Abstract
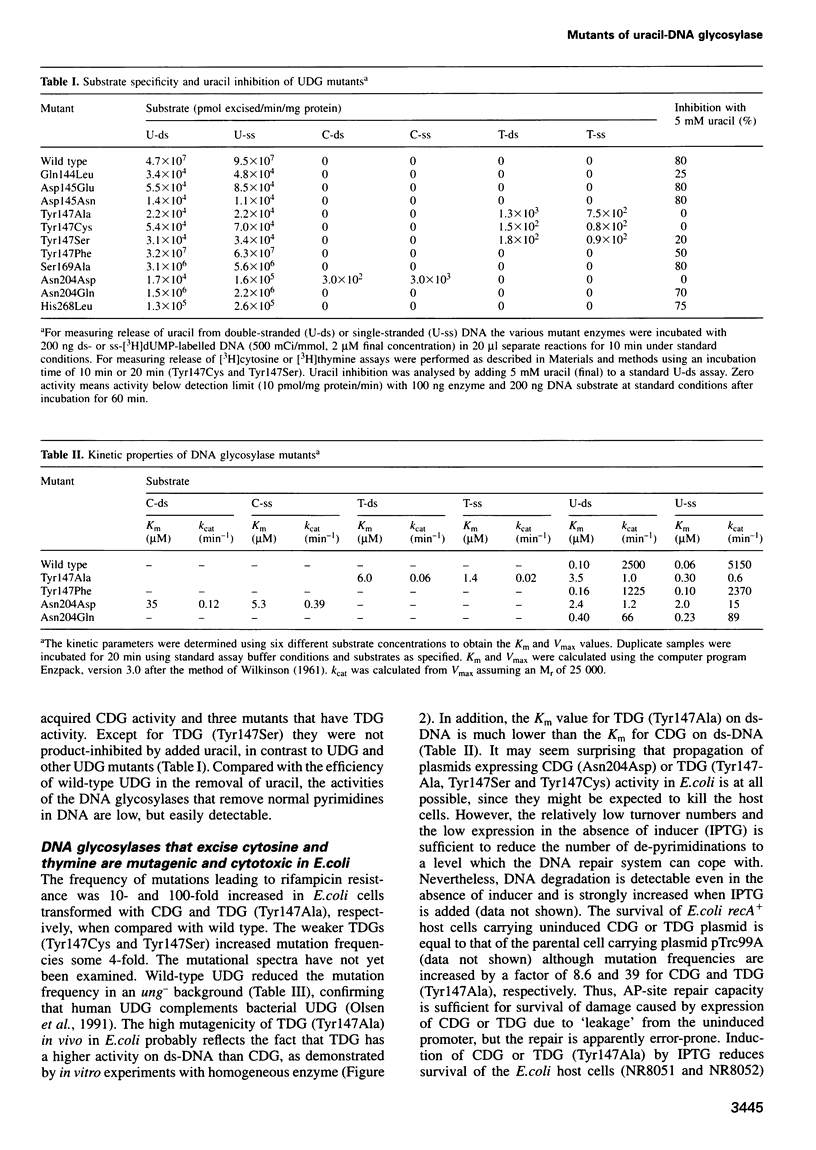
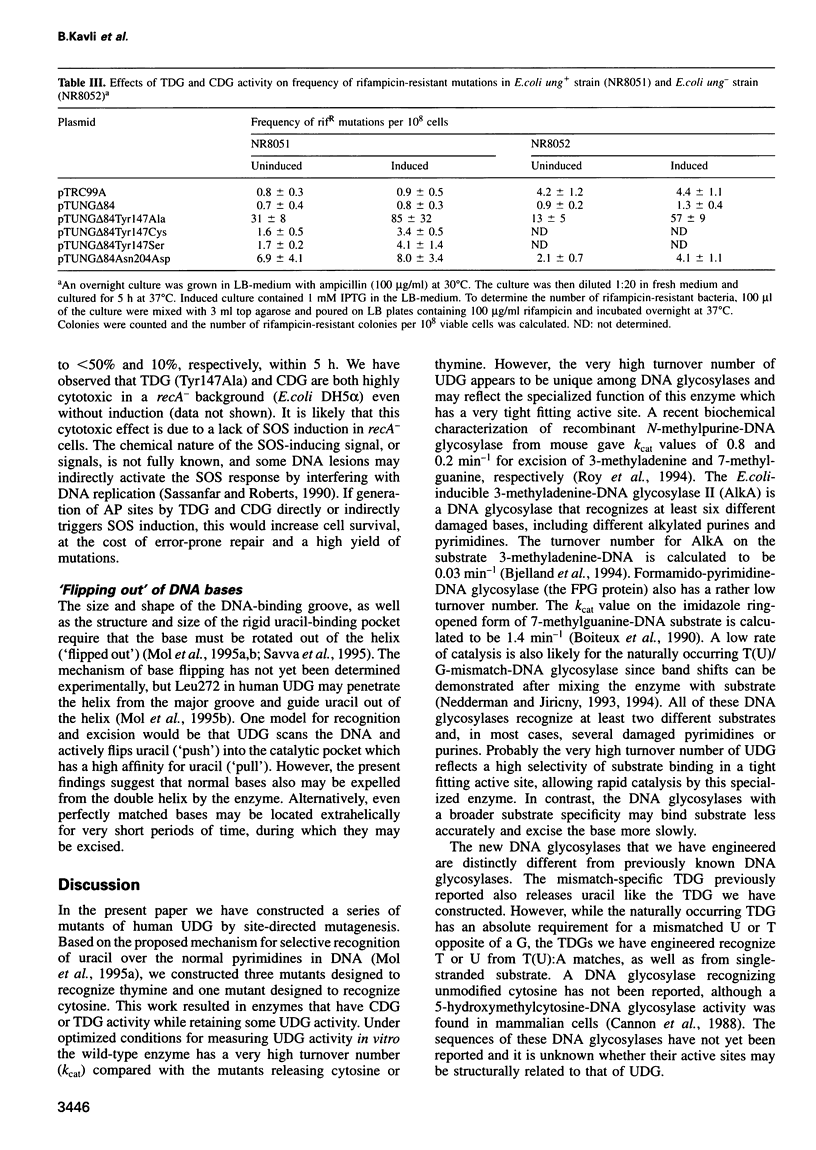
Uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) protects the genome by removing mutagenic uracil residues resulting from deamination of cytosine. Uracil binds in a rigid pocket at the base of the DNA-binding groove of human UDG and the specificity for uracil over the structurally related DNA bases thymine and cytosine is conferred by shape complementarity, as well as by main chain and Asn204 side chain hydrogen bonds. Here we show that replacement of Asn204 by Asp or Tyr147 by Ala, Cys or Ser results in enzymes that have cytosine-DNA glycosylase (CDG) activity or thymine-DNA glycosylase (TDG) activity, respectively. CDG and the TDG all retain some UDG activity. CDG and TDG have kcat values in the same range as typical multisubstrate-DNA glycosylases, that is at least three orders of magnitude lower than that of the highly selective and efficient wild-type UDG. Expression of CDG or TDG in Escherichia coli causes 4- to 100-fold increases in the yield of rifampicin-resistant mutants. Thus, single amino acid substitutions in UDG result in less selective DNA glycosylases that release normal pyrimidines and confer a mutator phenotype upon the cell. Three of the four new pyrimidine-DNA glycosylases resulted from single nucleotide substitutions, events that may also happen in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D. E., Lindahl T., Sedgwick B. DNA repair. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):424–433. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90007-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjelland S., Birkeland N. K., Benneche T., Volden G., Seeberg E. DNA glycosylase activities for thymine residues oxidized in the methyl group are functions of the AlkA enzyme in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30489–30495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., O'Connor T. R., Lederer F., Gouyette A., Laval J. Homogeneous Escherichia coli FPG protein. A DNA glycosylase which excises imidazole ring-opened purines and nicks DNA at apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3916–3922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krokan H., Wittwer C. U. Uracil DNa-glycosylase from HeLa cells: general properties, substrate specificity and effect of uracil analogs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2599–2613. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Heat-induced deamination of cytosine residues in deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3405–3410. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mol C. D., Arvai A. S., Sanderson R. J., Slupphaug G., Kavli B., Krokan H. E., Mosbaugh D. W., Tainer J. A. Crystal structure of human uracil-DNA glycosylase in complex with a protein inhibitor: protein mimicry of DNA. Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):701–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90467-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mol C. D., Arvai A. S., Slupphaug G., Kavli B., Alseth I., Krokan H. E., Tainer J. A. Crystal structure and mutational analysis of human uracil-DNA glycosylase: structural basis for specificity and catalysis. Cell. 1995 Mar 24;80(6):869–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrnes B., Giercksky K. E., Krokan H. Interindividual variation in the activity of O6-methyl guanine-DNA methyltransferase and uracil-DNA glycosylase in human organs. Carcinogenesis. 1983 Dec;4(12):1565–1568. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.12.1565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neddermann P., Jiricny J. Efficient removal of uracil from G.U mispairs by the mismatch-specific thymine DNA glycosylase from HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1642–1646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neddermann P., Jiricny J. The purification of a mismatch-specific thymine-DNA glycosylase from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21218–21224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen L. C., Aasland R., Krokan H. E., Helland D. E. Human uracil-DNA glycosylase complements E. coli ung mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4473–4478. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen L. C., Aasland R., Wittwer C. U., Krokan H. E., Helland D. E. Molecular cloning of human uracil-DNA glycosylase, a highly conserved DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3121–3125. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy R., Brooks C., Mitra S. Purification and biochemical characterization of recombinant N-methylpurine-DNA glycosylase of the mouse. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 20;33(50):15131–15140. doi: 10.1021/bi00254a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassanfar M., Roberts J. W. Nature of the SOS-inducing signal in Escherichia coli. The involvement of DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 5;212(1):79–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savva R., McAuley-Hecht K., Brown T., Pearl L. The structural basis of specific base-excision repair by uracil-DNA glycosylase. Nature. 1995 Feb 9;373(6514):487–493. doi: 10.1038/373487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slupphaug G., Eftedal I., Kavli B., Bharati S., Helle N. M., Haug T., Levine D. W., Krokan H. E. Properties of a recombinant human uracil-DNA glycosylase from the UNG gene and evidence that UNG encodes the major uracil-DNA glycosylase. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 10;34(1):128–138. doi: 10.1021/bi00001a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye B. K., Nyman P. O., Lehman I. R., Hochhauser S., Weiss B. Transient accumulation of Okazaki fragments as a result of uracil incorporation into nascent DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):154–157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




