Abstract
Over the past two decades the pharmaceutical industry has been driven by the biological sciences. The discovery and description of the biological mechanisms that underlie disease states accompanied by an unraveling of these mechanisms has provided drug, and more recently biotechnological, companies with a barrage of new therapeutic targets. Paradoxically, as a result of such biological and biochemical advances, new sources of drug leads are in short supply. Considerable efforts in trying to create potential drug candidates has led to the parturition of combinatorial chemical libraries. In this review I will examine some of the main technologies for generating and deducing active components from combinatorial libraries that have been segregated into two schools of thought: (i) the creation and decoding of combinatorial libraries by so-called tagged methodologies, and (ii) the production and deconvolution of chemical libraries by untagged protocols.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake J., Litzi-Davis L. Evaluation of peptide libraries: an iterative strategy to analyze the reactivity of peptide mixtures with antibodies. Bioconjug Chem. 1992 Nov-Dec;3(6):510–513. doi: 10.1021/bc00018a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho C. Y., Moran E. J., Cherry S. R., Stephans J. C., Fodor S. P., Adams C. L., Sundaram A., Jacobs J. W., Schultz P. G. An unnatural biopolymer. Science. 1993 Sep 3;261(5126):1303–1305. doi: 10.1126/science.7689747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull M. G., Miller J. F., Schatz P. J. Screening for receptor ligands using large libraries of peptides linked to the C terminus of the lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cwirla S. E., Peters E. A., Barrett R. W., Dower W. J. Peptides on phage: a vast library of peptides for identifying ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6378–6382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt S. H., Kiely J. S., Stankovic C. J., Schroeder M. C., Cody D. M., Pavia M. R. "Diversomers": an approach to nonpeptide, nonoligomeric chemical diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6909–6913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin J. J., Panganiban L. C., Devlin P. E. Random peptide libraries: a source of specific protein binding molecules. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.2143033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley C. T., Houghten R. A. The use of positional scanning synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for the rapid determination of opioid receptor ligands. Life Sci. 1993;52(18):1509–1517. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90113-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker D. J., Vickers T. A., Hanecak R., Driver V., Anderson K. Rational screening of oligonucleotide combinatorial libraries for drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1853–1856. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
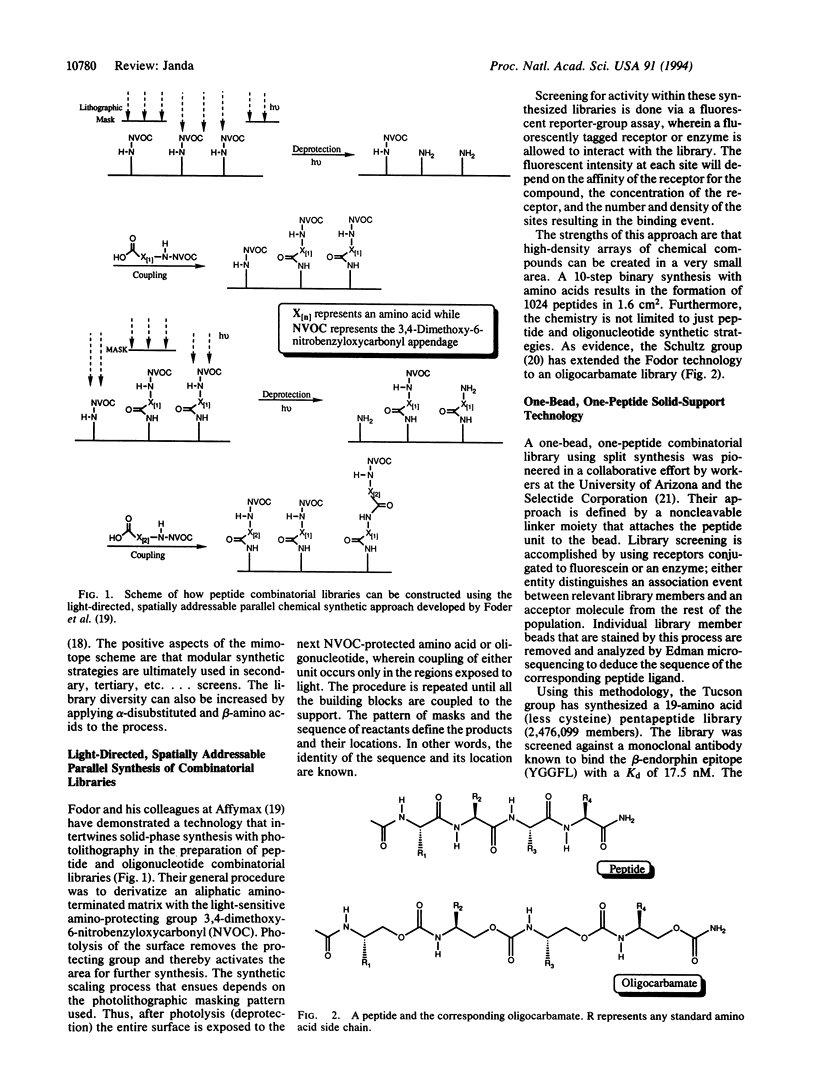
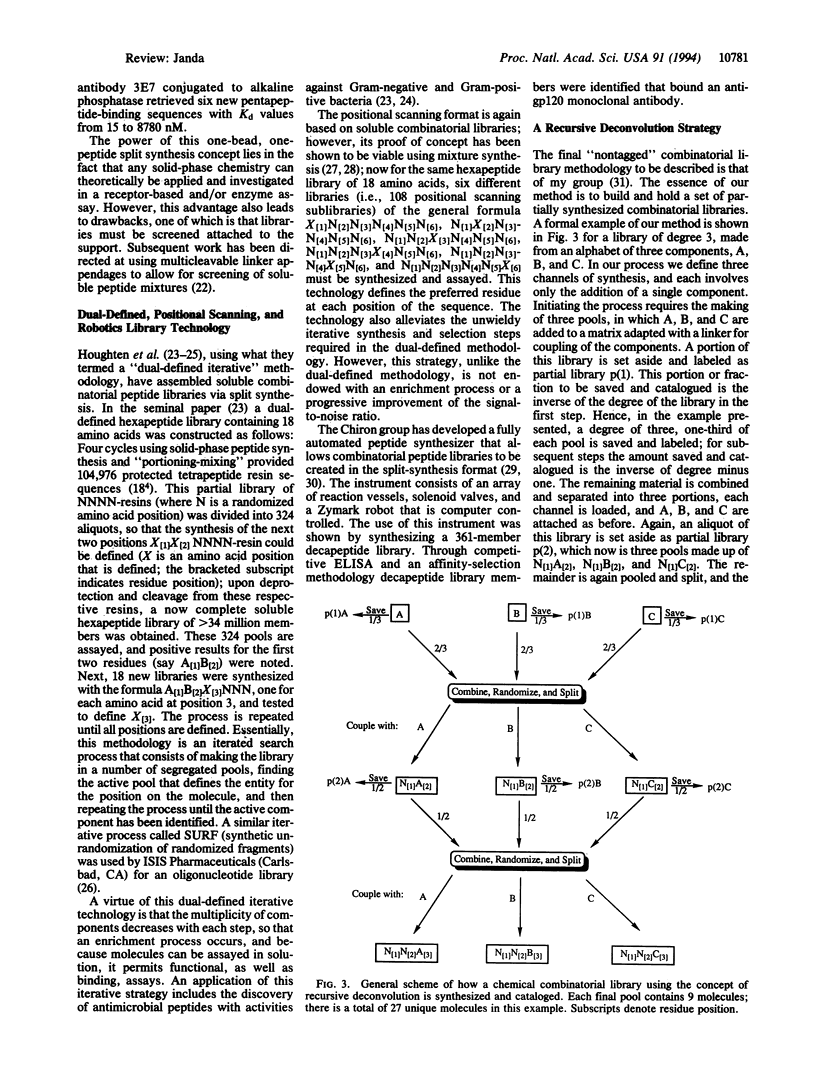
- Fodor S. P., Read J. L., Pirrung M. C., Stryer L., Lu A. T., Solas D. Light-directed, spatially addressable parallel chemical synthesis. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):767–773. doi: 10.1126/science.1990438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furka A., Sebestyén F., Asgedom M., Dibó G. General method for rapid synthesis of multicomponent peptide mixtures. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1991 Jun;37(6):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1991.tb00765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallop M. A., Barrett R. W., Dower W. J., Fodor S. P., Gordon E. M. Applications of combinatorial technologies to drug discovery. 1. Background and peptide combinatorial libraries. J Med Chem. 1994 Apr 29;37(9):1233–1251. doi: 10.1021/jm00035a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J. A priori delineation of a peptide which mimics a discontinuous antigenic determinant. Mol Immunol. 1986 Jul;23(7):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Tribbick G., Schoofs P. G. Strategies for epitope analysis using peptide synthesis. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Sep 24;102(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanft J. R., Mason E. T., Landsman A. S., Kashuk K. B. A new radiographic classification for hallux limitus. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1993 Jul-Aug;32(4):397–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson J. Pharmaceutical screening: from off-the-wall to off-the-shelf. The many routes to successful drug discovery. Biotechnology (N Y) 1993 Jun;11(6):683–688. doi: 10.1038/nbt0693-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
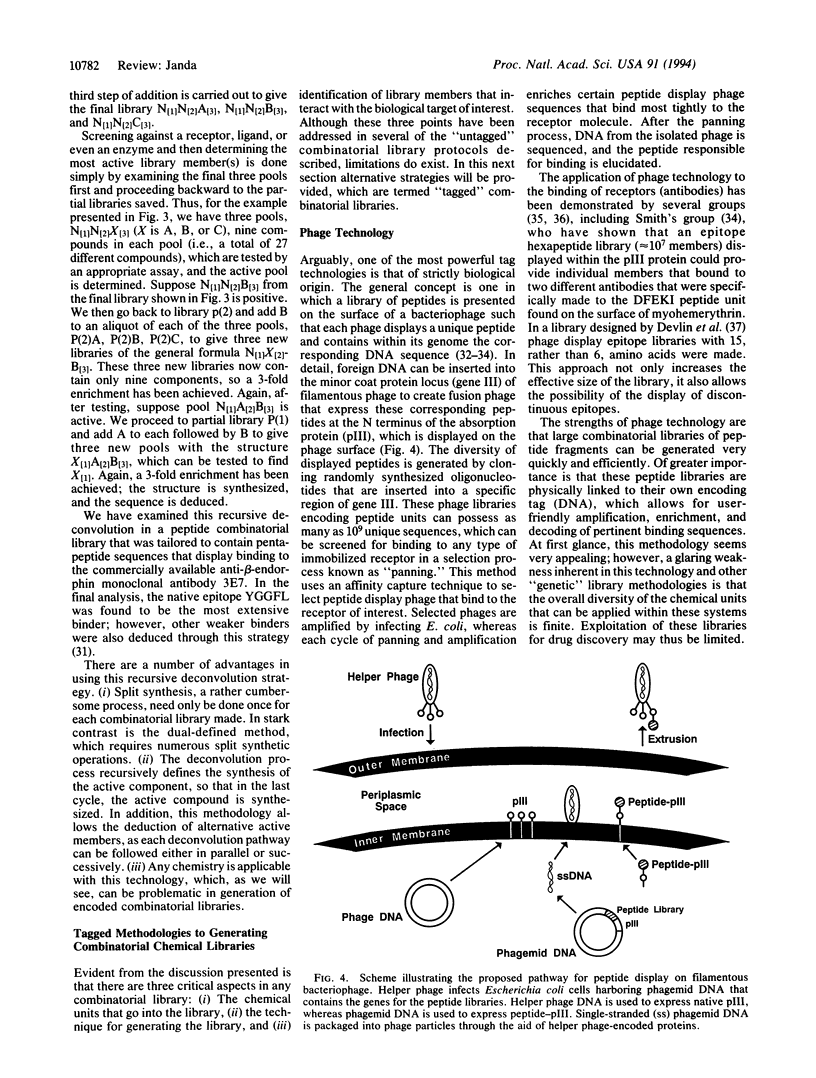
