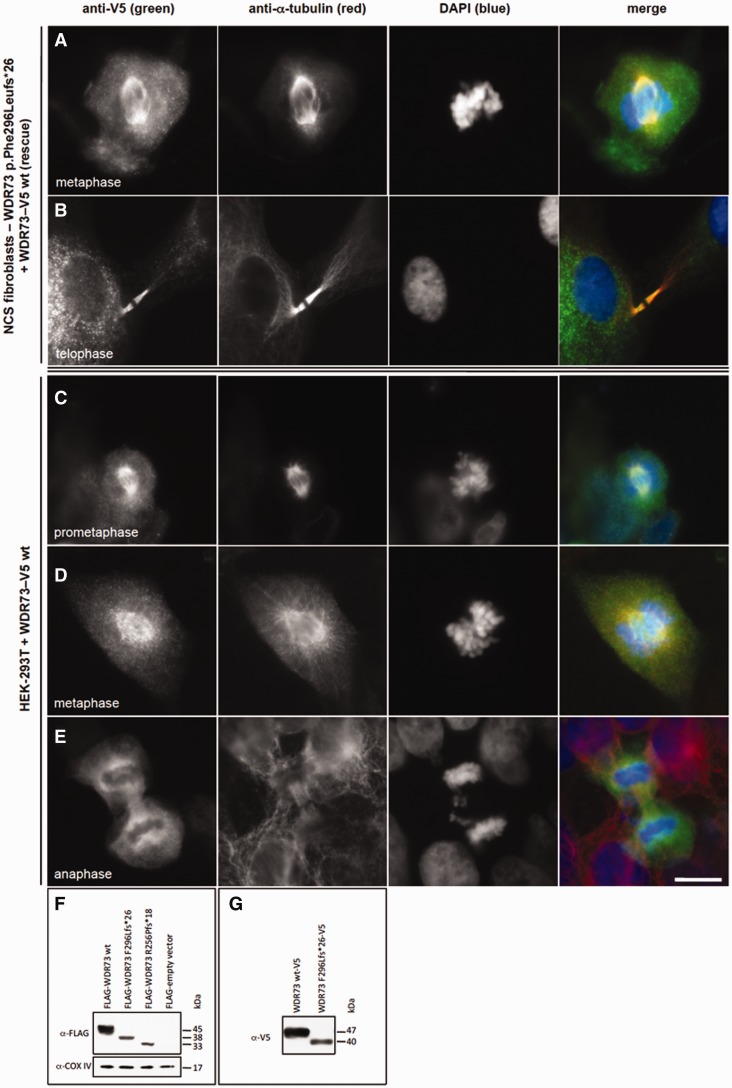
Figure 6.
Recombinant WDR73-V5 fusion protein rescues cell cycle defect in NCS patient fibroblasts. (A and B) Anti-V5 immunofluorescence (green) demonstrates that WDR73 C-terminal V5 fusion protein (WDR73–V5) overexpressed in NCS patient fibroblasts localizes to the mitotic microtubules (anti-α-tubulin) during metaphase (A) and telophase (B), rescuing the cell cycle defect in these cells. (C–E) Overexpression of WDR73 C-terminal V5 fusion protein (WDR73-V5) in HEK-293T cells. Anti-V5 immunofluorescence is in green; anti-α-tubulin in red. During pro-metaphase (C) and metaphase (D) recombinant WDR73-V5 colocalizes with α-tubulin at the mitotic spindle and aster microtubules. (E) WDR73-V5 localizes to the spindle poles, the kinetochore microtubules and the midzone microtubules during anaphase. Scale bars: A–E = 10 µm. (F–G) Western blots of recombinant N-terminal FLAG WDR73 fusion proteins (F) and WDR73 C-terminal V5 fusion proteins (G) overexpressed for 40–48 h in HEK-293T cells. Anti-COX IV was labelled as a protein loading control. The abundance of FLAG-WDR73 p.Phe296Leufs*26 (F296Lfs*26) was 2.6- to 5.6-fold lower and FLAG-WDR73 p.Arg256Profs*18 (R256Pfs*18) was 1.6- to 6.5-fold lower than that of FLAG-WDR73 wild-type (wt) across four replicates despite transfection of equivalent amounts of plasmid DNA, suggesting instability of the truncated proteins.