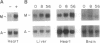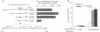Abstract
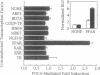
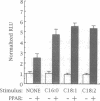
Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) catalyzes a pivotal reaction in mitochondrial fatty acid (FA) beta-oxidation. To examine the potential role of FAs and their metabolites in the regulation of MCAD gene expression, we measured MCAD mRNA levels in animals fed inhibitors of mitochondrial long-chain FA import. Administration of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I inhibitors to mice or rats resulted in tissue-limited increases in steady-state MCAD mRNA levels. HepG2 cell cotransfection experiments with MCAD promoter reporter plasmids demonstrated that this was a transcriptional effect mediated by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR). The activity mapped to a nuclear receptor response element that functioned in a heterologous promoter context and specifically bound immunoreactive PPAR in rat hepatic nuclear extracts, confirming an in vivo interaction. PPAR-mediated transactions of this promoter and element were also induced by exogenously added FA and fibric acid derivatives. Induction of PPAR transactivation by perturbation of this discrete metabolic step is unusual and indicates that intracellular FA metabolites that accumulate during such inhibition can regulate MCAD expression and are likely candidates for PPAR ligand(s). These results dictate an expanded role for the PPAR in the regulation of FA metabolism.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baes M., Gulick T., Choi H. S., Martinoli M. G., Simha D., Moore D. D. A new orphan member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that interacts with a subset of retinoic acid response elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1544–1552. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. E., Gulick T., Moore D. D., Kelly D. P. A pleiotropic element in the medium-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene promoter mediates transcriptional regulation by multiple nuclear receptor transcription factors and defines novel receptor-DNA binding motifs. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4360–4372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. E., Gulick T., Raisher B. D., Caira T., Ladias J. A., Moore D. D., Kelly D. P. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 activates medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene transcription by interacting with a complex regulatory element. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13805–13810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer C., Krey G., Keller H., Givel F., Helftenbein G., Wahli W. Control of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway by a novel family of nuclear hormone receptors. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas B., Harding H. P., Choi H. S., Lehmann K. A., Chung M., Lazar M. A., Moore D. D. A new orphan member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily closely related to Rev-Erb. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Aug;8(8):996–1005. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.8.7997240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebel T., Arand M., Oesch F. Induction of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor by fenofibrate in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 31;309(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80734-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlicher M., Demoz A., Svensson D., Tollet P., Berge R. K., Gustafsson J. A. Structural and metabolic requirements for activators of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Dec 14;46(12):2177–2184. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90607-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlicher M., Widmark E., Li Q., Gustafsson J. A. Fatty acids activate a chimera of the clofibric acid-activated receptor and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4653–4657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issemann I., Green S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):645–650. doi: 10.1038/347645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issemann I., Prince R., Tugwood J., Green S. A role for fatty acids and liver fatty acid binding protein in peroxisome proliferation? Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Nov;20(4):824–827. doi: 10.1042/bst0200824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaikaus R. M., Chan W. K., Lysenko N., Ray R., Ortiz de Montellano P. R., Bass N. M. Induction of peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation and liver fatty acid-binding protein by peroxisome proliferators. Mediation via the cytochrome P-450IVA1 omega-hydroxylase pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9593–9603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H., Dreyer C., Medin J., Mahfoudi A., Ozato K., Wahli W. Fatty acids and retinoids control lipid metabolism through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-retinoid X receptor heterodimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. P., Gordon J. I., Alpers R., Strauss A. W. The tissue-specific expression and developmental regulation of two nuclear genes encoding rat mitochondrial proteins. Medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase and mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):18921–18925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Noonan D. J., Heyman R. A., Evans R. M. Convergence of 9-cis retinoic acid and peroxisome proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of their receptors. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):771–774. doi: 10.1038/358771a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladias J. A., Karathanasis S. K. Regulation of the apolipoprotein AI gene by ARP-1, a novel member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Science. 1991 Feb 1;251(4993):561–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1899293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muerhoff A. S., Griffin K. J., Johnson E. F. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor mediates the induction of CYP4A6, a cytochrome P450 fatty acid omega-hydroxylase, by clofibric acid. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19051–19053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao M., Parimoo B., Tanaka K. Developmental, nutritional, and hormonal regulation of tissue-specific expression of the genes encoding various acyl-CoA dehydrogenases and alpha-subunit of electron transfer flavoprotein in rat. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24114–24124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gunning P., Blau H., Kedes L. Human actin genes are single copy for alpha-skeletal and alpha-cardiac actin but multicopy for beta- and gamma-cytoskeletal genes: 3' untranslated regions are isotype specific but are conserved in evolution. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1783–1791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisher B. D., Gulick T., Zhang Z., Strauss A. W., Moore D. D., Kelly D. P. Identification of a novel retinoid-responsive element in the promoter region of the medium chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20264–20269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez J. C., Gil-Gómez G., Hegardt F. G., Haro D. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor mediates induction of the mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase gene by fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):18767–18772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. A., Hale D. E., Coates P. M., Hall C. L., Corkey B. E., Yang W., Kelley R. I., Gonzales E. L., Williamson J. R., Baker L. Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency in children with non-ketotic hypoglycemia and low carnitine levels. Pediatr Res. 1983 Nov;17(11):877–884. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198311000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens T. W., Higgins A. J., Cook G. A., Harris R. A. Two mechanisms produce tissue-specific inhibition of fatty acid oxidation by oxfenicine. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 15;227(2):651–660. doi: 10.1042/bj2270651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugwood J. D., Issemann I., Anderson R. G., Bundell K. R., McPheat W. L., Green S. The mouse peroxisome proliferator activated receptor recognizes a response element in the 5' flanking sequence of the rat acyl CoA oxidase gene. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):433–439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05072.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull D. M., Bartlett K., Younan S. I., Sherratt H. S. The effects of 2[5(4-chlorophenyl)pentyl]oxirane-2-carbonyl-Co-A on mitochondrial oxidations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Feb 1;33(3):475–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Fahrner T. J., Johnston M., Milbrandt J. Identification of the DNA binding site for NGFI-B by genetic selection in yeast. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1296–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.1925541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Marcus S. L., Sajjadi F. G., Alvares K., Reddy J. K., Subramani S., Rachubinski R. A., Capone J. P. Identification of a peroxisome proliferator-responsive element upstream of the gene encoding rat peroxisomal enoyl-CoA hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7541–7545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. F., Kelly D. P., Kim J. J., Zhou Y. Q., Ogden M. L., Whelan A. J., Strauss A. W. Structural organization and regulatory regions of the human medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):81–89. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]