Abstract
Objective
To determine the efficacy of acupuncture for hypertension.
Method
Seven electronic databases were searched on April 13, 2014 to include eligible randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Data were extracted and risk of bias was assessed. Subgroup analyses and meta- analysis were performed.
Results
23 RCTs involving 1788 patients were included. Most trials had an unclear risk of bias regarding allocation concealment, blinding, incomplete outcome data and selective reporting. Compared with sham acupuncture plus medication, a meta-analysis of 2 trials revealed that acupuncture as an adjunct to medication was more effective on systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressure change magnitude (n=170, SBP: mean difference (MD)= -7.47,95% confidence intervals (CI):-10.43 to -4.51,I2 =0%; DBP: -4.22,-6.26 to -2.18, 0%).A subgroup analysis of 4 trials also showed acupuncture combined with medication was superior to medication on efficacy rate (n=230, odds ratio (OR)=4.19, 95%CI: 1.65 to 10.67, I2 =0%). By contrast, compared with medication, acupuncture alone showed no significant effect on SBP /DBP after intervention and efficacy rate in the subgroup analysis. (7 trials with 510 patients, SBP: MD=-0.56, 95%CI:-3.02 to 1.89,I2 =60%; DBP: -1.01,-2.26 to 0.24, 23%; efficacy rate: 10 trials with 963 patients, OR=1.14, 95% CI: 0.70 to 1.85, I2 =54%).Adverse events were inadequately reported in most RCTs.
Conclusion
Our review provided evidence of acupuncture as an adjunctive therapy to medication for treating hypertension, while the evidence for acupuncture alone lowing BP is insufficient. The safety of acupuncture is uncertain due to the inadequate reporting of it. However, the current evidence might not be sufficiently robust against methodological flaws and significant heterogeneity of the included RCTs. Larger high-quality trials are required.
Introduction
Essential hypertension (EH), which affects up to one billion individuals worldwide and is attributable each year for more than 7 million deaths and loss of 64 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) [1], remains a major public health challenge in both developed and developing countries despite all the progress in prevention and management of it [2].
Antihypertensive medication serves as a major therapy for treating hypertension. However, due to various side effects or safety concerns, such as drug resistance which could affect therapeutic efficacy, this therapy is far from satisfactory. Thus, seeking for an effective and less harmful treatment becomes an important goal for treating EH.
As a non-pharmacological intervention, acupuncture is an ancient Chinese therapy by inserting needles to the acu-points on the body surface along meridians to treat a wide range of diseases. Case reports and trials with small sample sizes suggested that acupuncture was an effective therapeutic intervention for treating EH [3]. It could be used on patients who want to avoid drug therapy or as an alternative option to reduce dosages of antihypertensive agents. But two previous systematic reviews claimed that the evidence of acupuncture for lowering blood pressure (BP) was inconclusive, mainly due to the paucity of rigorous trials [4, 5]. However, both of them failed to include all relevant RCTs published in China. And their literature searches were performed up to 2010. Several new RCTs have since been published. And though in the past two years, another 2 systematic reviews have been published. One of them [6] only included 4 randomized sham-controlled clinical trials and the other one [7] included sufficient trials but not all of them were rigorously randomized controlled trials (RCTs).And there were some flaws in this review in term of methodology, data extraction and eligibility of included RCTs as well [8]. And there was another systematic review to evaluate the long-term efficacy of acupuncture on hypertension but it just included Chinese RCTs [9]. Some quasi-RCTs were also included in the review so its conclusion may not be solid. Thus, it is timely to update the evidence whether acupuncture could treat EH. Therefore, we conducted this systematic review to critically assess all the currently rigorous RCTs to evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture for hypertension. And safety evaluation of acupuncture was assessed as well.
Methods
The PRISMA checklist is available as supporting information; See S1 Appendix.
Database and Search strategy
We searched the following databases from their inception through April 13, 2014: PUBMED, EMBASE, Cochrane Central Register of controlled trials, International Clinical Trials Register Platform of WHO, Chinese Scientific Journal Database, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and Chinese Evidence-Based Medicine Database. The following search terms were used individually or jointly: ‘hypertension’, ‘essential hypertension’, ‘blood pressure’, ‘acupuncture’, ‘electroacupuncture’, ‘clinical trial’, and ‘randomized controlled trial’. No language restrictions were imposed. The search strategy for each database is available in S2 Appendix. We also carefully scanned the references of all the eligible articles of RCTs to identify further publications.
Inclusion Criteria
RCTs which involved acupuncture as a therapeutic intervention for treating hypertension were included. Patients were diagnosed as hypertensive, with a systolic BP (SBP) ≥140 mm Hg and/or a diastolic BP (DBP)≥90 mm Hg. All RCTs should meet the following criteria: (1) sham and/or active control procedure was used (2) primary outcomes included BP before and after treatment, or BP change magnitude between baseline and post-intervention, or efficacy rate.
Exclusion criteria was as below: (1)pseudo-randomized trials simply claimed to be randomized with totally no description of the method of random sequence generation.(2) RCTs using laser acupuncture, acupressure, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (without needing insertion) as controls or using interventions whose efficacy is not yet established (i.e., herbal medicine) in the control group. (3) trials which failed to offer proper data to extract.
Data Extraction
Two reviewers (Hai-Zhen Zheng, Jia-Shen Li) independently evaluated all the eligible articles for inclusion, followed by data extraction in term of author, country, participants, acupuncture treatment, control types, treatment course, sessions of treatment, primary and secondary outcomes(i.e., SBP/DBP after intervention, SBP/DBP change magnitude, efficacy rate and adverse events), using a pre-defined data extraction form (Table 1). Disagreements were resolved by consensus or arbitration by a third reviewer (Xiao-Feng Zhao). All continuous data regarding BP which was presented as mean ±standard deviation (SD) were extracted if reported. Missing data or further information was sought from the primary authors via email if necessary.
Table 1. Characteristics and main outcomes of Included Studies.
