Abstract
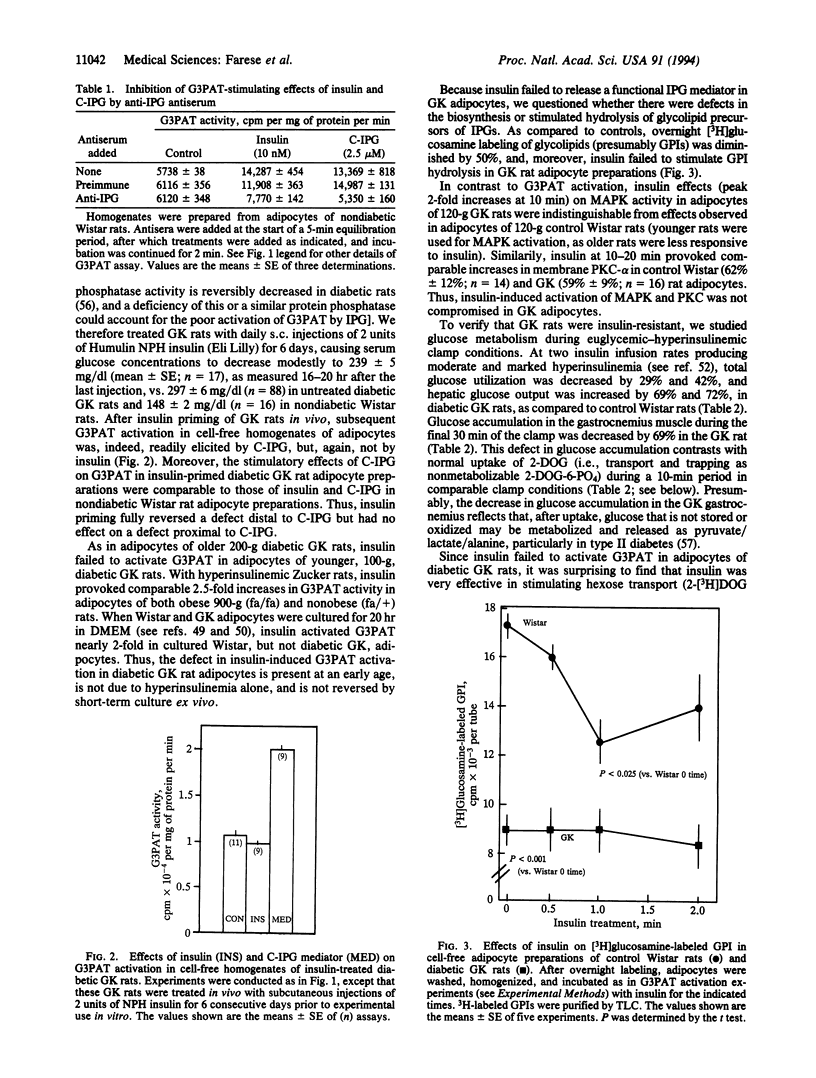
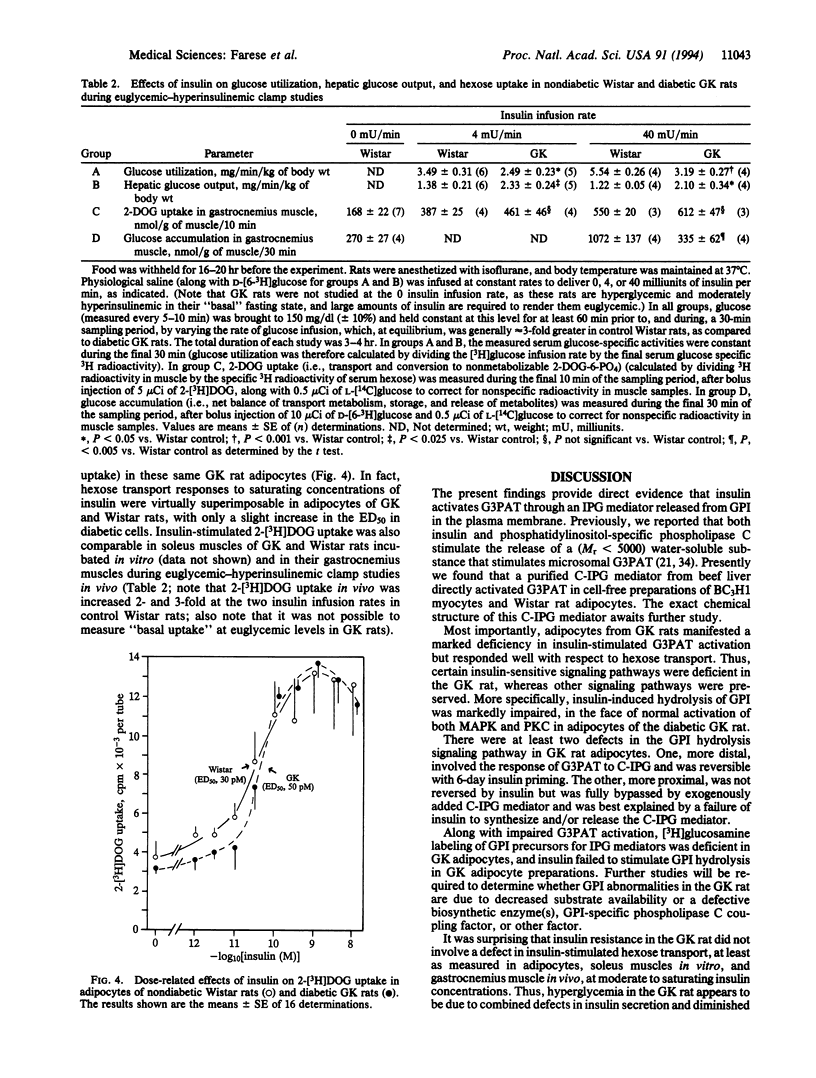
Type II diabetic Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rats were insulin-resistant in euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp studies. We therefore examined insulin signaling systems in control Wistar and diabetic GK rats. Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (G3PAT), which is activated by headgroup mediators released from glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI), was activated by insulin in intact and cell-free adipocyte preparations of control, but not diabetic, rats. A specific chiro-inositol-containing inositol phosphoglycan (IPG) mediator, prepared from beef liver, bypassed this defect and comparably activated G3PAT in cell-free adipocyte preparations of both diabetic GK and control rats. A myo-inositol-containing IPG mediator did not activate G3PAT. Relative to control adipocytes, labeling of GPI by [3H]glucosamine was diminished by 50% and insulin failed to stimulate GPI hydrolysis in GK adipocytes. In contrast to GPI-dependent G3PAT activation, insulin-stimulated hexose transport was intact in adipocytes and soleus and gastrocnemius muscles of the GK rat, as was insulin-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and protein kinase C. We conclude that (i) chiro-inositol-containing IPG mediator activates G3PAT during insulin action, (ii) diabetic GK rats have a defect in synthesizing or releasing functional chiro-inositol-containing IPG, and (iii) defective IPG-regulated intracellular glucose metabolism contributes importantly to insulin resistance in diabetic GK rats.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold T. P., Standaert M. L., Hernandez H., Watson J., Mischak H., Kazanietz M. G., Zhao L., Cooper D. R., Farese R. V. Effects of insulin and phorbol esters on MARCKS (myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate) phosphorylation (and other parameters of protein kinase C activation) in rat adipocytes, rat soleus muscle and BC3H-1 myocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 1;295(Pt 1):155–164. doi: 10.1042/bj2950155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asplin I., Galasko G., Larner J. chiro-inositol deficiency and insulin resistance: a comparison of the chiro-inositol- and the myo-inositol-containing insulin mediators isolated from urine, hemodialysate, and muscle of control and type II diabetic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5924–5928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini P. M., Zannetti A., Donchenko V., Dini L., Luly P. Insulin effect on isolated rat hepatocytes: diacylglycerol-phosphatidic acid interrelationship. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Oct 27;1137(2):208–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90203-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltensperger K., Kozma L. M., Cherniack A. D., Klarlund J. K., Chawla A., Banerjee U., Czech M. P. Binding of the Ras activator son of sevenless to insulin receptor substrate-1 signaling complexes. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1950–1952. doi: 10.1126/science.8391166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begum N., Sussman K. E., Draznin B. Differential effects of diabetes on adipocyte and liver phosphotyrosine and phosphoserine phosphatase activities. Diabetes. 1991 Dec;40(12):1620–1629. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.12.1620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K., Galasko G., Huang L., Kellogg J., Larner J. Studies on the insulin mediator. II. Separation of two antagonistic biologically active materials from fraction II. Diabetes. 1980 Aug;29(8):659–661. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.8.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., Konda T. S., Standaert M. L., Davis J. S., Pollet R. J., Farese R. V. Insulin increases membrane and cytosolic protein kinase C activity in BC3H-1 myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3633–3639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Lavoinne A., Nakielny S., Caudwell F. B., Watt P., Cohen P. The molecular mechanism by which insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis in mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):302–308. doi: 10.1038/348302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan J. J., Saltis J., Wek S. A., Simpson I. A., Londos C. Insulin, oxytocin, and vasopressin stimulate protein kinase C activity in adipocyte plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1052–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Barnes