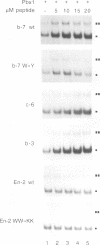
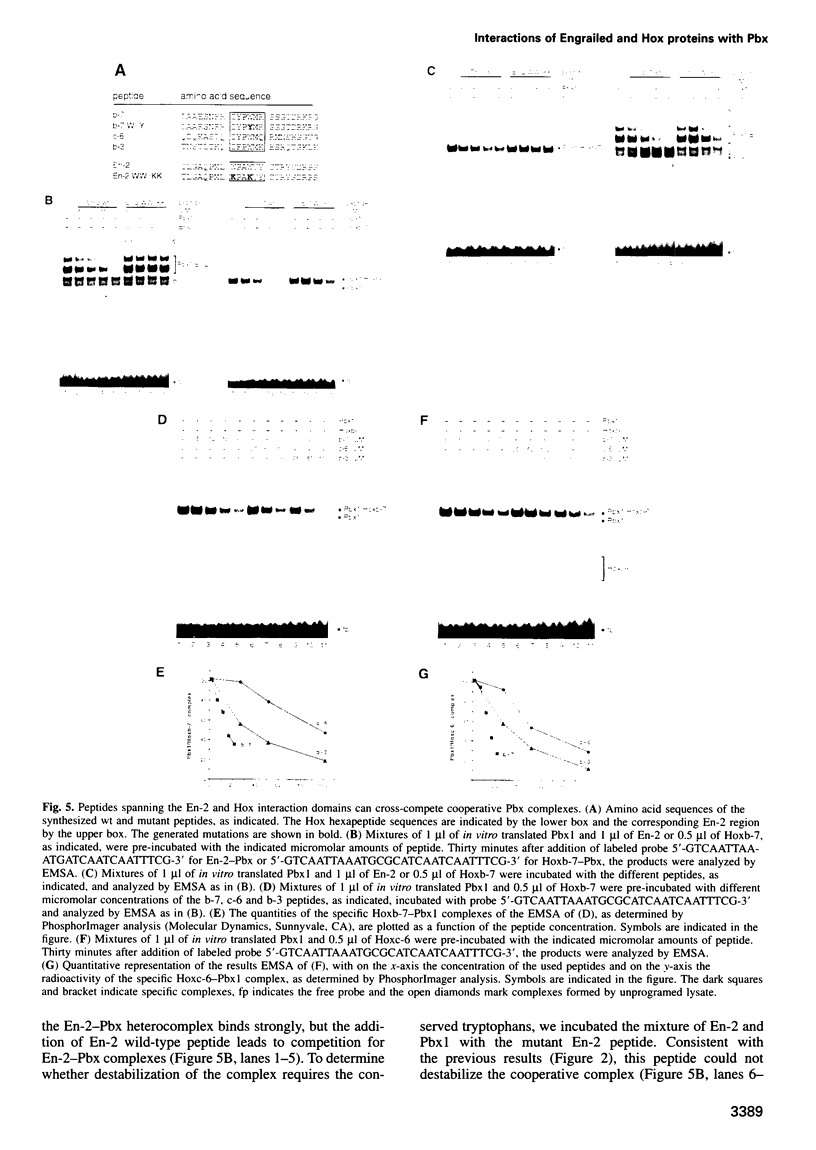
Abstract
Hox gene products have the ability to interact with either extradenticle or pbx gene products to bind cooperatively to DNA. The region in Hox proteins that is required for this interaction is located N-terminal of the homeodomain and contains a highly conserved hexapeptide. We now show that the engrailed gene products also contain a Pbx interaction motif positioned within a previously conserved region, the EH2 domain. The EH2 domain is located N-terminal of the homeodomain. Two tryptophan residues present in the Drosophila and murine Engrailed EH2 domain are required for cooperativity with extradenticle and Pbx, respectively. A second conserved domain, EH3, is required as well for cooperativity with Pbx, since deletions or an insertion in this region reduce cooperative DNA binding. Peptides containing the Pbx interaction motif of either Engrailed or Hox are capable of destabilizing Engrailed-Pbx and Hox-Pbx cooperative DNA binding. These data indicate that the Pbx interaction motifs present in Hox and engrailed gene products recognize a common structure present in the Pbx family of homeodomain proteins.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billeter M., Qian Y. Q., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W., Wüthrich K. Determination of the nuclear magnetic resonance solution structure of an Antennapedia homeodomain-DNA complex. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 20;234(4):1084–1093. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Jaffe L., Capovilla M., Botas J., Mann R. S. The DNA binding specificity of Ultrabithorax is modulated by cooperative interactions with extradenticle, another homeoprotein. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90525-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Mann R. S. The segment identity functions of Ultrabithorax are contained within its homeo domain and carboxy-terminal sequences. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):796–811. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Shen W. F., Rozenfeld S., Lawrence H. J., Largman C., Cleary M. L. Pbx proteins display hexapeptide-dependent cooperative DNA binding with a subset of Hox proteins. Genes Dev. 1995 Mar 15;9(6):663–674. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.6.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboule D., Dollé P. The structural and functional organization of the murine HOX gene family resembles that of Drosophila homeotic genes. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1497–1505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegel W. A., Singson A. W., Margolis J. S., Bang A. G., Posakony J. W., Murre C. Dpbx, a new homeobox gene closely related to the human proto-oncogene pbx1 molecular structure and developmental expression. Mech Dev. 1993 May;41(2-3):155–161. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90045-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G., Schier A., LeMotte P., Gehring W. J. The specificities of Sex combs reduced and Antennapedia are defined by a distinct portion of each protein that includes the homeodomain. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1087–1103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90386-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., von Hippel P. H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 1;182(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Levine M. Divergent homeo box proteins recognize similar DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):858–861. doi: 10.1038/332858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Parker E., Krasnow M. A. Extradenticle protein is a selective cofactor for the Drosophila homeotics: role of the homeodomain and YPWM amino acid motif in the interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):739–743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Murre C., Sun X. H., Baltimore D. A new homeobox gene contributes the DNA binding domain of the t(1;19) translocation protein in pre-B ALL. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoepfler P. S., Kamps M. P. The pentapeptide motif of Hox proteins is required for cooperative DNA binding with Pbx1, physically contacts Pbx1, and enhances DNA binding by Pbx1. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;15(10):5811–5819. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.10.5811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R. Hox genes in vertebrate development. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. A homeodomain substitution changes the regulatory specificity of the deformed protein in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Scott M. P. Sequence of a Drosophila segmentation gene: protein structure homology with DNA-binding proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):25–31. doi: 10.1038/310025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. A., Morata G. Homeobox genes: their function in Drosophila segmentation and pattern formation. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T., Stark M. R., Johnson A. D., Wolberger C. Crystal structure of the MATa1/MAT alpha 2 homeodomain heterodimer bound to DNA. Science. 1995 Oct 13;270(5234):262–269. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5234.