Abstract
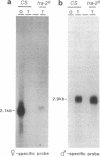
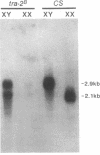
The Drosophila exuperantia (exu) gene encodes overlapping sex-specific, germline-dependent mRNAs. In this work, the structural differences between these sex-specific exu mRNAs were determined by sequence analysis of 9 ovary and 10 testis cDNAs. The transformer 2 (tra-2) gene functions in sex determination of female somatic cells through its role in regulating female-specific splicing of doublesex (dsx) RNA. We report here that tra-2 is required in male germ cells for efficient male-specific processing of exu RNA; in the absence of tra-2, X/Y males produce a new mRNA which is processed at its 3' end so that it contains sequences normally specific to the female 3' untranslated region. Although the processing event that requires tra-2 occurs in an untranslated region of the exu transcript, the isolation and characterization of a male-specific exu allele which deletes male 3' untranslated sequence indicate that this processing is biologically significant.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein H., Gorman M., Nöthiger R. The sex-determining gene tra-2 of Drosophila encodes a putative RNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amrein H., Maniatis T., Nöthiger R. Alternatively spliced transcripts of the sex-determining gene tra-2 of Drosophila encode functional proteins of different size. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3619–3629. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Ridge K. A. Sex and the single cell. I. On the action of major loci affecting sex determination in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1980 Feb;94(2):383–423. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S. Sex in flies: the splice of life. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):521–524. doi: 10.1038/340521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Wolfner M. F. A molecular analysis of doublesex, a bifunctional gene that controls both male and female sexual differentiation in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):477–489. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belote J. M., Baker B. S. Sex determination in Drosophila melanogaster: analysis of transformer-2, a sex-transforming locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belote J. M., Baker B. S. The dual functions of a sex determination gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1983 Feb;95(2):512–517. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belote J. M., Handler A. M., Wolfner M. F., Livak K. J., Baker B. S. Sex-specific regulation of yolk protein gene expression in Drosophila. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90148-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berleth T., Burri M., Thoma G., Bopp D., Richstein S., Frigerio G., Noll M., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The role of localization of bicoid RNA in organizing the anterior pattern of the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1749–1756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Chou T. B., Mims I., Zachar Z. On/off regulation of gene expression at the level of splicing. Trends Genet. 1988 May;4(5):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Baker B. S. Drosophila doublesex gene controls somatic sexual differentiation by producing alternatively spliced mRNAs encoding related sex-specific polypeptides. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):997–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90633-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goralski T. J., Edström J. E., Baker B. S. The sex determination locus transformer-2 of Drosophila encodes a polypeptide with similarity to RNA binding proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1011–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90634-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelrigg T., Watkins W. S., Marcey D., Tu C., Karow M., Lin X. R. The exuperantia gene is required for Drosophila spermatogenesis as well as anteroposterior polarity of the developing oocyte, and encodes overlapping sex-specific transcripts. Genetics. 1990 Nov;126(3):607–617. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley M. L., Maniatis T. Sex-specific splicing and polyadenylation of dsx pre-mRNA requires a sequence that binds specifically to tra-2 protein in vitro. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):579–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90090-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshijima K., Inoue K., Higuchi I., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Control of doublesex alternative splicing by transformer and transformer-2 in Drosophila. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):833–836. doi: 10.1126/science.1902987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Luk S. K., Kilpatrick M. Protein encoded by the exuperantia gene is concentrated at sites of bicoid mRNA accumulation in Drosophila nurse cells but not in oocytes or embryos. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2455–2466. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T. Mechanisms of alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):33–34. doi: 10.1126/science.1824726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcey D., Watkins W. S., Hazelrigg T. The temporal and spatial distribution pattern of maternal exuperantia protein: evidence for a role in establishment but not maintenance of bicoid mRNA localization. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4259–4266. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattox W., Baker B. S. Autoregulation of the splicing of transcripts from the transformer-2 gene of Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):786–796. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattox W., Palmer M. J., Baker B. S. Alternative splicing of the sex determination gene transformer-2 is sex-specific in the germ line but not in the soma. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):789–805. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattox W., Ryner L., Baker B. S. Autoregulation and multifunctionality among trans-acting factors that regulate alternative pre-mRNA processing. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19023–19026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown M., Belote J. M., Boggs R. T. Ectopic expression of the female transformer gene product leads to female differentiation of chromosomally male Drosophila. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):887–895. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90369-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagoshi R. N., Baker B. S. Regulation of sex-specific RNA splicing at the Drosophila doublesex gene: cis-acting mutations in exon sequences alter sex-specific RNA splicing patterns. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):89–97. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagoshi R. N., McKeown M., Burtis K. C., Belote J. M., Baker B. S. The control of alternative splicing at genes regulating sexual differentiation in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90384-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nöthiger R., Jonglez M., Leuthold M., Meier-Gerschwiler P., Weber T. Sex determination in the germ line of Drosophila depends on genetic signals and inductive somatic factors. Development. 1989 Nov;107(3):505–518. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.3.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota T., Fukunaga A., Kawabe M., Oishi K. Interactions between sex-transformation mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Hemolymph vitellogenins and gonad morphology. Genetics. 1981 Nov-Dec;99(3-4):429–441. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.3-4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryner L. C., Baker B. S. Regulation of doublesex pre-mRNA processing occurs by 3'-splice site activation. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2071–2085. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schupbach T., Wieschaus E. Germline autonomy of maternal-effect mutations altering the embryonic body pattern of Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1986 Feb;113(2):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüpbach T. Autosomal mutations that interfere with sex determination in somatic cells of Drosophila have no direct effect on the germline. Dev Biol. 1982 Jan;89(1):117–127. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90300-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüpbach T., Wieschaus E. Female sterile mutations on the second chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Maternal effect mutations. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):101–117. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:527–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Driever W., Berleth T., Richstein S., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Multiple steps in the localization of bicoid RNA to the anterior pole of the Drosophila oocyte. Development. 1989;107 (Suppl):13–19. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.Supplement.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]