Abstract
Purpose
Traditionally, the surgical repair of umbilical hernia in cirrhotic patients with ascites is avoided because of a significant recurrence rate and perioperative morbidity/mortality. However, recent reports recommend early elective surgery in these patients because surgery-related complications can be reduced with minimally invasive surgery and development of perioperative patient care. The current study was conducted to analyze safety and feasibility of umbilical hernia repairs performed in a single institute.
Methods
A single center retrospective analysis of patients' data was conducted. Eighteen patients with umbilical hernia accompanied by liver cirrhosis underwent hernia repair in the period between 2005 and 2012. The charts of these patients were reviewed and demographic data, postoperative complications, and recurrence were recorded.
Results
Eleven males and seven females with a mean age of 62.9 years were analyzed. Two of the patients were classified as Child's class A, 11 as Child's class B, and five as Child's class C. Four patients underwent emergency surgery because of perforations in the hernia sac in two cases and incarcerated hernias in the other two cases. Of the 18 patients who underwent surgery, four (22%) experienced a recurrence, three (17%) developed edema at the surgical sites, one (5%) experienced hepatic coma, and one (5%) showed postoperative variceal hemorrhage. All of these events occurred after emergency surgery.
Conclusion
In contrast to traditional concepts, early and elective repair of umbilical hernia can be performed easily and safely in cirrhotic patients.
Keywords: Hernia, Ascites, Laparoscopy
INTRODUCTION
The prevalence of umbilical hernia in cirrhotic patients with ascites is up to 20% [1]. Traditionally, the surgical treatment of umbilical hernia in those patients was avoided because of a significant recurrence rate and postoperative morbidity/mortality [2]. However, conservative treatment is also associated with high mortality rates because of the strong likelihood of emergency situations, such as incarcerated hernias or rupture of the hernia sac [3,4,5,6]. Thus, controversies regarding the treatment modality and timing of umbilical hernia repair in cirrhotic patients remain.
There is a lack of high-level, randomized, controlled studies of umbilical hernia patients accompanied by liver cirrhosis to form the basis of treatment protocols. However, an increasing number of reports are recommending early elective surgery in umbilical hernia patients with liver cirrhosis because surgery-related complications can be reduced with laparoscopic surgery and development of perioperative patient care [5,7,8,9]. The current study was conducted to analyze umbilical hernia repairs performed in a single institute to determine the risk of complications resulting from the surgery, to determine the recurrence rates, and to aid decision making regarding appropriate treatment methods.
METHODS
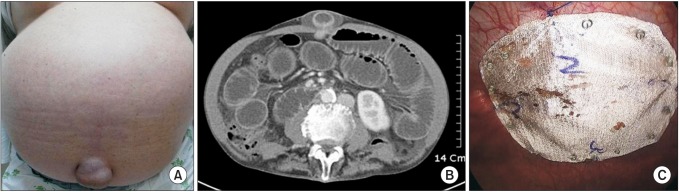
The inpatient and ambulatory medical records of 18 umbilical hernia patients accompanied by liver cirrhosis who underwent surgery performed by the same surgeon at an urban tertiary medical center in South Korea, between January 2005 and August 2012 were analyzed retrospectively. Liver cirrhosis was diagnosed through clinical, biochemical, and histological test results. Patients diagnosed with umbilical hernia through ultrasonography or computed tomography in addition to physical examinations, were included in the study (Fig. 1). The degree of hepatic dysfunction was classified using Child's classification.
Fig. 1. (A) Gross appearance of umbilical hernia in cirrhotic patient. (B) Typical CT finding of umbilical hernia. (C) Laparoscopic intraperitoneal onlay mesh repair, mesh fixation using fascial clsoure and endo-stapler.
Open repairs were performed in three cases. Simple absorbable sutures were used in one case. In two cases, polypropylene meshes were fixed to the external layers of the fascia.
Laparoscopic surgery was performed in the remaining 15 cases using a 10-mm laparoscopic port for a 30° telescope and two additional 5-mm ports for surgical instruments. When necessary adhesiolysis was performed using scissors without an energy source. The hernia was identified and any contents were reduced. The surrounding area was prepared for mesh placement and under laparoscopic vision the defect was palpated and the skin was marked with a sterile pen. The mesh size was chosen with a minimum overlap of 5 cm around the defect. Prior to intra-abdominal placement, four Prolene (Ethicon, Edinburgh, UK) sutures were placed at the midpoints of the mesh superiorly, inferiorly, the left and right lateral margins, to assist placement of the mesh and corresponding markings for the sutures were made on the external abdominal wall with a sterile pen.
