Abstract
Purpose: As H1 and H3 receptors’ roles has been defined in peripheral pains in some papers and because histamine is known for its role in inflammatory responses; this study investigated the possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of ketotifen and fexofenadine as relatively safe long acting anti histamines in both chronic chemical pain and acute inflammation in rats.
Methods: In this study, male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 225-250 grams were used. In order to evaluate the chemical chronic pain, sub-plantar injection of formalin applied and the pain scores were recorded every 15 seconds during 60 minutes. Carrageenan injection to the right hind paw was used for induction of acute inflammation and the paw edema was measured every 60 minutes for 4 hours.
Results: Based on the results, both ketotifen and fexofenadine were able to significantly diminish chemical acute and chronic pain as well as inflammation in comparison with the control group and the effects were acceptable according to the standard treatment. Both effects for fexofenadine started later than those of ketotifen.
Conclusion: According to the outcomes of the study, ketotifen and fexofenadine demonstrated significant analgesic and anti-inflammatory characteristics in both models of chemical pain and acute inflammation in laboratory animals.
Keywords: Ketotifen, Fexofenadine, Analgesic, Anti-inflammatory, Formalin test, Carrageenan test
Introduction
The possible role of histamine in pain and inflammation was reported in 1958 for the first time,1 but was under estimated till 1983.2 Later on, lots of papers suggest different aspects of histamine as the main autocoid in allergic symptoms. Yet very few papers, suggest it as an inflammatory mediator until 2003 during which, a study on knockout mice represented the role of anti-histamines in inflammation.3 Apparently the next step was to determine the role of different histamine blocking agents in the management of allergic reactions as well as pain and inflammation; While the role of H1 anti histamines in this area was neglected, may be because of their vast effects according to their CNS penetration property.
The major clinical treatment for allergic diseases at the present is suppression of inflammation symptoms.4 Allergic reactions involve the release of histamine or other mediators from mast cells, cellular infiltration and inflammation respectively.5 Allergy symptoms can be relieved effectively by suppressing any of these events.6
Fexofenadine, the active metabolite of terfenadine, is selective histaminic H1 receptor antagonist currently indicated for use in seasonal allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria worldwide,7 which was believed not to cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) till 2009.8 Fexofenadine is rapidly absorbed and has a long duration of action, making it suitable for once daily administration.9 It undergoes minimal metabolism,10 therefore is used as a probe substrate for the P-glycoprotein efflux transporter (P-gp). Fexofenadine has been shown to suppress eosinophil-induced inflammatory cytokine release from epithelial cells,11 and to inhibit the release of chemotransmitters from basophils in vitro.12
Ketotifen also was suggested to improve allergic inflammation by decreasing lymphocytes in bronchial asthma13 and later on known as a mast cell stabilizer.14-15 There is no approved evidence for analgesic property of ketotifen except a controlled trial carried out in year 1994 in order to control neurofibroma-associated pain and itching using ketotifen again as a mast cell stabilizer.16
Despite the importance and high prevalence of conditions related to pain and inflammation, the number of new analgesics and anti-inflammations that have been introduced into clinical practice remains low.17 Among the most widely used medications for inflammation, are non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) which their world wide use is because of their demonstrated efficacy in reducing pain and inflammation.18
Although effective at relieving pain and inflammation, NSAIDs are associated with serious adverse events specially in chronic administration.19 Thus, many pharmaceutical industries and researchers have dedicated their efforts to search for safer drugs representing the same effect or even less potencies but with less adverse effects.
Histaminic receptors especially H13,20 and H421-23 receptors have been shown to interfere with pain and inflammation. Therefore it can be deducted that their antagonists could possibly inhibit pain and inflammation.24
Based on the above mentioned evidences, we have investigated, for the first time, the anti-nociceptive and anti –inflammatory effects of fexofenadine and ketotifen in chronic pain induction model using formalin test; as well as an inflammation model of carrageenan induced paw edema in rats.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Male Sprague-Dawley rats (225-250g) were used in the present study. Animals were bred in animal department, School of Pharmacy, and were housed in the animal holding unit with a 12h light-darkness cycle and air-conditioning (22 ±2°C; 45-55% humidity), in Plexi-glass cages with free access to food and water.
The animals were handled and used according to the animal handling protocol of Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran; which was approved by ethics committee. All animals were given a 3 day time to get acclimatized with laboratory conditions before experiments begin.
