Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
To report a case of a preterm infant with complex meconium ileus at birth and cystic fibrosis.
CASE DESCRIPTION:
A male infant was born by vaginal delivery at 33 weeks and 5 days of gestational age with respiratory distress and severe abdominal distension. The exploratory laparotomy in the first day of life identified meconium ileus and secondary peritonitis. Ileal resection and ileostomy were performed, followed by reconstruction of the bowel transit at 20 days of life. At 11 days of life, the first immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) was 154 ng/mL (reference value = 70), and oral pancreatic enzymes replacement therapy was started. After 23 days, the second IRT was 172ng/mL (reference value = 70). At 35 days of age he was discharged with referrals to primary care and to a special clinic for CF for the determination of sweat chloride. He was received in the outpatient clinic for neonatal screening for CF at 65 days of life presenting malnutrition and respiratory distress. The sweat chloride test was performed, with a positive result (126mEq/L).
COMMENTS:
This case illustrates the rapid evolution of CF in a premature patient with complex meconium ileus as the first clinical manifestation.
Keywords: Cystic fibrosis, Meconium ileus, Prematurity
Introduction
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) is the most prevalent lethal autosomal recessive disorder, affecting 1:2,000 caucasians. It is caused by the alteration of a gene located on the long arm of chromosome 7 that encodes a protein of 1,480 amino acids, the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), which functions as a chloride channel on the apical membrane of epithelial cells.1 This alteration results in a change of the viscosity of secretions, with the production of thick mucus, leading mainly to malabsorption, loss of electrolytes in sweat and alteration of pulmonary secretions. There are more than 1,900 known genetic mutations, as well as disease modifying genes.2 This phenotypic heterogeneity involves different clinical presentations, ranging from mild to severe, which can determine a lethal outcome. The classic presentation of CF is chronic lung disease (recurrent pulmonary infections), exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (diarrhea and malnutrition), loss of salt, and obstructive azoospermia syndrome.3 In cases without clinical manifestations suggestive of CF in the first month of life, neonatal screening may lead to early detection and allows immediate treatment of pancreatic insufficiency, nutritional deficiencies and pulmonary involvement, improving survival and facilitating the design of treatment strategies.4
Less frequently, meconium ileus (MI) may be the first manifestation of CF in the neonatal period, occurring in approximately 20% of patients with pancreatic insufficiency. This clinical picture is caused by obstruction of the terminal ileus with thick meconium containing high amounts of protein. Complex MI is a severe condition, significantly more frequent in patients without CF of lower gestational age and birth weight than in patients with CF. MI is classified as complex when associated with ileal perforation.5 , 6 About 80% of cases of MI are due to CF, and it would be ideal to perform an early sweat chloride test before 48 hours of life, although this is not always feasible.7 , 8 Children with MI appear to have normal pulmonary function at CF diagnosis, with slower progression of lung disease than those diagnosed due to respiratory symptoms.9 , 10 However, it is currently believed that lung inflammation may occur early, and may even precede the onset of infection in infants with newly diagnosed cystic fibrosis.11
The objective of the present communication is to report the case of a child with complex MI who had a poor early evolution despite the clinical suspicion of CF.
Case description
A male infant was received in the outpatient clinic for neonatal screening for CF at 65 days of life. He was born by vaginal delivery, weighing 2,100g at 33 weeks and 5 days of gestational age, with Apgar scores of 6 and 9. His mother was a 19-year-old primigravida who had attended nine prenatal consultations with negative serology for vertical infections and normal obstetrical ultrasound. Immediately after birth, the infant was referred to the neonatal critical care unit due to early respiratory distress and severe abdominal distension. A plain abdominal radiograph revealed absence of air in the lower abdomen. The patient underwent exploratory laparotomy in the first day of life, which identified MI and secondary peritonitis due to intestinal perforation. Ileal resection and ileostomy were performed, followed by reconstruction of the bowel transit at 20 days of life. He had early and late neonatal sepsis during the hospital stay, requiring prolonged antibiotic therapy. Parenteral nutrition was gradually transitioned to infant formula up to a volume of 160mL/kg/day. At 11 days of life the result of the first immunoreactive trypsin (IRT) was 154ng/mL, and oral pancreatic enzymes replacement therapy was started (1,000U/kg/dose every 3 hours before feeding). After 23 days, the second IRT was 172ng/mL. At 35 days of age he was weighing 2,040 g and was discharged with referrals to primary care and to a special clinic for CF for the determination of sweat chloride.