The composite meshes were then inserted via 10-mm trocar and placed over the defect. A suture passer device was used to pull and tie in the subcutaneous layer. The mesh was fixed circumferentially with spiral tacks using a standard double crowning technique. The operative field was inspected and the trocars were removed under direct vision. The fascial layer was closed in the 10-mm incisions with no placement of drains. All cases were done under general anesthesia. All patients in this series had only medical control of ascites during perioperative period and surgical drains were maintained until adequate wound healing.
RESULTS
The 18 patients who underwent surgery were aged between 46 and 82 years, and the mean age of the patients was 62.9 years. Eleven patients were males, and seven were females. Two of the patients were classified as Child's class A, 11 as Child's class B, and five as Child's class C. Four patients underwent emergency surgery, two cases due to perforation of the hernia sac and the other two cases due to incarceration (Table 1).
Table 1. Demographics and clinical characteristics of 18 patients underwent umbilical hernia repair.
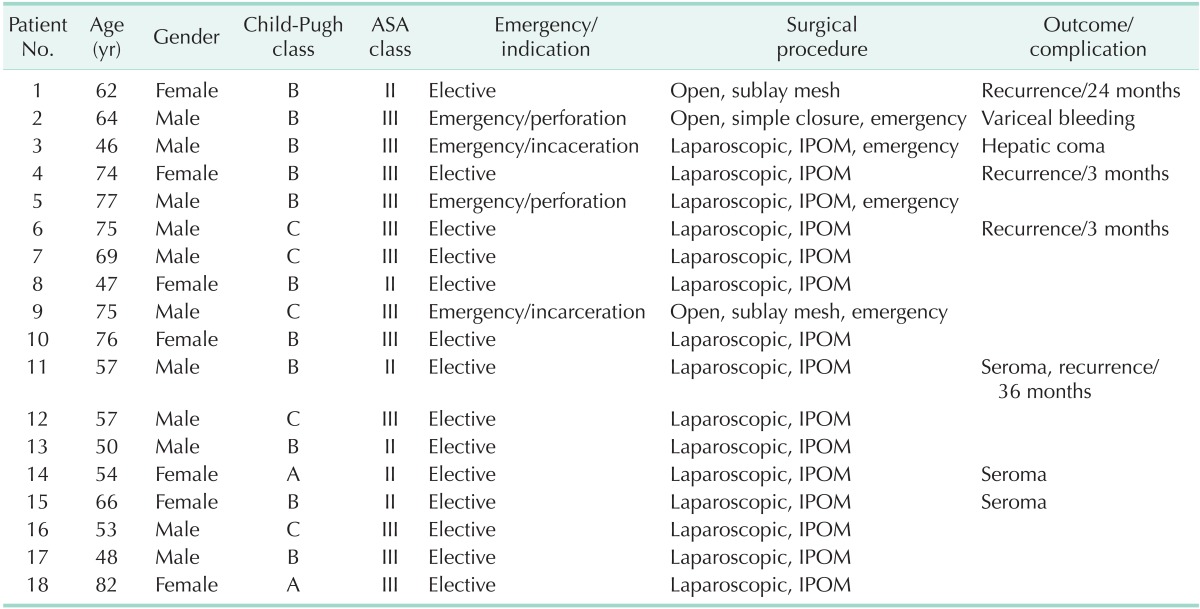
ASA, American Society of Anesthesiologists; IPOM, Intraperitoneal Onlay Mesh repair.
Of the 18 patients who underwent surgery, four (22%) experienced a recurrence, three (17%) developed seroma at the surgical sites, one (5%, Child's B) experienced hepatic coma, and one (5%, Child's C) showed postoperative variceal hemorrhage (Table 2). All of these events occurred after emergency surgery (Table 1). Uncontrollable ascites were responsible for the recurrences in the four cases during a median follow-up period of 19.5 months (range, 3 to 33 months). There was no perioperative mortality (Table 2).
Table 2. Surgical and postoperative data.

Values are presented as median (range) or number.
DISCUSSION
The occurrence of umbilical hernia in liver cirrhosis patients is the result of various factors, including abdominal muscle weakening due to under nutrition, high intra-abdominal pressure due to ascites and supraumbilical fascial opening resulting from hepatic vein expansion in patients accompanied by portal vein hypertension [2]. Therefore, the prevalence of umbilical hernia in cirrhotic patients with ascites is up to 20%, and recurrence rate as high as 60% after surgical correction has been reported [10,11]. In 1960, in a study conducted with 16 patients, Baron [12] reported a mortality rate of 31% after umbilical hernia repairs, with all deaths apparently due to esophageal or gastric variceal hemorrhage. It was assumed that the variceal hemorrhage occurred because the bypass circulation between the portal vein and the systemic vein was blocked after surgery. Subsequently, umbilical hernia surgery in cirrhotic patients was regarded as very risky. However, the risk of variceal hemorrhage did not increase after surgery in studies conducted thereafter. Accordingly, early elective surgery was recommended to prevent complications after emergency surgery. [6,13,14] Nevertheless, surgical treatment is avoided in many cases because of the risk of complications related to the surgery and high recurrence rates.
