Scheme 1.
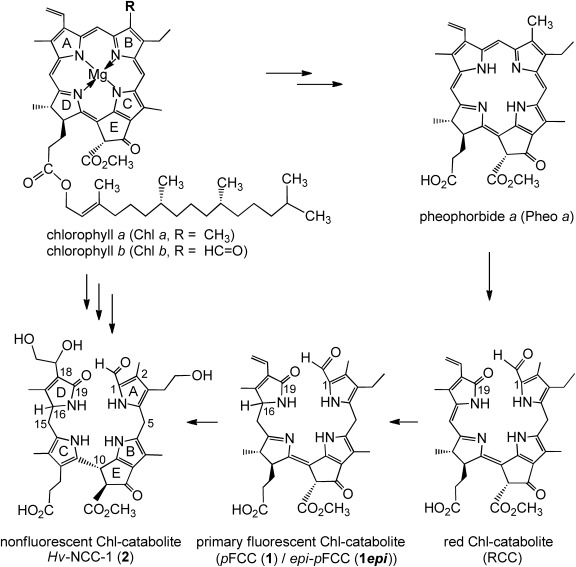
Structural outline of chlorophyll breakdown in senescent leaves. Chlorophylls a&b (Chl a&Chl b) are first degraded to pheophorbide a (Pheo a). Ring opening of the chlorin macrocycle of Pheo a provides an enzyme bound red chlorophyll catabolite (RCC), which is subsequently reduced to the “primary” fluorescent chlorophyll catabolite (pFCC, 1) or its 16-epimer (epi-pFCC, 1epi). pFCCs (1/1epi) undergo further modifications and isomerization to “non-fluorescent” chlorophyll catabolites (NCCs), such as Hv-NCC-1 (2), first detected in primary leaves of barley (Hordeum vulgare).[3b, 4]