D. E., Davis J. S., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J. Effects of insulin and protein synthesis inhibitors on phospholipid metabolism, diacylglycerol levels, and pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in BC3H-1 cultured myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7094–7100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Cooper D. R., Konda T. S., Nair G., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J. Insulin provokes co-ordinated increases in the synthesis of phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylinositol phosphates and the phosphatidylinositol-glycan in BC3H-1 myocytes. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):185–188. doi: 10.1042/bj2560185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Standaert M. L., Arnold T., Yu B., Ishizuka T., Hoffman J., Vila M., Cooper D. R. The role of protein kinase C in insulin action. Cell Signal. 1992 Mar;4(2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(92)90077-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Standaert M. L., Francois A. J., Ways K., Arnold T. P., Hernandez H., Cooper D. R. Effects of insulin and phorbol esters on subcellular distribution of protein kinase C isoforms in rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):319–323. doi: 10.1042/bj2880319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folli F., Saad M. J., Backer J. M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and association with insulin receptor substrate 1 in liver and muscle of the intact rat. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22171–22177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García de Herreros A., Dominguez I., Diaz-Meco M. T., Graziani G., Cornett M. E., Guddal P. H., Johansen T., Moscat J. Requirement of phospholipase C-catalyzed hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine for maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes in response to insulin and ras p21. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6825–6829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Sim A. T., Carling D., Honnor R. C., Tsukitani Y., Cohen P., Hardie D. G. Effects of the tumour promoter okadaic acid on intracellular protein phosphorylation and metabolism. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):78–81. doi: 10.1038/337078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich K. A., Toledo S. P., Brunton L. L., Watson M. J., Daniel-Issakani S., Strulovici B. Insulin stimulates the activity of a novel protein kinase C, PKC-epsilon, in cultured fetal chick neurons. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15076–15082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. M., Standaert M. L., Nair G. P., Farese R. V. Differential effects of pertussis toxin on insulin-stimulated phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis and glycerolipid synthesis de novo. Studies in BC3H-1 myocytes and rat adipocytes. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3315–3322. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka T., Cooper D. R., Farese R. V. Insulin stimulates the translocation of protein kinase C in rat adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):337–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81565-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka T., Cooper D. R., Hernandez H., Buckley D., Standaert M., Farese R. V. Effects of insulin on diacylglycerol-protein kinase C signaling in rat diaphragm and soleus muscles and relationship to glucose transport. Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):181–190. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. L., Mato J. M., Merida I., Jarett L. Glucose transport and antilipolysis are differentially regulated by the polar head group of an insulin-sensitive glycophospholipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6404–6407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennington A. S., Hill C. R., Craig J., Bogardus C., Raz I., Ortmeyer H. K., Hansen B. C., Romero G., Larner J. Low urinary chiro-inositol excretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 9;323(6):373–378. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008093230603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund J. K., Khalaf N., Kozma L., Czech M. P. Activation of protein kinases by insulin and non-hydrolyzable GTP analogs in permeabilized 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7646–7649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J., Huang L. C., Schwartz C. F., Oswald A. S., Shen T. Y., Kinter M., Tang G. Z., Zeller K. Rat liver insulin mediator which stimulates pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate contains galactosamine and D-chiroinositol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 30;151(3):1416–1426. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J., Huang L. C., Tang G., Suzuki S., Schwartz C. F., Romero G., Roulidis Z., Zeller K., Shen T. Y., Oswald A. S. Insulin mediators: structure and formation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):965–971. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J. Insulin-signaling mechanisms. Lessons from the old testament of glycogen metabolism and the new testament of molecular biology. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):262–275. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavan B. E., Lienhard G. E. The insulin-elicited 60-kDa phosphotyrosine protein in rat adipocytes is associated with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5921–5928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Barahona M., Kaplan P. L., Cornet M. E., Diaz-Meco M. T., Larrodera P., Diaz-Laviada I., Municio A. M., Moscat J. Kinetic evidence of a rapid activation of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by Ki-ras oncogene. Possible involvement in late steps of the mitogenic cascade. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9022–9026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttrell L. M., Hewlett E. L., Romero G., Rogol A. D. Pertussis toxin treatment attenuates some effects of insulin in BC3H-1 murine myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6134–6141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaulay S. L., Larkins R. G. Isolation of insulin-sensitive phosphatidylinositol-glycan from rat adipocytes. Its impaired breakdown in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):427–435. doi: 10.1042/bj2710427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machicao F., Mushack J., Seffer E., Ermel B., Häring H. U. Mannose, glucosamine and inositol monophosphate inhibit the effects of insulin on lipogenesis. Further evidence for a role for inositol phosphate-oligosaccharides in insulin action. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):909–916. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Kelly K. L., Abler A., Jarett L. Identification of a novel insulin-sensitive glycophospholipid from H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2131–2137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitrakou A., Kelley D., Veneman T., Jenssen T., Pangburn T., Reilly J., Gerich J. Contribution of abnormal muscle and liver glucose metabolism to postprandial hyperglycemia in NIDDM. Diabetes. 1990 Nov;39(11):1381–1390. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.11.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, White M. F. The new elements of insulin signaling. Insulin receptor substrate-1 and proteins with SH2 domains. Diabetes. 1993 May;42(5):643–650. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.5.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair G. P., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J., Cooper D. R., Farese R. V. Effects of insulin and phorbol esters on diacylglycerol generation and synthesis and hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine in BC3H-1 myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):1345–1349. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler J. E., Romero G., Huang L. C., Zhang C. G., Larner J. Insulin mediators are the signal transduction system responsible for insulin's actions on human placental steroidogenesis. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):2951–2956. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-2951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortmeyer H. K., Bodkin N. L., Lilley K., Larner J., Hansen B. C. Chiroinositol deficiency and insulin resistance. I. Urinary excretion rate of chiroinositol is directly associated with insulin resistance in spontaneously diabetic rhesus monkeys. Endocrinology. 1993 Feb;132(2):640–645. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.2.8425483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak Y., Huang L. C., Lilley K. J., Larner J. In vivo conversion of [3H]myoinositol to [3H]chiroinositol in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16904–16910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak Y., Larner J. Identification and characterization of chiroinositol-containing phospholipids from bovine liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 30;184(2):1042–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90696-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero G., Garmey J. C., Veldhuis J. D. The involvement of inositol phosphoglycan mediators in the modulation of steroidogenesis by insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I. Endocrinology. 