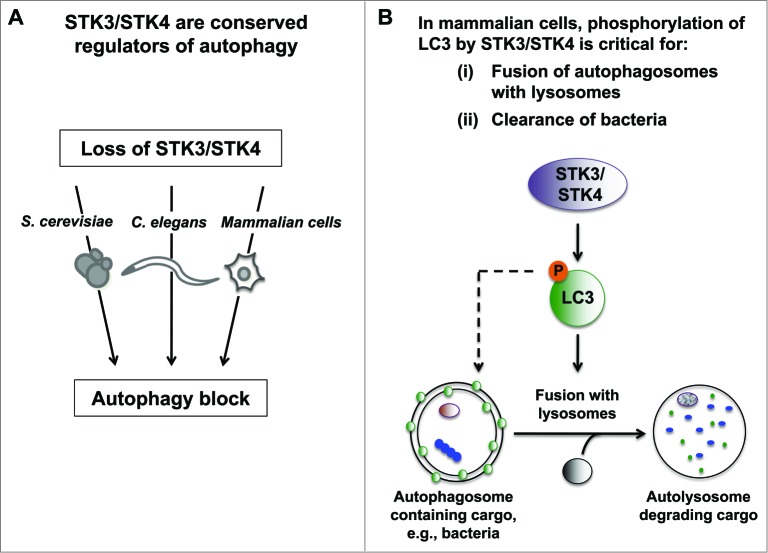
Figure 1.
Novel role for Hippo kinases STK3/STK4 in regulation of autophagy. (A) Loss of STK3/STK4 kinase orthologs results in an autophagy block in S. cerevisiae, C. elegans and in mammalian cells (i.e., mouse embryo fibroblasts and myoblasts). (B) STK3/STK4 directly phosphorylate LC3B at amino acid Thr50 in mammalian cells. This phosphorylation event plays an important role in mediating fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes, and is important for mouse embryo fibroblasts to clear intracellular bacteria. Since Thr50 is not conserved in C. elegans and S. cerevisiae, we propose that alternate sites and/or alternate substrates are utilized by STK3/STK4 to regulate autophagy in these organisms.