Chemicals
Chemicals include: Carrageenan lambda type I and formalin 35% obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. Fexofenadine (Batch No.ABEH000696) and ketotifen (Batch No.ABDH005217) powders purchased from Soha (Iran). Normal saline serum and diclofenac ampoules were bought from Abureihan (Iran), and Tolid Darou (Iran) Respectively.
Experimental design
All the experiments designed in a way that the number of animals decreases to an optimum level with the best result and reproducibility.
9 groups of animals received 3 different doses of ketotifen, fexofenadine and diclofenac in both formalin test and carrageenan induced inflammation in order to find the appropriate dose which has been reported in this study. The dose-response curves were omitted in order to abstracting the result section.
Carrageenan-induced Paw Edema in Rats
72 Male Sprague-Dawley (S.D) rats were rendered in nine groups of each 8. All animals received a sub-plantar injection of 50 µl 1% (w/v) solution of sterile carrageenan in saline to the right hind paw which caused acute inflammation.24 Six groups of animals received 3 different doses of fexofenadine (10, 15, 20 mg/kg) and ketotifen (1, 1.5, 2 mg/kg), half an hour before carrageenan administration. Animals in the negative control group received normal saline (5ml/kg) and animals in the reference group received 25 mg/kg of Diclofenac, as the standard anti-inflammatory treatment.25 The vehicle control group received carboxy methyl cellulose (5%), as the solvent for fexofenadine. It should be mentioned that ketotifen was dissolved in normal saline itself. According to the reference,24 paw edema was measured before, and at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th hours after induction of inflammation, using a caliper vernier (scale.0.1mm). All treatments injected intraperitoneally (I.P).
Formalin Test and the Pain Score
In order to perform this test, 40 male S.D rats were rendered in 5 groups with 8 rats in each. Prior to injections, the animals were placed in a cone shaped chamber for 30 min. The experimental design is described below:
Negative control group received 5ml/kg of normal saline while positive control group treated with 25mg/kg of diclofenac as the standard drug. Animals in test groups received fexofenadine (15 mg/kg as the optimum dose) and ketotifen (1.5mg/kg as the optimum dose). The vehicle control group received CMC (5%). All treatments were administered I.P, followed by a sub-plantar injection of 50 µl formalin 2.5%.
The animals were then transferred to the mirror box (a plexi glass box with a 45 degree mirror at the bottom) in order to monitor the position of the animal in the chamber for accurate observation. They were observed by recording the reflexes every 15 seconds. The quantitative data was counted per 5 minutes and recorded based on the pain score on each time interval. The data gathered within 60 minutes. The first 5 minutes after injection for all groups was taken in account as acute phase, and 16-40 minutes as chronic phase.25
Statistical Analysis
In order to perform comparative statistical analysis SPSS 17.0 software was applied. The homogeneity of data was assessed using one way Analysis of Variances (ANOVA) while the possible differences between groups were reported using Tukey post-hoc test. All the results were expressed as (mean ± SEM) and P values less than 0.05 (P < 0.05) were determined as significant level of differences.
Results
Effects of Ketotifen on Carrageenan-induced Inflammation
After a sub-plantar injection of carrageenan the thickness of hind paw was measured in the rats received diclofenac, ketotifen and normal saline as positive control, test, and negative control groups respectively.
As it is shown in Figure 1, ketotifen (1.5 mg/kg) was able to decrease the hind-paw thickness significantly in comparison with negative control group (P < 0.001). The anti-inflammatory responses were weaker than that of diclofenac as the standard treatment, but not significantly (P ≥ 0.05). The effects for ketotifen started after the second hour of inflammation (Figure 1).
Figure 1 .