- Houghten R. A., Appel J. R., Blondelle S. E., Cuervo J. H., Dooley C. T., Pinilla C. The use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for the identification of bioactive peptides. Biotechniques. 1992 Sep;13(3):412–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Pinilla C., Blondelle S. E., Appel J. R., Dooley C. T., Cuervo J. H. Generation and use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for basic research and drug discovery. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):84–86. doi: 10.1038/354084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Salmon S. E., Hersh E. M., Hruby V. J., Kazmierski W. M., Knapp R. J. A new type of synthetic peptide library for identifying ligand-binding activity. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):82–84. doi: 10.1038/354082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebl M., Pátek M., Kocis P., Krchnák V., Hruby V. J., Salmon S. E., Lam K. S. Multiple release of equimolar amounts of peptides from a polymeric carrier using orthogonal linkage-cleavage chemistry. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1993 Feb;41(2):201–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1993.tb00132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon P. E., Raventos H., Lynch E., Morrow J., King M. C. The gene for an inherited form of deafness maps to chromosome 5q31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5181–5184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniszyn J., Jr, Hartsuck J. A., Tang J. Mode of inhibition of acid proteases by pepstatin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7088–7094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall G. R. Structure--activity relations of antagonists of the renin--angiotensin system. Fed Proc. 1976 Nov;35(13):2494–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needels M. C., Jones D. G., Tate E. H., Heinkel G. L., Kochersperger L. M., Dower W. J., Barrett R. W., Gallop M. A. Generation and screening of an oligonucleotide-encoded synthetic peptide library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10700–10704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaiev V., Stierandová A., Krchnák V., Seligmann B., Lam K. S., Salmon S. E., Lebl M. Peptide-encoding for structure determination of nonsequenceable polymers within libraries synthesized and tested on solid-phase supports. Pept Res. 1993 May-Jun;6(3):161–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlmeyer M. H., Swanson R. N., Dillard L. W., Reader J. C., Asouline G., Kobayashi R., Wigler M., Still W. C. Complex synthetic chemical libraries indexed with molecular tags. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):10922–10926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondetti M. A., Rubin B., Cushman D. W. Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):441–444. doi: 10.1126/science.191908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmley S. F., Smith G. P. Antibody-selectable filamentous fd phage vectors: affinity purification of target genes. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90495-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchett A. A., Harris E., Tristram E. W., Wyvratt M. J., Wu M. T., Taub D., Peterson E. R., Ikeler T. J., ten Broeke J., Payne L. G. A new class of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):280–283. doi: 10.1038/288280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinilla C., Appel J. R., Blanc P., Houghten R. A. Rapid identification of high affinity peptide ligands using positional scanning synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries. Biotechniques. 1992 Dec;13(6):901–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H., Sun E., Singh J. Synthesis of dideoxy-pepstatin. Mechanism of inhibition of porcine pepsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):762–767. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90367-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J. Use of peptide libraries to map the substrate specificity of a peptide-modifying enzyme: a 13 residue consensus peptide specifies biotinylation in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology (N Y) 1993 Oct;11(10):1138–1143. doi: 10.1038/nbt1093-1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. K., Smith G. P. Searching for peptide ligands with an epitope library. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):386–390. doi: 10.1126/science.1696028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.4001944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann R. N., Kerr J. M., Siani M. A., Banville S. C., Santi D. V. Identification of highest-affinity ligands by affinity selection from equimolar peptide mixtures generated by robotic synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4505–4509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]