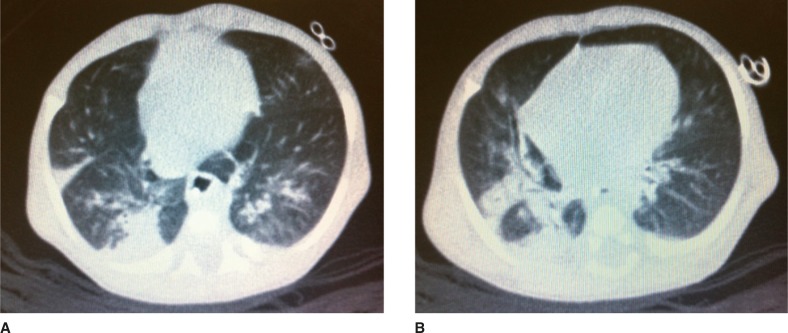
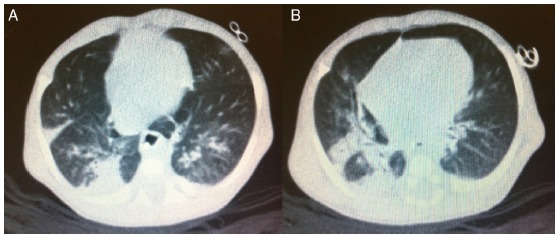
After 65 days of life, the sweat chloride test was performed in the reference service with a positive result (126mEq/L). That same day, the patient was attended at the follow-up clinic for neonatal screening for CF. According to his mother, the same guidelines were maintained regarding the volume of infant formula and the dosage of pancreatic enzymes, which she was instructed to offer mashed in water. He weighed 2,610 g and his length was 48cm. He had gained 19g/day after discharge. He had tachypnea (62 respiratory cycles/minute), pallor (2/4+) and persistent dry cough. His chest X-ray revealed pulmonary hyperinflation and condensation compatible with pneumonic disease. The patient was hospitalized and the laboratory tests performed during hospitalization are shown in Table 1. The C-reactive protein (CRP) test performed at admission was 18.8mg/dL (Reference Value <0.5mg/dL by turbidimetry). Laboratory tests for respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus and influenza, as well as blood cultures were negative. A pulmonary CT scan was performed on the 6th day of hospital stay (Fig. 1).
Table 1. Exams performed at the beginning and at the end of hospitalization of the patient at the referral service for CF management.
| Laboratory test | Reference values | Day of hospitalization | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 6 | 35 | ||
| Serum | |||||
| Hb (g/dL) | 10-14 | 6.6 | 9.4 | 8.8 | |
| Ht (%) | 28-42 | 21 | 30 | 26 | |
| WBC (/µL) | 5,000-15,000 | 15,000 | 7,300 | ||
| Differential (%) | (7B/5Me/2My) | No immature forms | |||
| Platelets (/µL) | 150-300.103 | 662,000 | 532,000 | 391,000 | |
| Na+ (mEq/L) | 135-145 | 125 | 121 | 137 | 135 |
| K+ (mEq/L) | 3.5-5.0 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 4.5 | 4.3 |
| Cl– (mmol/L) | 98-1,107 | 94 | 92 | 101 | 105 |
| Total Protein (g/dL) | 6.0 | 5.2 | 5.7 | ||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.5 | 3.2 | 4.0 | ||
| B12 Vitamin (pg/mL) | 175-878 | >1,000 | |||
| Zinc (mcg/%) | 50-120 | 74.5 | |||
| Arterial Blood Gas | |||||
| pH (mmHg) | 7.35-7.45 | 7.45 | 7.43 | 7.35 | |
| pO2 (mmHg) | 75-100 | 61.0 | 72.7 | 78.4 | |
| pCO2 (mmHg) | 35-45 | 37.6 | 40.0 | 40.3 | |
| HCO3 (mmHg) | 21-28 | 25.6 | 25.9 | 21.7 | |
| BE (mmol/L) | 0±2 | +2 | +1.9 | –3.0 | |
| SaO2 (%) | 95-98 | 94.1 | 95 | 96 | |
| URT Secretion | |||||
| Culture | Staphylococcus aureus | Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Burkholderia cepaccia | Negative | ||
| Faecal | |||||
| Steatrocrit (%) | <10 | — | — | 50 | 35 |
b, bands; me, metamyelocites; my, myelocytes; URT, upper respiratory tract.
