Abstract
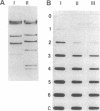
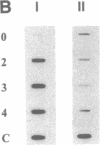
A novel assay to detect strand-specific DNA repair after cellular exposure to cisplatin at IC50 levels, is used to measure rapid repair in the divergent upstream gene (DUG), a human MutS homolog, and in the bidirectional promoter for dihydrofolate reductase gene (DHFR) and the contiguous upstream DUG. Single-stranded DNA capable of hybridizing to gene-specific probes is generated enzymatically by the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of T4 DNA polymerase. The presence of cisplatin lesions inhibit the exonucleolytic activity of T4 DNA polymerase and block the formation of single-stranded DNA. This decreases the amount of complementary sequence produced when assayed by gene-specific probe hybridization. With the progression of repair, increasing quantities of single-stranded DNA become available for probe hybridization. This assay was applied to human A2780 ovarian carcinoma cells treated with cisplatin at the beginning of G1 phase. A dose-response experiment showed that the assay was applicable down to cisplatin concentrations of 2.5 microM. To assay for strand-specific gene repair, the synchronized cells were treated with cisplatin and then allowed time to repair in drug-free medium. Extensive removal of cisplatin lesions after 2 hr of cellular repair during early G1 phase in the DUG and the DUG/DHFR promoter was measured, with no evidence of repair in the unexpressed delta-globin gene. The extent of preferential DNA repair was much more distinct than has been observed previously at high-drug dosage in asynchronous cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohr V. A. Gene specific DNA repair. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Nov;12(11):1983–1992. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.11.1983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Okumoto D. S., Hanawalt P. C. Survival of UV-irradiated mammalian cells correlates with efficient DNA repair in an essential gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3830–3833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn S. L., Pil P. M., Essigmann J. M., Housman D. E., Lippard S. J. Isolation and characterization of human cDNA clones encoding a high mobility group box protein that recognizes structural distortions to DNA caused by binding of the anticancer agent cisplatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2307–2311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G. Cellular responses to cisplatin. The roles of DNA-binding proteins and DNA repair. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):787–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. It was a very good year for DNA repair. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch P. W., Chan G. L., Haseltine W. A. T4 DNA polymerase (3'-5') exonuclease, an enzyme for the detection and quantitation of stable DNA lesions: the ultraviolet light example. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3285–3304. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapkin R., Sancar A., Reinberg D. Where transcription meets repair. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman A. Reevaluation of interaction of cis-dichloro(ethylenediamine)platinum(II) with DNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3912–3915. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichtinger-Schepman A. M., van der Veer J. L., den Hartog J. H., Lohman P. H., Reedijk J. Adducts of the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) with DNA: formation, identification, and quantitation. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):707–713. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii H., Shimada T. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones derived from the divergently transcribed gene in the region upstream from the human dihydrofolate reductase gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10057–10064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. M., Lehman I. R. On the exonuclease activity of phage T4 deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3139–3146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Ali-Osman F. Glutathione-associated cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) metabolism and ATP-dependent efflux from leukemia cells. Molecular characterization of glutathione-platinum complex and its biological significance. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20116–20125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennerwein M. M., Eastman A. A polymerase chain reaction-based method to detect cisplatin adducts in specific genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6209–6214. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowski D. P., Illenye S., Van Houten B. Analysis of DNA damage and repair in murine leukemia L1210 cells using a quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3485–3494. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler D. R., Hanawalt P. C. Digestion of damaged DNA by the T7 DNA polymerase-exonuclease. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):451–453. doi: 10.1042/bj2930451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larminat F., Zhen W., Bohr V. A. Gene-specific DNA repair of interstrand cross-links induced by chemotherapeutic agents can be preferential. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2649–2654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loehrer P. J., Einhorn L. H. Drugs five years later. Cisplatin. Ann Intern Med. 1984 May;100(5):704–713. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-5-704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miltenberger R. J., Cortner J., Farnham P. J. An inhibitory Raf-1 mutant suppresses expression of a subset of v-raf-activated genes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15674–15680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P. Mechanisms and biological effects of mismatch repair. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:229–253. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New L., Liu K., Crouse G. F. The yeast gene MSH3 defines a new class of eukaryotic MutS homologues. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 May;239(1-2):97–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00281607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. J., Eastman A., Bostick-Bruton F., Reed E. Acquired cisplatin resistance in human ovarian cancer cells is associated with enhanced repair of cisplatin-DNA lesions and reduced drug accumulation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):772–777. doi: 10.1172/JCI115080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampino N. J., Johnston P. G. Microfluorometric size measurements of human and phage DNA correlate with the degree of in vitro cisplatin treatment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1344–1351. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91721-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage E., Moustacchi E. Sequence context effects on 8-methoxypsoralen photobinding to defined DNA fragments. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3307–3314. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymkowski D. E., Yarema K., Essigmann J. M., Lippard S. J., Wood R. D. An intrastrand d(GpG) platinum crosslink in duplex M13 DNA is refractory to repair by human cell extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10772–10776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. G., Setlow R. B. Inactivation of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase in HeLa cells by cisplatin. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Sep;10(9):1681–1684. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.9.1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. K., Masters J. N., Attardi G. Human dihydrofolate reductase gene organization. Extensive conservation of the G + C-rich 5' non-coding sequence and strong intron size divergence from homologous mammalian genes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 25;176(2):169–187. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhen W., Link C. J., Jr, O'Connor P. M., Reed E., Parker R., Howell S. B., Bohr V. A. Increased gene-specific repair of cisplatin interstrand cross-links in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3689–3698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]