On the other hand, more recent reports have indicated much lower morbidity and mortality rates [15]. The reduction in postoperative complications and related deaths is the result of improvements in perioperative patient care and recent developments in surgical techniques [15]. Kirkpatrick and Schubert [16] reported that compared to before 1975, patients' postoperative mortality rates had decreased and their prognoses had improved and that waiting to perform surgery until complications of umbilical hernia occurred was associated with higher morbidity rates and mortality rates. Maniatis and Hunt [17], who reviewed the literature published between 1956 and 1995, reported that whereas elective surgery was associated with a mortality rate of 2%, emergency surgery showed a mortality rate of 14%. Mckay et al. [15] also reported a mortality rate of 2.7% based on a review of the literature published since 1980. Thus, it can be seen that the postoperative mortality rate of umbilical hernia patients accompanied by liver cirrhosis has decreased dramatically since the 1980s. In the current study, none of the 18 patients who underwent surgery died.
The use of meshes in umbilical hernia repairs greatly reduced recurrence rates compared to the conventional suture method, although the frequency of postoperative complications did not differ [3]. However, the fixation of meshes to the extraperitoneal fascia is known to be associated with relatively high frequencies of complications, such as hematoma, seroma, and chronic pain because it requires a longer operation time and excessive detachment [9]. Therefore, to reduce the detachment and the operation time, open or laparoscopic intraperitoneal mesh insertion was proposed [18,19]. However, intraperitoneal mesh insertion increased the risk of postoperative intestinal adhesion and other complications [20]. Thereafter, Mutter et al. [21] advised that using composite meshes could prevent intestinal adhesion and reduce the incidence of complications. Insertion of composite mesh into the abdominal cavity using a laparoscope can be a simple and optimum method of reducing recurrences and complications [8,9].
In addition laparoscopic surgery itself offers a minimally invasive and tension-free technique that yields less morbidity and lower recurrence rate than the open repair [7,22]. There are several advantages of laparoscopic surgery in patients with liver cirrhosis, including lower perioperative blood loss and reduction in the wound and mesh infection rate [7]. In the current study, there were no severe postoperative complications in the 15 patients who underwent laparoscopic surgery and intraperitoneal mesh insertion. For these reasons we prefer laparoscopic repair with mesh insertion in cirrhotic patients.
Although favorable results have been reported recently with early hernia corrections, most of the findings are based on small-scale retrospective studies [15]. In addition, the patients included in these studies who underwent elective surgery were selected because of their low risks related to surgery or anesthesia. Thus, it is quite likely that selection biases occurred [15]. According to data reported by Belghiti and Durand [1], patients with more severe hepatic cirrhosis are less likely to undergo elective surgery. The ratios of patients according to Child's classification who underwent elective surgery were 80% in class A, 52% in class B, and 17% in class C [1]. This is important because the incidence rate of complications and the mortality rate increase dramatically in patients with Child's class C compared to those with class A disease. In the current study, 13 of the 18 subjects (72%) were in Child's class A and B groups.
Ascites are not only a cause of umbilical hernia, but also a major cause of postoperative recurrences. In the current study, ascites were responsible for all four recurrence cases (22%), indicating that prevention of postoperative ascites is important in order to prevent umbilical hernia recurrences. The results of three retrospective studies reported 10% to 50% of recurrence rate and indicated that umbilical hernia recurred frequently in patients with ascites [23,24,25]. These studies suggested that prevention of postoperative ascites was the most important factor in avoiding recurrences. A variety of methods have been used to control ascites in addition to medical treatment. These include the insertion of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, a peritoneovenous shunt, a peritoneal dialysis tube, or a drainage tube, in addition to continuous percutaneous drainage [15]. However, there is insufficient evidence to determine which of these methods is best, and there is no defined time for maintenance of the drainage tube. Therefore, the risk of complications, such as infection, associated with recurrences and ascites should be controlled.
In the current study, early and active repair of umbilical hernia was performed easily and safely without ascites leaks, regardless of the degree of hepatic dysfunction, although the number of patients was limited. Given that all cases of postoperative recurrences were due to uncontrollable ascites, the control of ascites after umbilical hernia repair appears to be important to prevention of recurrences. To confirm this, conduct of large-scale prospective randomized controlled studies is considered necessary.
