Abstract
The crystal structure of (E)-dodec-2-enoic acid, C12H22O2, an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid with a melting point (295 K) near room temperature, is characterized by carboxylic acid inversion dimers linked by pairs of O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The carboxylic acid group and the following three carbon atoms of the chain of the (E)-dodec-2-enoic acid molecule lie almost in one plane (r.m.s. deviation for the four C atoms and two O atoms = 0.012 Å), whereas the remaining carbon atoms of the hydrocarbon chain adopt a nearly fully staggered conformation [moduli of torsion angles vary from 174.01 (13) to 179.97 (13)°].
Keywords: crystal structure, hydrogen bonding, dimer, unsaturated carboxylic acid, fatty acid
Related literature
For the synthesis of unsaturated α,β-carboxylic acids including the title compound by adapted routes established by Knoevenagel (1898 ▸) and Doebner (1902 ▸), see: Shabtai et al. (1981 ▸). For crystal structure determinations of related α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids, see, for acrylic acid: Higgs et al. (1963 ▸), Chatani et al. (1963 ▸), Boese et al. (1999 ▸), or Oswald et al. (2011 ▸); see, for crotonic acid: Shimizu et al. (1974 ▸); see, for (E)-pent-2-enoic acid: Peppel et al. (2015a
▸); see, for (E)-hex-2-enoic acid: Peppel et al. (2015b
▸); see, for (E)-undecen-2-enoic acid: Sonneck et al. (2015 ▸). For structures of co-crystals containing (E)-hex-2-enoic acid, see: Aakeröy et al. (2003 ▸), or Stanton & Bak (2008 ▸).
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H22O2
M r = 198.29
Triclinic,
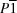
a = 4.6475 (2) Å
b = 5.4169 (2) Å
c = 24.7041 (10) Å
α = 91.547 (2)°
β = 91.788 (2)°
γ = 102.3158 (19)°
V = 606.96 (4) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.56 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.44 × 0.30 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014 ▸) T min = 0.80, T max = 0.94
12048 measured reflections
2117 independent reflections
1964 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.026
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.046
wR(F 2) = 0.131
S = 1.13
2117 reflections
129 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2014 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2013 ▸); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014/7 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸); molecular graphics: SHELXL2014/7; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL2014/7.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015011937/hb7452sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015011937/hb7452Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015011937/hb7452Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015011937/hb7452fig1.tif
Molecular structure of the title compound with atom labelling and displacement ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015011937/hb7452fig2.tif
Packing diagram showing intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
CCDC reference: 1407997
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1H1O2i | 0.84 | 1.80 | 2.6319(15) | 170 |
Symmetry code: (i) 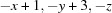 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank P. Thiele (University of Rostock) for the DSC measurements and Professor Dr. J. G. de Vries (LIKAT) for helpful support.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Synthesis and crystallization
Malonic acid (25.0 g, 240.2 mmol, 1.0 eq) is dissolved in dry pyridine (38.0 g, 480.5 mmol, 2.0 eq) at room temperature in a three-necked flask equipped with a magnetic stir bar and a reflux condenser under a mild flow of argon. Decanal (37.5 g, 240.2 mmol, 1.0 eq) is then added in one portion and the resulting clear solution is further stirred for 72 h at room temperature under argon. Afterwards, the resulting light yellow to orange solution is brought to an acidic pH value by adding phosphoric acid at 0 °C (42.5wt. %, 138.5 g, 600.6 mmol, 2.5 eq). The resulting two layers are extracted three times with 150 mL portions of ethyl acetate and reduced to a volume of ca. 150 mL in vacuo. To remove impurities from aldol condensation the raw acid is converted into the corresponding sodium salt by addition of an aqueous solution of sodium carbonate (20.4 g, 192.2 mmol, 0.8 eq in 200 mL). After stirring for 30 minutes the water phase is separated and extracted three times with 150 mL portions of ethyl acetate. The water phase is then acidified with concentrated hydrochloric acid (37.0wt. %, 35.5 g, 360.4 mmol, 1.5 eq), the organic phase is separated and the water phase is again extracted three times with 150 mL portions of ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases are dried over Na2SO4 and evaporated to dryness under diminished pressure. The resulting raw product is further purified by distillation in vacuo yielding the product in purity >99% (GC). M. p. 22 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 12.15 (br s, 1H, OH); 7.09 (dt, 3J = 15.6 Hz, 3J = 7.0 Hz, 1H, -CH-); 5.82 (dt, 3J = 15.6 Hz, 4J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, -CH-); 2.26-2.19 (m, 2H, -CH2-); 1.50-1.42 (m, 2H, -CH2-); 1.32-1.24 (m, 12H, 6x -CH2-); 0.90-0.86 (m, 3H, -CH3-). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 172.53 (CO); 152.68 (CH); 120.76 (CH); 32.47 (CH2); 32.02 (CH2); 29.61 (CH2), 29.52 (CH2), 29.43 (CH2); 29.29 (CH2); 28.02 (CH2); 22.81 (CH2); 14.23 (CH3). MS (EI, 70eV): m/z = 198 (M+, 0), 99 (16), 98 (12), 97 (17), 96 (14), 95 (11), 86 (17), 84 (18), 83 (16), 82 (12), 81 (20), 73 (34), 71 (13), 70 (15), 69 (21), 68 (18), 67 (20), 57 (29), 56 (22), 55 (47), 54 (11), 53 (20), 45 (14), 43 (70), 42 (19), 41 (100), 40 (14), 39 (52), 29 (58). HRMS (ESI-TOF/MS): calculated for C12H22O2 ([M—H]-) 197.1547, found 197.15481. Elemental analysis for C12H22O2 % (calc.): C 72.53 (72.68); H 11.24 (11.18). Suitable single crystals were grown by slow evaporation of an ethanolic solution at -30 °C over one week.