1993 Apr;132(4):1561–1568. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.4.8462454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero G., Gámez G., Huang L. C., Lilley K., Luttrell L. Anti-inositolglycan antibodies selectively block some of the actions of insulin in intact BC3H1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1476–1480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Fox J. A., Sherline P., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin-stimulated hydrolysis of a novel glycolipid generates modulators of cAMP phosphodiesterase. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):967–972. doi: 10.1126/science.3016898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R. Insulin generates an enzyme modulator from hepatic plasma membranes: regulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and adenylate cyclase. Endocrinology. 1987 Mar;120(3):967–972. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-3-967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafrir E. Animal models of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1992 Oct;8(3):179–208. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Batzer A., Li N., Lee C. H., Lowenstein E., Mohammadi M., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. The function of GRB2 in linking the insulin receptor to Ras signaling pathways. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1953–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.8316835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B. Muscle proteins related to microtubule associated protein-2 are substrates for an insulin-stimulatable kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):565–571. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80457-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrettaz J., Jeanrenaud B. In vivo hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance in genetically obese (fa/fa) rats. Endocrinology. 1983 Apr;112(4):1346–1351. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-4-1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga M., Matsumoto M., Igarashi M., Eguchi H., Sekikawa A., Sasaki H. Insulin antibody does not cause insulin resistance during glucose clamping in rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1992 Dec;18(3):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(92)90139-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vila M. C., Farese R. V. Insulin rapidly increases glycerol-3-phosphate-acyltransferase activity in rat adipocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Feb 1;284(2):366–368. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vila M. C., Milligan G., Standaert M. L., Farese R. V. Insulin activates glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (de novo phosphatidic acid synthesis) through a phospholipid-derived mediator. Apparent involvement of Gi alpha and activation of a phospholipase C. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8735–8740. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Horn R. S., Adler A., Albert K. A., Walaas O. Insulin increases membrane protein kinase C activity in rat diaphragm. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 17;220(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80837-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei J. W., Yeh S. R. Effects of insulin on glucose uptake in cultured cells from the central nervous system of rodent. Int J Biochem. 1991;23(9):851–856. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(91)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Farese R. V. Insulin activates myelin basic protein (p42 MAP) kinase by a protein kinase C-independent pathway in rat adipocytes. Dissociation from glucose transport. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 1;333(3):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80672-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries-Smits A. M., Burgering B. M., Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J., Bos J. L. Involvement of p21ras in activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):602–604. doi: 10.1038/357602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