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
- 1.Belghiti J, Durand F. Abdominal wall hernias in the setting of cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis. 1997;17:219–226. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1007199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shlomovitz E, Quan D, Etemad-Rezai R, McAlister VC. Association of recanalization of the left umbilical vein with umbilical hernia in patients with liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2005;11:1298–1299. doi: 10.1002/lt.20579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Arroyo A, Garcia P, Perez F, Andreu J, Candela F, Calpena R. Randomized clinical trial comparing suture and mesh repair of umbilical hernia in adults. Br J Surg. 2001;88:1321–1323. doi: 10.1046/j.0007-1323.2001.01893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lemmer JH, Strodel WE, Knol JA, Eckhauser FE. Management of spontaneous umbilical hernia disruption in the cirrhotic patient. Ann Surg. 1983;198:30–34. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198307000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Marsman HA, Heisterkamp J, Halm JA, Tilanus HW, Metselaar HJ, Kazemier G. Management in patients with liver cirrhosis and an umbilical hernia. Surgery. 2007;142:372–375. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2007.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.O'Hara ET, Oliai A, Patek AJ, Jr, Nabseth DC. Management of umbilical hernias associated with hepatic cirrhosis and ascites. Ann Surg. 1975;181:85–87. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197501000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Belli G, D'Agostino A, Fantini C, Cioffi L, Belli A, Russolillo N, et al. Laparoscopic incisional and umbilical hernia repair in cirrhotic patients. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2006;16:330–333. doi: 10.1097/01.sle.0000213745.15773.c1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gonzalez R, Mason E, Duncan T, Wilson R, Ramshaw BJ. Laparoscopic versus open umbilical hernia repair. JSLS. 2003;7:323–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jarsaillon P. Laparoscopic treatment of an umbilical hernia using a new composite mesh. Hernia. 2000;4:517–521. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hansen JB, Thulstrup AM, Vilstup H, Sørensen HT. Danish nationwide cohort study of postoperative death in patients with liver cirrhosis undergoing hernia repair. Br J Surg. 2002;89:805–806. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.2002.02114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sarit C, Eliezer A, Mizrahi S. Minimally invasive repair of recurrent strangulated umbilical hernia in cirrhotic patient with refractory ascites. Liver Transpl. 2003;9:621–622. doi: 10.1053/jlts.2003.50078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Baron HC. Umbilical hernia secondary to cirrhosis of the liver: complications of surgical correction. N Engl J Med. 1960;263:824–828. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196010272631702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lemmer JH, Strodel WE, Eckhauser FE. Umbilical hernia incarceration: a complication of medical therapy of ascites. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983;78:295–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pescovitz MD. Umbilical hernia repair in patients with cirrhosis: no evidence for increased incidence of variceal bleeding. Ann Surg. 1984;199:325–327. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198403000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.McKay A, Dixon E, Bathe O, Sutherland F. Umbilical hernia repair in the presence of cirrhosis and ascites: results of a survey and review of the literature. Hernia. 2009;13:461–468. doi: 10.1007/s10029-009-0535-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kirkpatrick S, Schubert T. Umbilical hernia rupture in cirrhotics with ascites. Dig Dis Sci. 1988;33:762–765. doi: 10.1007/BF01540442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Maniatis AG, Hunt CM. Therapy for spontaneous umbilical hernia rupture. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90:310–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Arnaud JP, Cervi C, Tuech JJ, Cattan F. Surgical treatment of post-operative incisional hernias by intra-peritoneal insertion of a Dacron mesh. Hernia. 1997;1:97–99. [Google Scholar]
- 19.LeBlanc KA, Booth WV. Laparoscopic repair of incisional abdominal hernias using expanded polytetrafluoroethylene: preliminary findings. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1993;3:39–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Marchal F, Brunaud L, Sebbag H, Bresler L, Tortuyaux JM, Boissel P. Treatment of incisional hernias by placement of an intraperitoneal prosthesis: a series of 128 patients. Hernia. 1999;3:141–147. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mutter D, Rodeheaver G, Diemunsch P, Therin M, Moody D, Raffaeli M. A new composite mesh (collagen-polyester) for intra-abdominal laparoscopic hernia repair. Surg Endosc. 1998;12:595. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Itani KM, Neumayer L, Reda D, Kim L, Anthony T. Repair of ventral incisional hernia: the design of a randomized trial to compare open and laparoscopic surgical techniques. Am J Surg. 2004;188(6A Suppl):22S–29S. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2004.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Belghiti J, Desgrandchamps F, Farges O, Fekete F. Herniorrhaphy and concomitant peritoneovenous shunting in cirrhotic patients with umbilical hernia. World J Surg. 1990;14:242–246. doi: 10.1007/BF01664882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Leonetti JP, Aranha GV, Wilkinson WA, Stanley M, Greenlee HB. Umbilical herniorrhaphy in cirrhotic patients. Arch Surg. 1984;119:442–445. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1984.01390160072014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Runyon BA, Juler GL. Natural history of repaired umbilical hernias in patients with and without ascites. Am J Gastroenterol. 1985;80:38–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


