Full text
PDF
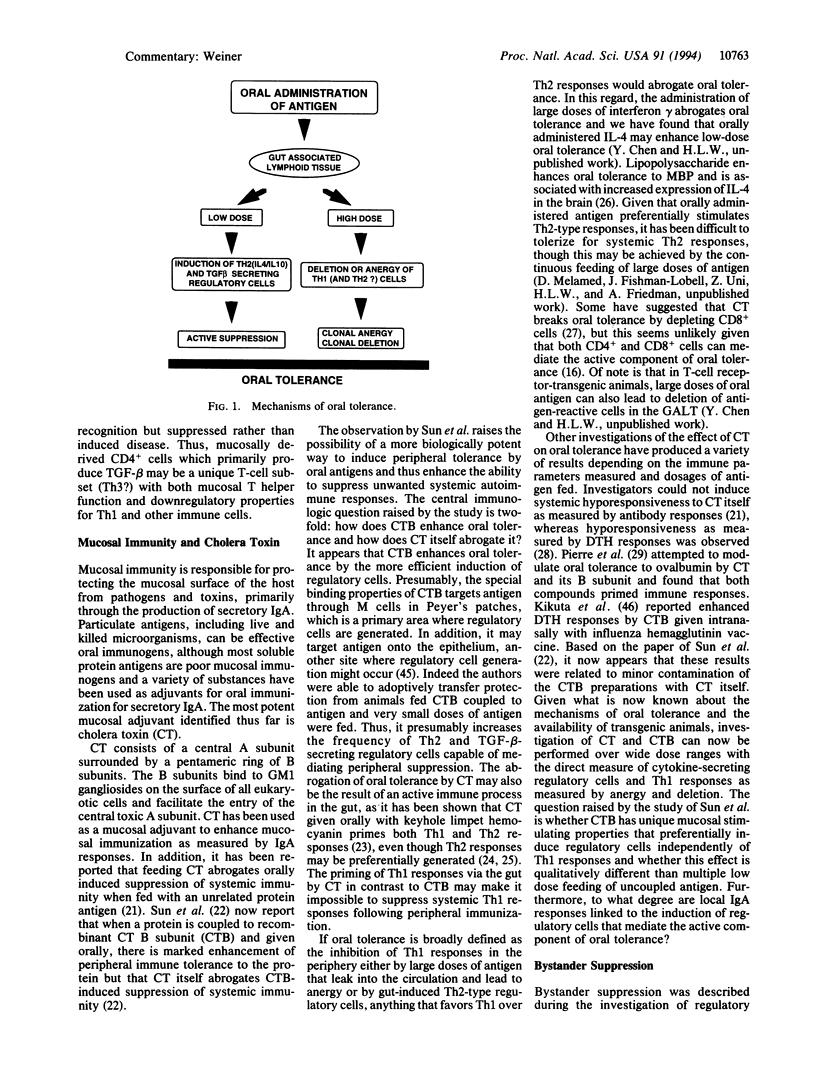


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandtzaeg P. Overview of the mucosal immune system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;146:13–25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74529-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brod S. A., al-Sabbagh A., Sobel R. A., Hafler D. A., Weiner H. L. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral administration of myelin antigens: IV. Suppression of chronic relapsing disease in the Lewis rat and strain 13 guinea pig. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jun;29(6):615–622. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce M. G., Ferguson A. The influence of intestinal processing on the immunogenicity and molecular size of absorbed, circulating ovalbumin in mice. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):295–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Kuchroo V. K., Inobe J., Hafler D. A., Weiner H. L. Regulatory T cell clones induced by oral tolerance: suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Science. 1994 Aug 26;265(5176):1237–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.7520605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin Y. H., Cai J. P., Xu X. M. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 and IL-4 regulate the adhesiveness of Peyer's patch high endothelial venule cells for lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 15;148(4):1106–1112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. H., Tuohy V. K., Raine C. S. Development of reactivity to new myelin antigens during chronic relapsing autoimmune demyelination. Cell Immunol. 1993 Feb;146(2):261–269. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daynes R. A., Araneo B. A., Dowell T. A., Huang K., Dudley D. Regulation of murine lymphokine production in vivo. III. The lymphoid tissue microenvironment exerts regulatory influences over T helper cell function. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):979–996. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Cholera toxin feeding did not induce oral tolerance in mice and abrogated oral tolerance to an unrelated protein antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2892–2897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Solomon S. Activation of cholera toxin-specific T cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3711–3716. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3711-3716.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A., Weiner H. L. Induction of anergy or active suppression following oral tolerance is determined by antigen dosage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6688–6692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregerson D. S., Obritsch W. F., Donoso L. A. Oral tolerance in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Distinct mechanisms of resistance are induced by low dose vs high dose feeding protocols. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5751–5761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. W., Sayegh M. H., Kwok C. A., Weiner H. L., Carpenter C. B. Oral, but not intravenous, alloantigen prevents accelerated allograft rejection by selective intragraft Th2 cell activation. Transplantation. 1993 May;55(5):1112–1118. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199305000-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C. Islet cell antigens in insulin-dependent diabetes: Pandora's box revisited. Immunol Today. 1992 Sep;13(9):348–352. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90170-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby S., Jensenius J. C., Svehag S. E. Passage of undegraded dietary antigen into the blood of healthy adults. Further characterization of the kinetics of uptake and the size distribution of the antigen. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Oct;24(4):447–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby S., Mestecky J., Moldoveanu Z., Holland S., Elson C. O. Oral tolerance in humans. T cell but not B cell tolerance after antigen feeding. J Immunol. 1994 May 1;152(9):4663–4670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörnquist E., Lycke N. Cholera toxin adjuvant greatly promotes antigen priming of T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Sep;23(9):2136–2143. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Clare-Salzler M., Tian J., Forsthuber T., Ting G. S., Robinson P., Atkinson M. A., Sercarz E. E., Tobin A. J., Lehmann P. V. Spontaneous loss of T-cell tolerance to glutamic acid decarboxylase in murine insulin-dependent diabetes. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):69–72. doi: 10.1038/366069a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. A., Ferguson A. The immunological consequences of feeding cholera toxin. I. Feeding cholera toxin suppresses the induction of systemic delayed-type hypersensitivity but not humoral immunity. Immunology. 1989 Mar;66(3):410–415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlero de Rosbo N., Milo R., Lees M. B., Burger D., Bernard C. C., Ben-Nun A. Reactivity to myelin antigens in multiple sclerosis. Peripheral blood lymphocytes respond predominantly to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2602–2608. doi: 10.1172/JCI116875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury S. J., Hancock W. W., Weiner H. L. Oral tolerance to myelin basic protein and natural recovery from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis are associated with downregulation of inflammatory cytokines and differential upregulation of transforming growth factor beta, interleukin 4, and prostaglandin E expression in the brain. J Exp Med. 1992 Nov 1;176(5):1355–1364. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.5.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuta K., Kurata H., Nagamine T., Aizawa C., Ueno Y., Kurata T., Tamura S. Enhancement of DTH response by cholera toxin B subunit inoculated intranasally together with influenza HA vaccine. Microbiol Immunol. 