| Author | Hypertension classification | N(male/female); Age(range of age); Intervention/control | Intervention | Acupuncture points | Control | Treatment Course | Sessions of treatment | Duration of one session | Background of acupuncturists | Main Outcome Measurement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dongjie Zhao(2003)[12] | EHT, stage I and stage II | 30(19/11);40.30y(34-57y) | 30(18/12);46.10y(40-62y) | Acupuncture plus lifestyle modification | CV4,ST36, ST40,SP6, LR3 | Lifestyle modification | 40d | 30 | 20min | NR | BP before and after intervention |
| Qingming Wu(2003)[13] | EHT, stage I and stage II | 40(23/17);48.55y | 40(21/19)47.85y | Acupuncture | LI4,LR3, GV20 | Captopril | 30d | 30 | 20min | NR | BP before and after intervention |
| Jin Chen(2006)[14] | EHT | 30(12/18);72y(58-85y) | 30(16/14);68.6y (45-84y) | Abdominal acupuncture plus antihypertensive medicine | CV12,CV10,CV6,CV4,ST24,ST26,CV8 | Tailored antihypertension | 7d | 5 | 30min | NR | 1.Efficacy rate 2.BP before and after intervention |
| Jun Chen(2010)[15] | EHT, stage I | 30(14/16);48.2y (39-71y) | 30(17/13);50.5y (35-69y) | Acupuncture plus antihypertensive medicine | GB20,LR2 | Felodipine | 15d | 15 | 30min | NR | Efficacy rate |
| Chaohui Zhang(2004)[16] | EHT, stage I and stage II | 30(22/8);56.50y | 30(20/10);55.50y | Acupuncture | GB20,LR2 | Compoundserpine | 30d | 30 | 30min | NR | Efficacy rate |
| Dianhui Yang(2010)[17] | EHT, stage I and stage II | 30;(28- 44y) | 30;(30- 45y) | Electric acupuncture | LR3,LI11 | Captopril | 14d | 14 | 30min | NR | BP before and after intervention |
| Yuhong Guo(2007)[18] | EHT, stage I and stage II | 40(22/18);43.83y(32-64y) | 40(23/17); 44.2y(29-65y) | Acupuncture | GV20,LI11,ST40,LR3,KI3,ST36,SP6 | Enalapril | 30d | 30 | 30min | NR | BP before and after intervention |
| Macklin(2006)[19] | EHT with BP after suspension of antihypertensive medications between 140/90 mm Hg and 179/109mmHg | Ind:64 (34/30); 56.8y;Std:64(35/ 29); 55.9y | 64(35/29);53.2y | Acupuncture | Individualized acupuncture* Standard acupuncture* and auricular points* | Sham acupuncture | 42d | 12 | 30min | YES | 1.BP change magnitude 2.Adverse events |
| Xiaoqing Lee(2008)[20] | EHT, stage I and stage II | 67(36/31);59.50y | 65(39/26);58.18y | Acupuncture | LR3 | Captopril | 7d | 7 | 20min | NR | 1.Efficacy rate 2.Adverse events |
| Kim[21] | EHT, stage I | 12(8/4);52.08±8.69y | 16(8/8);52.38±10.3y | Acupuncture | ST36,PC6 | Sham acupuncture | 56d | 16 | 20min | YES | 1.BP before and after intervention 2.BP change magnitude |
| Yan Wei(2006)[22] | EHT | 40(21/19);57.95y | Group1: 40(23/17);55.36y;Group2:40(22/18);58.14y | Acupuncture | ST9,GV20,LI11,LR3,KI3 | Captopril | 45d | 45 | Not retaining needle | NR | Efficacy rate |
| Wenjun Wan(2009)[23] | EHT, stage I and stage II | 30(19/11);63.72y(45-68y) | 30(17/13);65.24y(46-67y | Electric acupuncture | LI11 | Nicardipine | 15d | 15 | 10min | NR | 1.BP before and after intervention 2. Efficacy Rate |
| Tao Qu(2009)[24] | EHT, stage I and stage II | 127(69/ 58);55.43y | 125(57/ 68);55.24y | Acupuncture | GB20 | Betaloc | 28d | 28 | 30min | NR | Efficacy rate |
| Bangguo Chen(2006)[25] | EHT, stage I and stage II | 30(20/10);54.75y(36-65y) | 30(21/9);51.72y (33-61y) | Acupuncture | GB20 | Betaloc | 28d | 28 | 30min | NR | 1. Efficacy rate 2.BP before and after intervention |
| Fan Huang(2007)[26] | EHT, stage I and stage II | 30(14/16);56.51y(45-70y) | 30(13/17);58.12y(47-70y) | Acupuncture plus Captopril | GB20,LI11, PC6,ST36, ST40,LR3 | Captopril | 28d | 28 | 30min | NR | 1.Efficacy rate 2.BP before and after intervention |
| Guoxiang Feng(2003)[27] | EHT, stage I and II | 30(18/12);47.35y | 30(14/16);48.35y | Acupuncture | LI4,LR3,GV20 | Captopril | 30d | 30 | 20min | NR | Efficacy rate |
| Zhikun Shen(2007)[28] | Resistant hypertension, stage I,II and III | 25(15/10);57.32y(45∼76y) | 25(16/9);58.21y(44∼79y) | Acupuncture plus Nifedipine | ST 36 | Nifedipine | 25d | 20 | 30min | NR | 1.Efficacy rate 2.BP before and after intervention |
| Yue Yang(2010)[29] | EHT | 20(none);none | generalized acupuncture:20(none);none; medicine:20(none);none | Acupuncture | ST9,LI4, LI11,ST36,LR3 | Medicine: hydrochlorothiazide; Generalized acupoints:ST9,LI11, SP6,ST36, GB20 | 21d | 21 | NR | NR | Efficacy rate |
| Chaoyang Ma(2011)[30] | EHT, stage I and II | 40(25/15);66.39y | 40(22/18);64.58y | Electric acupuncture | LI11 | Nicardipine | 15d | 15 | 10min | NR | 1.BP before and after intervention 2.Efficacy rate |
| Hui Liao (2006)[31] | EHT, stage I and II and III | 59(31/28);56.5±7.9y | 31(17/14);55.6±8.6y | Acupuncture | PC7, PC6, LR2, LR3, LR8, KI3, KI7, BL60, LI11, ST40 | Captopril | 14d | 28 | 30min | NR | 1. Efficacy rate 2.BP before and after intervention |
| Kraft K(1999)[32] | mild hypertension | 7 | 7 | Acupuncture | BL18,BL23,GB20,BV20, HT7,KI3, LR2,LR3,SP6 | Sham acupuncture | 42d | 12 | 3min | NR | BP change magnitude |
| Flachskampf FA(2007)[33] | mild or moderate arterial hypertension SBP:140-179mmHg DBP:90–109> mmHg | 72(39/33);58.80y | 68(27/41);58.00y | Acupuncture plus antihypertensive medication | LR2,LR3,LI11,LI4,ST36,ST40,BL18,BL23,GB20,EX-HN5,KI3,SP6,SP9,CV4,CV6, CV12 | Sham acupuncture plus antihypertensive medication | 42d | 22 | 30min | YES | 1.BP before and after intervention 2.BP change magnitude 3.Adverse events |
| Yin C(2007)[34] | SBP≥120 mmHg or DBP≥80 mmHg. Subjects with SBP>140 mmHg or DBP>90 mmHg were included only when they were already on antihypertensive medication. | 15(4/11);52y(49- 56y) | 15(5/10);54y(51- 57y) | Acupuncture plus antihypertensive medication | ST36,LI11, BL25,SP3, LU9,BL13, KI2,KI7,CV4,LI1,GB20,GV14 | Sham acupuncture plus antihypertensive medication | 56d | 17 | Not retaining needle | NR | 1.BP change magnitude 2.Adverse events |
Abbreviation: EHT, essential hypertension; NR, not report;
* Individualized acupuncture: BL18, BL20, BL23, BL64, CV4, CV6, CV12, GB20, GB21, GB34, GB43, GV4, GV20, HT7, KI3, LI4, LI11, LR2, LR3, PC6, ST6, ST8, ST36, ST40, ST44, EX-HN5, EX-HN3;
*Standard acupuncture:GB20,LI11,LR03,SP06,ST36;
*auricular points: Kindey, Shenmen, Heart, Step-down ditch.
Assessment for Risk of Bias
Risk of bias assessment of the included RCTs was independently performed by two reviewers (Hai-Zhen Zheng, Jia-Shen Li) using the Cochrane criteria [10]. Disagreements were resolved by discussion. Risk of bias of the following domains were assessed (1) random sequence generation (2)allocation concealment(3)blinding of participants and personnel (4)blinding of outcome assessment(5) incomplete outcome data (6)selective reporting(7)other bias. Considering the characteristic of acupuncture RCTs, other bias was defined as whether the trial reported the method of acupuncture operation, as well as Deqi sensation, a situation in which patients experience a radiating sensation considered to be indicative of effective needling. Our judgements on these domains were categorized as ‘low’ risk of bias, ‘high’ risk of bias or ‘unclear’ risk of bias based on the Cochrane assessment tool [10]. For examples, as for ‘low risk’ of bias for the domain of random sequence generation, the investigators should describe a random component in the sequence generation process such as referring to a random number table; using a computer random number generator or coin tossing.