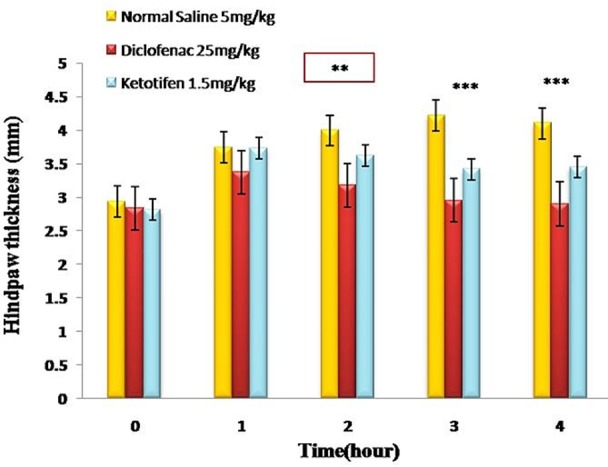
The anti-inflammatory effects of ketotifen and diclofenac towards hind paw edema. All values represent Mean ±S.E.M and are at least from 8 independent animals. ** (P <0.01), *** (P <0.001)
Effects of Fexofenadine on Carrageenan-induced Inflammation
In Figure 2 the anti-inflammatory effects of fexofenadine has been demonstrated. Fexofenadine (15 mg/kg) illustrated the best response in this test and showed a significant difference not only with negative control group but also with the vehicle control (P < 0.001). The anti-inflammatory effect started to be significant between second and third hour.
Figure 2 .
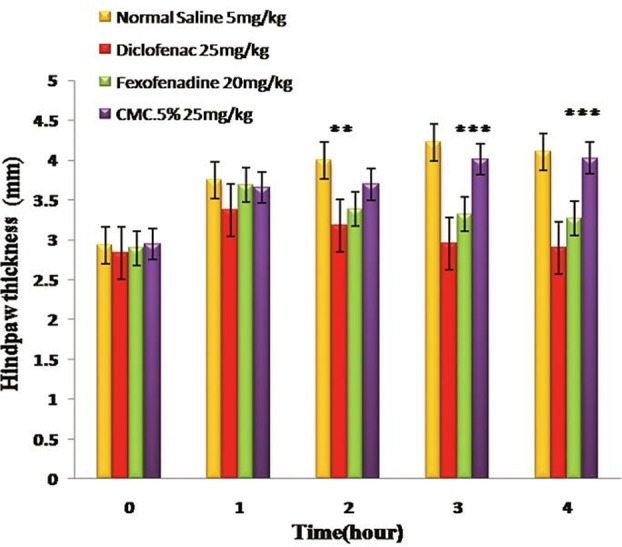
The anti-inflammatory effects of fexofenadine and diclofenac towards hind paw edema. All values represent Mean ±S.E.M and are at least from 8 independent animals. ** (P <0.05), *** (P <0.001)
Effects of Ketotifen on Formalin-induced Pain
In order to assess the analgesic effects of ketotifen, the pain score was calculated according to Dubuisson Dennis method26 during 60 minutes. The results obtained from this method indicated that our treatments were effective in controlling both acute and chronic pain phases, but not when the animal experienced the maximum level of pain. As demonstrated in Figure 3, there has been reported no significant difference between diclofenac and ketotifen (P ≥ 0.05) in both acute and chronic pain phases.
Figure 3 .
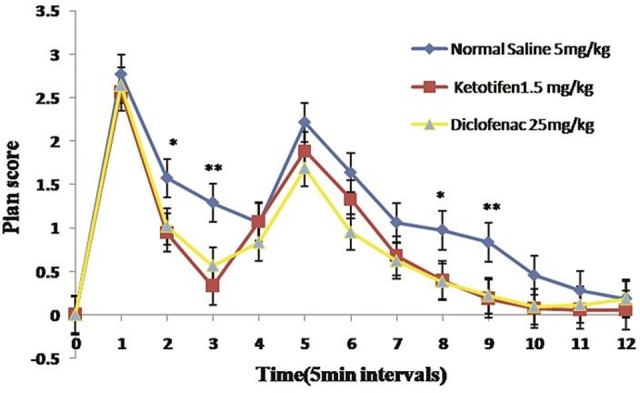
The effects of ketotifen and diclofenac on formaline induced hyper algesia. All values represent Mean ±S.E.M and are at least from 8 independent animals. * (P<0.05), ** (P <0.01)
Effects of Fexofenadine on Formalin-induced Pain
As it can be deducted from Figure 4, fexofenadine was not able to control acute phase of pain in comparison with negative control group (P ≥ 0.05). Indeed, it was able to control the pain intensity in chronic phase. Besides, there were significant differences between groups received diclofenac and fexofenadine (P < 0.05) in acute pain phases (Figure 4).
Figure 4 .
