Abstract
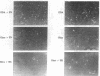
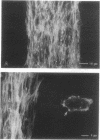
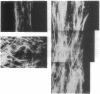
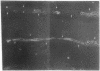
Chemically modified glass substrates were used to demonstrate differential adhesion, growth, and differentiation of endothelial cells. Endothelial cells were examined for adhesion and growth on glass, glass treated with N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyl trimethoxysilane (EDA), or EDA with a subsequent treatment with physically adsorbed extracellular matrix components human fibronectin and heparin sulfate. EDA and EDA/human fibronectin showed similar abilities to support adhesion, spreading, and proliferation of endothelial cells. In contrast, heparin sulfate inhibited endothelial cell adhesion to EDA. Differentiation of endothelial cells resulting in precapillary cord formation was triggered by addition of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). On EDA and EDA/human fibronectin bFGF causes confluent endothelial cell monolayers to differentiate and form cords, which resulted in a large-scale spatial redistribution of cells on the surface. Formation of organized neovascular assemblies was demonstrated on coplanar molecular patterns of EDA and a nonadhesive perfluorinated alkylsilane (tridecafluoro-1,1,2,2-tetrahydrooctyl)-1-dimethylchloros ilane (13F). Endothelial cells preferentially adhered to the EDA lines and after 24-48 hr, microfilaments aligned with the long axes of the patterned EDA region. Finally, endothelial cells that became confluent within the confines of the EDA region (bound by the nonadhesive, 13F domains) were observed to differentiate into neovascular cords in long-term culture (7-10 days) with bFGF.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter S. B. Haptotactic islands: a method of confining single cells to study individual cell reactions and clone formation. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Oct;48(1):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90298-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. B. Principles of cell motility: the direction of cell movement and cancer invasion. Nature. 1965 Dec 18;208(5016):1183–1187. doi: 10.1038/2081183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo C. J., Colburn P., Buonassisi V. Characterization and N-terminal sequence of a heparan sulphate proteoglycan synthesized by endothelial cells in culture. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):687–693. doi: 10.1042/bj2470687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulcey C. S., Georger J. H., Jr, Krauthamer V., Stenger D. A., Fare T. L., Calvert J. M. Deep UV photochemistry of chemisorbed monolayers: patterned coplanar molecular assemblies. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):551–554. doi: 10.1126/science.2020853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feder J., Marasa J. C., Olander J. V. The formation of capillary-like tubes by calf aortic endothelial cells grown in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Jul;116(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041160102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10931–10934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Form D. M., Pratt B. M., Madri J. A. Endothelial cell proliferation during angiogenesis. In vitro modulation by basement membrane components. Lab Invest. 1986 Nov;55(5):521–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. Behavior of cultured cells on substrata of variable adhesiveness. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 15;77(1):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90579-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell J. A., Massia S. P., Desai N. P., Drumheller P. D. Endothelial cell-selective materials for tissue engineering in the vascular graft via a new receptor. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Jun;9(6):568–572. doi: 10.1038/nbt0691-568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Folkman J. Mechanochemical switching between growth and differentiation during fibroblast growth factor-stimulated angiogenesis in vitro: role of extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):317–330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., D'Amore P. A. Regulators of angiogenesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:217–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Shing Y. Heparin affinity of anionic and cationic capillary endothelial cell growth factors: analysis of hypothalamus-derived growth factors and fibroblast growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinfeld D., Kahler K. H., Hockberger P. E. Controlled outgrowth of dissociated neurons on patterned substrates. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4098–4120. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04098.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowska K., Balachander N., Sukenik C. N., Culp L. A. Modulation of fibronectin adhesive functions for fibroblasts and neural cells by chemically derivatized substrata. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Nov;141(2):334–345. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe-Krentz L. J., Joyce J. G. Venous and aortic porcine endothelial cells cultured under standardized conditions synthesize heparan sulfate chains which differ in charge. Anal Biochem. 1991 Mar 2;193(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90001-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Kadish J., Wilkins L., Stemerman M. B., Weinstein R. Organizational behavior of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):511–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massia S. P., Hubbell J. A. Covalent surface immobilization of Arg-Gly-Asp- and Tyr-Ile-Gly-Ser-Arg-containing peptides to obtain well-defined cell-adhesive substrates. Anal Biochem. 1990 Jun;187(2):292–301. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90459-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massia S. P., Hubbell J. A. Human endothelial cell interactions with surface-coupled adhesion peptides on a nonadhesive glass substrate and two polymeric biomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res. 1991 Feb;25(2):223–242. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820250209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Vassalli J. D., Baird A., Guillemin R., Orci L. Basic fibroblast growth factor induces angiogenesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. H., Kang Y. H., Deschner S. H., Nielsen T. B. Morphologic plasticity and periodicity: porcine cerebral microvascular cells in culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1990 Feb;26(2):169–180. doi: 10.1007/BF02624109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Nariuchi H., Tsuruoka N., Nishihara T., Beitz J. G., Calabresi P., Frackelton A. R., Jr Actions of TNF and IFN-gamma on angiogenesis in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Dec;95(6 Suppl):85S–89S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A. B., Canfield A. E., Schor S. L., Grant M. E., Schor A. M. The response of endothelial cells to TGF beta-1 is dependent upon cell shape, proliferative state and the nature of the substratum. J Cell Sci. 1991 Aug;99(Pt 4):777–787. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.4.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager A., Callow A. D. New graft materials and current approaches to an acceptable small diameter vascular graft. ASAIO Trans. 1988 Apr-Jun;34(2):88–94. doi: 10.1097/00002480-198804000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]