S2. Refinement
H atoms were placed in idealized positions with d(C—H) = 0.95 Å (CH), 0.99 Å (CH2), 0.98 Å (CH3) and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) fixed at 1.2 Ueq(C) for CH and CH2 and 1.5 Ueq(C) for CH3. The carboxylic acid group was assigned by examining the C—O distances and H1 was placed using the AFIX 147 instruction (d(O—H) = 0.84 Å, Uiso(H) fixed at 1.5 Ueq(O)).
Figures
Fig. 1.
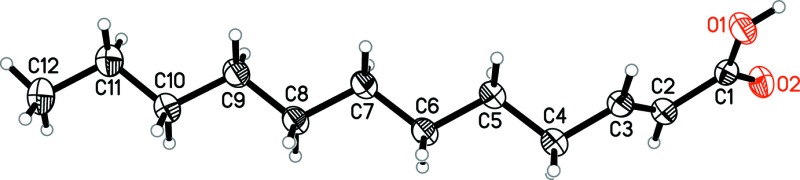
Molecular structure of the title compound with atom labelling and displacement ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
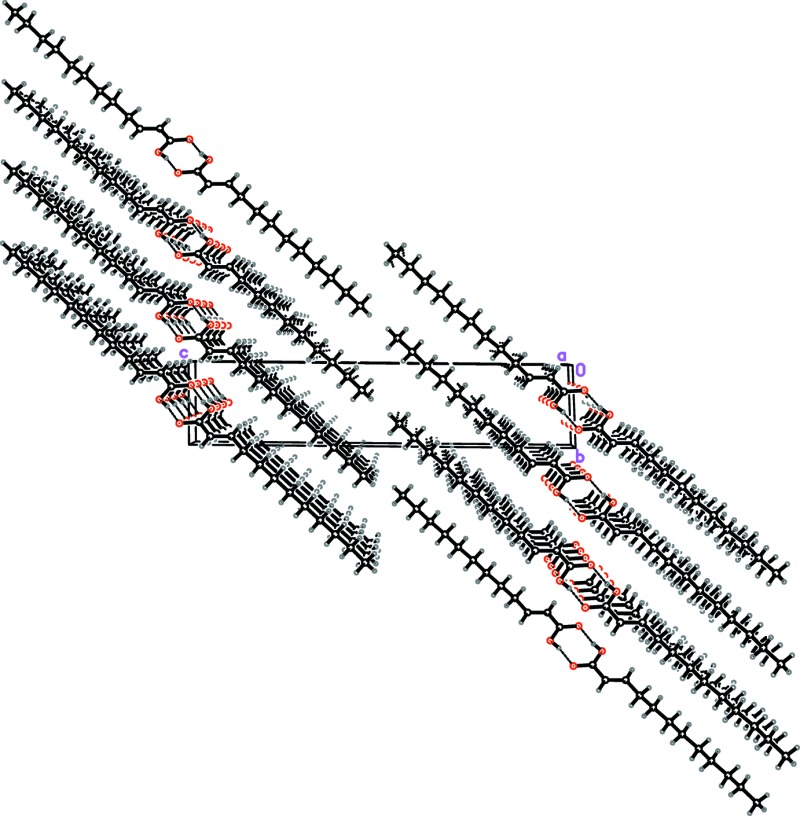
Packing diagram showing intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Crystal data
| C12H22O2 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 198.29 | F(000) = 220 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.085 Mg m−3 |
| a = 4.6475 (2) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| b = 5.4169 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 6666 reflections |
| c = 24.7041 (10) Å | θ = 3.6–66.9° |
| α = 91.547 (2)° | µ = 0.56 mm−1 |
| β = 91.788 (2)° | T = 150 K |
| γ = 102.3158 (19)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 606.96 (4) Å3 | 0.44 × 0.30 × 0.12 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2117 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: microfocus | 1964 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Multilayer monochromator | Rint = 0.026 |
| Detector resolution: 8.3333 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 66.0°, θmin = 3.6° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −5→5 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014) | k = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.80, Tmax = 0.94 | l = −29→29 |
| 12048 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.131 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0529P)2 + 0.282P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.13 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2117 reflections | Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3 |
| 129 parameters | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.7187 (3) | 1.2963 (3) | 0.03952 (6) | 0.0277 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.8819 (3) | 1.1356 (3) | 0.06965 (6) | 0.0314 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.9763 | 1.0250 | 0.0497 | 0.038* | |
| C3 | 0.9029 (3) | 1.1384 (3) | 0.12290 (6) | 0.0306 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.8092 | 1.2517 | 0.1421 | 0.037* | |
| C4 | 1.0622 (4) | 0.9777 (3) | 0.15566 (7) | 0.0332 (4) | |
| H4A | 1.2230 | 1.0881 | 0.1778 | 0.040* | |
| H4B | 1.1523 | 0.8714 | 0.1309 | 0.040* | |
| C5 | 0.8573 (3) | 0.8076 (3) | 0.19299 (6) | 0.0303 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.7510 | 0.9129 | 0.2148 | 0.036* | |
| H5B | 0.7090 | 0.6858 | 0.1706 | 0.036* | |
| C6 | 1.0184 (3) | 0.6615 (3) | 0.23115 (6) | 0.0304 (4) | |
| H6A | 1.1303 | 0.5606 | 0.2094 | 0.036* | |
| H6B | 1.1618 | 0.7832 | 0.2545 | 0.036* | |
| C7 | 0.8121 (4) | 0.4855 (3) | 0.26692 (6) | 0.0311 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.6701 | 0.3631 | 0.2435 | 0.037* | |
| H7B | 0.6985 | 0.5865 | 0.2882 | 0.037* | |
| C8 | 0.9696 (4) | 0.3400 (3) | 0.30579 (6) | 0.0313 (4) | |
| H8A | 1.0830 | 0.2386 | 0.2846 | 0.038* | |
| H8B | 1.1115 | 0.4622 | 0.3293 | 0.038* | |
| C9 | 0.7607 (4) | 0.1648 (3) | 0.34138 (7) | 0.0333 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.6186 | 0.0429 | 0.3178 | 0.040* | |
| H9B | 0.6474 | 0.2664 | 0.3626 | 0.040* | |
| C10 | 0.9160 (4) | 0.0181 (3) | 0.38039 (7) | 0.0341 (4) | |
| H10A | 1.0257 | −0.0866 | 0.3592 | 0.041* | |
| H10B | 1.0612 | 0.1398 | 0.4035 | 0.041* | |
| C11 | 0.7074 (4) | −0.1519 (4) | 0.41657 (8) | 0.0432 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.5556 | −0.2675 | 0.3936 | 0.052* | |
| H11B | 0.6057 | −0.0462 | 0.4393 | 0.052* | |
| C12 | 0.8622 (5) | −0.3083 (4) | 0.45332 (8) | 0.0495 (5) | |
| H12A | 0.9605 | −0.4159 | 0.4311 | 0.074* | |
| H12B | 0.7169 | −0.4145 | 0.4755 | 0.074* | |
| H12C | 1.0089 | −0.1952 | 0.4770 | 0.074* | |
| O1 | 0.5999 (3) | 1.4499 (2) | 0.06736 (5) | 0.0374 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.5041 | 1.5251 | 0.0464 | 0.056* | |