Figure 1. Pulmonary computer scanner images. A. Reveals several bands of atelectasis with bronchiectasis and some bronchi with thickened walls. B. Reveals other bronchial wall thickening, peribronchial inflammation, and extensive area of condensation.
An enteral diet was prescribed, with a volume of 150mL/kg/day of semi-elemental formula at 1:25 dilution. The dose of pancreatic enzymes was adjusted to 5,000 U before feeding, every 3 hours. A transfusion of red blood cells was performed. Enteral sodium (4mEq/kg/day) and potassium (1mEq/kg/day) were replaced. Multivitamins (24 drops/day) and zinc sulfate (1mg/kg/day) were prescribed. After culture, and based on the microorganism isolated from the upper respiratory tract secretion (Table 1), ceftazidime (200mg/kg/day), gentamicin (5mg/kg/day), and oxacillin (200mg/kg/day) were prescribed. Due to ileal resection, vitamin B12 (100mcg) was administered intramuscularly. On the seventh day of hospital stay, due to progressive worsening of the respiratory pattern, noninvasive ventilation (CPAP) was applied for two weeks. After stabilization of pulmonary disease he progressed with satisfactory weight gain. He was discharged after 40 days, weighing 3,490 g, without antibiotics, with sodium replacement (adjusted to 2mEq/kg/day) and ferrous sulfate (4mg/kg/day).
Discussion
It is known that the confirmation of CF may be difficult during the first days of life, but in the presence of meconium ileus this differential diagnosis should be compulsorily considered. The sweat chloride test can be performed after 48 hours of life, but more reliable results are obtained after the second week of life, with the patient weighing more than 2 kg, showing adequate hydration status and without significant systemic disease.12 The sweat chloride test is the gold standard for the diagnosis of CF; however, some situations may alter the results, such as dehydration, low weight, skin rash or a bad general condition.13 , 14 Despite the importance of an early sweat chloride test, the clinical status of the present patient was not appropriate for testing him during the first days of life.
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) genetic analysis also helps the diagnosis of CF when it detects two known mutations.15 This exam would have been useful for the present patient if it had detected the two characteristic mutations for CF, however, the exam is not routinely available in our center due to its high cost. The nationwide Brazilian Newborn Screening Program started in 2011, although it was first implemented in 2010 in the state of São Paulo.16 The method of two IRT samples was adopted, with the first sample being collected between 3 and 7 days of life and the second up to 30 days of life. If both (IRT) samples are positive (Reference Value ≥70ng/mL), CF is confirmed by two positive sweat chloride tests (Reference Value ≥60mEq/L). A sweat chloride test between 30 and 60mEq/L is "borderline" for neonates and does not immediately exclude or confirm the disease.17
Although the importance of two IRTs neonatal screenings for CF detection, the benefit seems smaller for infants with meconium ileus because neonates with CF and MI may have low initial IRT values.18 Even if IRT levels remain elevated, this would simply alert to the possible presence of CF without confirming the disease, because several factors increase the possibility of false-positive IRT values, including perinatal stress.19 Although low IRT values were expected for the present patient, the levels detected were high, supporting the suspicion of CF and probably also the decision of empirically starting the treatment of pancreatic insufficiency due to CF.