Statistical Analysis
Meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager V5.1. Continuous data were presented as mean difference (MD) and its 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity was examined using the I2 test, where I2 values of 50% or more were considered to be indicative of a substantial level of heterogeneity [11]. Fixed effects model was used if there was no significant heterogeneity; random effects model was employed when there was significant heterogeneity. Based on different outcome measures, if significant heterogeneity between studies was detected, we would investigate possible causes from clinical perspectives by conducting subgroup analysis. Various subgroup analyses were performed based on types of interventions (i.e., acupuncture VS western medicine, acupuncture plus western medicine VS western medicine), sample size (i.e., n≤60 VS n>60), sessions of treatment(i.e., i.e., n≤20 VS n>20) and type of stimulation (manual VS electric). Regarding dichotomous data (i.e., efficacy rate), results were presented as ORs with 95% CIs, using either a fixed or random-effects model depending on the statistical heterogeneity. Regarding some studies compared the effect of more than two intervention groups, the overall effects of acupuncture (i.e.,(group1 +group2) VS control) were tested.
Results
3.1 Literature Search
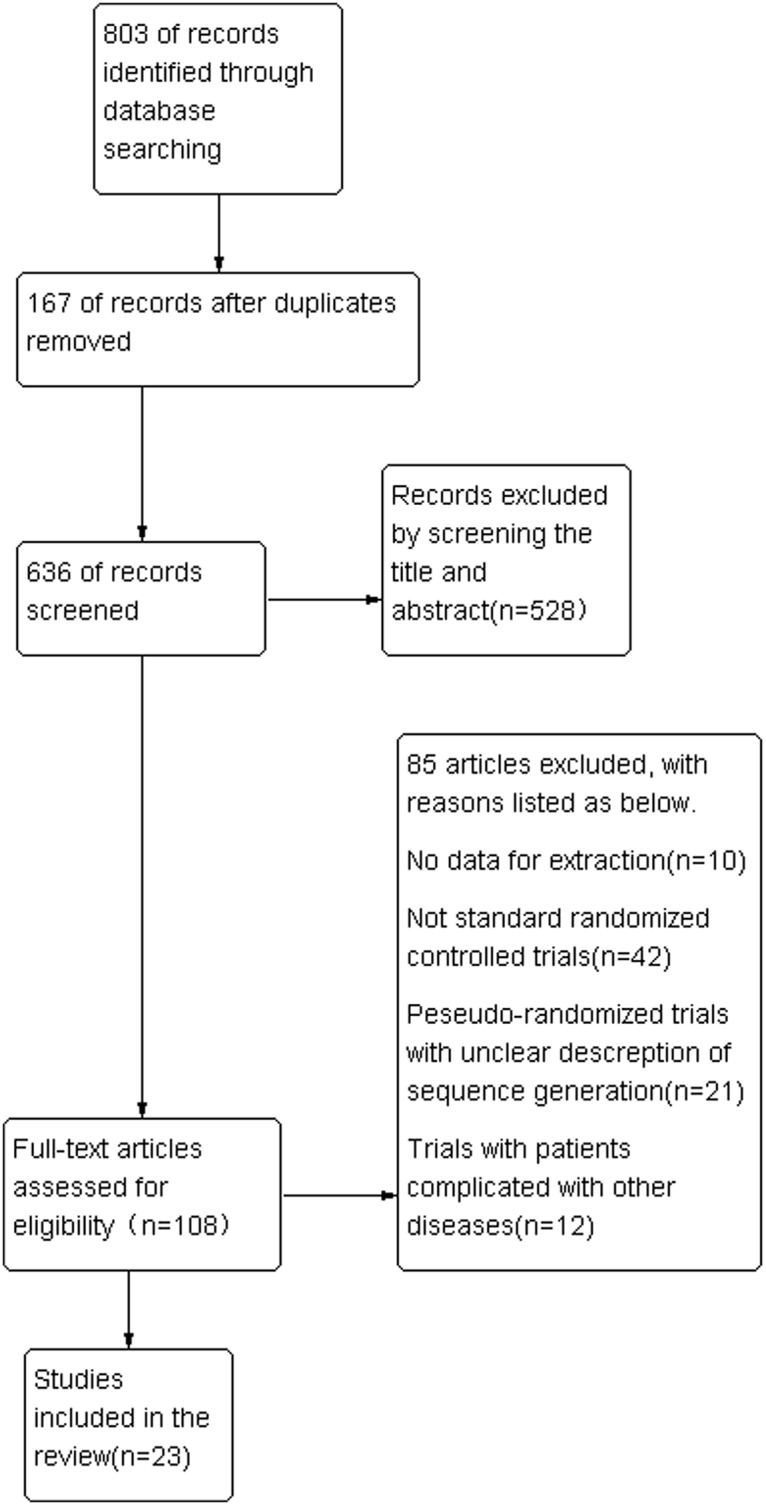
The process of literature search was displayed in the flowchart (as shown in Fig 1). After primary search in the target databases, 803 articles were screened. And 528 records were excluded by reading titles and abstracts. Full texts of 108 potentially relevant articles were assessed for eligibility and 85 RCTS of them were excluded by using our inclusion and exclusion criteria. Finally, 23 RCTs were eligible [12–34].
Fig 1. Flowchart of the trial selection process.
3.2 Study Characteristics
The characteristics and main outcomes of each trial were summarized in Table 1. The 23 RCTs included a total of 1788 patients with hypertension, with the average number of 78 per trial, ranging from 14 to 252. A majority of RCTs involved patients with mild or mild to moderate hypertension, except two studies enrolled participants with hypertension of Stage III[28, 31]. And 18 RCTs were conducted in China [12–18, 20, 22–31], 2 in Germany [32, 33], 2 in South Korea [21, 34] and 1 in the United States [19].
Varied acupuncture techniques were used in terms of selection of acupuncture-points, manipulation or stimulation methods. The most frequently used acupuncture points were LR3 (taichong, in 12 trials), LI11 (quchi, 11 trials), GB20 (fengchi, 10 trials), ST36 (zusanli, 8 trials), followed by LI4 (hegu, 5 trials), SP6 (sanyinjiao, 5 trials), CV4 (guanyuan, 5 trials), PC6 (neiguan, 4 trials).Participants received acupuncture treatment 3 to 30 min per session for mean 28.5 days, ranging from 7 to 56 days. 16 trials had a clear description of ‘Deqi’, which was associated with better effectiveness of acupuncture. Only 3 of the 24 trials introduced the background of acupuncturist [19, 21, 33] and the majority of the studied described the manipulation method of acupuncture. Besides, 11 trials reported the method of BP measurement by using 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring or mercury sphygmomanometer or automated sphygmomanometer.
3.3 Types of Interventions
Acupuncture group included acupuncture or electro-acupuncture alone, or combined with western medicine. And one trial involved acupuncture combined with lifestyle modification [12]. 16 trials employed acupuncture as sole treatment, whereas in 6 trials[14,15,26,28,33,34], acupuncture was used as an adjunctive therapy for medication. Types of control groups consist of western medicine, sham acupuncture, lifestyle modification and western medicine combined with sham acupuncture. Sham acupuncture alone was adopted in 3 RCTs [19, 21, 32] and 2 trials [33,34] used sham acupuncture plus western medicine. One study [12] employed lifestyle modification alone as control.
