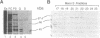Abstract
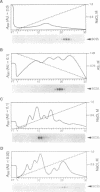
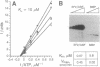
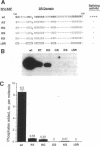
Members of the SR family of pre-mRNA splicing factors are phosphoproteins that share a phosphoepitope specifically recognized by monoclonal antibody (mAb) 104. Recent studies have indicated that phosphorylation may regulate the activity and the intracellular localization of these splicing factors. Here, we report the purification and kinetic properties of SR protein kinase 1 (SRPK1), a kinase specific for SR family members. We demonstrate that the kinase specifically recognizes the SR domain, which contains serine/arginine repeats. Previous studies have shown that dephosphorylated SR proteins did not react with mAb 104 and migrated faster in SDS gels than SR proteins from mammalian cells. We show that SRPK1 restores both mobility and mAB 104 reactivity to a SR protein SF2/ASF (splicing factor 2/alternative splicing factor) produced in bacteria, suggesting that SRPK1 is responsible for the generation of the mAb 104-specific phosphoepitope in vivo. Finally, we have correlated the effects of mutagenesis in the SR domain of SF2/ASF on splicing with those on phosphorylation of the protein by SRPK1, suggesting that phosphorylation of SR proteins is required for splicing.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein H., Hedley M. L., Maniatis T. The role of specific protein-RNA and protein-protein interactions in positive and negative control of pre-mRNA splicing by Transformer 2. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90512-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cáceres J. F., Krainer A. R. Functional analysis of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2/ASF structural domains. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4715–4726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. The 35-kDa mammalian splicing factor SC35 mediates specific interactions between U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles at the 3' splice site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Mayeda A., Maniatis T., Krainer A. R. General splicing factors SF2 and SC35 have equivalent activities in vitro, and both affect alternative 5' and 3' splice site selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11224–11228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D. Specific commitment of different pre-mRNAs to splicing by single SR proteins. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):82–85. doi: 10.1038/365082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul U., Seifert E., Schuh R., Jäckle H. Analysis of Krüppel protein distribution during early Drosophila development reveals posttranscriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gui J. F., Lane W. S., Fu X. D. A serine kinase regulates intracellular localization of splicing factors in the cell cycle. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):678–682. doi: 10.1038/369678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. J., Zuo P., Manley J. L., Baker B. S. The Drosophila RNA-binding protein RBP1 is localized to transcriptionally active sites of chromosomes and shows a functional similarity to human splicing factor ASF/SF2. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2569–2579. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohtz J. D., Jamison S. F., Will C. L., Zuo P., Lührmann R., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Manley J. L. Protein-protein interactions and 5'-splice-site recognition in mammalian mRNA precursors. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):119–124. doi: 10.1038/368119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. Purification and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 from HeLa cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1158–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigueur A., La Branche H., Kornblihtt A. R., Chabot B. A splicing enhancer in the human fibronectin alternate ED1 exon interacts with SR proteins and stimulates U2 snRNP binding. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2405–2417. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Zahler A. M., Krainer A. R., Roth M. B. Two members of a conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins are involved in pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1301–1304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermoud J. E., Cohen P., Lamond A. I. Ser/Thr-specific protein phosphatases are required for both catalytic steps of pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5263–5269. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potashkin J., Naik K., Wentz-Hunter K. U2AF homolog required for splicing in vivo. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):573–575. doi: 10.1126/science.8211184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Zahler A. M., Stolk J. A. A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):587–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Q., Mayeda A., Hampson R. K., Krainer A. R., Rottman F. M. General splicing factor SF2/ASF promotes alternative splicing by binding to an exonic splicing enhancer. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2598–2608. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi M., Yanagida M. A mitotic role for a novel fission yeast protein kinase dsk1 with cell cycle stage dependent phosphorylation and localization. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Mar;4(3):247–260. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.3.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Kornstädt U., Rossi F., Jeanteur P., Cathala G., Brunel C., Lührmann R. Thiophosphorylation of U1-70K protein inhibits pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):283–286. doi: 10.1038/363283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian M., Maniatis T. A splicing enhancer complex controls alternative splicing of doublesex pre-mRNA. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woppmann A., Will C. L., Kornstädt U., Zuo P., Manley J. L., Lührmann R. Identification of an snRNP-associated kinase activity that phosphorylates arginine/serine rich domains typical of splicing factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2815–2822. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Maniatis T. Specific interactions between proteins implicated in splice site selection and regulated alternative splicing. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1061–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90316-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Lane W. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):837–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Neugebauer K. M., Lane W. S., Roth M. B. Distinct functions of SR proteins in alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):219–222. doi: 10.1126/science.8385799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuo P., Manley J. L. Functional domains of the human splicing factor ASF/SF2. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4727–4737. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]