Abstract
Identification of the targets of autoreactive T cells is important for understanding the pathogenesis of many autoimmune diseases. In multiple sclerosis, myelin proteins are thought to be the targets of autoreactive T-cell responses. To date only major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted CD4+ T-cell responses to myelin proteins have been investigated. In the present study, the ability of self peptides derived from human myelin proteins to induce autoreactive CD8+ T-cell responses has been assessed. Peptide sequences from human myelin basic protein (MBP), proteolipid protein (PLP), myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG), and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein have been identified that bind to and form stable complexes with HLA-A2. MBP 110-118, PLP 80-88, MAG 287-295, MAG 509-517, and MAG 556-564 were all able to induce peptide-specific HLA-A2-restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) responses in vitro in HLA-A2+ individuals. CTLs specific for MBP 110-118 and MAG 556-564 could recognize endogenously processed antigens presented by HLA-A2. CTL clones reactive to MBP 110-118 and MAG 556-564 produced tumor necrosis factor alpha and a subset of these clones also produced interferon gamma. These results demonstrate that (i) self peptides derived from human myelin proteins can induce autoreactive CD8+ CTLs and (ii) these CD8+ T cells produce cytokines thought to be important in mediating demyelinating disease. These studies provide an experimental approach for the assessment of CD8+ T-cell responses in such autoimmune diseases.
Full text
PDF

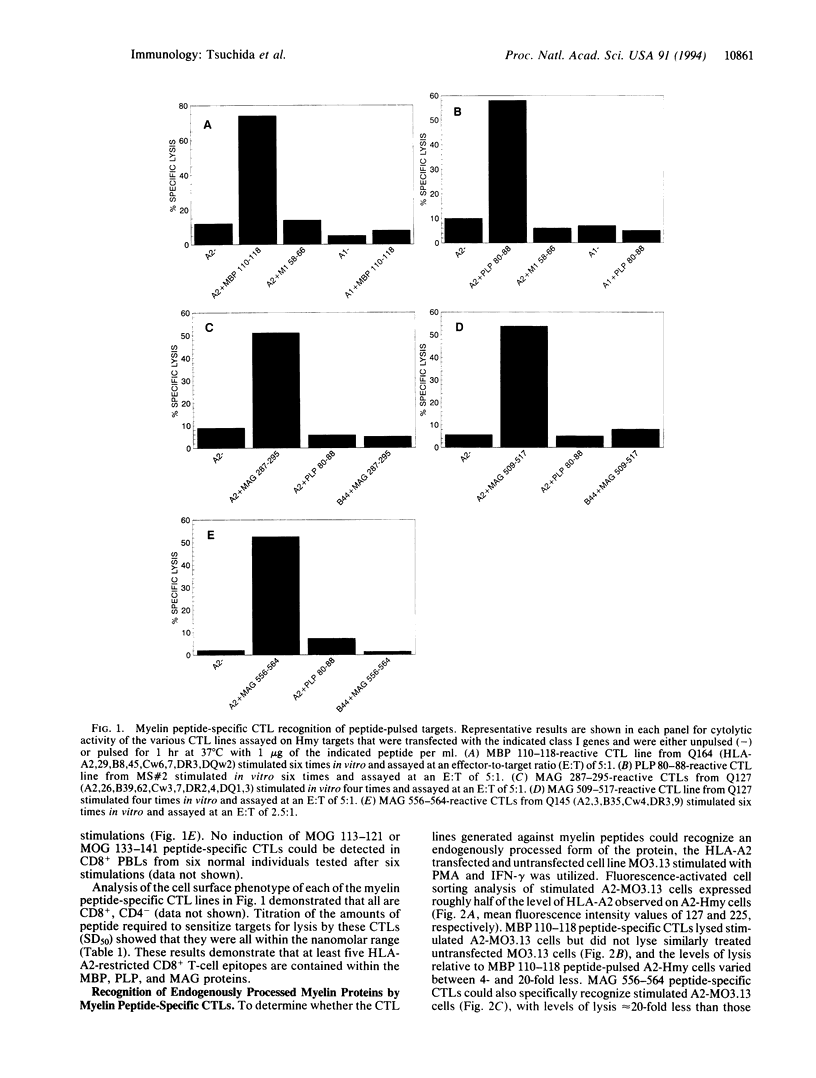
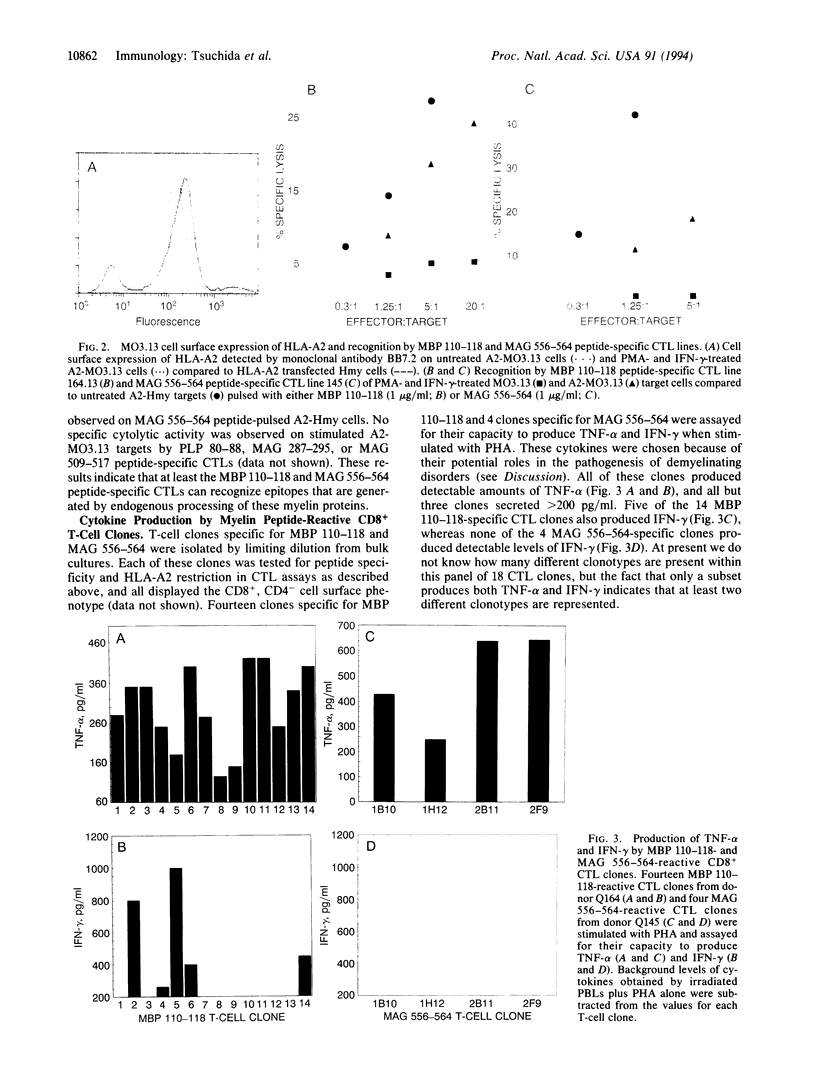

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booss J., Esiri M. M., Tourtellotte W. W., Mason D. Y. Immunohistological analysis of T lymphocyte subsets in the central nervous system in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Dec;62(1-3):219–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J., Rosenzweig A., Zweiman B., Lisak R. P. Isolation of myelin basic protein-reactive T-cell lines from normal human blood. Cell Immunol. 1983 Oct 15;81(2):435–440. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. K., Bourdette D. N., Offner H., Whitham R., Wang R. Y., Hashim G. A., Vandenbark A. A. Frequency of T cells specific for myelin basic protein and myelin proteolipid protein in blood and cerebrospinal fluid in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 May;38(1-2):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl H. J., Schaich M., Budzinski R. M., Stoffel W. Individual exons encode the integral membrane domains of human myelin proteolipid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9807–9811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotch F., Rothbard J., Howland K., Townsend A., McMichael A. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize a fragment of influenza virus matrix protein in association with HLA-A2. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):881–882. doi: 10.1038/326881a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier Y., Ruijs T. C., Robitaille Y., Olivier A., Antel J. P. Immunohistochemical studies of adult human glial cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Feb;21(2-3):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90166-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Benjamin D. S., Burks J., Weiner H. L. Myelin basic protein and proteolipid protein reactivity of brain- and cerebrospinal fluid-derived T cell clones in multiple sclerosis and postinfectious encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):68–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Johnson K., Merrill J. E. Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):607–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan K. T., Shimojo N., Walk S. F., Engelhard V. H., Maloy W. L., Coligan J. E., Biddison W. E. Mutations in the alpha 2 helix of HLA-A2 affect presentation but do not inhibit binding of influenza virus matrix peptide. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):725–736. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H., Zhang S. I., Pernis B. Role of CD8+ T cells in murine experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1213–1215. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Hafler D. A., Fallis R. J., Lees M. B., Brady R. O., Quarles R. H., Weiner H. L. Cell-mediated immunity to myelin-associated glycoprotein, proteolipid protein, and myelin basic protein in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Nov;13(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamholz J., de Ferra F., Puckett C., Lazzarini R. Identification of three forms of human myelin basic protein by cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4962–4966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlero de Rosbo N., Milo R., Lees M. B., Burger D., Bernard C. C., Ben-Nun A. Reactivity to myelin antigens in multiple sclerosis. Peripheral blood lymphocytes respond predominantly to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2602–2608. doi: 10.1172/JCI116875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh D. R., Fung-Leung W. P., Ho A., Gray D., Acha-Orbea H., Mak T. W. Less mortality but more relapses in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in CD8-/- mice. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liblau R. S., Fugger L. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and disease progression in multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 23;326(4):272–273. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201233260415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Jaraquemada D., Flerlage M., Richert J., Whitaker J., Long E. O., McFarlin D. E., McFarland H. F. Fine specificity and HLA restriction of myelin basic protein-specific cytotoxic T cell lines from multiple sclerosis patients and healthy individuals. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):540–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., McFarland H. F., McFarlin D. E. Immunological aspects of demyelinating diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:153–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota K., Matsui M., Milford E. L., Mackin G. A., Weiner H. L., Hafler D. A. T-cell recognition of an immunodominant myelin basic protein epitope in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):183–187. doi: 10.1038/346183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panitch H. S., Hirsch R. L., Schindler J., Johnson K. P. Treatment of multiple sclerosis with gamma interferon: exacerbations associated with activation of the immune system. Neurology. 1987 Jul;37(7):1097–1102. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.7.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. C., Bednarek M. A., Coligan J. E. Scheme for ranking potential HLA-A2 binding peptides based on independent binding of individual peptide side-chains. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 1;152(1):163–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelfrey C. M., Trotter J. L., Tranquill L. R., McFarland H. F. Identification of a novel T cell epitope of human proteolipid protein (residues 40-60) recognized by proliferative and cytolytic CD4+ T cells from multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jul;46(1-2):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90231-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pette M., Fujita K., Kitze B., Whitaker J. N., Albert E., Kappos L., Wekerle H. Myelin basic protein-specific T lymphocyte lines from MS patients and healthy individuals. Neurology. 