Abstract
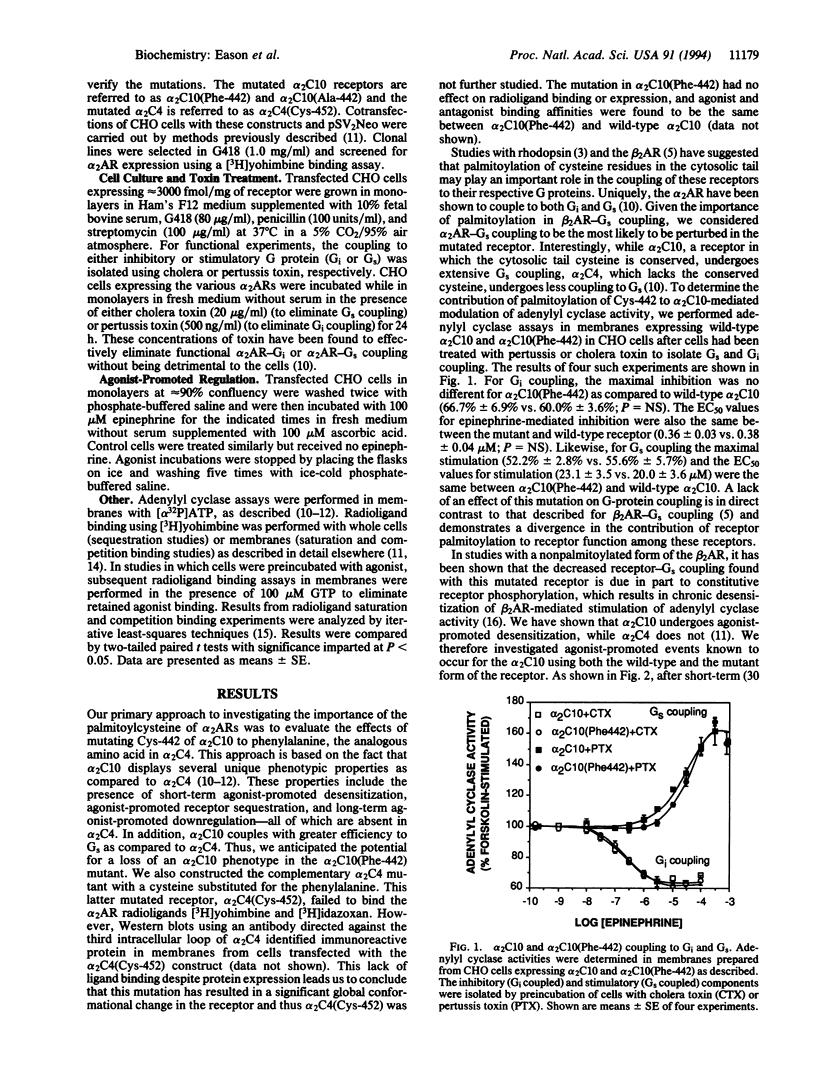
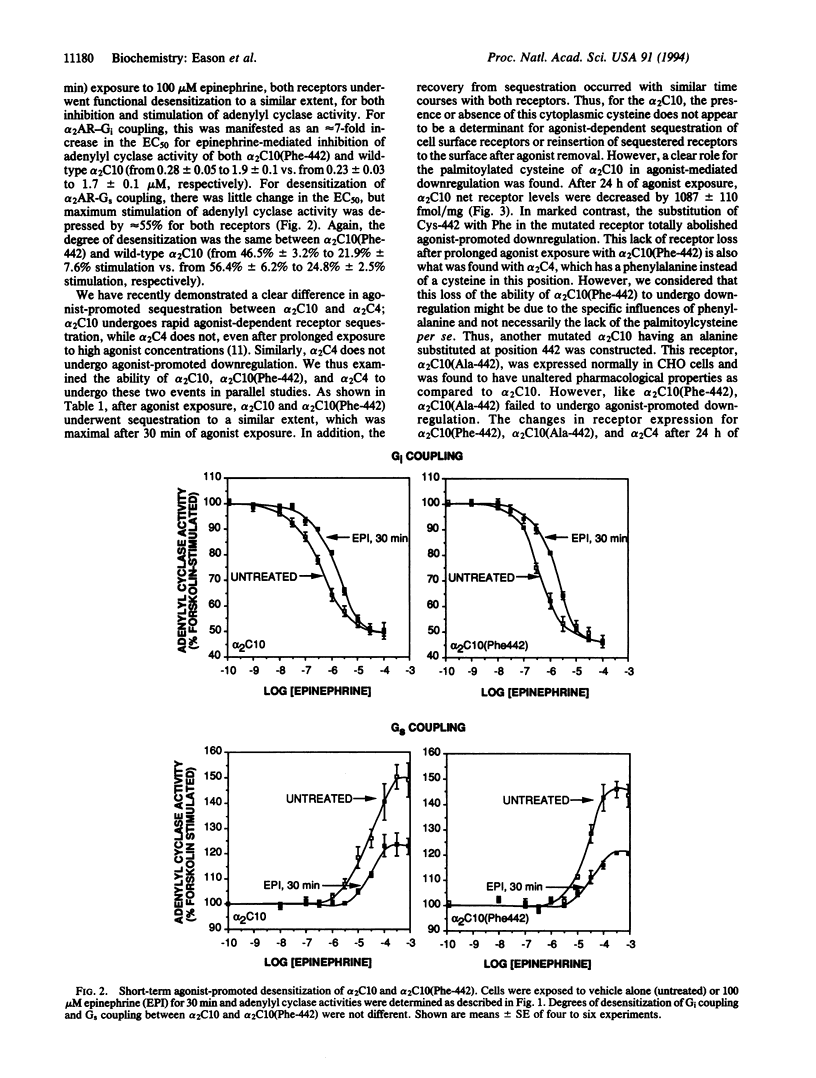
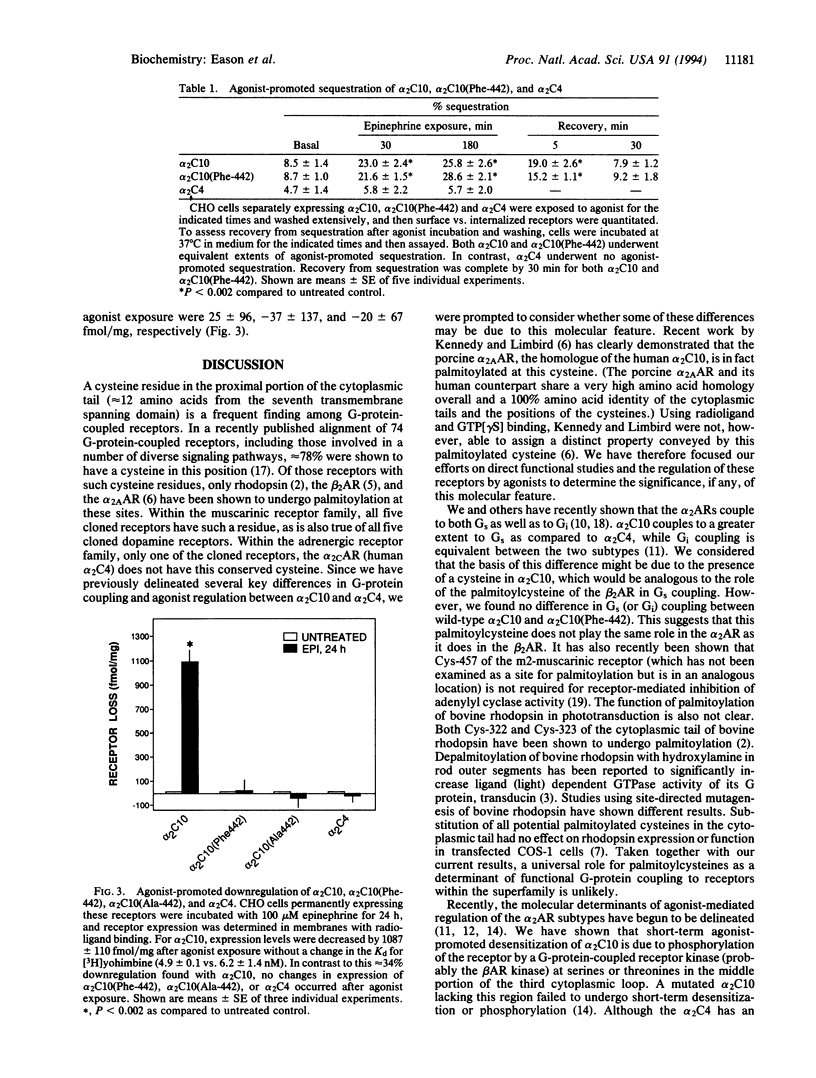
Most guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptors have a conserved cysteine in the C-terminal cytoplasmic tail near the seventh transmembrane spanning region. This cysteine is known to be palmitoylated in rhodopsin, the beta 2-adrenergic receptor (beta 2AR) and the alpha 2A-adrenergic receptor (alpha 2AAR). For the beta 2AR, this cysteine has been shown to be important for stimulatory G protein (Gs) coupling and agonist-promoted desensitization. For the alpha 2AAR (human alpha 2 C10) palmitoylation occurs at Cys-442, but it is not known what function such fatty acid acylation subserves. The closely related alpha 2CAR subtype denoted alpha 2C4 lacks a cysteine in this region and has different G-protein-coupling characteristics and agonist regulatory properties as compared to alpha 2C10. To assess the role of the palmitoylcysteine in alpha 2AR function, we constructed a mutated alpha 2C10 having a phenylalanine (the analogous amino acid in the alpha 2C4 in this position) substituted for Cys-442, denoted alpha 2C10(Phe-442), and expressed this along with wild-type alpha 2C10 and alpha 2C4 in CHO cells. Functional coupling to inhibitory G protein (Gi) and to Gs was identical between wild-type alpha 2C10 and alpha 2C10(Phe-442). Agonist-promoted desensitization of both the Gi and Gs-mediated pathways was also found to be unaffected by this mutation. Cellular trafficking induced by agonist exposure was evaluated by delineation of intracellular (sequestered) versus cell surface receptors and by determination of net receptor loss. Mutation of Cys-442 did not alter the extent or rate of agonist-promoted sequestration induced by agonists or the recovery from sequestration. However, the downregulation of receptor number after prolonged agonist exposure was completely abolished by this mutation and converted alpha 2C10 to an alpha 2C4 phenotype in regard to this adaptive response. Another mutated alpha 2C10, in which Cys-442 was replaced by alanine, also failed to downregulate. Thus, the function of this cytoplasmic palmitoylcysteine is distinctly different between the alpha 2AR and other G-protein-coupled receptors such as the beta 2AR and rhodopsin, and this suggests that this molecular attribute may subserve diverse roles among members of this family of receptors. For the alpha 2ARs, this may represent an evolved feature that provides for differing needs for regulation of the alpha 2C10 and alpha 2C4 subtypes by agonist.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Lean A., Hancock A. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Validation and statistical analysis of a computer modeling method for quantitative analysis of radioligand binding data for mixtures of pharmacological receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;21(1):5–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eason M. G., Kurose H., Holt B. D., Raymond J. R., Liggett S. B. Simultaneous coupling of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors to two G-proteins with opposing effects. Subtype-selective coupling of alpha 2C10, alpha 2C4, and alpha 2C2 adrenergic receptors to Gi and Gs. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15795–15801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eason M. G., Liggett S. B. Functional alpha 2-adrenergic receptor-Gs coupling undergoes agonist-promoted desensitization in a subtype-selective manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 May 28;193(1):318–323. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eason M. G., Liggett S. B. Subtype-selective desensitization of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Different mechanisms control short and long term agonist-promoted desensitization of alpha 2C10, alpha 2C4, and alpha 2C2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25473–25479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federman A. D., Conklin B. R., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R., Bourne H. R. Hormonal stimulation of adenylyl cyclase through Gi-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):159–161. doi: 10.1038/356159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Sakmar T. P., Chen H. B., Khorana H. G. Cysteine residues 110 and 187 are essential for the formation of correct structure in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8459–8463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. E., Limbird L. E. Mutations of the alpha 2A-adrenergic receptor that eliminate detectable palmitoylation do not perturb receptor-G-protein coupling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8003–8011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Parmentier M., Lefort A., Dinsart C., Van Sande J., Maenhaut C., Simons M. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):569–572. doi: 10.1126/science.2541503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett S. B., Freedman N. J., Schwinn D. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Structural basis for receptor subtype-specific regulation revealed by a chimeric beta 3/beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett S. B., Ostrowski J., Chesnut L. C., Kurose H., Raymond J. R., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Sites in the third intracellular loop of the alpha 2A-adrenergic receptor confer short term agonist-promoted desensitization. Evidence for a receptor kinase-mediated mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4740–4746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett S. B., Raymond J. R. Pharmacology and molecular biology of adrenergic receptors. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Apr;7(2):279–306. doi: 10.1016/s0950-351x(05)80178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett S., Mouillac B., Bonin H., Bouvier M. Altered phosphorylation and desensitization patterns of a human beta 2-adrenergic receptor lacking the palmitoylated Cys341. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):349–356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. F., O'Brien P. J., Pepperberg D. R. Depalmitylation with hydroxylamine alters the functional properties of rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20118–20123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien P. J., Zatz M. Acylation of bovine rhodopsin by [3H]palmitic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5054–5057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Bouvier M. Palmitoylation of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Mutation of Cys341 in the carboxyl tail leads to an uncoupled nonpalmitoylated form of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7564–7569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Abdulaev N. G., Bogachuk A. S. Two adjacent cysteine residues in the C-terminal cytoplasmic fragment of bovine rhodopsin are palmitylated. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst W. C., Snyder L. A., Schuster D. I., Brosius J., Sealfon S. C. Sequence alignment of the G-protein coupled receptor superfamily. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;11(1):1–20. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Olah M. E., Jacobson K. A., Stiles G. L. Distinct pathways of desensitization of A1- and A2-adenosine receptors in DDT1 MF-2 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):639–647. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6301–6305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Koppen C. J., Nathanson N. M. The cysteine residue in the carboxyl-terminal domain of the m2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor is not required for receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase. J Neurochem. 1991 Dec;57(6):1873–1877. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb06397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Zastrow M., Link R., Daunt D., Barsh G., Kobilka B. Subtype-specific differences in the intracellular sorting of G protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):763–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