| O2 | 0.7029 (3) | 1.2789 (2) | −0.01126 (4) | 0.0363 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0262 (7) | 0.0246 (8) | 0.0319 (8) | 0.0035 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0044 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0306 (8) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0352 (9) | 0.0100 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0046 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0274 (8) | 0.0291 (8) | 0.0358 (9) | 0.0071 (6) | 0.0010 (6) | 0.0042 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0309 (8) | 0.0359 (9) | 0.0347 (9) | 0.0110 (7) | −0.0009 (6) | 0.0067 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0300 (8) | 0.0306 (8) | 0.0318 (8) | 0.0104 (7) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0032 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0294 (8) | 0.0295 (8) | 0.0334 (8) | 0.0095 (7) | −0.0032 (6) | 0.0030 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0311 (8) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0335 (8) | 0.0102 (7) | −0.0021 (6) | 0.0033 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0311 (8) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0342 (8) | 0.0098 (7) | −0.0023 (6) | 0.0040 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0327 (8) | 0.0335 (9) | 0.0347 (9) | 0.0096 (7) | −0.0019 (7) | 0.0051 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0351 (9) | 0.0342 (9) | 0.0347 (9) | 0.0109 (7) | −0.0010 (7) | 0.0061 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0415 (10) | 0.0459 (11) | 0.0433 (10) | 0.0103 (8) | 0.0025 (8) | 0.0147 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0554 (12) | 0.0499 (11) | 0.0450 (11) | 0.0127 (9) | 0.0035 (9) | 0.0192 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0442 (7) | 0.0364 (7) | 0.0367 (6) | 0.0193 (5) | 0.0013 (5) | 0.0060 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0453 (7) | 0.0357 (7) | 0.0307 (6) | 0.0143 (5) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0053 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—O2 | 1.2543 (19) | C7—H7B | 0.9900 |
| C1—O1 | 1.2881 (19) | C8—C9 | 1.524 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.473 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.316 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C9—C10 | 1.524 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.496 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.527 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.518 (2) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9900 | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4B | 0.9900 | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.525 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.523 (2) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9900 | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C5—H5B | 0.9900 | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C6—C7 | 1.522 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9900 | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9900 | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.524 (2) | O1—H1 | 0.8400 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9900 | ||
| O2—C1—O1 | 123.37 (14) | H7A—C7—H7B | 107.7 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 119.24 (14) | C9—C8—C7 | 113.34 (13) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 117.38 (13) | C9—C8—H8A | 108.9 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.91 (15) | C7—C8—H8A | 108.9 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 118.5 | C9—C8—H8B | 108.9 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 118.5 | C7—C8—H8B | 108.9 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 125.30 (15) | H8A—C8—H8B | 107.7 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 117.4 | C8—C9—C10 | 113.76 (13) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 117.4 | C8—C9—H9A | 108.8 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 112.03 (13) | C10—C9—H9A | 108.8 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.2 | C8—C9—H9B | 108.8 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.2 | C10—C9—H9B | 108.8 |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.2 | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.7 |