3.4 Investigation of Heterogeneity and Subgroup Analysis
Regarding different outcome measurements, significant heterogeneity between included RCTs was found (Figs 2–6: I2 = 94% for ‘SBP after intervention’, I2 = 73% for ‘DBP after intervention’, I2 = 89% for ‘SBP change magnitude’, I2 = 63% for ‘DBP change magnitude’ and I2 = 59% for ‘efficacy rate’, respectively). Possible causes for heterogeneity were searched by performing subgroup analysis. Based on the clinical perspective, a subgroup analysis was performed based on types of intervention (i.e., acupuncture VS western medicine, acupuncture plus western medicine VS western medicine) because this might be one of the main factors causing heterogeneity clinically. Additionally, various subgroup analyses were also performed based on sample size (i.e., n≤60 VS n>60), sessions of treatment(i.e., i.e., n≤20 VS n>20) and type of stimulation (manual VS electric). Results of subgroup analyses were displayed in Tables 2–4. As for outcome measures ‘SBP/DBP change magnitude’, it turned out that types of intervention could be one possible cause for clinical heterogeneity. However, regarding outcome measures ‘SBP/DBP after intervention’ and ‘efficacy rate’, potential sources of heterogeneity could not be determined from clinical perspective. It might be caused by methodological diversity of the identified RCTs such as study designs and risk of bias.
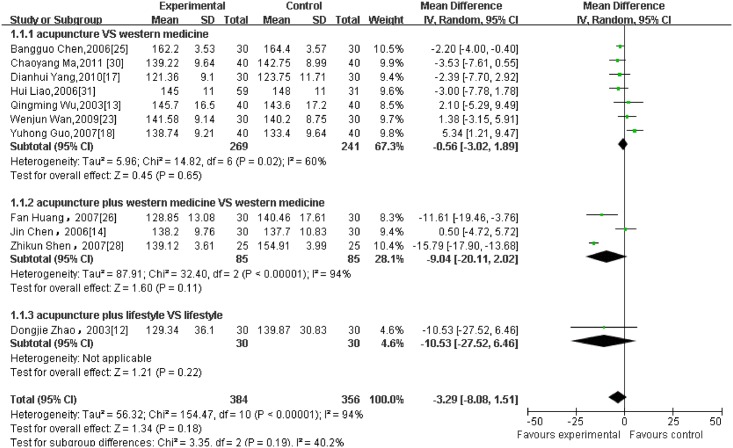
Fig 2. The forest plot of outcome measure ‘SBP after intervention.’.
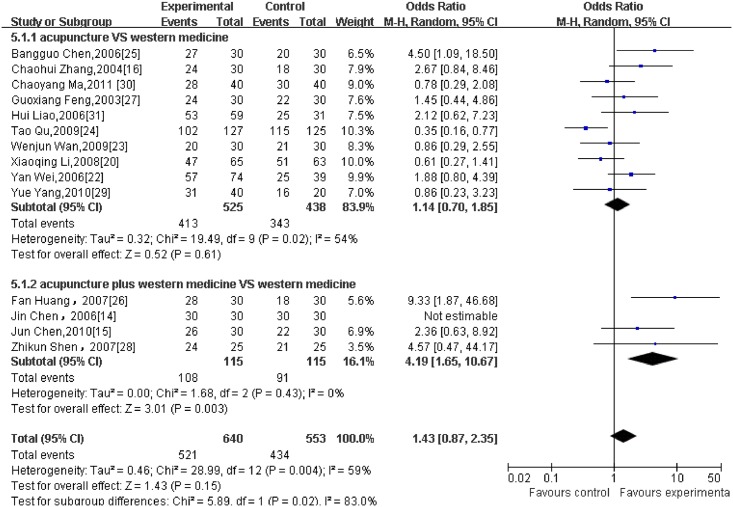
Fig 6. The forest plot of outcome measure ‘Efficacy Rate.’.
Table 2. Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity on SBP/DBP after intervention.
| Outcome Title | Number of studies | Number of patients | Effect size WMD(95%CI) | Test for overall effect P-value | Heterogeneity; I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP after intervention | |||||
| 1.Type of intervention | |||||
| Acupuncture | 7 | 510 | -0.56 [-3.02, 1.89] | 0.65 | 60% |
| Acupuncture plus western medicine | 3 | 170 | -9.04 [-20.11, 2.02] | 0.11 | 94% |
| Acupuncture plus lifestyle | 1 | 60 | -10.53[-27.52, 6.46] | 0.22 | - |
| 2.Number of sessions | |||||
| n≤20 | 5 | 310 | -4.11 [-12.26, 4.05] | 0.32 | 95% |
| n>20 | 6 | 430 | -1.85 [-6.06, 2.36] | 0.39 | 75% |
| 3.Sample size | |||||
| n≤60 | 7 | 410 | -5.42 [-11.91, 1.07] | 0.10 | 95% |
| n>60 | 4 | 330 | 0.12 [-4.58, 4.81] | 0.96 | 73% |
| 4.Type of stimulation | |||||
| Electro | 3 | 200 | -1.56 [-4.59, 1.47] | 0.31 | 23% |
| Manual | 8 | 540 | -4.05 [-10.36, 2.27] | 0.21 | 95% |
| DBP after intervention | |||||
| 1.Type of intervention | |||||
| Acupuncture | 7 | 510 | -1.01 [-2.26, 0.24] | 0.11 | 23% |
| Acupuncture plus western medicine | 3 | 170 | -2.87 [-8.45, 2.72] | 0.31 | 86% |
| Acupuncture plus lifestyle | 1 | 60 | -7.52 [-15.06, 0.02] | 0.05 | - |
| 2.Number of sessions | |||||
| n≤20 | 5 | 310 | -2.99 [-4.32, -1.66] | P<0.0001 | 85% |
| n>20 | 6 | 430 | -1.80 [-2.97, -0.63] | 0.003 | 42% |
| 3.Sample size | |||||
| n≤60 | 7 | 410 | -3.39 [-4.46, -2.33] | P<0.00001 | 75% |
| n>60 | 4 | 330 | -0.06 [-1.61, 1.49] | 0.94 | 0% |
| 4.Type of stimulation | |||||
| Electro | 3 | 200 | -0.43 [-2.20, 1.34] | 0.63 | 0% |
| Manual | 8 | 540 | -2.94 [-3.95, -1.93] | P<0.00001 | 78% |
Abbreviation: SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; WMD, weighted mean difference; CI, confidence interval.
Table 4. Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity on efficacy rate.
| Outcome Title | Number of studies | Number of patients | Effect size WMD(95%CI) | Test for overall effect P-value | Heterogeneity; I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.Type of intervention | |||||
| Acupuncture | 11 | 1023 | 1.14 [0.70, 1.85] | 0.61 | 54% |
| Acupuncture plus western medicine | 4 | 230 | 4.19 [1.65, 10.67] | 0.003 | 0% |
| 2.Number of sessions | |||||
| n≤20 | 7 | 498 | 0.96 [0.59 1.54] | 0.85 | 18% |
| n>20 | 8 | 755 | 1.40 [0.98, 2.01] | 0.04 | 69% |
| 3.Sample size | |||||
| n≤60 | 10 | 590 | 2.13 [1.36, 3.34] | 0.0009 | 28% |
| n>60 | 5 | 663 | 0.79 [0.53, 1.17] | 0.24 | 63% |
| 4.Type of stimulation | |||||
| Manual | 2 | 140 | 1.32 [0.96, 1.80] | 0.09 | 64% |
| Electro | 13 | 1113 | 0.81 [0.39, 1.69] | 0.58 | 0% |
Abbreviation: WMD, weighted mean difference; CI, confidence interval.
