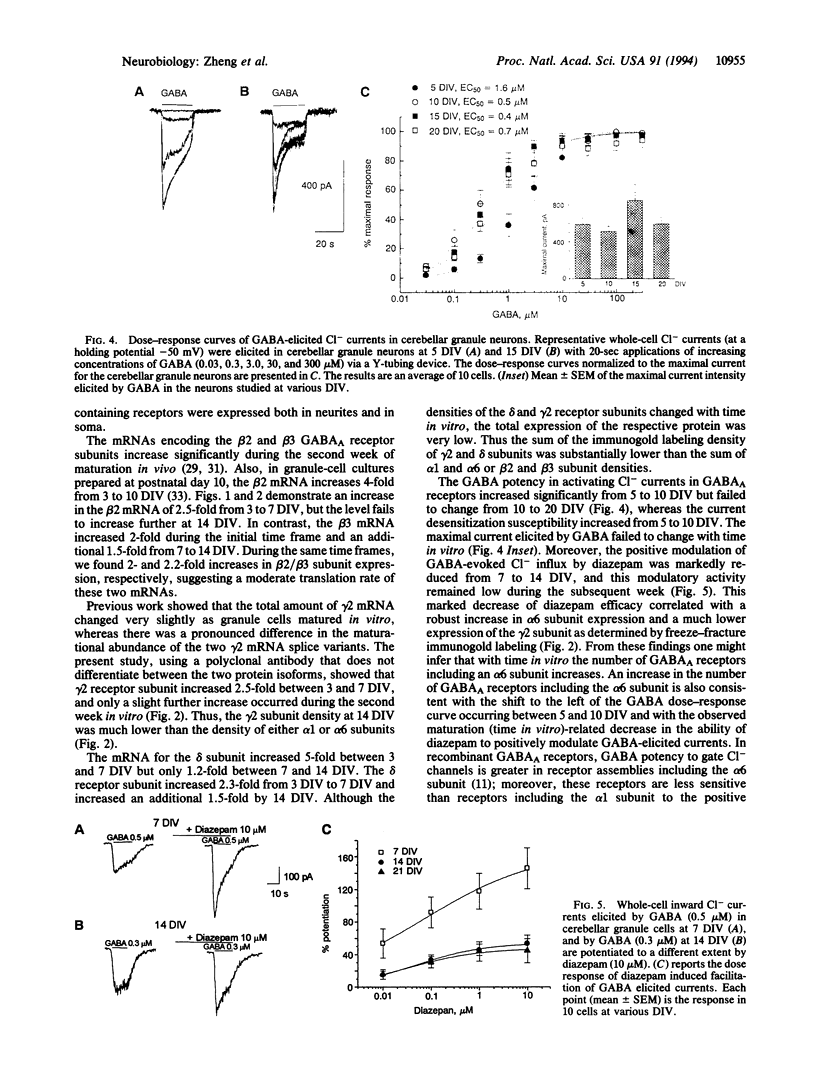
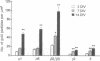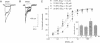Abstract
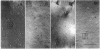
The amounts of mRNAs encoding alpha 1, alpha 6, beta 2, beta 3, gamma 2, and delta subunits of gamma-aminobutyrate type A (GABAA) receptors and the gold immunolabeling density of their translation products were monitored during the growth of neonatal rat granule cells in primary culture. We investigated possible correlations (i) between temporal changes in mRNA content and expression density of their respective translation products and (ii) between the quantitative changes of receptor subunit expression, the GABA EC50 for Cl- channel activation, and diazepam efficacy in modulating GABA action on the Cl- channels. At 3 days in vitro, the amount of GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs and the expression of their respective translation products were very low. During the next 2 weeks both parameters for every subunit studied increased asynchronously; moreover, at 14 days in vitro the sum of gamma 2 and delta subunit expression was smaller than the expression of the alpha 1 or alpha 6 or beta 2/beta 3 subunits. This suggests that during in vitro maturation each subunit may be regulated independently and invites speculation as to possible changes in specific GABAA receptor subtype abundance during development in vitro. The maximal current intensity elicited by GABA failed to increase from 5 to 14 days in vitro, though the amount of mRNA encoding various subunits and the expression density of their respective translation products increased. Thus, qualitative changes in the GABAA receptor subtypes expressed and/or abnormalities in the subunit assembly very likely account for the uniformity of the maximal current intensity elicited by GABA during in vitro development. Also, during maturation of neuronal cultures from 5 to 20 days in vitro the extent of the positive modulation of GABA action by diazepam decreased dramatically. This finding might be related to an increase in the abundance of GABAA receptors including the alpha 6 subunit and/or to the expression, during granule cell maturation in vitro, of GABAA receptors devoid of gamma 2 subunits.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baude A., Sequier J. M., McKernan R. M., Olivier K. R., Somogyi P. Differential subcellular distribution of the alpha 6 subunit versus the alpha 1 and beta 2/3 subunits of the GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor complex in granule cells of the cerebellar cortex. Neuroscience. 1992 Dec;51(4):739–748. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90513-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie C. E., Siegel R. E. Developmental cues modulate GABAA receptor subunit mRNA expression in cultured cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1784–1792. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01784.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benke D., Mertens S., Trzeciak A., Gillessen D., Mohler H. GABAA receptors display association of gamma 2-subunit with alpha 1- and beta 2/3-subunits. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4478–4483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benke D., Mertens S., Trzeciak A., Gillessen D., Mohler H. Identification and immunohistochemical mapping of GABAA receptor subtypes containing the delta-subunit in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 20;283(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80573-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovolin P., Santi M. R., Memo M., Costa E., Grayson D. R. Distinct developmental patterns of expression of rat alpha 1, alpha 5, gamma 2S, and gamma 2L gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor subunit mRNAs in vivo and in vitro. J Neurochem. 1992 Jul;59(1):62–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovolin P., Santi M. R., Puia G., Costa E., Grayson D. Expression patterns of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor subunit mRNAs in primary cultures of granule neurons and astrocytes from neonatal rat cerebella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9344–9348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruncho H. J., Costa E. Double-immunolabelling analysis of GABAA receptor subunits in label-fracture replicas of cultured rat cerebellar granule cells. Receptors Channels. 