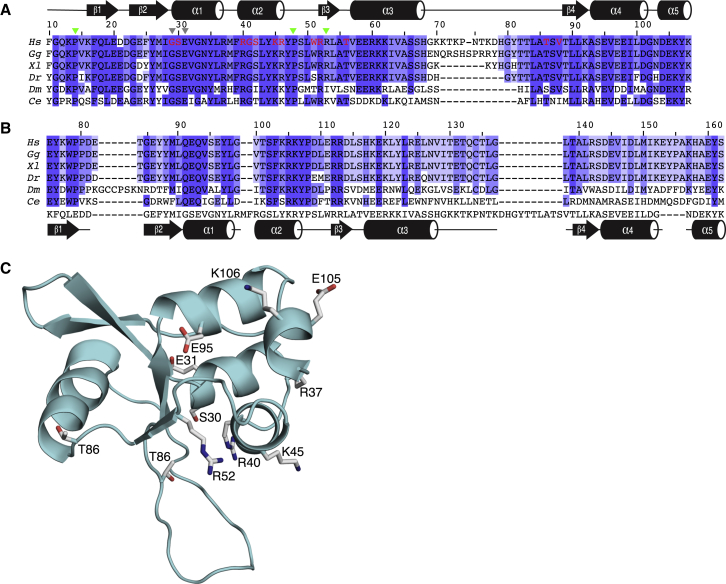
Figure 2.
Sequence Conservation in the INI1 and BAF45a Domains
(A) Sequence alignment of the N-terminal winged helix domains of INI1 homologs from representative species. The secondary structure of the domain is shown above the sequences, with sheets and helices indicated by arrows and cylinders. Species abbreviations: Hs, Homo sapiens; Gg, Gallus gallus; Xl, Xenopus laevis; Dr, Danio rerio; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans. The numbering is for the human protein. Residues mutated in familial schwannomatosis are indicated by green triangles. Residues mutated in sporadic disease are indicated with gray triangles. Residues that undergo large changes in chemical shift upon DNA binding are colored red.
(B) Structure-based alignment of the homologous domain in BAF45a proteins from the same species. The sequence and secondary structure of the INI1 domain are shown below the alignment.
(C) Cartoon representation of the INI1 N-terminal domain, with the side chains of highly conserved residues shown as sticks.