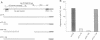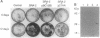Abstract
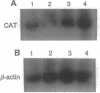
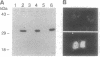
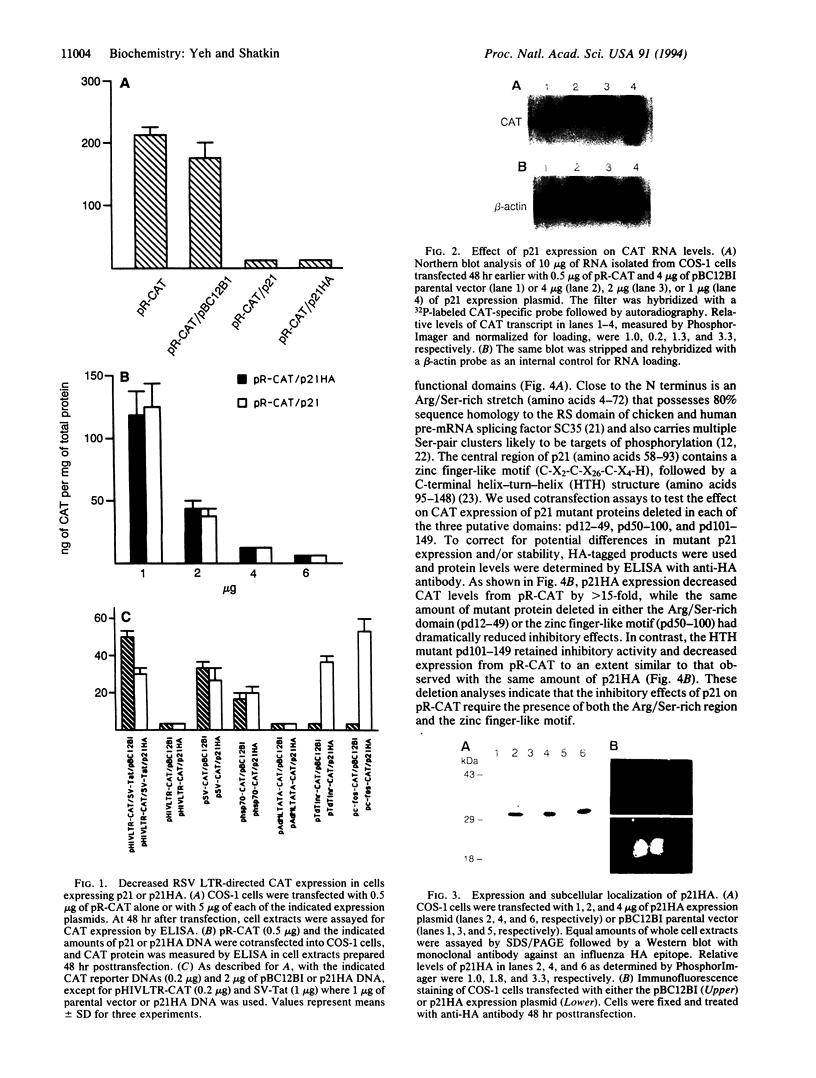
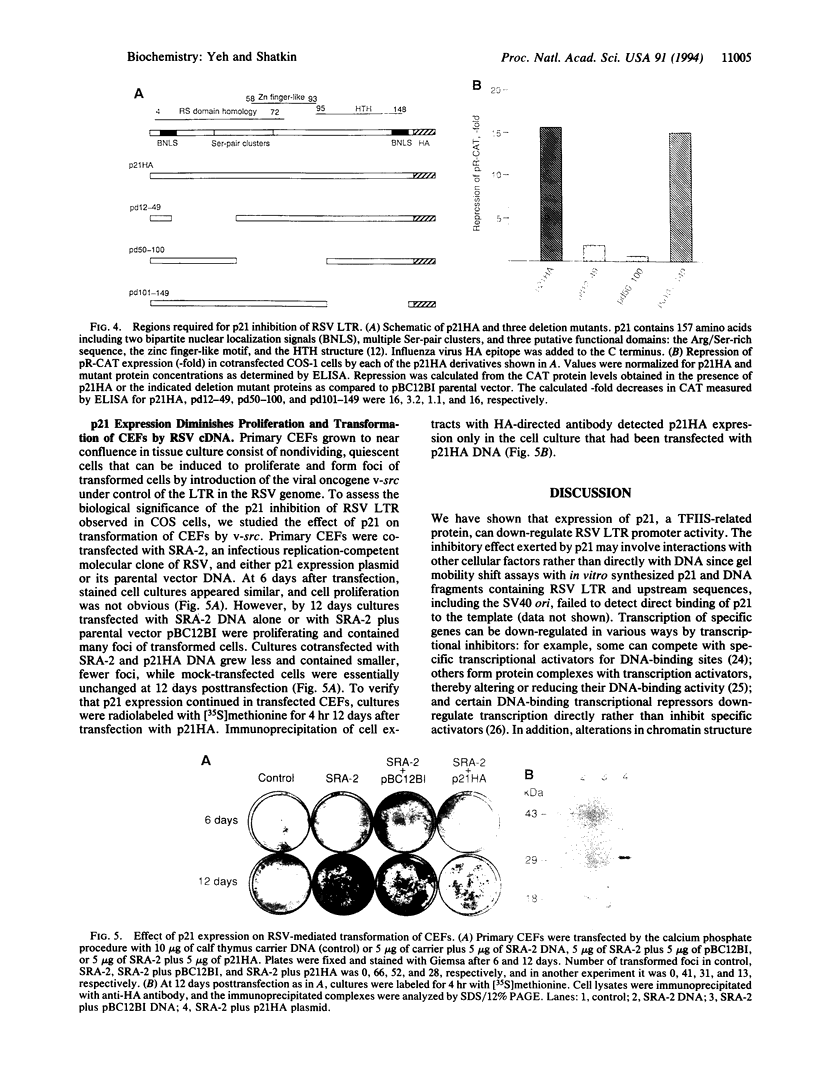
We have previously isolated a HeLa cell cDNA encoding a 21-kDa polypeptide that is 48% similar to transcription factor IIS. To explore the possibility that p21 plays a role in transcriptional regulation in vivo, we tested the effect of p21 expression on the synthesis of reporter chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) in transfected COS-1 cells. CAT formation under control of the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat (RSV LTR) promoter was decreased nearly 20-fold in cells coexpressing p21. In contrast, CAT production under control of other sequence elements was only slightly reduced (human immunodeficiency virus type 1 LTR, simian virus 40 early promoter), unaffected (human heat shock protein of 70-kDa promoter, adenovirus major late promoter TATA box), or increased (terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase initiator element, c-fos promoter) by p21 coexpression as compared to cells cotransfected with the parental vector. The abundance of steady-state CAT transcripts from RSV LTR was also decreased by p21 expression in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that transcription of RSV LTR/CAT is under negative control by p21. Consistent with an effect on transcription, p21 was localized in nuclei of transfected cells. Deletion analysis of p21 indicated that the sequences essential for inhibition of RSV LTR function include the previously identified ARg/Ser-rich region and zinc finger-like motif. Proliferation of chicken embryo fibroblasts transfected with an infectious molecular clone of RSV was diminished by p21 expression, which also resulted in fewer transformed foci.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal K., Baek K. H., Jeon C. J., Miyamoto K., Ueno A., Yoon H. S. Stimulation of transcript elongation requires both the zinc finger and RNA polymerase II binding domains of human TFIIS. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 6;30(31):7842–7851. doi: 10.1021/bi00245a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulden A., Sealy L. Identification of a third protein factor which binds to the Rous sarcoma virus LTR enhancer: possible homology with the serum response factor. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):204–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S. The basics of basal transcription by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Functional analysis of the transcription control region located within the avian retroviral long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):438–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Transcriptional activity of avian retroviral long terminal repeats directly correlates with enhancer activity. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.515-521.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T., Karin M. JunB differs from c-Jun in its DNA-binding and dimerization domains, and represses c-Jun by formation of inactive heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):479–490. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber M., Sealy L. Rous sarcoma virus enhancer factor I is a ubiquitous CCAAT transcription factor highly related to CBF and NF-Y. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22243–22254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Isolation of a complementary DNA that encodes the mammalian splicing factor SC35. Science. 1992 Apr 24;256(5056):535–538. doi: 10.1126/science.1373910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Zuo P., Manley J. L. Primary structure of the human splicing factor ASF reveals similarities with Drosophila regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90626-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giantini M., Shatkin A. J. Stimulation of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase mRNA translation by reovirus capsid polypeptide sigma 3 in cotransfected COS cells. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2415–2421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2415-2421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Negative effect of the transcriptional activator GAL4. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):721–724. doi: 10.1038/334721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Parsons J. T. Identification of transcriptional elements within the long terminal repeat of Rous sarcoma virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1834–1845. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H. Identification of three sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins which interact with the Rous sarcoma virus enhancer and upstream promoter elements. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2186–2190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2186-2190.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression by the Drosophila even-skipped protein: definition of a minimal repression domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):491–503. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Weiner A. M. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA requires compatible snRNA promoter elements. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Pastan I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human DNA binding factor that represses transcription. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Krebs E. G. Consensus sequences as substrate specificity determinants for protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15555–15558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Grossel M. J., Figge J., Hansen U. M. Drosophila Krüppel protein is a transcriptional repressor. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):76–79. doi: 10.1038/346076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. H., Vartikar J., Pipas J. M., Laimins L. A. Specific repression of TATA-mediated but not initiator-mediated transcription by wild-type p53. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):281–283. doi: 10.1038/363281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. The structure and function of retroviral long terminal repeats. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:49–92. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. RNA splicing. Question of commitment. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):14–14. doi: 10.1038/365014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulia T., Krumm A., Groudine M. Distinct properties of c-myc transcriptional elongation are revealed in Xenopus oocytes and mammalian cells and by template titration, 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole (DRB), and promoter mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5647–5658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H., Asselin C., Dufort D., Yang J. Q., Gupta K., Marcu K. B., Nepveu A. A cis-acting element in the promoter region of the murine c-myc gene is necessary for transcriptional block. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5340–5349. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryden T. A., Beemon K. Avian retroviral long terminal repeats bind CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1155–1164. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha S., Brickman J. M., Lehming N., Ptashne M. New eukaryotic transcriptional repressors. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):648–652. doi: 10.1038/363648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey L., Chalkley R. At least two nuclear proteins bind specifically to the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):787–798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiest D. K., Hawley D. K. In vitro analysis of a transcription termination site for RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5782–5795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Transcription: in tune with the histones. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):13–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B., Hunt C., Morimoto R. Structure and expression of the human gene encoding major heat shock protein HSP70. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):330–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh C. H., Shatkin A. J. A HeLa-cell-encoded p21 is homologous to transcription elongation factor SII. Gene. 1994 Jun 10;143(2):285–287. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II: a multi-step process. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;44:67–108. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vegvar H. E., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. 3' end formation of U1 snRNA precursors is coupled to transcription from snRNA promoters. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]