Abstract
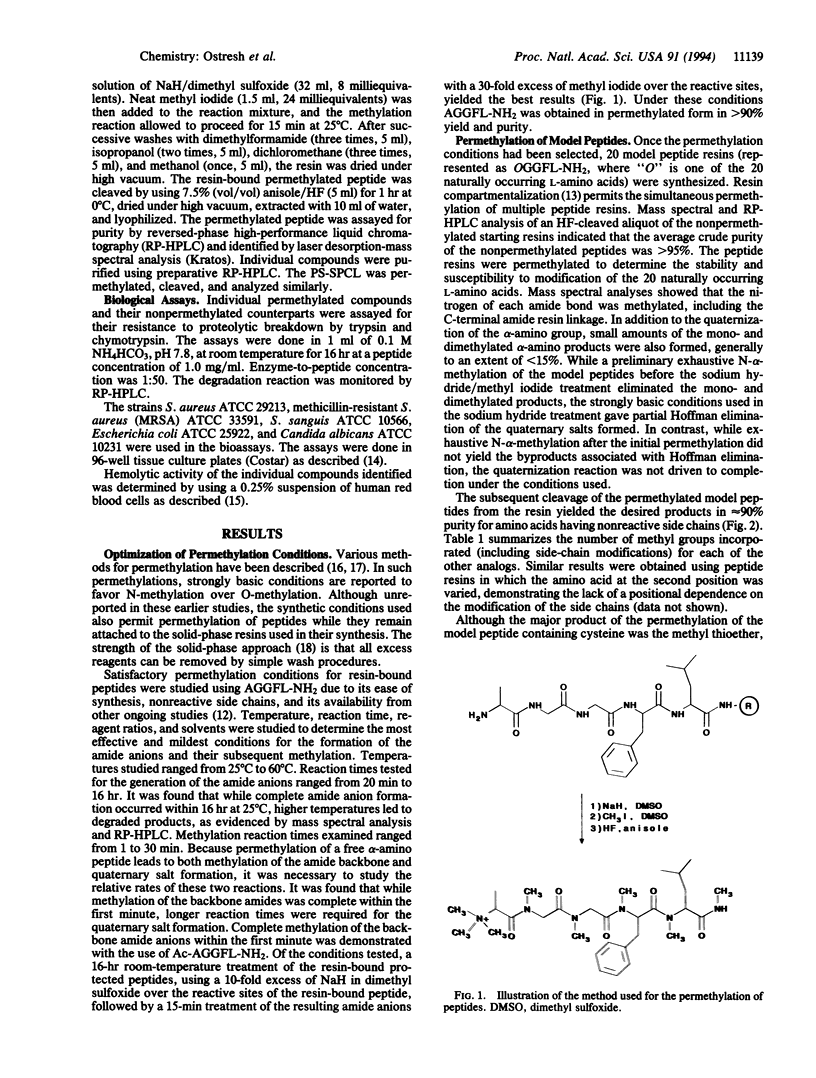
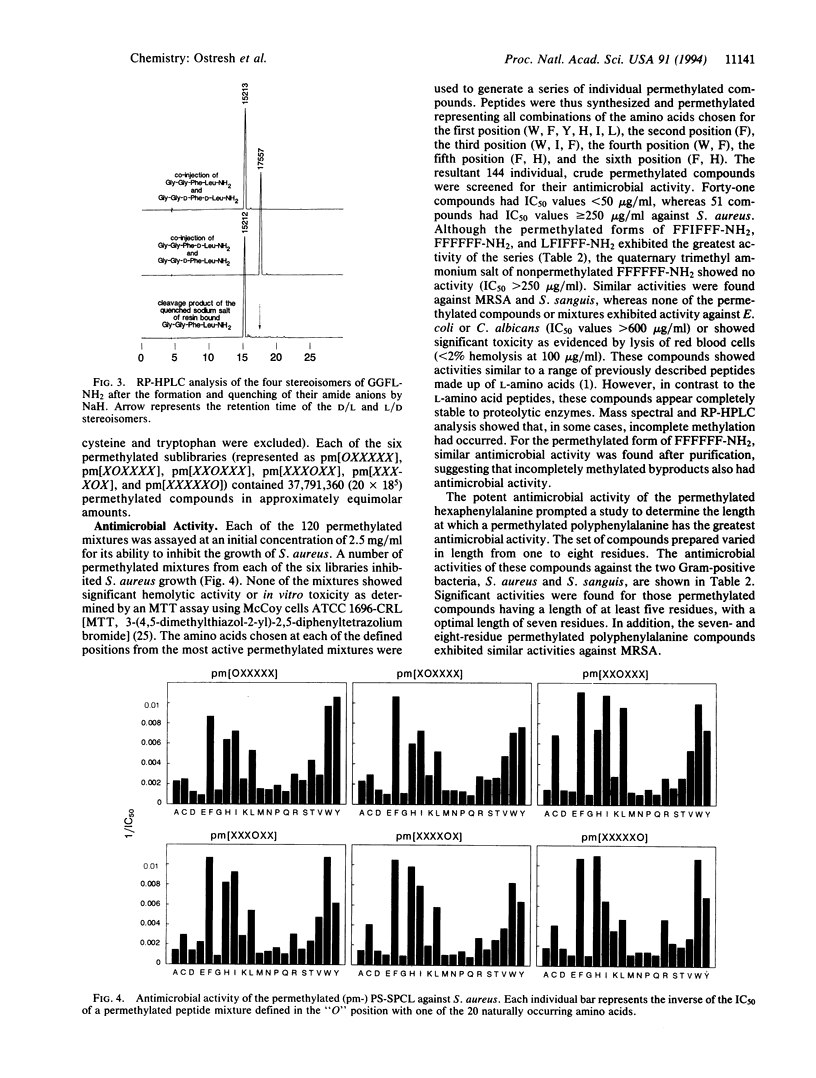
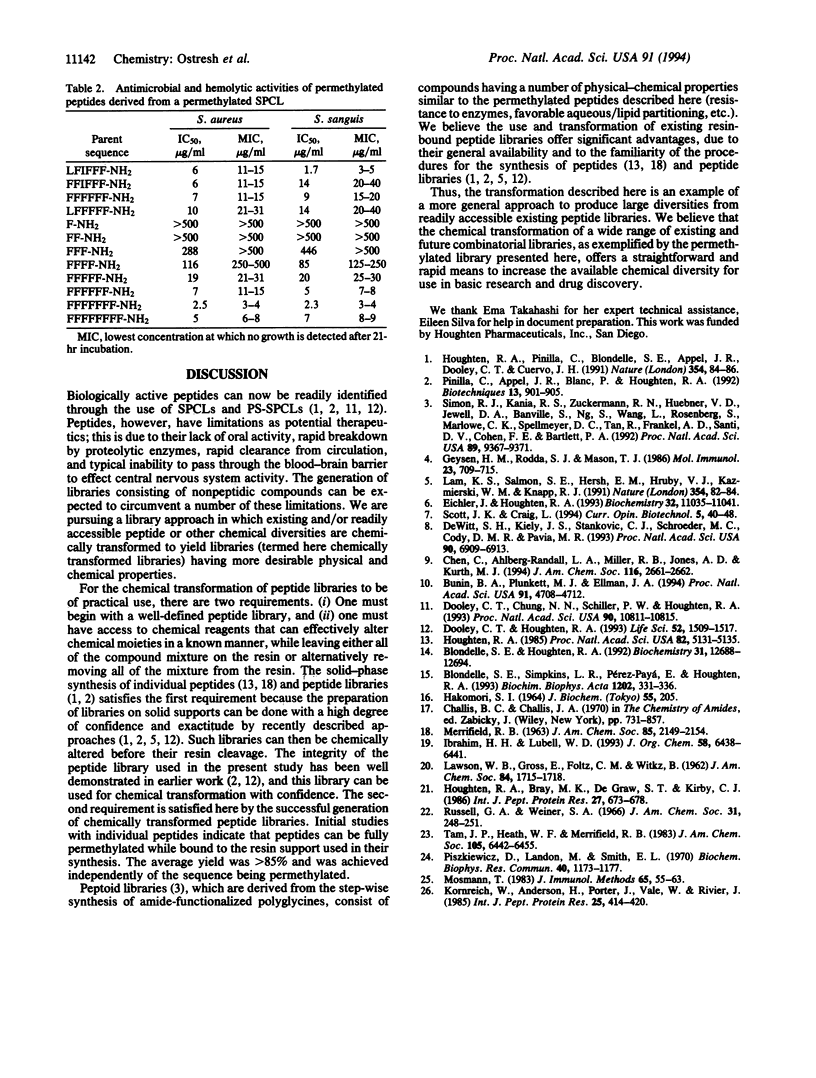
The generation of diverse chemical libraries using a "libraries from libraries" concept is described. The central features of the approaches presented are the use of well-established solid-phase synthesis methods for the generation of combinatorial libraries, combined with the chemical transformation of such libraries while they remain attached to the solid support. The chemical libraries that are generated by this process have very different physical, chemical, and biological properties compared to the libraries from which they were derived. A wide range of chemical transformations are possible for peptide-based or other libraries, and an almost unlimited range of useful chemical diversities can be envisioned. In the example presented, the amide functionalities in an existing combinatorial library made up of peptides were permethylated while the library remained attached to the solid-phase support used in its synthesis. After removal of the permethylated mixtures from their solid support, this library, now lacking the typical -CONH- amide bonds of peptides, can be tested in solution with virtually all existing assay systems to identify individual compounds having specific biological activities of interest. An illustration of the use of such libraries is presented, in which the described permethylated library was used to identify individual permethylated compounds having potent antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blondelle S. E., Houghten R. A. Design of model amphipathic peptides having potent antimicrobial activities. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 22;31(50):12688–12694. doi: 10.1021/bi00165a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondelle S. E., Simpkins L. R., Pérez-Payá E., Houghten R. A. Influence of tryptophan residues on melittin's hemolytic activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 6;1202(2):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(93)90024-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunin B. A., Plunkett M. J., Ellman J. A. The combinatorial synthesis and chemical and biological evaluation of a 1,4-benzodiazepine library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4708–4712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt S. H., Kiely J. S., Stankovic C. J., Schroeder M. C., Cody D. M., Pavia M. R. "Diversomers": an approach to nonpeptide, nonoligomeric chemical diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6909–6913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley C. T., Chung N. N., Schiller P. W., Houghten R. A. Acetalins: opioid receptor antagonists determined through the use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10811–10815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley C. T., Houghten R. A. The use of positional scanning synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for the rapid determination of opioid receptor ligands. Life Sci. 1993;52(18):1509–1517. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90113-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichler J., Houghten R. A. Identification of substrate-analog trypsin inhibitors through the screening of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 19;32(41):11035–11041. doi: 10.1021/bi00092a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J. A priori delineation of a peptide which mimics a discontinuous antigenic determinant. Mol Immunol. 1986 Jul;23(7):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Bray M. K., Degraw S. T., Kirby C. J. Simplified procedure for carrying out simultaneous multiple hydrogen fluoride cleavages of protected peptide resins. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1986 Jun;27(6):673–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1986.tb01064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornreich W., Anderson H., Porter J., Vale W., Rivier J. Peptide N-alkylamides by solid phase synthesis. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1985 Apr;25(4):414–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1985.tb02194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Salmon S. E., Hersh E. M., Hruby V. J., Kazmierski W. M., Knapp R. J. A new type of synthetic peptide library for identifying ligand-binding activity. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):82–84. doi: 10.1038/354082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinilla C., Appel J. R., Blanc P., Houghten R. A. Rapid identification of high affinity peptide ligands using positional scanning synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries. Biotechniques. 1992 Dec;13(6):901–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Landon M., Smith E. L. Anomalous cleavage of aspartyl-proline peptide bonds during amino acid sequence determinations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1173–1178. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90918-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. H., Levy C. C. Polyamine accumulation and biosynthesis in a mouse L1210 leukemia. Cancer Res. 1971 Mar;31(3):248–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. K., Craig L. Random peptide libraries. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1994 Feb;5(1):40–48. doi: 10.1016/s0958-1669(05)80068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. J., Kania R. S., Zuckermann R. N., Huebner V. D., Jewell D. A., Banville S., Ng S., Wang L., Rosenberg S., Marlowe C. K. Peptoids: a modular approach to drug discovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9367–9371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