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L., McGinnis W. Mapping functional specificity in the Dfd and Ubx homeo domains. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):1071–1081. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan C., Hanks M. C., Noble-Topham S., Nallainathan D., Provart N. J., Joyner A. L. Cloning and sequence comparison of the mouse, human, and chicken engrailed genes reveal potential functional domains and regulatory regions. Dev Genet. 1992;13(5):345–358. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020130505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q., Knoepfler P. S., Scheele J., Wright D. D., Kamps M. P. Both Pbx1 and E2A-Pbx1 bind the DNA motif ATCAATCAA cooperatively with the products of multiple murine Hox genes, some of which are themselves oncogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;15(7):3786–3795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.7.3786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magli M. C., Barba P., Celetti A., De Vita G., Cillo C., Boncinelli E. Coordinate regulation of HOX genes in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monica K., Galili N., Nourse J., Saltman D., Cleary M. L. PBX2 and PBX3, new homeobox genes with extensive homology to the human proto-oncogene PBX1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6149–6157. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuteboom S. T., Peltenburg L. T., van Dijk M. A., Murre C. The hexapeptide LFPWMR in Hoxb-8 is required for cooperative DNA binding with Pbx1 and Pbx2 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9166–9170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourse J., Mellentin J. D., Galili N., Wilkinson J., Stanbridge E., Smith S. D., Cleary M. L. Chromosomal translocation t(1;19) results in synthesis of a homeobox fusion mRNA that codes for a potential chimeric transcription factor. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90657-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peers B., Sharma S., Johnson T., Kamps M., Montminy M. The pancreatic islet factor STF-1 binds cooperatively with Pbx to a regulatory element in the somatostatin promoter: importance of the FPWMK motif and of the homeodomain. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):7091–7097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.7091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., Wieschaus E. Mutations in the Drosophila gene extradenticle affect the way specific homeo domain proteins regulate segmental identity. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1209–1223. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan M. L., Rambaldi I., Featherstone M. S. Cooperative interactions between HOX and PBX proteins mediated by a conserved peptide motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;15(8):3989–3997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.8.3989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöpperl H., Bienz M., Studer M., Chan S. K., Aparicio S., Brenner S., Mann R. S., Krumlauf R. Segmental expression of Hoxb-1 is controlled by a highly conserved autoregulatory loop dependent upon exd/pbx. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1031–1042. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Otting G., Furukubo-Tokunaga K., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. NMR structure determination reveals that the homeodomain is connected through a flexible linker to the main body in the Drosophila Antennapedia protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10738–10742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauskolb C., Peifer M., Wieschaus E. extradenticle, a regulator of homeotic gene activity, is a homolog of the homeobox-containing human proto-oncogene pbx1. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1101–1112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90731-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauskolb C., Wieschaus E. Coordinate regulation of downstream genes by extradenticle and the homeotic selector proteins. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3561–3569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. R., Johnson A. D. Interaction between two homeodomain proteins is specified by a short C-terminal tail. Nature. 1994 Sep 29;371(6496):429–432. doi: 10.1038/371429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vershon A. K., Johnson A. D. A short, disordered protein region mediates interactions between the homeodomain of the yeast alpha 2 protein and the MCM1 protein. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90054-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng W., Andrew D. J., Mathies L. D., Horner M. A., Scott M. P. Ectopic expression and function of the Antp and Scr homeotic genes: the N terminus of the homeodomain is critical to functional specificity. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):339–352. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk M. A., Murre C. extradenticle raises the DNA binding specificity of homeotic selector gene products. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):617–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk M. A., Peltenburg L. T., Murre C. Hox gene products modulate the DNA binding activity of Pbx1 and Pbx2. Mech Dev. 1995 Jul;52(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(95)00394-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]