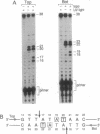
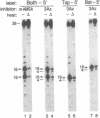
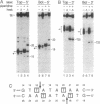
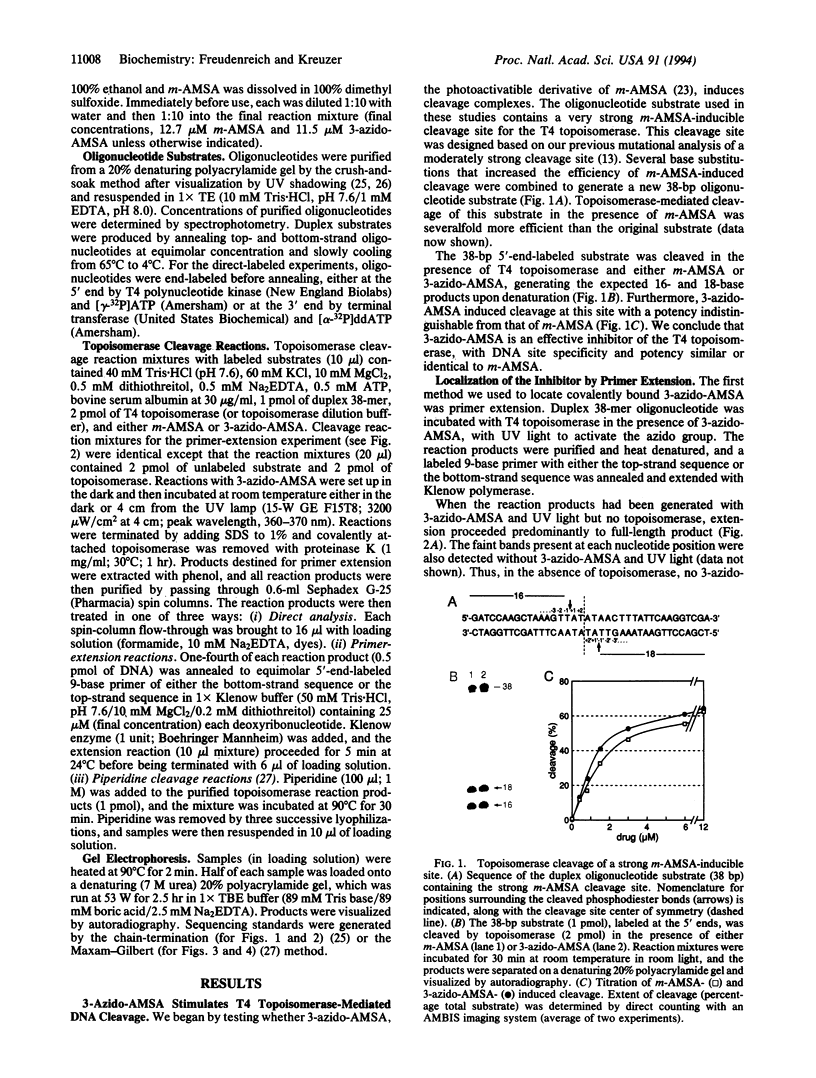
Abstract
Type II topoisomerases are the targets of several classes of chemotherapeutic agents that stabilize an intermediate of the catalytic cycle with the enzyme covalently linked to cleaved DNA. We have used 3-azido-AMSA [4'-(3-azido-9-acridinylamino)methanesulfon-m-anisidide], a photo-activatible analog of the inhibitor m-AMSA [4'-(9-acridinylamino)methanesulfon-m-anisidide], to localize the inhibitor binding site in a cleavage complex consisting of an oligonucleotide substrate and the bacteriophage T4 type II DNA topoisomerase. Upon photoactivation, the inhibitor covalently attached to the substrate only in the presence of topoisomerase. Sites of inhibitor attachment were detected by primer-extension analysis and by piperidine-induced cleavage of the covalently modified substrate. 3-Azido-AMSA reacted with bases immediately adjacent to the two phosphodiester bonds cleaved by the enzyme. Therefore, topoisomerase creates or stabilizes preferential binding sites for the inhibitor precisely at the two sites of DNA cleavage.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Capranico G., De Isabella P., Tinelli S., Bigioni M., Zunino F. Similar sequence specificity of mitoxantrone and VM-26 stimulation of in vitro DNA cleavage by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 30;32(12):3038–3046. doi: 10.1021/bi00063a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capranico G., Kohn K. W., Pommier Y. Local sequence requirements for DNA cleavage by mammalian topoisomerase II in the presence of doxorubicin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6611–6619. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capranico G., Tinelli S., Zunino F., Kohn K. W., Pommier Y. Effects of base mutations on topoisomerase II DNA cleavage stimulated by mAMSA in short DNA oligomers. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 12;32(1):145–152. doi: 10.1021/bi00052a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capranico G., Zunino F. DNA topoisomerase-trapping antitumour drugs. Eur J Cancer. 1992;28A(12):2055–2060. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(92)90255-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Joyce C. M., Beardsley G. P. Novel blunt-end addition reactions catalyzed by DNA polymerase I of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 5;198(1):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arpa P., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase-targeting antitumor drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 17;989(2):163–177. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Isabella P., Capranico G., Zunino F. The role of topoisomerase II in drug resistance. Life Sci. 1991;48(23):2195–2205. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Franco R. J. Inhibitors of DNA topoisomerases. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2253–2259. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossé P., René B., Le Bret M., Paoletti C., Saucier J. M. Sequence requirements for mammalian topoisomerase II mediated DNA cleavage stimulated by an ellipticine derivative. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2861–2868. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenreich C. H., Kreuzer K. N. Differentially labeled mutant oligonucleotides for analysis of protein-DNA interactions. Biotechniques. 1994 Jan;16(1):104–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenreich C. H., Kreuzer K. N. Mutational analysis of a type II topoisomerase cleavage site: distinct requirements for enzyme and inhibitors. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2085–2097. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05857.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Liu L. F. Evidence for the reversibility of cellular DNA lesion induced by mammalian topoisomerase II poisons. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9713–9715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff A. C., Ward R. E., 4th, Kreuzer K. N. Mutational alteration of the breakage/resealing subunit of bacteriophage T4 DNA topoisomerase confers resistance to antitumor agent m-AMSA. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Mar;221(1):27–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00280363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaxel C., Capranico G., Kerrigan D., Kohn K. W., Pommier Y. Effect of local DNA sequence on topoisomerase I cleavage in the presence or absence of camptothecin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20418–20423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Jongeneel C. V. Escherichia coli phage T4 topoisomerase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:144–160. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leteurtre F., Fesen M., Kohlhagen G., Kohn K. W., Pommier Y. Specific interaction of camptothecin, a topoisomerase I inhibitor, with guanine residues of DNA detected by photoactivation at 365 nm. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 31;32(34):8955–8962. doi: 10.1021/bi00085a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Morris D. R. Sites of reaction of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase on pBR322 in vivo as revealed by oxolinic acid-induced plasmid linearization. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A., Gellert M. Mechanistic aspects of DNA topoisomerases. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:69–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A. The molecular basis of quinolone action. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Oct;30(4):409–414. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.4.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Cozzarelli N. R. Site-specific cleavage of DNA by E. coli DNA gyrase. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier Y., Capranico G., Orr A., Kohn K. W. Local base sequence preferences for DNA cleavage by mammalian topoisomerase II in the presence of amsacrine or teniposide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5973–5980. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece R. J., Maxwell A. DNA gyrase: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(3-4):335–375. doi: 10.3109/10409239109114072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Kohlbrenner W. E., Weigl D., Baranowski J. Mechanism of quinolone inhibition of DNA gyrase. Appearance of unique norfloxacin binding sites in enzyme-DNA complexes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2973–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Mitscher L. A., Sharma P. N., O'Donnell T. J., Chu D. W., Cooper C. S., Rosen T., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by quinolone antibacterials: a cooperative drug--DNA binding model. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3886–3894. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh T. L., Hoyos P., Kolodziej E., Stowell J. G., Baird W. M., Byrn S. R. Properties of the nucleic acid photoaffinity labeling agent 3-azidoamsacrine. J Med Chem. 1990 Apr;33(4):1225–1230. doi: 10.1021/jm00166a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan D. M., Latham M. D., Rowe T. C., Ross W. E. Purification and characterization of an altered topoisomerase II from a drug-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5680–5687. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmott C. J., Maxwell A. A single point mutation in the DNA gyrase A protein greatly reduces binding of fluoroquinolones to the gyrase-DNA complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jan;37(1):126–127. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwelling L. A., Hinds M., Chan D., Mayes J., Sie K. L., Parker E., Silberman L., Radcliffe A., Beran M., Blick M. Characterization of an amsacrine-resistant line of human leukemia cells. Evidence for a drug-resistant form of topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16411–16420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]