Abstract
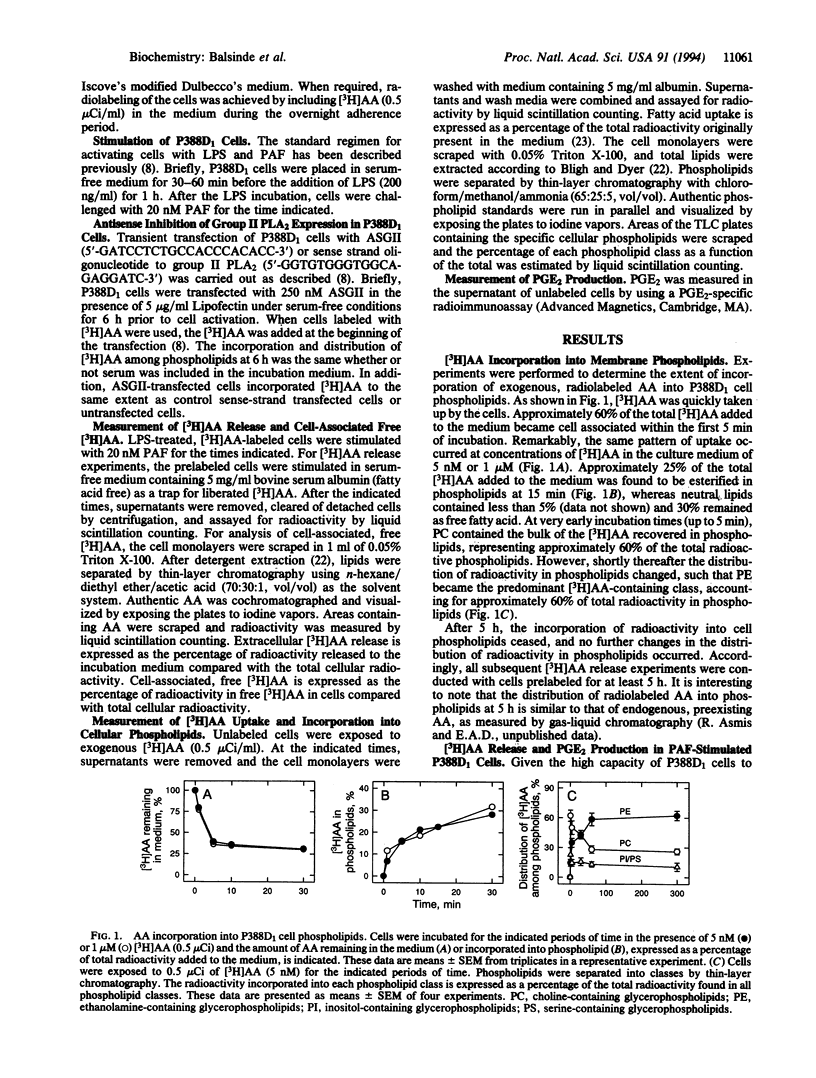
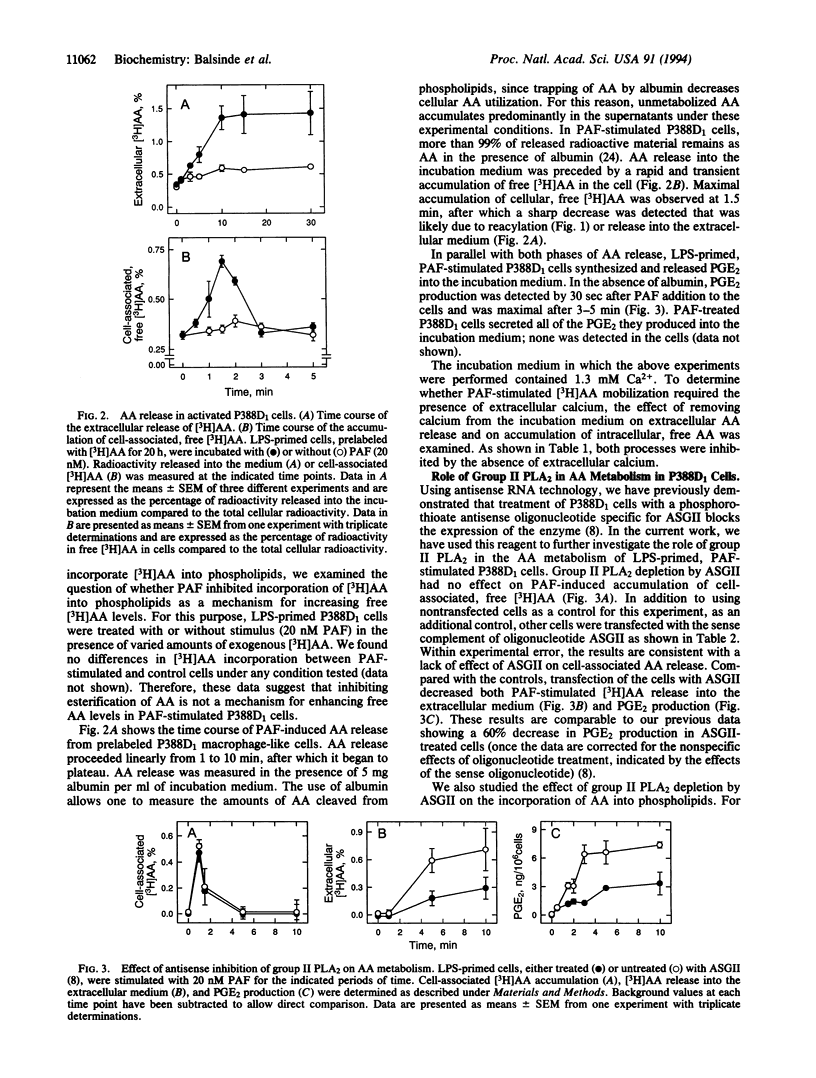
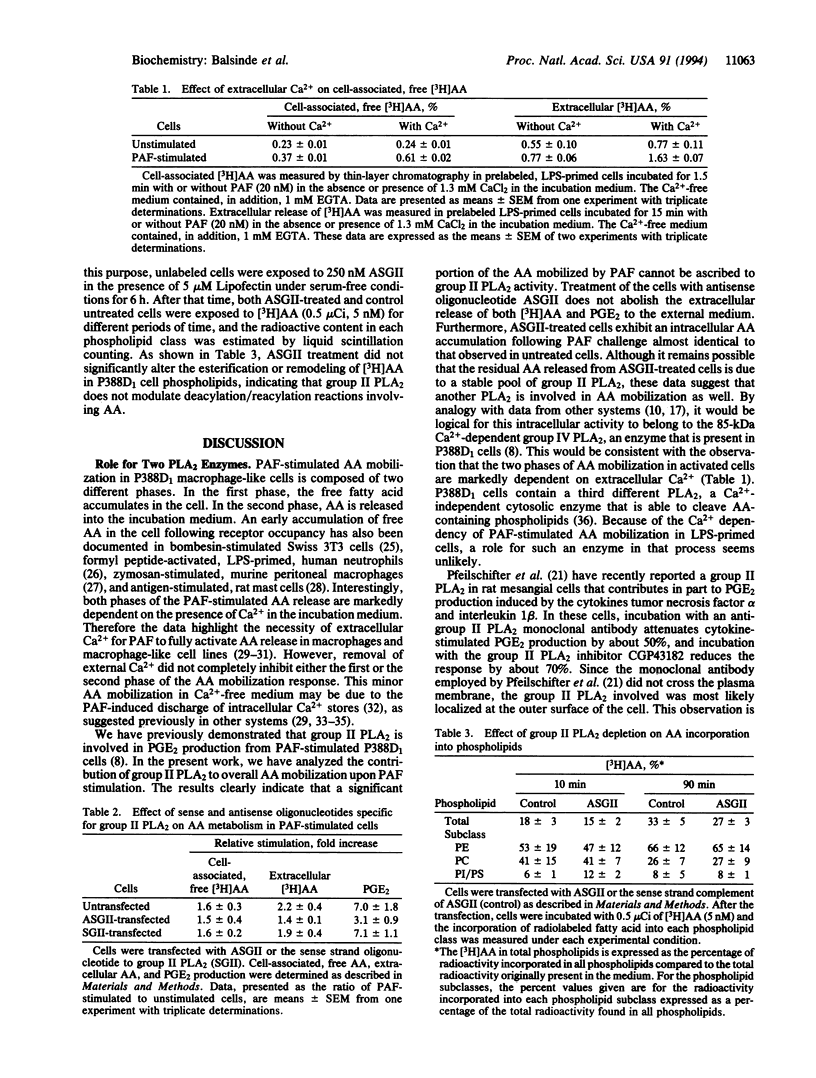
Macrophage-like P388D1 cells mobilize arachidonic acid (AA) and produce prostaglandin E2 upon stimulation with bacterial lipopolysaccharide and platelet-activating factor. We have now demonstrated that AA mobilization in these cells is composed of two distinct events: a transient phase in which AA accumulates in the cell and a sustained phase in which the fatty acid accumulates in the incubation medium. Both phases are markedly dependent on the presence of Ca2+ in the extracellular medium. Treatment with an antisense oligonucleotide to group II phospholipase A2 inhibits the accumulation of AA in the incubation medium, but has no effect on the accumulation of this fatty acid in the cell. In addition, treatment with antisense oligonucleotide to group II phospholipase A2 has no effect on the uptake or the esterification of AA. Collectively, these results indicate that, in addition to the previously demonstrated role of group II phospholipase A2 in AA mobilization in activated P388D1 cells, another phospholipase A2, distinct from the group II enzyme, is implicated in raising the levels of intracellular AA during the early steps of P388D1 cell activation and in modulating deacylation/reacylation reactions involving AA. The data suggest that each of the different phospholipase A2 enzymes present in P388D1 cells serves a distinct role in cell function.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann E. J., Kempner E. S., Dennis E. A. Ca(2+)-independent cytosolic phospholipase A2 from macrophage-like P388D1 cells. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):9227–9233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asmis R., Randriamampita C., Tsien R. Y., Dennis E. A. Intracellular Ca2+, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and additional signalling in the stimulation by platelet-activating factor of prostaglandin E2 formation in P388D1 macrophage-like cells. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 15;298(Pt 3):543–551. doi: 10.1042/bj2980543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsinde J., Fernández B., Solís-Herruzo J. A., Diez E. Pathways for arachidonic acid mobilization in zymosan-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 22;1136(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90087-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsinde J., Fernández B., Solís-Herruzo J. A. Increased incorporation of arachidonic acid into phospholipids in zymosan-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages. Eur J Biochem. 1994 May 1;221(3):1013–1018. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsinde J. Mechanism of arachidonic acid liberation in ethanol-treated mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 21;1169(1):54–58. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(93)90081-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour S. E., Dennis E. A. Antisense inhibition of group II phospholipase A2 expression blocks the production of prostaglandin E2 by P388D1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21875–21882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley B. J., Barchowsky A., Dolor R. J., Whorton A. R. Regulation of arachidonic acid release in vascular endothelium. Ca(2+)-dependent and -independent pathways. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 1;280(Pt 2):281–287. doi: 10.1042/bj2800281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao W., Liu H., DeBuysere M., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Identification of receptors for platelet-activating factor in rat Kupffer cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13591–13598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie S., Smith G. L., Crichton C. A., Jackson C. G., Hallam C., Wakelam M. J. Bombesin stimulates the rapid activation of phospholipase A2-catalyzed phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6056–6062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. A. Diversity of group types, regulation, and function of phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13057–13060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. A., Rhee S. G., Billah M. M., Hannun Y. A. Role of phospholipase in generating lipid second messengers in signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2068–2077. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.1901288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Weiss J. Phagocytosis of bacteria and phospholipid degradation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):29–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández B., Balsinde J. Calcium- and G-protein-dependent activation of arachidonic acid release by concanavalin-A-stimulated mouse macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Mar 10;1176(1-2):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90193-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández B., Balsinde J. Receptor-mediated activation of arachidonic acid release in mouse peritoneal macrophages is linked to extracellular calcium influx. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):1036–1040. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonteh A. N., Bass D. A., Marshall L. A., Seeds M., Samet J. M., Chilton F. H. Evidence that secretory phospholipase A2 plays a role in arachidonic acid release and eicosanoid biosynthesis by mast cells. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 1;152(11):5438–5446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonteh A. N., Chilton F. H. Mobilization of different arachidonate pools and their roles in the generation of leukotrienes and free arachidonic acid during immunologic activation of mast cells. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):563–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonteh A. N., Chilton F. H. Rapid remodeling of arachidonate from phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine pools during mast cell activation. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1784–1791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly F., Breton M., Wolf C., Ninio E., Colard O. Heterogeneity of arachidonate and paf-acether precursor pools in mast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 May 8;1125(3):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishino J., Ohara O., Nomura K., Kramer R. M., Arita H. Pancreatic-type phospholipase A2 induces group II phospholipase A2 expression and prostaglandin biosynthesis in rat mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5092–5098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Roberts E. F., Manetta J. V., Hyslop P. A., Jakubowski J. A. Thrombin-induced phosphorylation and activation of Ca(2+)-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26796–26804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is coupled to hormonally regulated release of arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister M. D., Glaser K. B., Ulevitch R. J., Dennis E. A. Inhibition studies on the membrane-associated phospholipase A2 in vitro and prostaglandin E2 production in vivo of the macrophage-like P388D1 cell. Effects of manoalide, 7,7-dimethyl-5,8-eicosadienoic acid, and p-bromophenacyl bromide. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8520–8528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake A., Yamamoto H., Enomori T., Kawashima H. Exogenous group II phospholipase A2 induces prostaglandin E2 production in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb 21;253(1-2):155–161. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90770-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Kudo I., Inoue K. Molecular nature of phospholipases A2 involved in prostaglandin I2 synthesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Possible participation of cytosolic and extracellular type II phospholipases A2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):839–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Kudo I., Suwa Y., Inoue K. Release of 14-kDa group-II phospholipase A2 from activated mast cells and its possible involvement in the regulation of the degranulation process. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 1;209(1):257–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Lin L. L., Kharbanda S., Knopf J., Kufe D. Macrophage colony stimulating factor activates phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by cytoplasmic phospholipase A2. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4917–4922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson C. P., Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Chemotactic peptide stimulation of arachidonic acid release in HL60 cells, an interaction between G protein and phospholipase C mediated signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 16;1095(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernas P., Masliah J., Olivier J. L., Salvat C., Rybkine T., Bereziat G. Type II phospholipase A2 recombinant overexpression enhances stimulated arachidonic acid release. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1298–1305. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91035-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Schalkwijk C., Briner V. A., van den Bosch H. Cytokine-stimulated secretion of group II phospholipase A2 by rat mesangial cells. Its contribution to arachidonic acid release and prostaglandin synthesis by cultured rat glomerular cells. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2516–2523. doi: 10.1172/JCI116860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu Z. H., de Carvalho M. S., Leslie C. C. Regulation of phospholipase A2 activation by phosphorylation in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24506–24513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. I., Deems R. A., Jesaitis A. J., Dennis E. A., Ulevitch R. J. Phospholipase activities of the P388D1 macrophage-like cell line. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Apr;238(1):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk C. G., de Vet E., Pfeilschifter J., van den Bosch H. Interleukin-1 beta and transforming growth factor-beta 2 enhance cytosolic high-molecular-mass phospholipase A2 activity and induce prostaglandin E2 formation in rat mesangial cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Nov 15;210(1):169–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk C., Pfeilschifter J., Märki F., van den Bosch H. Interleukin-1 beta- and forskolin-induced synthesis and secretion of group II phospholipase A2 and prostaglandin E2 in rat mesangial cells is prevented by transforming growth factor-beta 2. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8846–8851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Zrike J. M., Hamill A. L., Kempe J., Cohn Z. A. Regulation of arachidonic acid metabolites in macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):324–335. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L. Prostanoid biosynthesis and mechanisms of action. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 2):F181–F191. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.2.F181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suga H., Murakami M., Kudo I., Inoue K. Participation in cellular prostaglandin synthesis of type-II phospholipase A2 secreted and anchored on cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Dec 15;218(3):807–813. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surette M. E., Palmantier R., Gosselin J., Borgeat P. Lipopolysaccharides prime whole human blood and isolated neutrophils for the increased synthesis of 5-lipoxygenase products by enhancing arachidonic acid availability: involvement of the CD14 antigen. J Exp Med. 1993 Oct 1;178(4):1347–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson U., Houweling M., Holst E., Sundler R. Phosphorylation and activation of the arachidonate-mobilizing phospholipase A2 in macrophages in response to bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 1;213(1):81–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venable M. E., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M., Prescott S. M. Platelet-activating factor: a phospholipid autacoid with diverse actions. J Lipid Res. 1993 May;34(5):691–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C., Aepfelbacher M., Haag H., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Weber P. C. Tumor necrosis factor induces enhanced responses to platelet-activating factor and differentiation in human monocytic Mono Mac 6 cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):852–859. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



