrifugation. Cell pellets were resuspended in lysis buffer (50 mM Tris pH 7.8, 500 mM NaCl, and 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol). Cell walls were broken by sonication, and the cell debris was clarified by centrifugation at 20,000 × g. All subsequent purification steps were performed at 4 °C. The supernatant was loaded onto Ni-NTA affinity resin (His60; GE Healthcare) equilibrated with lysis buffer. Following washes with buffer B (20 mM Tris pH 7.8, 1 M NaCl and 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol) and buffer A (20 mM Tris pH 7.8, 50 mM NaCl, and 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol), the bound proteins were eluted in elution buffer (20 mM Tris pH 8.5, 50 mM NaCl, 250 mM imidazole, and 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol). The N-terminal GST-fusion tag was cleaved with TEV protease in buffer C (20 mM Hepes pH 8.5, 50 mM NaCl, and 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol) overnight at 4 °C. After a reverse Ni-NTA step to remove the GST-fusion Tag, the cleaved protein was loaded onto a HiTrap Q Sepharose HP column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated in buffer C. The bound protein was eluted by using a linear gradient of 20 column volumes to buffer D (20 mM Hepes pH 8.5, 1 M NaCl, and 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol). ceGLD2/ceGLD3 complexes were further purified by size exclusion chromatography on a Superdex 200 column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated with buffer E (20 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, and 4 mM DTT). Proteins were subsequently concentrated to ∼8–15 mg/mL and either used up directly for crystallization setups or flash frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until further use. The selenomethionine-derivatized protein and all mutants were purified accordingly. Protein concentrations for biochemical experiments were determined by optical density measurements at 280 nm, followed by quantitation on SDS-polyacrylamide gels.
Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy.
Far UV (UV) circular dichroism (CD) spectra of GLD-31–110 (0.15 mg/mL) and GLD-388–460 (0.18 mg/mL) were recorded on a Jasco J-810 Spectropolarimeter at 20 °C in 20 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, and 10% (vol/vol) glycerol in a 1-mm path-length cuvette. Four scans were taken from 250 to 190 nm in 0.1-nm increments. The scans were averaged and corrected by substraction of the buffer spectrum.
Thermofluor Assays.
Solutions containing 5 μL of protein (2 mg/mL) and 45 μL of buffer [20 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 10% (vol/vol) glycerol] with 3.9× of Sypro Orange (Invitrogen) were added to the wells of a 96-well Twin-tec plate (Eppendorf). The plate was sealed and heated in a real-time PCR system (Eppendorf) from 20 to 80 °C in increments of 0.5 °C. Fluorescence changes were monitored simultaneously. The wavelengths for excitation and emission were 470 and 550 nm, respectively. To obtain the temperature midpoint for the protein unfolding transition (Tm), a Boltzmann model was used to fit the fluorescence data after normalization.
Coexpression and Pulldown Assays.
Coexpression tests for pulldown were done in 24-deep well plates (Whatman). TB (4 mL) was inoculated with a 1:100 dilution of cotransformed BL21 Gold pLyS TB preculture and incubated 6 h at 37 °C and 800 rpm. Protein expression was induced with 1 mM IPTG, and cells were incubated shaking at 20 °C overnight. Cells were harvested by centrifugation. The supernatant was discarded. Cell pellets were lysed by addition of 2 mL of lysis buffer (250 mM NaCl, 50 mM NaH2PO4, 25 mM imidazole pH 7.5, 10 mM MgCl2, 750 U/mL Benzonase), shaking for 10 min at 20 °C and sonication at 4 °C. For total lysate control, 50 μL of each well were taken. Pulldown experiments were done in a TeVacs Vaccum station (Tecan). For pulldown, 200 μL of Ni-beads suspension (GE Healthcare) were added to each well and incubated at 10 min at 800 rpm. The lysate/bead mixtures were transferred to a 96-well receiver plate (20 μm; Eppendorf), and liquid was removed by vacuum. Beads were washed five times with lysis buffer and dried after the last washing step. For elution, 66 μL of elution buffer (250 mM NaCl, 50 mM NaH2PO4, 700 mM Imidazole pH 7.5) was added to the beads and incubated for 5 min at 20 °C. The eluate was collected by centrifugation (15 min, 4,000 rpm, 4 °C). Protein concentration was determined in a 96-well UV plate (using Tecan Genios Pro) at 280 nm, and the same amount of protein was loaded onto a SDS/PAGE.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry Core Facility and Crystallization Facility, the staff members at the beamlines PXII and PXIII of the Swiss Light Source, and members of our laboratories for useful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. This study was supported by the Max Planck Gesellschaft; the European Commission from European Research Council Advanced Investigator Grant 294371, Marie Curie ITN RNPnet; and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft Grants SFB646, SFB1035, GRK1721, FOR1680, CIPSM (to E.C.), FOR855 and EC369/3-1 (to C.R.E.), and BU2451/1-2 (to K.N.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
Data deposition: The atomic coordinates have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank, www.pdb.org (PDB ID code 4ZRL).