Table 3. Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity on SBP/DBP change magnitude.
| Outcome Title | Number of studies | Number of patients | Effect size WMD(95%CI) | Test for overall effect P-value | Heterogeneity; I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP change magnitude | |||||
| 1.Type of intervention | |||||
| Acupuncture | 2 | 216 | 0.30 [-0.27, 0.88] | 0.30 | 0% |
| Acupuncture plus western medicine | 2 | 170 | -7.47 [-10.43, -4.51] | P<0.00001 | 0% |
| 2.Number of sessions | |||||
| n≤20 | 2 | 218 | -4.51 [-15.43, 6.42] | 0.42 | 85% |
| n>20 | 2 | 168 | -2.25 [-12.31, 7.81] | 0.66 | 87% |
| 3.Sample size | |||||
| n≤60 | 2 | 58 | -3.55 [-17.55, 10.45] | 0.62 | 85% |
| n>60 | 2 | 328 | -3.19 [-10.32, 3.94] | 0.38 | 95% |
| DBP change magnitude | |||||
| 1.Type of intervention | |||||
| Acupuncture | 2 | 216 | -1.40 [-2.37, -0.44] | 0.004 | 8% |
| Acupuncture plus western medicine | 2 | 170 | -4.22 [-6.26, -2.18] | P<0.0001 | 0% |
| 2.Number of sessions | |||||
| n≤20 | 2 | 218 | -2.68 [-6.55, 1.18] | 0.17 | 52% |
| n>20 | 2 | 168 | -1.97 [-6.65, 2.71] | 0.41 | 73% |
| 3.Sample size | |||||
| n≤60 | 2 | 58 | -2.24 [-8.91, 4.43] | 0.51 | 69% |
| n>60 | 2 | 328 | -2.51 [-4.91, -0.12] | 0.04 | 80% |
Abbreviation: SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; WMD, weighted mean difference; CI, confidence interval.
3.5 Outcome and Effect Estimates
Based on various outcome measures (BP after intervention, BP change magnitude, Efficacy Rate) of the included RCTs, different pooled data of 22 RCTs were used in meta-analysis respectively. One trial [32] was excluded from meta-analysis because it reported BP value as medians and inter-quatile ranges. The effect estimates of acupuncture were shown in the forest plots (Figs 2–6).
All continuous data were presented as mean± SD. It is worth noting that, with respect to efficacy rate, it is often reported as a primary outcome by categorization of BP reduction in three levels (1.markedly effective, 2.effective, 3.inefficacious) in trials of hypertension in China. Efficacy rate means the percentage of the total number of participants who were categorized in the first two levels. And the criteria for categorization of the three levels are commonly defined as below in China [35]:
(1)Markedly effective: at the end of treatment, DBP decreased by 10 mmHg reaching the normal range, or DBP has not yet returned to normal but has been reduced ≥ 20 mmHg;(2)Effective: at the end of treatment, DBP decreased to less than 10 mmHg reaching the normal range, or DBP decreased by 10–19 mmHg but did not reach the normal range, or SBP reduction ≥ 30 mmHg);(3)Inefficacious: DBP reduction is not as significant as the first two levels at the end of treatment.
3.5.1 BP after intervention
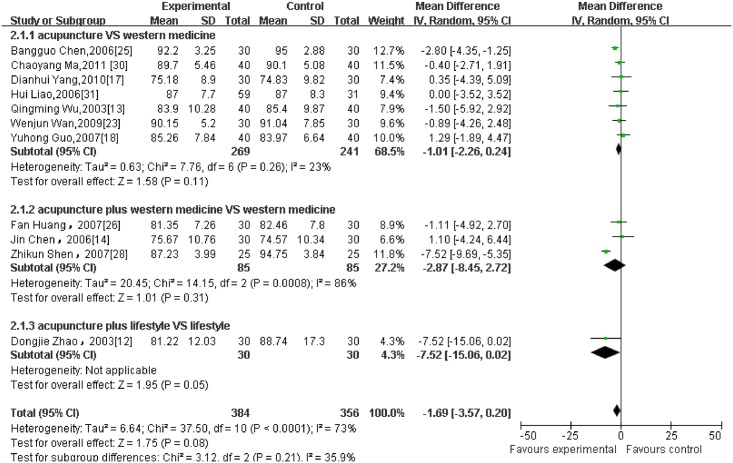
11 RCTs which reported BP (presented as mean ± SD) at the end of treatment as the primary outcome were pooled in the meta-analysis (as shown in Figs 2 and 3). 7 of them were divided into the subgroup of acupuncture versus western medicine. The result failed to establish a favorable effect of acupuncture on both SBP and DBP after intervention. (7 trials with 510 patients, SBP: MD = -0.56, 95%CI:-3.02 to 1.89, I2 = 60%; DBP: MD = -1.01, 95%CI:-2.26 to 0.24, I2 = 23%). 3 studies were combined as a subgroup analysis of acupuncture plus medication versus medication alone. Similarly, the result did not show a significant difference in favour of acupuncture, with significant heterogeneity. (3 trials with 170 patients, SBP:-9.04,-20.11 to 2.02, I2 = 94%; DBP:-2.87,-8.45 to 2.72, I2 = 86%). Compared with lifestyle modification, acupuncture was not superior on post-treatment SBP/ DBP as well. (1 trial with 60 patients, SBP: −10.53, −27.52 to 6.46; DBP: −7.52, −15.06 to 0.02)
Fig 3. The forest plot of outcome measure ‘DBP after intervention.’.
3.5.2 BP change magnitude
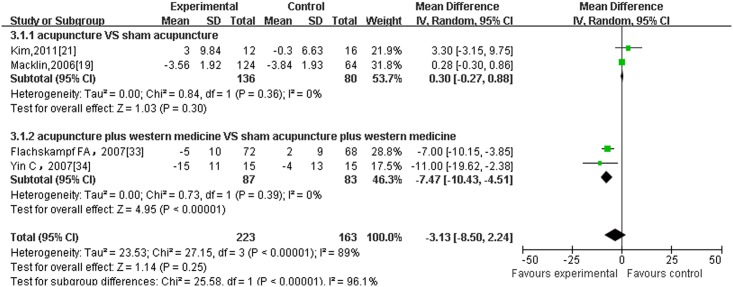
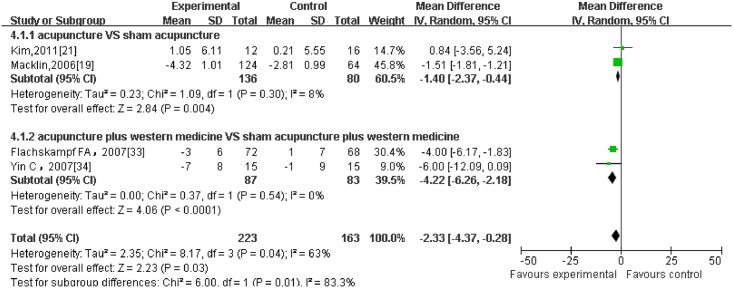
5 trial [19,21,32,33,34] reported SBP and DBP change magnitude(presented as mean ± SD) between baseline and post-intervention as principal outcomes and after excluding one trial[32]from meta-analysis because it reported BP value as medians and inter-quatile ranges,2 of them were pooled in the subgroup of acupuncture versus sham acupuncture. And it turned out that there were no significant differences between acupuncture and sham acupuncture (Fig 4: 2 trials with 216 patients, SBP: 0.30, -0.27 to 0.88, I2 = 0%) while acupuncture arms achieved more significant effect modification on DBP change magnitude than sham acupuncture, with low heterogeneity (Fig 5: 2 trials with 216 patients, DBP: -1.40, -2.37 to -0.44, I2 = 8%). The other 2 RCTs compared ‘acupuncture plus medication’ with ‘sham acupuncture plus medication’ and they were combined in this subgroup. The result yielded a beneficial effect of acupuncture combined with western medicine compared to sham acupuncture plus western medicine, with no heterogeneity. (Figs 4 and 5: 2 trials with 170 patients, SBP: -7.47, -10.43 to -4.51, I2 = 0%; DBP:-4.22, -6.26 to -2.18, I2 = 0%)
Fig 4. The forest plot of outcome measure ‘SBP change magnitude.’.