1990 Nov;40(11):1770–1776. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.11.1770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S. Biology of disease. Analysis of autoimmune demyelination: its impact upon multiple sclerosis. Lab Invest. 1984 Jun;50(6):608–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Fujita N., Kurihara T., Kuwano R., Sakimura K., Takahashi Y., Miyatake T. cDNA cloning and amino acid sequence for human myelin-associated glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 29;163(3):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K., Raine C. S., Cross A. H. Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy abrogates autoimmune demyelination. Ann Neurol. 1991 Nov;30(5):694–700. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K., Raine C. S., Farooq M., Norton W. T., Brosnan C. F. Cytokine cytotoxicity against oligodendrocytes. Apoptosis induced by lymphotoxin. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1522–1529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethna M. P., Lampson L. A. Immune modulation within the brain: recruitment of inflammatory cells and increased major histocompatibility antigen expression following intracerebral injection of interferon-gamma. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Nov;34(2-3):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90121-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief M. K., Thompson E. J. In vivo relationship of tumor necrosis factor-alpha to blood-brain barrier damage in patients with active multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 May;38(1-2):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Howell D. N., Salter R. D., Dawson J. R., Cresswell P. NK susceptibility varies inversely with target cell class I HLA antigen expression. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1657–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J., Link H., Olsson T., Xiao B. G., Andersson G., Ekre H. P., Linington C., Diener P. T and B cell responses to myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1490–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Bodmer H. Antigen recognition by class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:601–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Reinherz E. L., Raine C. S. Multiple sclerosis: distribution of T cell subsets within active chronic lesions. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):308–310. doi: 10.1126/science.6217550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J. L., Hickey W. F., van der Veen R. C., Sulze L. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from multiple sclerosis patients recognize myelin proteolipid protein and selected peptides. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Jul;33(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D., Cawthon R., O'Connell P., Xu G. F., Stevens J., Culver M., Carey J., White R. The gene encoding the oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein is embedded within the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):906–912. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Bennink J. R. Cell biology of antigen processing and presentation to major histocompatibility complex class I molecule-restricted T lymphocytes. Adv Immunol. 1992;52:1–123. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60875-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Burger D., Saruhan G., Jeannet M., Steck A. J. The T-lymphocyte response against myelin-associated glycoprotein and myelin basic protein in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1993 Feb;43(2):403–407. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.2.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]