Abstract
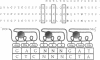
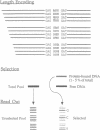
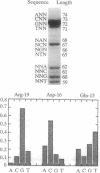
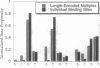
The screening of combinatorial libraries is becoming a powerful method for identifying or refining the structures of ligands for binding proteins, enzymes, and other receptors. We describe an oligonucleotide library search procedure in which the identity of each member is encoded in the length of oligonucleotides. This encoding scheme allows binding-site preferences to be evaluated via DNA length determination by denaturing gel electrophoresis. We have applied this method to determine the binding-site preferences for 18 Cys2His2 zinc finger domains as the central domain within a fixed context of flanking zinc fingers. An advantage of the method is that the relative affinities of all members of the library can be estimated in addition to simply determining the sequence of the optimal or consensus ligand. The zinc finger domain specificities determined will be useful for modular zinc finger protein design.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander P., Fahnestock S., Lee T., Orban J., Bryan P. Thermodynamic analysis of the folding of the streptococcal protein G IgG-binding domains B1 and B2: why small proteins tend to have high denaturation temperatures. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 14;31(14):3597–3603. doi: 10.1021/bi00129a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Zinc finger domains: hypotheses and current knowledge. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:405–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S., Lerner R. A. Encoded combinatorial chemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5381–5383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjarlais, Berg J. M. Redesigning the DNA-binding specificity of a zinc finger protein: a data base-guided approach. Proteins. 1992 Jul;13(3):272–272. doi: 10.1002/prot.340130309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjarlais J. R., Berg J. M. Redesigning the DNA-binding specificity of a zinc finger protein: a data base-guided approach. Proteins. 1992 Feb;12(2):101–104. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjarlais J. R., Berg J. M. Toward rules relating zinc finger protein sequences and DNA binding site preferences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7345–7349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjarlais J. R., Berg J. M. Use of a zinc-finger consensus sequence framework and specificity rules to design specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2256–2260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):818–822. doi: 10.1038/346818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor S. P., Read J. L., Pirrung M. C., Stryer L., Lu A. T., Solas D. Light-directed, spatially addressable parallel chemical synthesis. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):767–773. doi: 10.1126/science.1990438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Pinilla C., Blondelle S. E., Appel J. R., Dooley C. T., Cuervo J. H. Generation and use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for basic research and drug discovery. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):84–86. doi: 10.1038/354084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Whole genome PCR: application to the identification of sequences bound by gene regulatory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3645–3653. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needels M. C., Jones D. G., Tate E. H., Heinkel G. L., Kochersperger L. M., Dower W. J., Barrett R. W., Gallop M. A. Generation and screening of an oligonucleotide-encoded synthetic peptide library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10700–10704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlmeyer M. H., Swanson R. N., Dillard L. W., Reader J. C., Asouline G., Kobayashi R., Wigler M., Still W. C. Complex synthetic chemical libraries indexed with molecular tags. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):10922–10926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarai A., Takeda Y. Lambda repressor recognizes the approximately 2-fold symmetric half-operator sequences asymmetrically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6513–6517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiesen H. J., Bach C. Target Detection Assay (TDA): a versatile procedure to determine DNA binding sites as demonstrated on SP1 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3203–3209. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):505–510. doi: 10.1126/science.2200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Funk W. D. CASTing for multicomponent DNA-binding complexes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Mar;18(3):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90156-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann R. N., Kerr J. M., Siani M. A., Banville S. C., Santi D. V. Identification of highest-affinity ligands by affinity selection from equimolar peptide mixtures generated by robotic synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4505–4509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]