Abstract
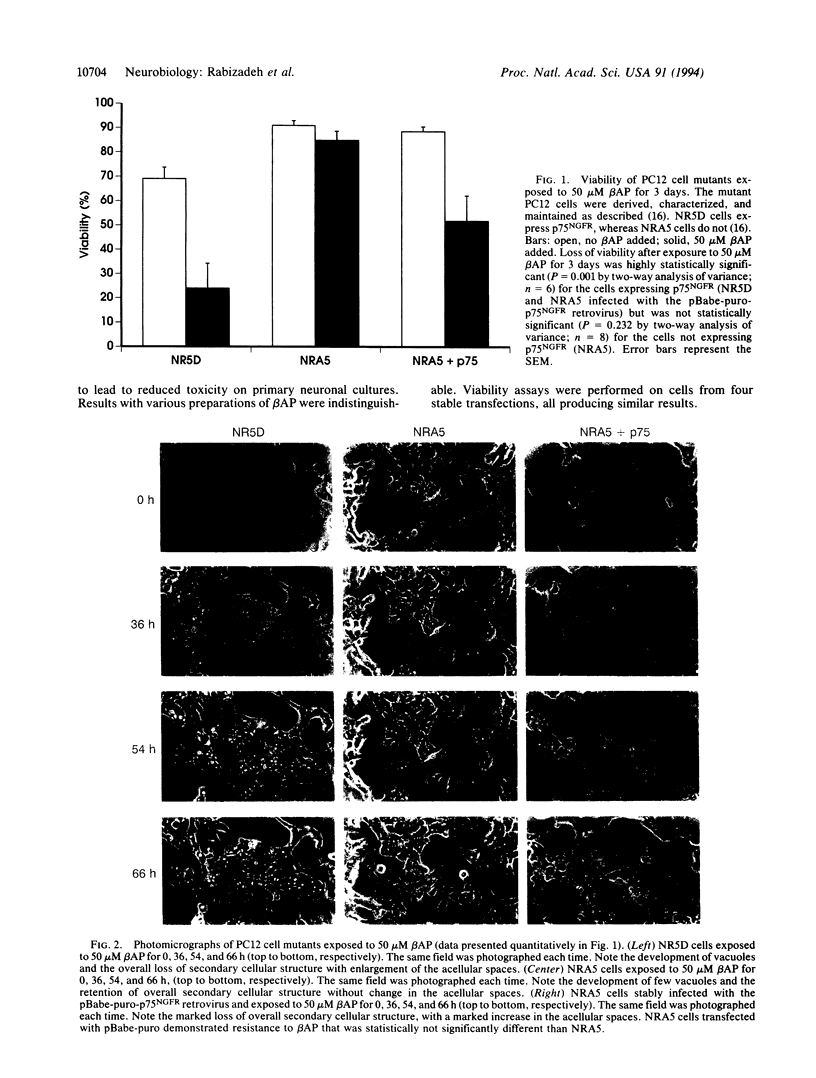
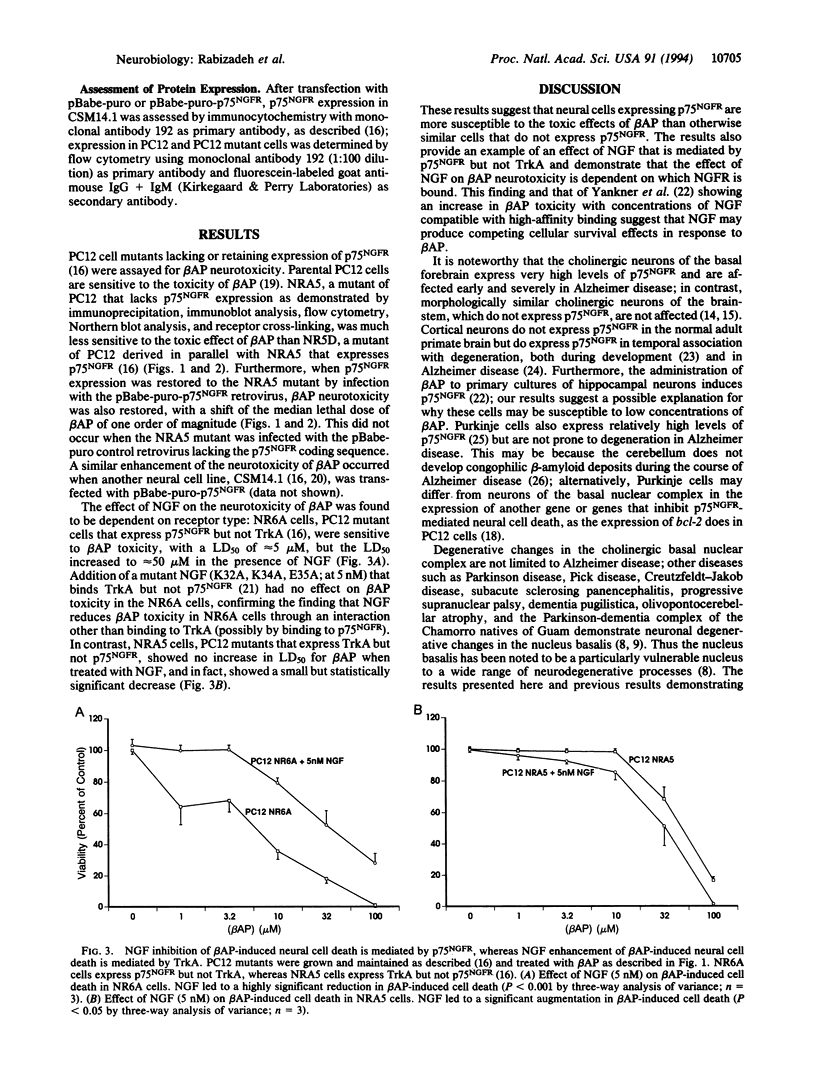
The low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR) p75NGFR induces apoptosis in the absence of nerve growth factor (NGF) binding but enhances neural survival when bound by NGF. Basal forebrain cholinergic neurons express the highest levels of p75NGFR in the adult human brain and are preferentially involved in Alzheimer disease, raising the question of whether there may be a functional relationship between the expression of p75NGFR and basal forebrain cholinergic neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer disease. The expression of p75NGFR by wild-type and mutant PC12 cells potentiated cell death induced by beta-amyloid peptide. NGF binding to p75NGFR inhibited the toxicity of beta-amyloid peptide, whereas NGF binding to TrkA, the high-affinity NGFR, enhanced it. These results suggest a possible link between beta-amyloid peptide toxicity and preferential degeneration of cells expressing p75NGFR.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arendt T., Taubert G., Bigl V., Arendt A. Amyloid deposition in the nucleus basalis of Meynert complex: a topographic marker for degenerating cell clusters in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;75(3):226–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00690530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averback P. Lesions of the nucleus ansae peduncularis in neuropsychiatric disease. Arch Neurol. 1981 Apr;38(4):230–235. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510040056009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behl C., Davis J., Cole G. M., Schubert D. Vitamin E protects nerve cells from amyloid beta protein toxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 31;186(2):944–950. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90837-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigl V., Woolf N. J., Butcher L. L. Cholinergic projections from the basal forebrain to frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, and cingulate cortices: a combined fluorescent tracer and acetylcholinesterase analysis. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jun;8(6):727–749. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen D. M., Davison A. N. Biochemical studies of nerve cells and energy metabolism in Alzheimer's disease. Br Med Bull. 1986 Jan;42(1):75–80. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun A., Gustafson L. Distribution of cerebral degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. A clinico-pathological study. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr (1970) 1976 Dec 31;223(1):15–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00367450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher L. L., Semba K. Reassessing the cholinergic basal forebrain: nomenclature schemata and concepts. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Dec;12(12):483–485. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. L., Benson D. F. The role of the nucleus basalis of Meynert in dementia: review and reconsideration. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1987;1(3):128–155. doi: 10.1097/00002093-198701030-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Maloney A. J. Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1403–1403. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91936-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis P. T., Palmer A. M., Sims N. R., Bowen D. M., Davison A. N., Esiri M. M., Neary D., Snowden J. S., Wilcock G. K. Neurochemical studies of early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Possible influence on treatment. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 4;313(1):7–11. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507043130102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Ebendal T., Barbany G., Murray-Rust J., Blundell T. L., Persson H. Disruption of the low affinity receptor-binding site in NGF allows neuronal survival and differentiation by binding to the trk gene product. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joachim C. L., Morris J. H., Selkoe D. J. Diffuse senile plaques occur commonly in the cerebellum in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1989 Aug;135(2):309–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. J., Joshua D. E., Williams G. T., Smith C. A., Gordon J., MacLennan I. C. Mechanism of antigen-driven selection in germinal centres. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):929–931. doi: 10.1038/342929a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mah S. P., Zhong L. T., Liu Y., Roghani A., Edwards R. H., Bredesen D. E. The protooncogene bcl-2 inhibits apoptosis in PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1993 Mar;60(3):1183–1186. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinecke D. L., Rakic P. Low-affinity p75 nerve growth factor receptor expression in the embryonic monkey telencephalon: timing and localization in diverse cellular elements. Neuroscience. 1993 May;54(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90386-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson E. J., Higgins G. A., Kordower J. H. Nerve growth factor receptor immunoreactivity in the new world monkey (Cebus apella) and human cerebellum. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Jun 22;308(4):555–575. doi: 10.1002/cne.903080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson E. J., Kordower J. H. Cortical neurons express nerve growth factor receptors in advanced age and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):569–573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabizadeh S., Oh J., Zhong L. T., Yang J., Bitler C. M., Butcher L. L., Bredesen D. E. Induction of apoptosis by the low-affinity NGF receptor. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):345–348. doi: 10.1126/science.8332899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf N. J., Gould E., Butcher L. L. Nerve growth factor receptor is associated with cholinergic neurons of the basal forebrain but not the pontomesencephalon. Neuroscience. 1989;30(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf N. J., Hernit M. C., Butcher L. L. Cholinergic and non-cholinergic projections from the rat basal forebrain revealed by combined choline acetyltransferase and Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin immunohistochemistry. Neurosci Lett. 1986 May 23;66(3):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf N. J., Jacobs R. W., Butcher L. L. The pontomesencephalotegmental cholinergic system does not degenerate in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jan 30;96(3):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Caceres A., Duffy L. K. Nerve growth factor potentiates the neurotoxicity of beta amyloid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9020–9023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Duffy L. K., Kirschner D. A. Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2218531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]