Fig 5. The forest plot of outcome measure ‘DBP change magnitude.’.
3.5.3 Efficacy rate
14 RCTs reported efficacy rate as the main outcome and all data were pooled in the forest plot (Fig 6). Of these trials, 4 were pooled as a meta-analysis of acupuncture plus western medicine versus medication alone. And the outcome demonstrated that acupuncture as an adjunct to western medicine achieved more favourable effect than medication. (4 trials with 230 patients, OR = 4.19, 95%CI: 1.65 to 10.67, I2 = 0%).The other 10 RCTs were combined in the subgroup analysis of acupuncture versus western medicine. And the result failed to yield a beneficial effect of acupuncture. (10 trials with 963 patients, OR = 1.14, 95% CI: 0.70 to 1.85, I2 = 54%)
3.6 Risk of Bias Assessment
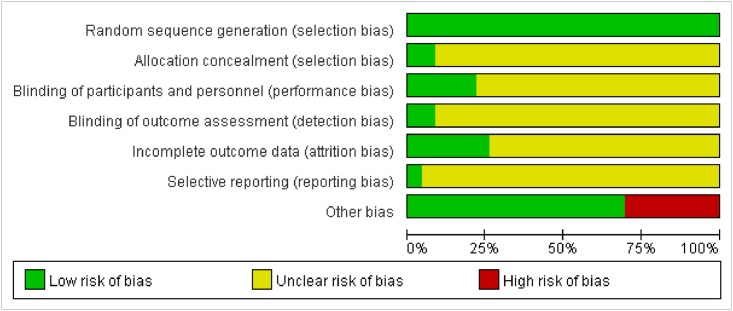
We summarized the risk of bias assessment for each included study in Figs 7 and 8, which was based on the Cochrane criterion [10]. The risk of bias of the included RCTs was generally low for random sequence generation and other sources of bias. The majority of the trials used table of random number to fulfill the random sequence generation, whereas 3 RCTs adopted block randomization[17,21,33] and 2 studies referred to the drawing method[29,31].
Fig 7. The risk of bias assessment for each included study.
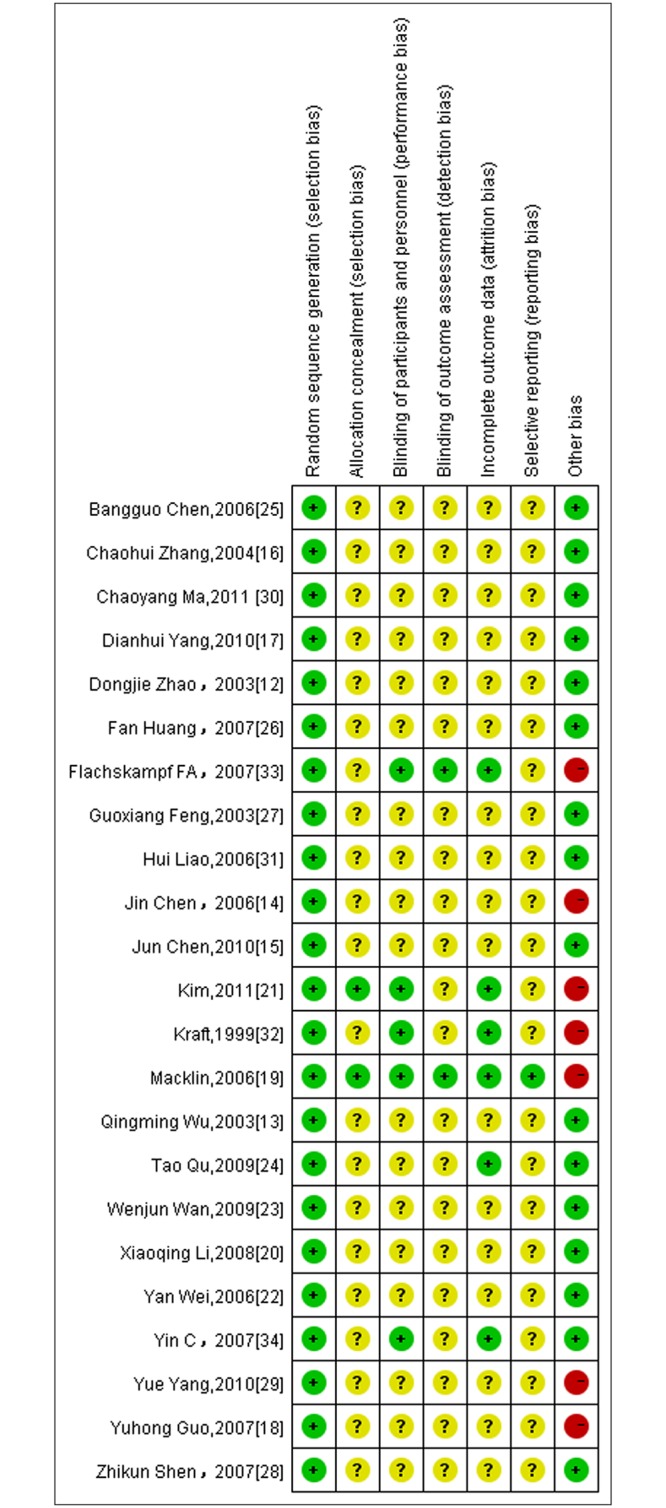
Fig 8. Risk of bias summary of included RCTs.
Details about allocation concealment were only mentioned in 2 RCTs [19,21], so the domain of allocation concealment was generally rated ‘unclear’ in most trials. With respect to blinding, only 3 trials had a description of double-blind [19, 21, 34] and single-blind was used in 2 trials [32, 33].
6 trials reported dropouts or withdraws [19,21,24,32,33,34], 4 of which provided the reasons[21,32–34] and 2 mentioned that outcomes were analyzed by intention-to-treat analysis[19,33]. Selective reporting was generally ‘unclear’ in the included RCTs due to the inaccessibility of the trail protocol.
Information on follow-up was addressed in 4 trials [19,21,28,33] and outcome in two trials showed BP gradually bounced to pre-treatment levels [19,33], while another study [28] didn’t find the occurrence of BP bounce.
3.7 Safety Evaluation
Most included RCTs had inadequate reporting on adverse events. Only 4 trials [19, 20, 33, 34] described them. One RCT reported spot-bleeding [34] and one [19] mentioned occurrence of study-related serious adverse events such as hypertensive urgencies and congestive heart failure during follow-up. And minor adverse event such as pain was recorded in one trial [33].
Discussion
Principal Findings
Our meta-analysis suggested that acupuncture plus western medicine had a more significant effect on both SBP and DBP change magnitude than sham acupuncture plus medication, which indicated that acupuncture has an add-on effect for western medicine. Similarly, regarding efficacy rate, outcome proved that acupuncture in combination with western medicine was superior to sole medication.