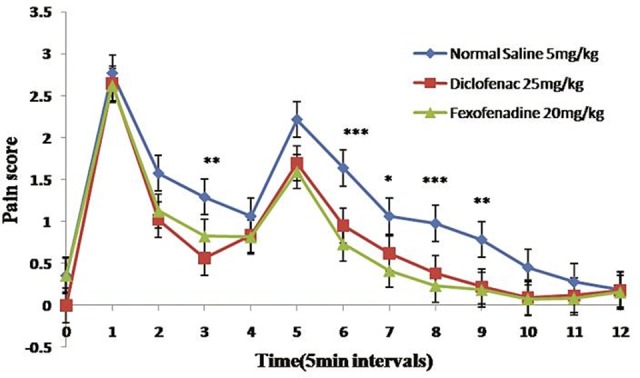
The effects of fexofenadine and diclofenac on formaline induced hyper algesia. All values represent Mean ±S.E.M and are at least from 8 independent animals. * (P <0.05), ** (P <0.01), *** (P <0.001)
Discussion
Based on the bibliographical searches, there were no studies carried out the assessment of both anti-inflammatory and anti nociceptive effects of two long acting H1 blocking agents ketotifen -with wide range of central effects- and fexofenadine ( a safe H1 blocker with little central effects). This study reported these effects for the first time and suggested some possible related mechanisms.
In this study two different methods has been applied in order to identify the possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of ketotifen and fexofenadine in rats.
Anti-inflammatory effects of ketotifen and fexofenadine
Results obtained from carrageenan test indicated a remarkable anti-inflammatory effect for ketotifen with a significant difference with the negative control group. This finding is in conformity with a research published in 2003 suggesting some novel mechanisms such as diminishing production of eotaxin and expression of CD29, in addition to the former well known mast-cell stabilizing effect of ketotifen, in management of inflammatory symptoms of allergy.27 Besides it has been reported recently that ketotifen is able to decrease pro-inflammatory mediators, including nitric oxide, interleukin-1beta, and interleukin-6, production in rats with gouty inflammation.28 The delay in responses to ketotifen might be because of its different mechanism with diclofenac in controlling the acute inflammation, but more studies needed to fulfill this claim.
Fexofenadine also represented anti-inflammatory effects in this study. The first possible anti-inflammatory effect for fexofenadine was introduced by Abdelaziz who suggested that suggest that fexofenadine may reduce nasal inflammation by modulating the release of proinflammatory mediators and adhesion molecules from human nasal epithelial cell.11 Later on, another study suggested that This study shows that terfenadine and fexofenadine exert a biologic effect directly on epithelial cells and fibroblasts reducing some adhesion molecules expression and release.29
Besides another research mentioned that fexofenadine is capable of modulating T-Cell functions which resulted in preventing airway inflanmmation.30 Recently, other aspects of fexofenadine interfering with inflammation has been reported such as reducing methacholine-induced contractions of tracheal smooth muscle.31 Fexofenadine’s pro-drug has been suggested to use in chronically active ulcerative colitis in combination with sulfasalazine.32 As this drug has a dose-dependent kinetics of penetrating into the CNS,10 more studies needed to determine its central vs. peripheral effects. The most strong evidence in this field is a research in 2006 which has been proved that fexofenadine showed selective arachidonic acid-mediated COX-2 inhibitory enzyme activity and suggested that, the selective COX-2 inhibitor activity by fexofenadine may contribute to its anti-inflammatory properties.33
Anti nociceptive effects of ketotifen and fexofenadine
In 1989 two H1 blocking agents were introduced to have analgesic effects on acute surface pain while H2 blocker agents were proved to do nothing with pain.34 Later on, an interaction between pain-relieving drugs and the brain histaminergic system was reported and multiple analgesic mechanisms suggested for antihistamines such as improgan and even cimetidine.35 In addition, the role of histamine in different types of pain include central,36 peripheral,37 acute38 chronic39 or organ related pains such as muscle pain40 was declared and the number of studies about antihistaminic agents administration as analgesic drugs have been augmented and hyper algesic role of H1 receptors have been proved strongly.3,20
In this study ketotifen was capable of inhibiting both acute and chronic phase in formalin induced pain model. The efficacy of ketotifen in pain managemen was suggested for the first time in 1993,16 which was followed by very few researches but yet, the main emphasis was on its anti allergic with a few reports on its anti-inflammatory effects. Therefore no possible mechanisms for analgesic effects of ketotifen was released or reported yet. According to the results of this study and to this finding that ketotifen is able to penetrate BBB and interfere with paleospinothalamic pain transfer pathway; it can be deducted that this inhibition through unknown mediators might be the main mechanism for analgesic responses for ketotifen.