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1504648112/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Eckmann CR, Rammelt C, Wahle E. Control of poly(A) tail length. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011;2(3):348–361. doi: 10.1002/wrna.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moore MJ, Proudfoot NJ. Pre-mRNA processing reaches back to transcription and ahead to translation. Cell. 2009;136(4):688–700. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Goldstrohm AC, Wickens M. Multifunctional deadenylase complexes diversify mRNA control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(4):337–344. doi: 10.1038/nrm2370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chen CY, Shyu AB. Mechanisms of deadenylation-dependent decay. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011;2(2):167–183. doi: 10.1002/wrna.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Norbury CJ. Cytoplasmic RNA: A case of the tail wagging the dog. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(10):643–653. doi: 10.1038/nrm3645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tadros W, Lipshitz HD. Setting the stage for development: mRNA translation and stability during oocyte maturation and egg activation in Drosophila. Dev Dyn. 2005;232(3):593–608. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Radford HE, Meijer HA, de Moor CH. Translational control by cytoplasmic polyadenylation in Xenopus oocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1779(4):217–229. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Richter JD, Klann E. Making synaptic plasticity and memory last: Mechanisms of translational regulation. Genes Dev. 2009;23(1):1–11. doi: 10.1101/gad.1735809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Barckmann B, Simonelig M. Control of maternal mRNA stability in germ cells and early embryos. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1829(6-7):714–724. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang L, Eckmann CR, Kadyk LC, Wickens M, Kimble J. A regulatory cytoplasmic poly(A) polymerase in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2002;419(6904):312–316. doi: 10.1038/nature01039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Barnard DC, Ryan K, Manley JL, Richter JD. Symplekin and xGLD-2 are required for CPEB-mediated cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Cell. 2004;119(5):641–651. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.10.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kwak JE, Wang L, Ballantyne S, Kimble J, Wickens M. Mammalian GLD-2 homologs are poly(A) polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101(13):4407–4412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400779101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rouhana L, et al. Vertebrate GLD2 poly(A) polymerases in the germline and the brain. RNA. 2005;11(7):1117–1130. doi: 10.1261/rna.2630205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nakanishi T, et al. Possible role of mouse poly(A) polymerase mGLD-2 during oocyte maturation. Dev Biol. 2006;289(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cui J, Sackton KL, Horner VL, Kumar KE, Wolfner MF. Wispy, the Drosophila homolog of GLD-2, is required during oogenesis and egg activation. Genetics. 2008;178(4):2017–2029. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.084558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sartain CV, Cui J, Meisel RP, Wolfner MF. The poly(A) polymerase GLD2 is required for spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Development. 2011;138(8):1619–1629. doi: 10.1242/dev.059618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Suh N, Jedamzik B, Eckmann CR, Wickens M, Kimble J. The GLD-2 poly(A) polymerase activates gld-1 mRNA in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(41):15108–15112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607050103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cui J, Sartain CV, Pleiss JA, Wolfner MF. Cytoplasmic polyadenylation is a major mRNA regulator during oogenesis and egg activation in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 2013;383(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.08.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kwak JE, et al. GLD2 poly(A) polymerase is required for long-term memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(38):14644–14649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803185105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Udagawa T, et al. Bidirectional control of mRNA translation and synaptic plasticity by the cytoplasmic polyadenylation complex. Mol Cell. 2012;47(2):253–266. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Katoh T, et al. Selective stabilization of mammalian microRNAs by 3′ adenylation mediated by the cytoplasmic poly(A) polymerase GLD-2. Genes Dev. 2009;23(4):433–438. doi: 10.1101/gad.1761509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.D’Ambrogio A, Gu W, Udagawa T, Mello CC, Richter JD. Specific miRNA stabilization by Gld2-catalyzed monoadenylation. Cell Reports. 2012;2(6):1537–1545. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.10.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee M, et al. Adenylation of maternally inherited microRNAs by Wispy. Mol Cell. 2014;56(5):696–707. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kwak JE, Wickens M. A family of poly(U) polymerases. RNA. 2007;13(6):860–867. doi: 10.1261/rna.514007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Martin G, Keller W. RNA-specific ribonucleotidyl transferases. RNA. 2007;13(11):1834–1849. doi: 10.1261/rna.652807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schmidt MJ, Norbury CJ. Polyadenylation and beyond: Emerging roles for noncanonical poly(A) polymerases. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2010;1(1):142–151. doi: 10.1002/wrna.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Balbo PB, Bohm A. Mechanism of poly(A) polymerase: Structure of the enzyme-MgATP-RNA ternary complex and kinetic analysis. Structure. 2007;15(9):1117–1131. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.07.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Aravind L, Koonin EV. DNA polymerase beta-like nucleotidyltransferase superfamily: Identification of three new families, classification and evolutionary history. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27(7):1609–1618. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.7.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Eckmann CR, Kraemer B, Wickens M, Kimble J. GLD-3, a bicaudal-C homolog that inhibits FBF to control germline sex determination in C. elegans. Dev Cell. 2002;3(5):697–710. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Papin C, Rouget C, Mandart E. Xenopus Rbm9 is a novel interactor of XGld2 in the cytoplasmic polyadenylation complex. FEBS J. 2008;275(3):490–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim KW, et al. Antagonism between GLD-2 binding partners controls gamete sex. Dev Cell. 2009;16(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cragle C, MacNicol AM. Musashi protein-directed translational activation of target mRNAs is mediated by the poly(A) polymerase, germ line development defective-2. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(20):14239–14251. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.548271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Eckmann CR, Crittenden SL, Suh N, Kimble J. GLD-3 and control of the mitosis/meiosis decision in the germline of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 2004;168(1):147–160. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.029264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nakel K, Hartung SA, Bonneau F, Eckmann CR, Conti E. Four KH domains of the C. elegans Bicaudal-C ortholog GLD-3 form a globular structural platform. RNA. 2010;16(11):2058–2067. doi: 10.1261/rna.2315010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Martin G, Doublié S, Keller W. Determinants of substrate specificity in RNA-dependent nucleotidyl transferases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1779(4):206–216. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2007.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Holm L, Rosenstrom P. 2010. Dali server: Conservation mapping in 3D. Nucleic Acids Res 38(Web Server issue):W545–W549.
- 37.Hamill S, Wolin SL, Reinisch KM. Structure and function of the polymerase core of TRAMP, a RNA surveillance complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(34):15045–15050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003505107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yates LA, et al. Structural basis for the activity of a cytoplasmic RNA terminal uridylyl transferase. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012;19(8):782–787. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Munoz-Tello P, Gabus C, Thore S. Functional implications from the Cid1 poly(U) polymerase crystal structure. Structure. 2012;20(6):977–986. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lunde BM, Magler I, Meinhart A. Crystal structures of the Cid1 poly (U) polymerase reveal the mechanism for UTP selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(19):9815–9824. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Krissinel E, Henrick K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J Mol Biol. 2007;372(3):774–797. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.05.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kadyk LC, Kimble J. Genetic regulation of entry into meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development. 1998;125(10):1803–1813. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.10.1803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Minasaki R, Rudel D, Eckmann CR. Increased sensitivity and accuracy of a single-stranded DNA splint-mediated ligation assay (sPAT) reveals poly(A) tail length dynamics of developmentally regulated mRNAs. RNA Biol. 2014;11(2):111–123. doi: 10.4161/rna.27992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Munoz-Tello P, Gabus C, Thore S. A critical switch in the enzymatic properties of the Cid1 protein deciphered from its product-bound crystal structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(5):3372–338. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yates LA, et al. Structural plasticity of Cid1 provides a basis for its distributive RNA terminal uridylyl transferase activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(5):2968–2979. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bard J, et al. Structure of yeast poly(A) polymerase alone and in complex with 3′-dATP. Science. 2000;289(5483):1346–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5483.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Martin G, Keller W, Doublié S. Crystal structure of mammalian poly(A) polymerase in complex with an analog of ATP. EMBO J. 2000;19(16):4193–4203. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.16.4193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Martin G, Möglich A, Keller W, Doublié S. Biochemical and structural insights into substrate binding and catalytic mechanism of mammalian poly(A) polymerase. J Mol Biol. 2004;341(4):911–925. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.06.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rissland OS, Mikulasova A, Norbury CJ. Efficient RNA polyuridylation by noncanonical poly(A) polymerases. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27(10):3612–3624. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02209-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Butler JS, Platt T. RNA processing generates the mature 3′ end of yeast CYC1 messenger RNA in vitro. Science. 1988;242(4883):1270–1274. doi: 10.1126/science.2848317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Butler JS, Sadhale PP, Platt T. RNA processing in vitro produces mature 3′ ends of a variety of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10(6):2599–2605. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kabsch W. Xds. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2010;66(Pt 2):125–132. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909047337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pape T, Schneider TR. HKL2MAP: A graphical user interface for phasing with SHELX programs. J Appl Cryst. 2004;37(Pt 5):843–844. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Adams PD, et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2010;66(Pt 2):213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Cowtan K. The Buccaneer software for automated model building. 1. Tracing protein chains. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006;62(Pt 9):1002–1011. doi: 10.1107/S0907444906022116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG, Cowtan K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2010;66(Pt 4):486–501. doi: 10.1107/S0907444910007493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Schrodinger LLC. 2010. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.5.0.4.
- 58.Ashkenazy H, Erez E, Martz E, Pupko T, Ben-Tal N. 2010. ConSurf 2010: Calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res 38(Web Server issue):W529–W533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]