1990;34(3):337–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1990.tb01014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim P. H., Kagnoff M. F. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 is a costimulator for IgA production. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3411–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann P. V., Forsthuber T., Miller A., Sercarz E. E. Spreading of T-cell autoimmunity to cryptic determinants of an autoantigen. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):155–157. doi: 10.1038/358155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowney E. D. Immunologic unresponsiveness to a contact sensitizer in man. J Invest Dermatol. 1968 Dec;51(6):411–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Shlien R. Evidence for function of Ia molecules on gut epithelial cells in man. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1471–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarron R. M., Fallis R. J., McFarlin D. E. Alterations in T cell antigen specificity and class II restriction during the course of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Sep-Oct;29(1-3):73–79. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90149-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Lider O., Weiner H. L. Antigen-driven bystander suppression after oral administration of antigens. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):791–798. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Lider O., al-Sabbagh A., Weiner H. L. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral administration of myelin basic protein. V. Hierarchy of suppression by myelin basic protein from different species. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Aug;39(3):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90258-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierre P., Denis O., Bazin H., Mbongolo Mbella E., Vaerman J. P. Modulation of oral tolerance to ovalbumin by cholera toxin and its B subunit. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Dec;22(12):3179–3182. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos L. M., al-Sabbagh A., Londono A., Weiner H. L. Oral tolerance to myelin basic protein induces regulatory TGF-beta-secreting T cells in Peyer's patches of SJL mice. Cell Immunol. 1994 Sep;157(2):439–447. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. B., Holmgren J., Czerkinsky C. Cholera toxin B subunit: an efficient transmucosal carrier-delivery system for induction of peripheral immunological tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10795–10799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisch R., Yang X. D., Singer S. M., Liblau R. S., Fugger L., McDevitt H. O. Immune response to glutamic acid decarboxylase correlates with insulitis in non-obese diabetic mice. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):72–75. doi: 10.1038/366072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Dynesius-Trentham R. A., Orav E. J., Combitchi D., Lorenzo C., Sewell K. L., Hafler D. A., Weiner H. L. Effects of oral administration of type II collagen on rheumatoid arthritis. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1727–1730. doi: 10.1126/science.8378772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Friedman A., Miller A., Khoury S. J., al-Sabbagh A., Santos L., Sayegh M., Nussenblatt R. B., Trentham D. E., Hafler D. A. Oral tolerance: immunologic mechanisms and treatment of animal and human organ-specific autoimmune diseases by oral administration of autoantigens. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:809–837. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Mackin G. A., Matsui M., Orav E. J., Khoury S. J., Dawson D. M., Hafler D. A. Double-blind pilot trial of oral tolerization with myelin antigens in multiple sclerosis. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1321–1324. doi: 10.1126/science.7680493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitacre C. C., Gienapp I. E., Orosz C. G., Bitar D. M. Oral tolerance in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. III. Evidence for clonal anergy. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2155–2163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. D., Bailey M., Williams N. A., Stokes C. R. The in vitro production of cytokines by mucosal lymphocytes immunized by oral administration of keyhole limpet hemocyanin using cholera toxin as an adjuvant. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2333–2339. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu-Amano J., Kiyono H., Jackson R. J., Staats H. F., Fujihashi K., Burrows P. D., Elson C. O., Pillai S., McGhee J. R. Helper T cell subsets for immunoglobulin A responses: oral immunization with tetanus toxoid and cholera toxin as adjuvant selectively induces Th2 cells in mucosa associated tissues. J Exp Med. 1993 Oct 1;178(4):1309–1320. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.4.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Markovic-Plese S., Lacet B., Raus J., Weiner H. L., Hafler D. A. Increased frequency of interleukin 2-responsive T cells specific for myelin basic protein and proteolipid protein in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):973–984. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. Y., Lee C. S., Lider O., Weiner H. L. Suppression of adjuvant arthritis in Lewis rats by oral administration of type II collagen. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2489–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Sabbagh A., Miller A., Santos L. M., Weiner H. L. Antigen-driven tissue-specific suppression following oral tolerance: orally administered myelin basic protein suppresses proteolipid protein-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the SJL mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Sep;24(9):2104–2109. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