By contrast, no significant differences were found in acupuncture versus western medicine for lowing both SBP and DBP after intervention, which was also supported by the meta-analysis regarding efficacy rate. And compared with lifestyle modification, acupuncture had no beneficial effect on SBP/DBP after intervention as well. Similarly, there were no significant differences between acupuncture and sham acupuncture regarding SBP change magnitude while acupuncture arms achieved significant effect modification on DBP change magnitude compared with sham acupuncture.
On the basic of on the outcomes above, our review showed favorable evidence of acupuncture as an add-on therapy to western medicine for hypertension. And the evidence for acupuncture alone treating hypertension is insufficient. Additionally, the safety of acupuncture is still uncertain because of the poor description and we could not rule out the possibility of exclusion bias.
Strengths and Limitation
Compared with previously published systematic reviews [4–7], pseudo-randomized trials simply claimed to be randomized with totally no description of random sequence generation were excluded in our review, thus only relatively rigidly designed RCTs were eligible. Besides, we also performed a meta-analysis regarding efficacy rate to evaluate effectiveness of acupuncture, which was absent in other 4 reviews [4–7]. Compared with the review of Zhao[9],we didn’t impose language restrictions during searching databases so 5 eligible RCTs[19,21,32–34] carried out in foreign countries were also included.
However, some limitations of our review should be addressed. Firstly, most included RCTs were published in Chinese journals so potential publication bias might exist due to different social cultural backgrounds. Chinese patients have a preference for acupuncture treatment compared to medical intervention and Asian countries are reported to be more likely to publish positive results in acupuncture researches [36]. Secondly, most eligible RCTs were classified as ‘unclear’ risk of bias of most domains. Especially, a majority of RCTs were in lack of the details of blinding which might lead to performance bias and detection bias, so the truth of these claimed RCTs would unavoidably be questionable. And substantial heterogeneity between studies was also detected in some subgroup analyses, with I2 values ranging from 0% to 94%. I2 has low statistical power with small numbers of studies and its confidence intervals could be large [11].Consequently, all current evidence might not be sufficiently robust against potential methodological flaws and significant heterogeneity. Thirdly, some included trials reported informal outcome measurement scales like efficacy rate. It means the percentage of the number of participants who are documented to achieve BP reduction markedly at the end of treatment. Regarding efficacy rate, the subgroup analysis showed that acupuncture plus medicine achieved more significant effect than medication alone. However, no significant differences were found in this subgroup regarding SBP and DBP after intervention. One plausible explanation for the conflicting results is that the currently definition of efficacy rate [35] is not very powerful and rational. It places more emphasis on the reduction of DBP to judge whether acupuncture is effective for treating hypertension. It may underestimate the importance of SBP reduction for hypertension. And this parameter is also relatively unclear and subjective because it could not reflect the extent of SBP/DBP reduction in precise measurement. So it is worth noting that, with respect to efficacy rate, the meta-analysis result should be interpreted in caution.
Implications for Future Trials
Regarding the risk of bias assessment of the included RCTs using the Cochrane criteria [8], the majority of trials were evaluated as ‘unclear’ risk of bias in these domains: (1) allocation concealment(2) blinding of participants and investigators(3) blinding of outcome assessment(4) withdrawals/dropouts. Considering these defects of current trials, for future rigorously designed RCTs, these methodological domains should be assured. And in our review, risk of other bias in most trials published in Chinese journals was rated‘low’ but was assessed as ‘high’ in most Korea and American RCTs, which could be explained by the situation that in Chinese acupuncture trials, Deqi sensation are generally obtained because Chinese acupuncturists regard it as an important role in better efficacy according to theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine(TCM).
Regarding measurement of BP, trial evidence indicates that even small differences in SBP of 2–4mmHg are clinically important, thus accurate measurement is vital [37]. And 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is vastly superior to the periodic non-automated blood pressure recordings using a cuff and sphygmomanometer. So we set an additional quality criterion of whether the RCTs involved 24-hour ambulatory monitoring and it turned out that only 3 trials [17, 21, 32] were qualified for this criterion.
As for acu-points selection, it is noteworthy that PC6 is well-known to have strong cardiovascular actions. Electric-acupuncture at the PC5–PC6 points had the potential to influence parasympathetic outflow and cardiovascular function in a rat model [38]. But we noticed that PC6 was not commonly used in the included RCTs. It turned out that only 4 trials used it [19,21,26,31]. Similarly finding was noted for ST9. On the basic of TCM theory, ST9 plays an important role in managing BP through ‘Qi’. Acupuncture at this point could stimulate the carotid sinus initiating the baroreflex. Thus, for future trials, some vital acu-points proposed in model studies should be taken into considerate account in acupuncture prescriptions during clinical practice.
With respect to manipulation method of acupuncture, as a TCM therapy, the effectiveness of acupuncture has close connection with acupuncturists' skills, competence and understanding of TCM theory [39]. After all, acupuncture is more than just sticking needles into specific points on the body. Considering it, some argued that acupuncture did lower blood pressure but the effect weaken or even lost when shoehorning it into a rigorously designed western-type clinical trial. Whereas, others criticized that the effect of acupuncture is not dependent on point locations or needling technique. The SHARP study bent over backwards to provide acupuncturists with diagnostic and treatment flexibility, yet no effect of acupuncture was found [19]. Patients were randomly assigned to each of 3 intervention groups using ‘individualized’ ‘standardized’ and ‘sham’ acupuncture. It turned out that all intervention groups experienced reductions in both SBP and DBP.
Besides, sham acupuncture was adopted as control in 5 of the RCTs [19,21,32–34]. However, sham acupuncture may not be appropriate as a placebo against which to evaluate the therapeutic effect of real acupuncture [40].Thus, seeking for an alternative sham control procedure may be a major goal in future acupuncture practice. Moreover, adequate serious consideration should be given in the future regarding other specific factors of acupuncture therapy, such as the treatment course, the frequency of sessions, since the dose of acupuncture is associated with the efficacy of acupuncture as well.
Conclusion
In summary, our review provided evidence of efficacy of acupuncture as an adjunctive therapy to western medicine for treating hypertension, while the evidence for acupuncture alone lowing BP is insufficient. Additionally, the safety of acupuncture is still uncertain due to the inadequate reporting of it.
A major limitation was the generally unclear risk of bias of most methodological domains. Therefore, more rigorously designed and large-scale RCTs are necessary in the future, which should assure particularly adequate concealment of allocation and blinding of outcome assessors and adopt standardized measurements as the primary outcomes measured at long-term follow-up. Besides, with the presence of high heterogeneity of the included studies, a firm conclusion still could not be drawn on the efficacy of acupuncture for treating hypertension.
