Abstract
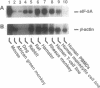
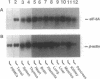
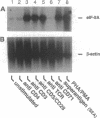
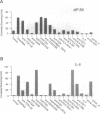
The hypusine-containing protein eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF-5A) is a cellular cofactor critically required for the function of the Rev transactivator protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). eIF-5A localizes in the nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments of mammalian cells, suggesting possible activities on the level of regulated mRNA transport and/or protein translation. In this report we show that eIF-5A gene expression is constitutively low but inducible with T-lymphocyte-specific stimuli in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of healthy individuals. In contrast, eIF-5A is constitutively expressed at high levels in human cell lines as well as in various human organs. Comparison of eIF-5A levels in the PBMCs of uninfected and HIV-1-infected donors shows a significant upregulation of eIF-5A gene expression in the PBMCs of HIV-1 patients, compatible with a possible role of eIF-5A in HIV-1 replication during T-cell activation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benne R., Brown-Luedi M. L., Hershey J. W. Protein synthesis initiation factors from rabbit reticulocytes: purification, characterization, and radiochemical labeling. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:15–35. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerdan C., Martin Y., Courcoul M., Brailly H., Mawas C., Birg F., Olive D. Prolonged IL-2 receptor alpha/CD25 expression after T cell activation via the adhesion molecules CD2 and CD28. Demonstration of combined transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2255–2261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chujor C. S., Kuhn B., Schwerer B., Bernheimer H., Levis W. R., Bevec D. Specific inhibition of mRNA accumulation for lymphokines in human T cell line Jurkat by mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Mar;87(3):398–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. L., Park M. H., Folk J. E. Posttranslational formation of hypusine in a single major protein occurs generally in growing cells and is associated with activation of lymphocyte growth. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):791–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90441-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Malim M. H. The HIV-1 Rev protein: prototype of a novel class of eukaryotic post-transcriptional regulators. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Sep;16(9):346–350. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90141-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckerskorn C., Mewes W., Goretzki H., Lottspeich F. A new siliconized-glass fiber as support for protein-chemical analysis of electroblotted proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):509–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. F., Lin Y., Mizel S. B., Bleackley R. C., Harnish D. G., Paetkau V. Induction of interleukin 2 messenger RNA inhibited by cyclosporin A. Science. 1984 Dec 21;226(4681):1439–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.6334364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foxwell B. M., Simon J., Herrero J. J., Taylor D., Woerly G., Cantrell D., Ryffel B. Anti-CD3 antibody-induced expression of both p55 and p75 chains of the high affinity interleukin-2 receptor on human T lymphocytes is inhibited by cyclosporin A. Immunology. 1990 Jan;69(1):104–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görg A., Postel W., Günther S. The current state of two-dimensional electrophoresis with immobilized pH gradients. Electrophoresis. 1988 Sep;9(9):531–546. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W., Smit-McBride Z., Schnier J. The role of mammalian initiation factor eIF-4D and its hypusine modification in translation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):160–162. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90159-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan B. D. Cyclosporine. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 21;321(25):1725–1738. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912213212507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang H. A., Hershey J. W. Effect of initiation factor eIF-5A depletion on protein synthesis and proliferation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):3934–3940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koettnitz K., Kappel B., Baumruker T., Hauber J., Bevec D. The genomic structure encoding human initiation factor eIF-5A. Gene. 1994 Jul 8;144(2):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Cyclosporin A inhibits T-cell growth factor gene expression at the level of mRNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lejbkowicz F., Goyer C., Darveau A., Neron S., Lemieux R., Sonenberg N. A fraction of the mRNA 5' cap-binding protein, eukaryotic initiation factor 4E, localizes to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9612–9616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. Rev and the fate of pre-mRNA in the nucleus: implications for the regulation of RNA processing in eukaryotes. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6180–6189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBratney S., Chen C. Y., Sarnow P. Internal initiation of translation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;5(6):961–965. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. H. The essential role of hypusine in eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4D (eIF-4D). Purification of eIF-4D and its precursors and comparison of their activities. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18531–18535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. H., Wolff E. C., Folk J. E. Hypusine: its post-translational formation in eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and its potential role in cellular regulation. Biofactors. 1993 May;4(2):95–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. H., Wolff E. C., Folk J. E. Is hypusine essential for eukaryotic cell proliferation? Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Dec;18(12):475–479. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90010-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. H., Wolff E. C., Smit-McBride Z., Hershey J. W., Folk J. E. Comparison of the activities of variant forms of eIF-4D. The requirement for hypusine or deoxyhypusine. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):7988–7994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Ng S. Y., Engel J., Gunning P., Kedes L. Evolutionary conservation in the untranslated regions of actin mRNAs: DNA sequence of a human beta-actin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1687–1696. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randak C., Brabletz T., Hergenröther M., Sobotta I., Serfling E. Cyclosporin A suppresses the expression of the interleukin 2 gene by inhibiting the binding of lymphocyte-specific factors to the IL-2 enhancer. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2529–2536. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07433.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhl M., Himmelspach M., Bahr G. M., Hammerschmid F., Jaksche H., Wolff B., Aschauer H., Farrington G. K., Probst H., Bevec D. Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A is a cellular target of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev activation domain mediating trans-activation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 1):1309–1320. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid J., Weissmann C. Induction of mRNA for a serine protease and a beta-thromboglobulin-like protein in mitogen-stimulated human leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):250–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Bevec D., Dukor P., Baeuerle P. A., Chedid L., Bahr G. M. Selection of a muramyl peptide based on its lack of activation of nuclear factor-kappa B as a potential adjuvant for AIDS vaccines. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Nov;90(2):188–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb07926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Erni B., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. I. Purification and characterization of seven initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):727–753. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit-McBride Z., Dever T. E., Hershey J. W., Merrick W. C. Sequence determination and cDNA cloning of eukaryotic initiation factor 4D, the hypusine-containing protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1578–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit-McBride Z., Schnier J., Kaufman R. J., Hershey J. W. Protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4D. Functional comparison of native and unhypusinated forms of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18527–18530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong-Starkesen S. E., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Signaling through T lymphocyte surface proteins, TCR/CD3 and CD28, activates the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):702–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent P., Bevec D., Maurer D., Besemer J., Di Padova F., Butterfield J. H., Speiser W., Majdic O., Lechner K., Bettelheim P. Interleukin 4 promotes expression of mast cell ICAM-1 antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3339–3342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]