Abstract
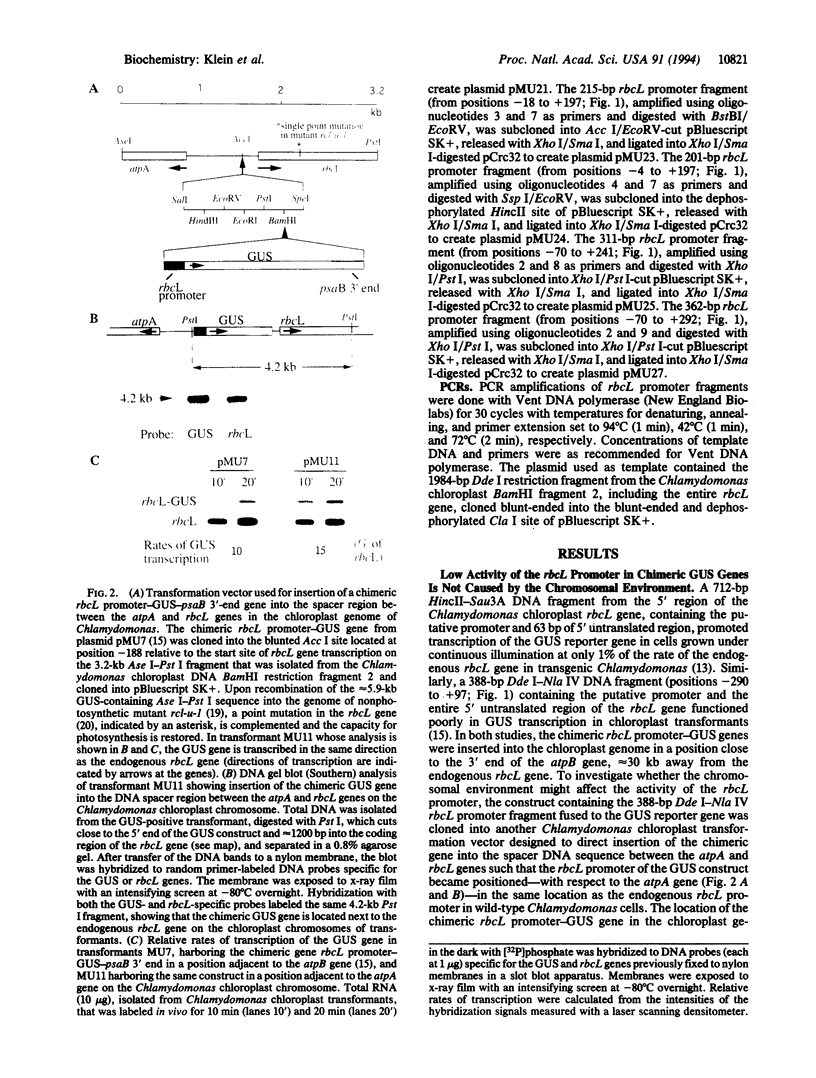
The chloroplast gene rbcL encodes the large subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase. In Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, this gene is transcribed more actively than any other protein-encoding chloroplast gene studied to date. To delineate the rbcL gene promoter, chimeric reporter genes containing fragments of the 5' region of the rbcL gene fused to the coding sequence of the bacterial uidA gene, encoding beta-glucuronidase, were stably introduced into the chloroplast genome of Chlamydomonas by microprojectile bombardment. The relative transcription rates of endogenous and introduced genes were determined in transgenic cell lines in vivo. The basic rbcL promoter is located within the region of the gene extending from positions -18 to +63, taking position +1 as the site of initiation of transcription. A chimeric reporter gene containing only the basic promoter is transcribed only 1-15% as actively as the endogenous rbcL gene, depending on the conditions under which cells are grown and tested. However, a chimeric gene containing rbcL sequences extending to position +170 or beyond is transcribed at about the same rate as the endogenous gene. Deletion of the sequence between positions +170 and +126, well within the protein-encoding region, reduces the rate of transcription to that of reporter genes with the basic promoter alone.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker E. J., Schloss J. A., Rosenbaum J. L. Rapid changes in tubulin RNA synthesis and stability induced by deflagellation in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2074–2081. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers A. D., Ellmore G. S., Klein U., Bogorad L. Transcriptional analysis of endogenous and foreign genes in chloroplast transformants of Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 1990 Nov;2(11):1059–1070. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.11.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers A. D., Klein U., Ellmore G. S., Bogorad L. Functional in vivo analyses of the 3' flanking sequences of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast rbcL and psaB genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Apr;238(3):339–349. doi: 10.1007/BF00291992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas. Methods Enzymol. 1993;217:510–536. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)17087-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D., Gatenby A. A. Mutational analysis of the maize chloroplast ATPase-beta subunit gene promoter: the isolation of promoter mutants in E. coli and their characterization in a chloroplast in vitro transcription system. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3641–3648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04129.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Does HIV-1 Tat induce a change in viral initiation rights? Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90126-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D., Mets L. First DNA sequence of a chloroplast mutation: a missense alteration in the ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase large subunit gene. Plasmid. 1983 May;9(3):321–324. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Sequence of the chloroplast DNA region of Chlamydomonas reinhardii containing the gene of the large subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase and parts of its flanking genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):775–793. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisermann A., Tiller K., Link G. In vitro transcription and DNA binding characteristics of chloroplast and etioplast extracts from mustard (Sinapis alba) indicate differential usage of the psbA promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3981–3987. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M. Transgenic expression of aminoglycoside adenine transferase in the chloroplast: a selectable marker of site-directed transformation of chlamydomonas. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4083–4089. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Elsner-Menzel C., Latshaw S., Narita J. O., Schaffer M. A., Zurawski G. A subpopulation of spinach chloroplast tRNA genes does not require upstream promoter elements for transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7541–7556. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Zurawski G. Analysis of promoter regions for the spinach chloroplast rbcL, atpB and psbA genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3375–3383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Zurawski G. Identification and mutational analysis of the promoter for a spinach chloroplast transfer RNA gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1637–1644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03831.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn D. Expression of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast tRNA(Glu) gene in a homologous in vitro transcription system is independent of upstream promoter elements. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Nov 1;298(2):505–513. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90442-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A. Tat and the HIV-1 promoter. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):461–468. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90012-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein U., De Camp J. D., Bogorad L. Two types of chloroplast gene promoters in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3453–3457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link G. DNA sequence requirements for the accurate transcription of a protein-coding plastid gene in a plastid in vitro system from mustard (Sinapis alba L.). EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1697–1704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Siegele D. A., Cowing D. W., Gross C. A. The regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:355–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvador M. L., Klein U., Bogorad L. 5' sequences are important positive and negative determinants of the longevity of Chlamydomonas chloroplast gene transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1556–1560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvador M. L., Klein U., Bogorad L. Light-regulated and endogenous fluctuations of chloroplast transcript levels in Chlamydomonas. Regulation by transcription and RNA degradation. Plant J. 1993 Feb;3(2):213–219. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.t01-13-00999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz A. A., Krebbers E. T., Schwarz Z., Gubbins E. J., Bogorad L. Nucleotide sequences of five maize chloroplast transfer RNA genes and their flanking regions. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5503–5511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun E., Wu B. W., Tewari K. K. In vitro analysis of the pea chloroplast 16S rRNA gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5650–5659. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svab Z., Hajdukiewicz P., Maliga P. Stable transformation of plastids in higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8526–8530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker R. L., Williams K. P., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Transcriptional activation by a DNA-tracking protein: structural consequences of enhancement at the T4 late promoter. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youderian P., Bouvier S., Susskind M. M. Sequence determinants of promoter activity. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]