1994;2(2):143–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruncho H. J., Puia G., Slobodyansky E., da Silva P. P., Costa E. Freeze-fracture immunocytochemical study of the expression of native and recombinant GABAA receptors. Brain Res. 1993 Feb 19;603(2):234–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91242-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducić I., Puia G., Vicini S., Costa E. Triazolam is more efficacious than diazepam in a broad spectrum of recombinant GABAA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 4;244(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90056-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert M., Shivers B. D., Lüddens H., Möhler H., Seeburg P. H. Subunit selectivity and epitope characterization of mAbs directed against the GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2043–2048. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert M., de Blas A. L., Möhler H., Seeburg P. H. A prominent epitope on GABAA receptors is recognized by two different monoclonal antibodies. Brain Res. 1992 Jan 8;569(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90368-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritschy J. M., Benke D., Mertens S., Oertel W. H., Bachi T., Möhler H. Five subtypes of type A gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors identified in neurons by double and triple immunofluorescence staining with subunit-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6726–6730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo V., Ciotti M. T., Coletti A., Aloisi F., Levi G. Selective release of glutamate from cerebellar granule cells differentiating in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7919–7923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambarana C., Beattie C. E., Rodríguez Z. R., Siegel R. E. Region-specific expression of messenger RNAs encoding GABAA receptor subunits in the developing rat brain. Neuroscience. 1991;45(2):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90238-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambarana C., Pittman R., Siegel R. E. Developmental expression of the GABAA receptor alpha 1 subunit mRNA in the rat brain. J Neurobiol. 1990 Dec;21(8):1169–1179. doi: 10.1002/neu.480210803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett K. M., Saito N., Duman R. S., Abel M. S., Ashton R. A., Fujimori S., Beer B., Tallman J. F., Vitek M. P., Blume A. J. Differential expression of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor subunits. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 May;37(5):652–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killisch I., Dotti C. G., Laurie D. J., Lüddens H., Seeburg P. H. Expression patterns of GABAA receptor subtypes in developing hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):927–936. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90338-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleingoor C., Ewert M., von Blankenfeld G., Seeburg P. H., Kettenmann H. Inverse but not full benzodiazepine agonists modulate recombinant alpha 6 beta 2 gamma 2 GABAA receptors in transfected human embryonic kidney cells. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Sep 16;130(2):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90389-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleingoor C., Wieland H. A., Korpi E. R., Seeburg P. H., Kettenmann H. Current potentiation by diazepam but not GABA sensitivity is determined by a single histidine residue. Neuroreport. 1993 Feb;4(2):187–190. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199302000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoflach F., Drescher U., Scheurer L., Malherbe P., Mohler H. Full and partial agonism displayed by benzodiazepine receptor ligands at recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):385–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. J., Seeburg P. H., Wisden W. The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. II. Olfactory bulb and cerebellum. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):1063–1076. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-01063.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. J., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. The distribution of thirteen GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. III. Embryonic and postnatal development. J Neurosci. 1992 Nov;12(11):4151–4172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-11-04151.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüddens H., Pritchett D. B., Köhler M., Killisch I., Keinänen K., Monyer H., Sprengel R., Seeburg P. H. Cerebellar GABAA receptor selective for a behavioural alcohol antagonist. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):648–651. doi: 10.1038/346648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan A. J., Brecha N., Khrestchatisky M., Sternini C., Tillakaratne N. J., Chiang M. Y., Anderson K., Lai M., Tobin A. J. Independent cellular and ontogenetic expression of mRNAs encoding three alpha polypeptides of the rat GABAA receptor. Neuroscience. 1991;43(2-3):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Olsen R. W. GABAA receptor channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:569–602. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinecke D. L., Rakic P. Developmental expression of GABA and subunits of the GABAA receptor complex in an inhibitory synaptic circuit in the rat cerebellum. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1990 Aug 1;55(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(90)90107-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase K., Ryu P. D., Randic M. Excitatory and inhibitory amino acids and peptide-induced responses in acutely isolated rat spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Aug 14;103(1):56–63. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayeem N., Green T. P., Martin I. L., Barnard E. A. Quaternary structure of the native GABAA receptor determined by electron microscopic image analysis. J Neurochem. 1994 Feb;62(2):815–818. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62020815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter M. O., Barker J. L., O'Carroll A. M., Lolait S. J., Mahan L. C. Differential and transient expression of GABAA receptor alpha-subunit mRNAs in the developing rat CNS. J Neurosci. 1992 Aug;12(8):2888–2900. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-08-02888.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puia G., Vicini S., Seeburg P. H., Costa E. Influence of recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acid-A receptor subunit composition on the action of allosteric modulators of gamma-aminobutyric acid-gated Cl- currents. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;39(6):691–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers B. D., Killisch I., Sprengel R., Sontheimer H., Köhler M., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H. Two novel GABAA receptor subunits exist in distinct neuronal subpopulations. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90257-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Takagi H., Richards J. G., Mohler H. Subcellular localization of benzodiazepine/GABAA receptors in the cerebellum of rat, cat, and monkey using monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci. 1989 Jun;9(6):2197–2209. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-06-02197.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Draguhn A., Ymer S., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Functional properties of recombinant rat GABAA receptors depend upon subunit composition. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng T., Santi M. R., Bovolin P., Marlier L. N., Grayson D. R. Developmental expression of the alpha 6 GABAA receptor subunit mRNA occurs only after cerebellar granule cell migration. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1993 Sep 17;75(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(93)90068-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]