In the formalin test two phases of pain should be distinguished. The acute and the chronic pain phases which assumed as the first 5 minutes after formalin sub-plantar injection and the time period between 16-45 minutes, respectively; there is a gap between these two phases (minutes 5-16) with the least nociception responses. It has been assumed that these two stages represent two different type of pain related to direct nerve stimulation (acute pain) followed by an inflammatory process (chronic stage). In this study fexofenadine was able to inhibit both acute and chronic phases but its effects in acute phase were weaker than that of both diclofenac and ketotifen. This can be either because of systemic pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine resulted in a longer t-max time in comparison to ketotifen10 or its special model for brain exposure which makes it difficult to penetrate from BBB.41-42
Even though there is a lack in documentary for analgesic properties of fexofenadine, this finding can be supported by a clinical finding of possible analgesic role of fexofenadine in incidence of myalgia while patients receive paclitaxel.43
According to the literature, a reduction in pain, inflammation and the signal transduction pathway(s) responsible for both above mentioned phenomenon in the acute stage results in a reduction in plasticity in dorsal root of spinal cord via deprivation in P substance 44 for ketotifen. In addition, some possible interactions between histaminic H1 receptor and opioid receptors have been suggested.44-45
Conclusion
It can be concluded that both ketotifen and fexofenadineis are capable of inhibiting pain and acute inflammation in rat models of sub-plantar injections of formalin and carrageenan respectively. The exact mechanism(s) for these effects need to be studied more, via receptor purification, using full antagonists, or Immuno histo chemistry assessments in the near future.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Vice Chancellor's Office for Research Affairs because of the grant supporting this study (No. A-11-323-5).
Ethical Issues
All animals received human care according to the guidelines published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH, 2000). The ethic regulations were followed in accordance with national and institutional guidelines for the protection of animal welfare during experiments.
Conflict of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
IP (Intra Peritoneal), CNS (Central Nervous System), BBB (Blood Brain Barrier). P-gp (P-glycoprotein), NSAIDS (Non Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs)
References
- 1.Stern P. Inflammation & pain in histamine-free skin. Acta Neuroveg (Wien) 1958;18(1-4):237–41. doi: 10.1007/bf01234819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Galletti R, Chiarini P, Duranti R, Strazzulla G, Guazzelli R, Matassi L. Reactivation of the algogenic component in experimental inflammation induced by histamine administration. Minerva Med. 1983;74(16):869–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yanai K, Mobarakeh JI, Kuramasu A, Sakurada S. Roles of histamine receptors in pain perception: a study using receptors gene knockout mice. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2003;122(5):391–9. doi: 10.1254/fpj.122.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tiligada E. Editorial: is histamine the missing link in chronic inflammation? J Leukoc Biol. 2012;92(1):4–6. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0212093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Somma T, Cinci L, Formicola G, Pini A, Thurmond R, Ennis M. et al. A selective antagonist of histamine H(4) receptors prevents antigen-induced airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction in guinea pigs: involvement of lipocortin-1. Br J Pharmacol. 2013;170(1):200–13. doi: 10.1111/bph.12264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Neumann D, Schneider EH, Seifert R. Analysis of histamine receptor knockout mice in models of inflammation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014;348(1):2–11. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.204214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Simpson K, Jarvis B. Fexofenadine: a review of its use in the management of seasonal allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria. Drugs. 2000;59(2):301–21. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200059020-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tashiro M, Sakurada Y, Iwabuchi K, Mochizuki H, Kato M, Aoki M. et al. Central effects of fexofenadine and cetirizine: measurement of psychomotor performance, subjective sleepiness, and brain histamine H1-receptor occupancy using 11C-doxepin positron emission tomography. J Clin Pharmacol. 2004;44(8):890–900. doi: 10.1177/0091270004267590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Craig-Mcfeely PM, Acharya NV, Shakir SA. Evaluation of the safety of fexofenadine from experience gained in general practice use in England in 1997. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2001;57(4):313–20. doi: 10.1007/s002280100292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chen C. Some pharmacokinetic aspects of the lipophilic terfenadine and zwitterionic fexofenadine in humans. Drugs R D. 2007;8(5):301–14. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200708050-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Abdelaziz MM, Devalia JL, Khair OA, Bayram H, Prior AJ, Davies RJ. Effect of fexofenadine on eosinophil-induced changes in epithelial permeability and cytokine release from nasal epithelial cells of patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;101(3):410–20. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(98)70256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Amon U, Amon S, Gibbs BF. In vitro studies with fexofenadine, a new nonsedating histamine H1 receptor antagonist, on isolated human basophils. Inflamm Res. 2000;49 Suppl 1:S13–4. doi: 10.1007/pl00000160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hoshino M. The effect of ketotifen on the inflammation of bronchial mucosa in atopic asthmatics. Arerugi. 1994;43(6):689–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Klooker TK, Braak B, Koopman KE, Welting O, Wouters MM, Van Der Heide S. et al. The mast cell stabiliser ketotifen decreases visceral hypersensitivity and improves intestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 2010;59(9):1213–21. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.213108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Serna H, Porras M, Vergara P. Mast cell stabilizer ketotifen [4-(1-methyl-4-piperidylidene)-4h-benzo[4,5]cyclohepta[1,2-b]thiophen-10(9H)-one fumarate] prevents mucosal mast cell hyperplasia and intestinal dysmotility in experimental Trichinella spiralis inflammation in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;319(3):1104–11. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.104620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Riccardi VM. A controlled multiphase trial of ketotifen to minimize neurofibroma-associated pain and itching. Arch Dermatol. 1993;129(5):577–81. doi: 10.1001/archderm.129.5.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Parkitny L, Mcauley JH, Di Pietro F, Stanton TR, O'connell NE, Marinus J. et al. Inflammation in complex regional pain syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology. 2013;80(1):106–17. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0b013e31827b1aa1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Inflammation-induced pain. How rheumatism patients profit from the proper NSAID choice. MMW Fortschr Med. 2012;154(8):74–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Scanzello CR, Moskowitz NK, Gibofsky A. The post-NSAID era: what to use now for the pharmacologic treatment of pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2008;10(1):49–56. doi: 10.1007/s11926-008-0009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mobarakeh JI, Sakurada S, Katsuyama S, Kutsuwa M, Kuramasu A, Lin ZY. et al. Role of histamine H(1) receptor in pain perception: a study of the receptor gene knockout mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;391(1-2):81–9. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cowart MD, Altenbach RJ, Liu H, Hsieh GC, Drizin I, Milicic I. et al. Rotationally constrained 2,4-diamino-5,6-disubstituted pyrimidines: a new class of histamine H4 receptor antagonists with improved druglikeness and in vivo efficacy in pain and inflammation models. J Med Chem. 2008;51(20):6547–57. doi: 10.1021/jm800670r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kamo A, Negi O, Tengara S, Kamata Y, Noguchi A, Ogawa H. et al. Histamine H(4) receptor antagonists ineffective against itch and skin inflammation in atopic dermatitis mouse model. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134(2):546–8. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cowden JM, Yu F, Banie H, Farahani M, Ling P, Nguyen S. et al. The histamine H4 receptor mediates inflammation and Th17 responses in preclinical models of arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(3):600–8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Coruzzi G, Adami M, Guaita E, De Esch IJ, Leurs R. Antiinflammatory and antinociceptive effects of the selective histamine H4-receptor antagonists JNJ7777120 and VUF6002 in a rat model of carrageenan-induced acute inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;563(1-3):240–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.02.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nasri S, Anoush M, Khatmi N. Evaluation of analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of fresh onion juice in experimental animals. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012;6(23):1679–84. doi: 10.5897/ajpp12.179. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Abbott FV, Franklin KB, Westbrook RF. The formalin test: scoring properties of the first and second phases of the pain response in rats. Pain. 1995;60(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(94)00095-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Martin AP, Urrets-Zavalia J, Berra A, Mariani AL, Gallino N, Gomez Demel E. et al. The effect of ketotifen on inflammatory markers in allergic conjunctivitis: an open, uncontrolled study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2003;3:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2415-3-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Hsu DZ, Chu PY, Chen SJ, Liu MY. Mast Cell Stabilizer Ketotifen Inhibits Gouty Inflammation in Rats. Am J Ther 2013. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e31829ea238 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 29.Paolieri F, Battifora M, Riccio AM, Bertolini C, Cutolo M, Bloom M. et al. Terfenadine and fexofenadine reduce in vitro ICAM-1 expression on human continuous cell lines. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1998;81(6):601–7. doi: 10.1016/s1081-1206(10)62712-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gelfand EW, Cui ZH, Takeda K, Kanehiro A, Joetham A. Fexofenadine modulates T-cell function, preventing allergen-induced airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110(1):85–95. doi: 10.1067/mai.2002.124770a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lai WS, Lin YY, Chu YH, Wang CH, Wang HW. Efficacy of fexofenadine in isolated rat tracheas. Rhinology. 2013;51(4):376–80. doi: 10.4193/Rhin12.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dhaneshwar S, Gautam H. Exploring novel colon-targeting antihistaminic prodrug for colitis. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;63(4):327–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Juergens UR, Gillissen A, Uen S, Racke K, Stober M, Darlath W. et al. New evidence of H1-receptor independent COX-2 inhibition by fexofenadine HCl in vitro. Pharmacology. 2006;78(3):129–35. doi: 10.1159/000096016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bjerring P. Effect of antihistamines on argon laser-induced cutaneous sensory and pain thresholds and on histamine-induced wheal and flare. Skin Pharmacol. 1989;2(4):210–6. doi: 10.1159/000210822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hough LB, Nalwalk JW, Svokos K, Leurs R, Timmermann H. Pain-relieving drugs and the brain histaminergic system: multiple analgesic mechanisms from histamine, improgan and cimetidine. Inflamm Res. 2004;53 Suppl 1:S43–4. doi: 10.1007/s00011-003-0320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Erfanparast A, Tamaddonfard E, Farshid AA, Khalilzadeh E. Effect of microinjection of histamine into the dorsal hippocampus on the orofacial formalin-induced pain in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;627(1-3):119–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.10.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cannon KE, Leurs R, Hough LB. Activation of peripheral and spinal histamine H3 receptors inhibits formalin-induced inflammation and nociception, respectively. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2007;88(1):122–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2007.07.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tamaddonfard E, Khalilzadeh E, Hamzeh-Gooshchi N, Seiednejhad-Yamchi S. Central effect of histamine in a rat model of acute trigeminal pain. Pharmacol Rep. 2008;60(2):219–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mobarakeh JI, Torkaman-Boutorabi A, Rahimi AA, Ghasri S, Nezhad RM, Hamzely A. et al. Interaction of histamine and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the formalin induced pain perception in rats. Biomed Res. 2011;32(3):195–201. doi: 10.2220/biomedres.32.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wasner G, Schwarz K, Schattschneider J, Binder A, Jensen TS, Baron R. Interaction between histamine-induced itch and experimental muscle pain. Eur J Pain. 2004;8(3):179–85. doi: 10.1016/s1090-3801(03)00099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gundogdu E, Mangas-Sanjuan V, Gonzalez-Alvarez I, Bermejo M, Karasulu E. In vitro-in situ permeability and dissolution of fexofenadine with kinetic modeling in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2012;37(1):65–75. doi: 10.1007/s13318-011-0059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhao R, Kalvass JC, Yanni SB, Bridges AS, Pollack GM. Fexofenadine brain exposure and the influence of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein after fexofenadine and terfenadine administration. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37(3):529–35. doi: 10.1124/dmd.107.019893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Garrison JA, Mccune JS, Livingston RB, Linden HM, Gralow JR, Ellis GK. et al. Myalgias and arthralgias associated with paclitaxel. Oncology (Williston Park) 2003;17(2):271–7; discussion 81-2, 86-8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nakao K, Ikeda K, Kurokawa T, Togashi Y, Umeuchi H, Honda T. et al. Effect of TRK-820, a selective kappa opioid receptor agonist, on scratching behavior in an animal model of atopic dermatitis. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2008;28(2):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rehni AK, Singh TG, Singh N, Arora S. Tramadol-induced seizurogenic effect: a possible role of opioid-dependent histamine H1 receptor activation-linked mechanism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2010;381(1):11–9. doi: 10.1007/s00210-009-0476-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