Neonates with MI should receive specific treatment for pancreatic insufficiency while pending confirmation of CF by the sweat chloride test. Weight gain during hospital stay indicates a good response.20 Current reports state that MI is no longer regarded as a poor prognostic factor in patients with effective treatment for CF.21 The present patient was discharged using pancreatic enzymes, with the mother dissolving them in water. This procedure illustrates the importance of an early and frequent monitoring of children with a suspected chronic, rare and severe disease by the reference service for CF treatment, both regarding support to the family and the refinement of the guidelines offered, so that they will be closely followed. It should be emphasized that this type of care involves, but does not replace patient monitoring by a general pediatrician. The management of pancreatic insufficiency involves the oral ingestion of intact microspheres of pancreatic enzymes immediately before breastfeeding, ranging from 2,000 to 4,000IU lipase for each 120mL of formula or breastfeeding. Although less physiological, the calculation can also be performed using a dose of 1,000IU lipase/kg/meal for children younger than 4 years, avoiding doses higher than 2,500IU/kg/meal and 10,000IU/kg/day, which could trigger fibrosing colonopathy.22
The lungs may be affected since the period of CF neonatal screening, with 81% of cases showing structural abnormalities, 45% bronchial wall thickening, and 21% lung infection.23 Cough and dyspnea in neonates and infants indicate the need to include CF in the list of differential diagnoses. Pulmonary inflammation or infection may already be present, with Staphylococcus aureus being the microorganism most frequently detected, followed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with significant respiratory symptoms. Researchers observed that infants with cystic fibrosis detected by newborn screening may have lung disease with bacterial infection since the first days of life.24 , 25 This is a source of concern, because it is linked to early onset of bronchiectasis and more severe lung inflammation.
The present case report illustrates the rapid multisystem evolution of CF in a premature patient with complex MI as the first clinical manifestation. It also shows the presence of paradoxical results of neonatal screening (IRT/IRT) in patients with MI, and the difficulties of the early chloride sweat testing and of genotyping for CF in MI cases. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of a rapid referral of patients with MI and suspected CF to a team of experts.
Footnotes
Funding This study did not receive funding.
References
- 1.Raskin S, Phillips JA 3rd , Krishnamani MR, Vnencak-Jones C, Parker RA, Rozov T, et al. DNA analysis of cystic fibrosis in Brazil by direct PCR amplification from Guthrie cards. Am J Med Genet. 1993;46:665-9. [DOI] [PubMed]; Raskin S, Phillips 3rd JA, Krishnamani MR, Vnencak-Jones C, Parker RA, Rozov T. DNA analysis of cystic fibrosis in Brazil by direct PCR amplification from Guthrie cards. Am J Med Genet. 1993;46:665–669. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stanke F, Becker T, Kumar V, Hedtfeld S, Becker C, Cuppens H, et al. Genes that determine immunology and inflammation modify the basic defect of impaired ion conductance in cystic fibrosis epithelia. J Med Genet Jan. 2011;48:24-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]; Stanke F, Becker T, Kumar V, Hedtfeld S, Becker C, Cuppens H. Genes that determine immunology and inflammation modify the basic defect of impaired ion conductance in cystic fibrosis epithelia. J Med Genet Jan. 2011;48:24–31. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2010.080937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sing CF, Risser DR, Howatt WF, Erickson RP. Phenotypic heterogeneity in cystic fibrosis. Am J Med Genet. 1982;13:179-95. [DOI] [PubMed]; Sing CF, Risser DR, Howatt WF, Erickson RP. Phenotypic heterogeneity in cystic fibrosis. Am J Med Genet. 1982;13:179–195. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320130209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Comeau AM, Accurso FJ, White TB, Campbell PW, Hoffman G, Parad RB, et al. Guidelines for implementation of cystic fibrosis newborn screening programs: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation workshop report. Pediatrics. 2007;119:e495-518. [DOI] [PubMed]; Comeau AM, Accurso FJ, White TB, Campbell PW, Hoffman G, Parad RB. Guidelines for implementation of cystic fibrosis newborn screening programs: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation workshop report. Pediatrics. 2007;119:e495–e518. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006-1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gorter RR, Karimi A, Sleeboom C, Kneepkens CM, Heij HA. Clinical and genetic characteristics of meconium ileus in newborns with and without cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010;50:569-72. [DOI] [PubMed]; Gorter RR, Karimi A, Sleeboom C, Kneepkens CM, Heij HA. Clinical and genetic characteristics of meconium ileus in newborns with and without cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010;50:569–572. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181bb3427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ziegler MM. Meconium ileus. Curr Probl Surg. 1994;31:731-77. [DOI] [PubMed]; Ziegler MM. Meconium ileus. Curr Probl Surg. 1994;31:731–777. doi: 10.1016/0011-3840(94)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fakhoury K, Durie PR, Levison H, Canny GJ. Meconium ileus in the absence of cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1992;67:1204-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]; Fakhoury K, Durie PR, Levison H, Canny GJ. Meconium ileus in the absence of cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1992;67:1204–1206. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.10_spec_no.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.AACB Sweat Testing Working Party. Australian Guidelines for the Performance of the Sweat Test for the Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis. Clin Biochem. 2006;27 Suppl i:S1-9. [PMC free article] [PubMed]; AACB Sweat Testing Working Party Australian Guidelines for the Performance of the Sweat Test for the Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis. Clin Biochem. 2006;27(i):S1–S9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tepper RS, Hiatt P, Eigen H, Scott P, Grosfeld J, Cohen M. Infants with cystic fibrosis: pulmonary function at diagnosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1988;5:15-8. [DOI] [PubMed]; Tepper RS, Hiatt P, Eigen H, Scott P, Grosfeld J, Cohen M. Infants with cystic fibrosis: pulmonary function at diagnosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1988;5:15–18. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950050105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hudson I, Phelan PD. Are sex, age at diagnosis, or mode of presentation prognostic factors for cystic fibrosis? Pediatr Pulmonol. 1987;3:288-97. [DOI] [PubMed]; Hudson I, Phelan PD. Are sex, age at diagnosis, or mode of presentation prognostic factors for cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1987;3:288–297. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950030503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Armstrong DS, Grimwood K, Carzino R, Carlin JB, Olinsky A, Phelan PD. Lower respiratory infection and inflammation in infants with newly diagnosed cystic fibrosis. BMJ. 1995;310:1571-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]; Armstrong DS, Grimwood K, Carzino R, Carlin JB, Olinsky A, Phelan PD. Lower respiratory infection and inflammation in infants with newly diagnosed cystic fibrosis. BMJ. 1995;310:1571–1572. doi: 10.1136/bmj.310.6994.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Farrell PM, Rosenstein BJ, White TB, Accurso FJ, Castellani C, Cutting GR, et al. Guidelines for diagnosis of cystic fibrosis in newborns through older adults: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation consensus report. J Pediatr. 2008;153:S4-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]; Farrell PM, Rosenstein BJ, White TB, Accurso FJ, Castellani C, Cutting GR. Guidelines for diagnosis of cystic fibrosis in newborns through older adults: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation consensus report. J Pediatr. 2008;153:S4–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.05.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Littlewood JM. The sweat test. Arch Dis Child. 1986;61:1041-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]; Littlewood JM. The sweat test. Arch Dis Child. 1986;61:1041–1043. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.11.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Di Sant'Agnese PA, Darling RC, Perera GA, Shea E. Abnormal electrolyte composition of sweat in cystic fibrosis of the pancreas; clinical significance and relationship to the disease. Pediatrics. 1953;12:549-63. [PubMed]; Di Sant'Agnese PA, Darling RC, Perera GA, Shea E. Abnormal electrolyte composition of sweat in cystic fibrosis of the pancreas; clinical significance and relationship to the disease. Pediatrics. 1953;12:549–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Castellani C, Cuppens H, Macek M Jr, Cassiman JJ, Kerem E, Durie P, et al. Consensus on the use and interpretation of cystic fibrosis mutation analysis in clinical practice. J Cyst Fibros. 2008;7:179-96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]; Castellani C, Cuppens H, Macek M, Jr, Cassiman JJ, Kerem E, Durie P. Consensus on the use and interpretation of cystic fibrosis mutation analysis in clinical practice. J Cyst Fibros. 2008;7:179–196. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2008.03.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kerem E, Conway S, Elborn S, Heijerman H. Consensus Committee. Standards of care for patients with cystic fibrosis: a European Consensus. J Cyst Fibros. 2005;4:7-26. [DOI] [PubMed]; Kerem E, Conway S, Elborn S, Heijerman H. Consensus Committee. Standards of care for patients with cystic fibrosis: a European Consensus. J Cyst Fibros. 2005;4:7–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2004.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.São Paulo. Justiça Federal & #091;página da Internet]. Ação Pública n. 0021921-14.2009.403.6100. Exame para diagnosticar fibrose cística em recém-nascidos é obrigatório [acessado em 30 de junho de 2014]. Disponível em: http://www.jfsp.jus.br/20110329-fibrosecistica/; São Paulo. Justiça Federal Ação Pública n. 0021921-14.2009.403.6100. Exame para diagnosticar fibrose cística em recém-nascidos é obrigatório. 2014. [30 de junho de 2014]. a Disponível em: http://www.jfsp.jus.br/20110329-fibrosecistica/
- 18.Heeley AF, Bangert SK. The neonatal detection of cystic fibrosis by measurement of immunoreactive trypsin in blood. Ann Clin Biochem. 1992;29:361-76. [DOI] [PubMed]; Heeley AF, Bangert SK. The neonatal detection of cystic fibrosis by measurement of immunoreactive trypsin in blood. Ann Clin Biochem. 1992;29:361–376. doi: 10.1177/000456329202900401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rock MJ, Mischler EH, Farrell PM, Bruns WT, Hassemer DJ, Laessig RH. Immunoreactive trypsinogen screening for cystic fibrosis: characterisation of infants with a false-positive screening test. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1989;6:42-8. [DOI] [PubMed]; Rock MJ, Mischler EH, Farrell PM, Bruns WT, Hassemer DJ, Laessig RH. Immunoreactive trypsinogen screening for cystic fibrosis: characterisation of infants with a false-positive screening test. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1989;6:42–48. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950060111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ribeiro JD, Ribeiro MA, Ribeiro AF. Controversies in cystic fibrosis From pediatrician to specialist. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2002;78 Suppl 2:S171-86. [DOI] [PubMed]; Ribeiro JD, Ribeiro MA, Ribeiro AF. Controversies in cystic fibrosis From pediatrician to specialist. J Pediatr (Rio J) 2002;78(2):S171–S186. doi: 10.2223/jped.896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Corey M, Farewell V. Determinants of mortality from cystic fibrosis in Canada, 1970-1989. Am J Epidemiol. 1996;143: 1007-17. [DOI] [PubMed]; Corey M, Farewell V. Determinants of mortality from cystic fibrosis in Canada, 1970-1989. Am J Epidemiol. 1996;143:1007–1017. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a008664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sinaasappel M, Stern M, Littlewood J, Wolfe S, Steinkamp G, Heijerman HG, et al. Nutrition in patients with cystic fibrosis: a European Consensus. J Cyst Fibros. 2002;1:51-75. [DOI] [PubMed]; Sinaasappel M, Stern M, Littlewood J, Wolfe S, Steinkamp G, Heijerman HG. Nutrition in patients with cystic fibrosis: a European Consensus. J Cyst Fibros. 2002;1:51–75. doi: 10.1016/s1569-1993(02)00032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mott LS, Park J, Murray CP, Gangell CL, De Klerk NH, Robinson PJ, et al. Progression of early structural lung disease in young children with cystic fibrosis assessed using CT. Thorax. 2012;67:509-16. [DOI] [PubMed]; Mott LS, Park J, Murray CP, Gangell CL, De Klerk NH, Robinson PJ. Progression of early structural lung disease in young children with cystic fibrosis assessed using CT. Thorax. 2012;67:509–516. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-200912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sly PD, Brennan S, Gangell C, De Klerk N, Murray C, Mott L, et al. Lung disease at diagnosis in infants with cystic fibrosis detected by newborn screening. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2009;180:146-52. [DOI] [PubMed]; Sly PD, Brennan S, Gangell C, De Klerk N, Murray C, Mott L. Lung disease at diagnosis in infants with cystic fibrosis detected by newborn screening. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2009;180:146–152. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200901-0069OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stick SM, Brennan S, Murray C, Douglas T, Von Ungern-Sternberg BS, Garratt LW, et al. Bronchiectasis in infants and preschool children diagnosed with cystic fibrosis after newborn screening. J Pediatr. 2009;155:623-8. [DOI] [PubMed]; Stick SM, Brennan S, Murray C, Douglas T, Von Ungern-Sternberg BS, Garratt LW. Bronchiectasis in infants and preschool children diagnosed with cystic fibrosis after newborn screening. J Pediatr. 2009;155:623–628. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]