Abstract
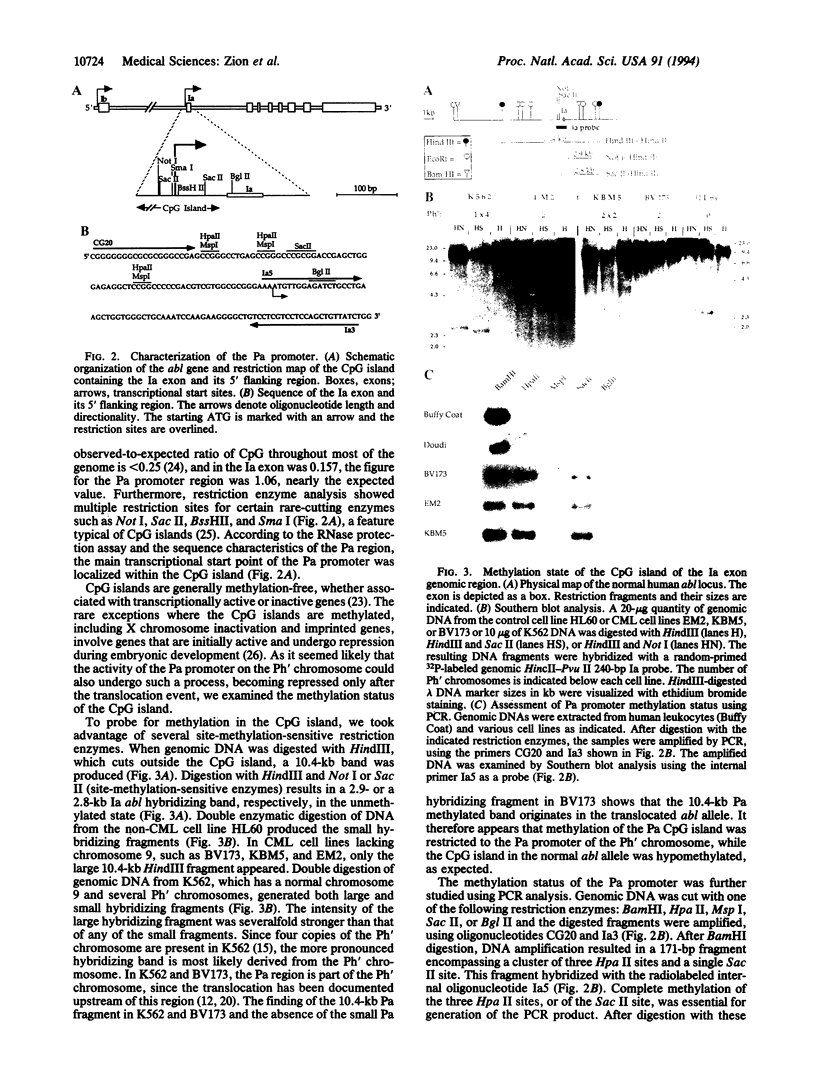
De novo methylation of CpG islands is a rare event in mammalian cells. It has been observed in the course of developmental processes, such as X chromosome inactivation and genomic imprinting. The methylation of DNA, an important factor in the epigenetic control of gene expression, may also be involved in tumorigenesis. After the t(9;22) chromosomal translocation and generation of the Philadelphia chromosome, the initiating event in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), most of the abl coding sequence is fused to the 5' region of the bcr gene. Expression of the hybrid bcr-abl gene is, therefore, regulated by the bcr promoter. In most cases of CML, one of the two abl promoters (Pa) is nested within the bcr-abl transcriptional unit and should be able to transcribe the type Ia 6-kb normal abl mRNA from the Philadelphia chromosome. However, we have found that the 6-kb transcript is present only in CML cell lines containing a normal abl allele and that the apparent inactivation of the nested Pa promoter is associated with allele-specific methylation. Furthermore, we have noticed that the Pa promoter is contained within a CpG island and undergoes progressive de novo methylation in the course of the disease. This is attested to by the fact that DNA samples from CML patients that are methylation-free at the time of diagnosis invariably become methylated in advanced CML. Since tumor progression in CML cannot always be inferred from the clinical presentation, assessment of de novo CpG methylation may prove to be of critical value in management of the disease. It could herald blastic transformation at a stage when bone marrow transplantation, the only potentially curative therapeutic procedure in CML, is still effective.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahuja H., Bar-Eli M., Advani S. H., Benchimol S., Cline M. J. Alterations in the p53 gene and the clonal evolution of the blast crisis of chronic myelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6783–6787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan N. C. Therapeutic options in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Blood Rev. 1989 Mar;3(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0268-960x(89)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antequera F., Boyes J., Bird A. High levels of de novo methylation and altered chromatin structure at CpG islands in cell lines. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Neriah Y., Bernards A., Paskind M., Daley G. Q., Baltimore D. Alternative 5' exons in c-abl mRNA. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Neriah Y., Daley G. Q., Mes-Masson A. M., Witte O. N., Baltimore D. The chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific P210 protein is the product of the bcr/abl hybrid gene. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):212–214. doi: 10.1126/science.3460176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards A., Rubin C. M., Westbrook C. A., Paskind M., Baltimore D. The first intron in the human c-abl gene is at least 200 kilobases long and is a target for translocations in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3231–3236. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. Genomic imprinting: imprints on islands. Curr Biol. 1993 May 1;3(5):275–277. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90177-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Groudine M. T. Rearrangement and amplification of c-abl sequences in the human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K-562. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4813–4817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley G. Q., Ben-Neriah Y. Implicating the bcr/abl gene in the pathogenesis of Philadelphia chromosome-positive human leukemia. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;57:151–184. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60998-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Griffin C. A., ar-Rushdi A., Valtieri M., Hoxie J., Finan J., Emanuel B. S., Rovera G., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Heterogeneity of chromosome 22 breakpoint in Philadelphia-positive (Ph+) acute lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1807–1811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. Hypomethylation distinguishes genes of some human cancers from their normal counterparts. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):89–92. doi: 10.1038/301089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas O. A., Argyriou-Tirita A., Lion T. Parental origin of chromosomes involved in the translocation t(9;22). Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):414–416. doi: 10.1038/359414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Stephenson J. R., Groffen J., Hansen P. F., de Klein A., Bartram C. R., Grosveld G. Localization of the c-ab1 oncogene adjacent to a translocation break point in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):239–242. doi: 10.1038/306239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P., Baltimore D. N-terminal mutations activate the leukemogenic potential of the myristoylated form of c-abl. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):449–456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X. Y., Trujillo J. M., Dao D., Liang J. C. Studies of BCR and ABL gene rearrangements in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients by conventional and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis using gel inserts. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989 Oct 15;42(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(89)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantarjian H. M., Smith T. L., McCredie K. B., Keating M. J., Walters R. S., Talpaz M., Hester J. P., Bligham G., Gehan E., Freireich E. J. Chronic myelogenous leukemia: a multivariate analysis of the associations of patient characteristics and therapy with survival. Blood. 1985 Dec;66(6):1326–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Beard C., Jaenisch R. Role for DNA methylation in genomic imprinting. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):362–365. doi: 10.1038/366362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu E., Hjelle B., Bishop J. M. Transforming genes in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1952–1956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock L. F., Takagi N., Martin G. R. Methylation of the Hprt gene on the inactive X occurs after chromosome inactivation. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills K. I., Sproul A. M., Burnett A. K. Methylation of the major breakpoint cluster region (M-bcr) in Philadelphia-positive CML. Leukemia. 1993 May;7(5):707–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelkin B. D., Przepiorka D., Burke P. J., Thomas E. D., Baylin S. B. Abnormal methylation of the calcitonin gene marks progression of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1991 Jun 1;77(11):2431–2434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Cedar H. DNA methylation and genomic imprinting. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):473–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renshaw M. W., Capozza M. A., Wang J. Y. Differential expression of type-specific c-abl mRNAs in mouse tissues and cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4547–4551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggins G. J., Zhang F., Warren S. T. Lack of imprinting of BCR. Nat Genet. 1994 Mar;6(3):226–226. doi: 10.1038/ng0394-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P., Beran M., Shtalrid M., Andersson B., Talpaz M., Blick M. Alternative 5' end of the bcr-abl transcript in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):93–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Recurring chromosome abnormalities in leukemia and lymphoma. Semin Hematol. 1990 Apr;27(2):122–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Toguchida J., Ohtani N., Yandell D. W., Rapaport J. M., Dryja T. P. Allele-specific hypermethylation of the retinoblastoma tumor-suppressor gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 May;48(5):880–888. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers C. L., McLaughlin J., Goga A., Havlik M., Witte O. The nuclear tyrosine kinase c-Abl negatively regulates cell growth. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P. L., Stall A. M., Hardin J. D., Bowdish K. S., Humaran T., Boast S., Harbison M. L., Robertson E. J., Goff S. P. Mice homozygous for the ablm1 mutation show poor viability and depletion of selected B and T cell populations. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1165–1175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90012-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segel G. B., Simon W., Lichtman M. A. Variables influencing the timing of marrow transplantation in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1986 Nov;68(5):1055–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtivelman E., Lifshitz B., Gale R. P., Canaani E. Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):550–554. doi: 10.1038/315550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtivelman E., Lifshitz B., Gale R. P., Roe B. A., Canaani E. Alternative splicing of RNAs transcribed from the human abl gene and from the bcr-abl fused gene. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90450-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöger R., Kubicka P., Liu C. G., Kafri T., Razin A., Cedar H., Barlow D. P. Maternal-specific methylation of the imprinted mouse Igf2r locus identifies the expressed locus as carrying the imprinting signal. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90160-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Moulding C., Battey J., Murphy W., Vasicek T., Lenoir G. M., Leder P. Activation and somatic mutation of the translocated c-myc gene in burkitt lymphoma cells. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tybulewicz V. L., Crawford C. E., Jackson P. K., Bronson R. T., Mulligan R. C. Neonatal lethality and lymphopenia in mice with a homozygous disruption of the c-abl proto-oncogene. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90011-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook C. A., Rubin C. M., Carrino J. J., Le Beau M. M., Bernards A., Rowley J. D. Long-range mapping of the Philadelphia chromosome by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):697–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]