| C5—C4—H4B | 109.2 | C11—C10—C9 | 113.50 (14) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 107.9 | C11—C10—H10A | 108.9 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 113.32 (13) | C9—C10—H10A | 108.9 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 108.9 | C11—C10—H10B | 108.9 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 108.9 | C9—C10—H10B | 108.9 |
| C6—C5—H5B | 108.9 | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.7 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 108.9 | C10—C11—C12 | 113.18 (15) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 107.7 | C10—C11—H11A | 108.9 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 113.10 (13) | C12—C11—H11A | 108.9 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 109.0 | C10—C11—H11B | 108.9 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.0 | C12—C11—H11B | 108.9 |
| C7—C6—H6B | 109.0 | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.8 |
| C5—C6—H6B | 109.0 | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 107.8 | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 113.85 (13) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 108.8 | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 108.8 | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7B | 108.8 | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7B | 108.8 | C1—O1—H1 | 109.5 |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | −178.37 (15) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −179.36 (13) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 1.9 (2) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 179.97 (13) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.24 (14) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.96 (13) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −120.08 (17) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 178.76 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −174.01 (13) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 176.92 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.05 (13) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···O2i | 0.84 | 1.80 | 2.6319 (15) | 170 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+3, −z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB7452).
References
- Aakeröy, C. B., Beatty, A. M., Helfrich, B. A. & Nieuwenhuyzen, M. (2003). Cryst. Growth Des. 3, 159–165.
- Boese, R., Bläser, D., Steller, I., Latz, R. & Bäumen, A. (1999). Acta Cryst. C55 IUC9900006.
- Bruker (2013). SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2014). APEX2 and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chatani, Y., Sakata, Y. & Nitta, I. (1963). J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Lett. 1, 419–421.
- Doebner, O. (1902). Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 35, 1136–1147.
- Higgs, M. A. & Sass, R. L. (1963). Acta Cryst. 16, 657–661.
- Knoevenagel, E. (1898). Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 31, 2596–2619.
- Oswald, I. D. H. & Urquhart, A. J. (2011). CrystEngComm, 13, 4503–4507.
- Peppel, T., Sonneck, M., Spannenberg, A. & Wohlrab, S. (2015a). Acta Cryst. E71, o316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Peppel, T., Sonneck, M., Spannenberg, A. & Wohlrab, S. (2015b). Acta Cryst. E71, o323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Shabtai, J., Ney-Igner, E. & Pines, H. (1981). J. Org. Chem. 46, 3795–3802.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shimizu, S., Kekka, S., Kashino, S. & Haisa, M. (1974). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 47, 1627–1631.
- Sonneck, M., Peppel, T., Spannenberg, A. & Wohlrab, S. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, o426–o427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Stanton, M. K. & Bak, A. (2008). Cryst. Growth Des. 8, 3856–3862.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015011937/hb7452sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015011937/hb7452Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015011937/hb7452Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015011937/hb7452fig1.tif
Molecular structure of the title compound with atom labelling and displacement ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015011937/hb7452fig2.tif
Packing diagram showing intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
CCDC reference: 1407997
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