Supporting Information
(DOC)
(DOC)
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
The current work was partially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2012CB518505) and the Inheritance Studio of famous veteran doctors of TCM of Xue-Ming Shi. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. The Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217–223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Ezzati M, Lopez AD, Rodgers A, Vander Hoorn S, Murray CJ. Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. The Lancet.2002;360(9343):1347–1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Zhang ZR. Acupuncture for hypertension. J Jiangxi Tradi Chin Med.1954; 5:53–55. [Google Scholar]
- 4. Lee H, Kim S-Y, Park J, Kim Y-j, Lee H, Park H-J. Acupuncture for lowering blood pressure: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Hypertens. 2009;22(1):122–128. 10.1038/ajh.2008.311 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kim L-W, Zhu J. Acupuncture for essential hypertension. Altern Ther Health Med. 2010;16(2):18–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Li D-Z, Zhou Y, Yang Y-N, Ma Y-T, Li X-M, Yu J, et al. Acupuncture for essential hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomized sham-controlled clinical trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Wang J, Xiong X, Liu W. Acupuncture for essential hypertension. Int J Cardiol. 2013;169(5):317–326. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Hu H-T, Zheng H-Z, Zhao X-F, Niu J-F. Letter regarding the article “Acupuncture for essential hypertension”. Int J Cardiol. 2014;177(2):610–615. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.09.121 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Zhao R, Fu LX, Xiong J, Li S, Wang ZL. The Effect of Acupuncture Therapy on Essential Hypertension:A Systematic Review of Long—term Effect. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion.2011; 27:46–51. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Higgins J, Altman D, Sterne J. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1. 0 [updated March 2011]. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version. 2011;5(0). [Google Scholar]
- 11. Deeks J, Higgins J, Altman D. Chapter 9: Analysing Data and Undertaking Meta-analyses: Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1. 0 [updated March 2011]. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version. 2011;5(0). [Google Scholar]
- 12. Zhao DJ, Fan QL. Effect of acupuncture on insulin resistance in the patient of hypertension. Zhongguo ZhenJiu.2003;23:165–167. [Google Scholar]
- 13. Wu QM, Feng GX. The correlation between hypertensive effect and plasma Ang II after warm acu-moxi on Kaisiguan(Extra) and Baihui(DV 20) points[article in Chinese]. New J Tradit Chin Med.2003; 35:45–47. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen J, Zou X. The clinical study of abdominal acupuncture therapy on essential hypertension. Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Master’s thesis;2006.
- 15. Chen J, Lee J, Wang ZR. Therapeutic effect on essential hypertension treated with combined therapy of acupuncture and medication. Zhongguo ZhenJiu.2010; 30:896–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Zhang CH, Zhou J, Wang Q, Ma X. Acupuncture for treatment of primary hypertension and effect on functions of vascular endothelium. Zhongguo ZhenJiu.2004; 24:539–540. [Google Scholar]
- 17. Yang DH. Effect of electroacupuncture on Quchi(LI11) and Taichong(L3) on blood pressure variability in young patients with hypertension. Zhongguo ZhenJiu.2010; 30:547–550 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Guo YH. Acupuncture treatment of hypertension clinical observation of insulin resistance. Acta Chin Med & Pharmacolo.2007; 35: 51 10.1016/j.ijom.2012.01.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Macklin EA, Wayne PM, Kalish LA, Valaskatgis P, Thompson J, Pian-Smith MC, et al. Stop Hypertension with the Acupuncture Research Program (SHARP) results of a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Hypertension. 2006;48(5):838–845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Lee XQ, Wang X, Wu HL. Acupuncture Taichong(LR3) point for the treatment of liver Yang hypertension pattern of hypertension randomized controlled clinical research. Liaoning J Tradi Chin Med.2008; 35:919–920. [Google Scholar]
- 21. Kim H-M, Cho S-Y, Park S-U, Sohn I-S, Jung W-S, Moon S-K, et al. Can acupuncture affect the circadian rhythm of blood pressure? A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. J Altern Complement Med. 2012;18(10):918–923. 10.1089/acm.2011.0508 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Wei Y, Sun ZR, Kou JY, Guo Y. Clinical observation of acupuncting Renying Point for lower hypertension. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion.2006; 22: 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- 23. Wan WJ, Ma ZY, Xiong XA,Wang L, Ding L, Zhang YX, et al. Clinical observation on therapeutic effect of electro-acupuncture at Quchi(LI 11) for treatment of essential hypertension. Zhongguo ZhenJiu.2009; 29:349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Qu T, Chen BG, Zhang HX, Zhou ZY, Li JW. Clinical research of acupuncting Fengchi point for hypertension. Hubei J Tradi Chin Med.2009; 31:8–9. [Google Scholar]
- 25. Chen BG, Qian CY, Zhang JN, Mao HR. Clinical observations on the hypertensive effect of point Fengchi acupuncture on hypertension. Shanghai ZhenJiu.2006; 25:15–16. [Google Scholar]
- 26. Huang F, Yao GX, Huang XL, Liu YN. Clinical observation on acupuncture for treatment of hypertension of phlegm-stasis blocking collateral type. Zhongguo ZhenJiu.2007; 27:403–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Feng GX, Wu QM. Clinical study treatment of essential hypertension with acupuncture at ‘Siguan’ points Pinus warming acupuncture-moxibustion at Baihui (GV20) point. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu.2003; 23:193–195. [Google Scholar]
- 28. Shen ZK, Shao CH, Jiang PY, Zhang HY, Yan QH, Chen KZ, et al. Clinical observation on acupuncture Zusanli and western medicine for treatment of 25 patients with resistant hypertension. Shanxi J Tradit Chin Med.2007; 28:1377–1379. [Google Scholar]
- 29. Yang Y, Zhou GT. A comparative study of the acupuncture formula in the treatment of hypertension. Acta Chin Med Pharmacol.2010; 38:106–107. [Google Scholar]
- 30. Ma CY, Wang YF, Wan WJ, Xiong XA, Wang Y, Wang L, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on Quchi (LI 11) on concentration of plasma NPY and NT in the patients with essential hypertension. New J Tradit Chin Med.2011; 43:89–91. [Google Scholar]
- 31. Liao H, Li DP, Chen Q, Yi L. Observation on therapeutic effect of ‘reducing south and reinforcing north’, needling method on hypertension of type of yang-hyperactivity due to yin-deficiency. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu.2006; 26:92–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Kraft K, Coulon S. Der Einfluss einer standardisierten Akupunkturbehandlung auf Beschwerden, Blutdruck und Serumlipide hypertensiver, postmenopausaler Frauen. Randomisierte, kontrollierte klinische Studie. Forsch Komplementarmed.1999; 6(2):74–79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Flachskampf FA, Gallasch J, Gefeller O, Gan J, Mao J, Pfahlberg AB, et al. Randomized trial of acupuncture to lower blood pressure. Circulation. 2007; 115(24):3121–3129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Yin C, Seo B, Park H-J, Cho M, Jung W, Choue R, et al. Acupuncture, a promising adjunctive therapy for essential hypertension: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Neurol Res. 2007;29(Supplement-1):98–103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Ma CY. Guiding principle of clinical research on new drugs of traditional Chinese Medicine. China: Press of Medical Science and Technology; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 36. Vickers A, Goyal N, Harland R, Rees R. Do certain countries produce only positive results? A systematic review of controlled trials. Control Clin Trials. 1998;19(2):159–166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Pater C. Beyond the Evidence of the New Hypertension Guidelines. Blood pressure measurement—is it good enough for accurate diagnosis of hypertension? Time might be in, for a paradigm shift (I). Curr Control Trials Cardiovasc Med.2005; 6: 6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Tjen-A-Looi SC, Guo Z-L, Li M, Longhurst JC. Medullary GABAergic mechanisms contribute to electroacupuncture modulation of cardiovascular depressor responses during gastric distention in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013;304(5):R321–332. 10.1152/ajpregu.00451.2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Liu T. Role of acupuncturists in acupuncture treatment. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2007;4(1):3–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Madsen MV, Gøtzsche PC, Hróbjartsson A. Acupuncture treatment for pain: systematic review of randomised clinical trials with acupuncture, placebo acupuncture, and no acupuncture groups. BMJ.2009; 338:a3115 10.1136/bmj.a3115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(DOC)
(DOC)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.