Abstract
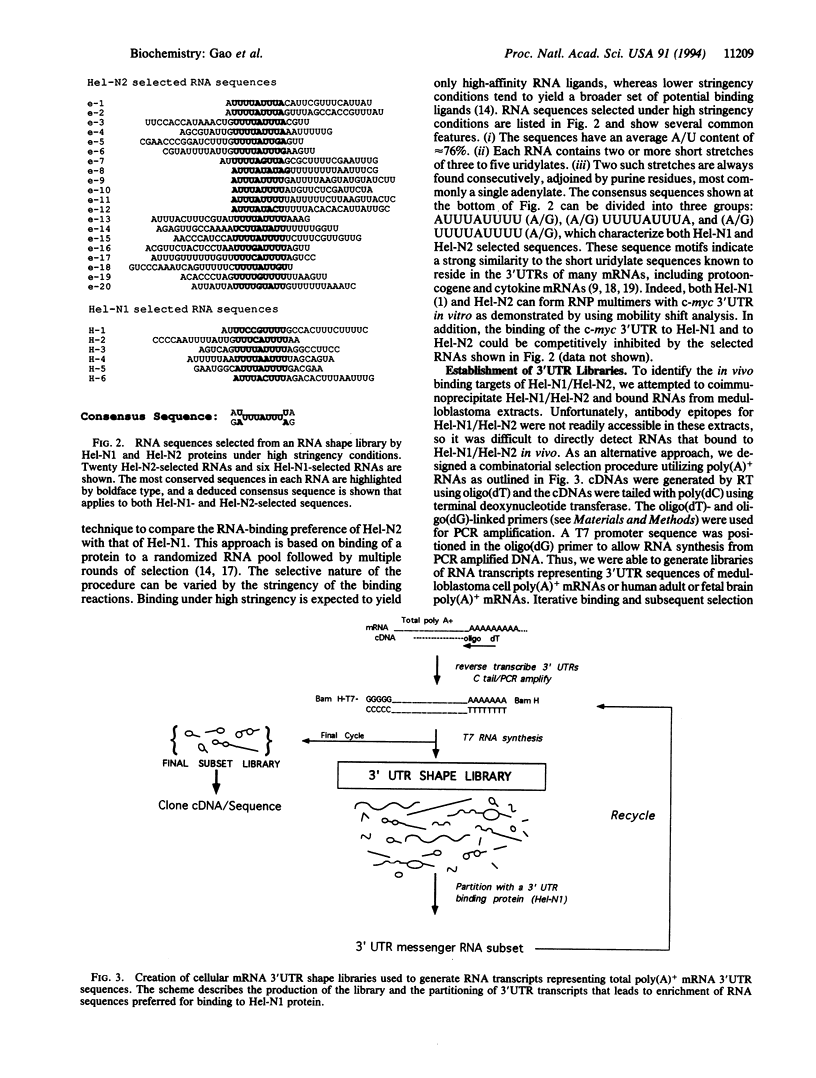
Hel-N1, a human RNA-binding protein, shares significant homology with Drosophila protein ELAV, which is essential for fly neuronal development. Hel-N1 has been shown to bind in vitro to 3' untranslated regions of mRNAs encoding c-myc, c-fos, granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and transcriptional repressor, Id. We report that Hel-N1 and a related form, Hel-N2, are expressed in human medulloblastoma cells, but their ratio differs significantly from that in adult brain and fetal brain. Selection of RNA targets from randomized combinatorial libraries yielded (A+U)-rich consensus sequences for both Hel-N1 and Hel-N2. As a means to identify cellular RNA targets for these proteins, we devised combinatorial shape libraries representing naturally derived 3' untranslated regions and were able to select a structurally related subset of transcripts that bound to Hel-N1. Approximately 10% of the proteins encoded by these subset mRNAs were identifiable in the data bases and most are implicated in cell growth regulation. This approach provides a means to gain access to novel genes expressed in various cell types by partitioning mRNAs containing common sequence elements using RNA-binding proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Dubnick M., Kerlavage A. R., Moreno R., Kelley J. M., Utterback T. R., Nagle J. W., Fields C., Venter J. C. Sequence identification of 2,375 human brain genes. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):632–634. doi: 10.1038/355632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams M. D., Kelley J. M., Gocayne J. D., Dubnick M., Polymeropoulos M. H., Xiao H., Merril C. R., Wu A., Olde B., Moreno R. F. Complementary DNA sequencing: expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1651–1656. doi: 10.1126/science.2047873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley C. T., Jr, Wilkinson K. D., Reines D., Warren S. T. FMR1 protein: conserved RNP family domains and selective RNA binding. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):563–566. doi: 10.1126/science.7692601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd C. G., Swanson M. S., Görlach M., Dreyfuss G. Primary structures of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2, B1, and C2 proteins: a diversity of RNA binding proteins is generated by small peptide inserts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9788–9792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carper S. W., Rocheleau T. A., Storm F. K. cDNA sequence of a human heat shock protein HSP27. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6457–6457. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Yen T. J. Multiple determinants of eukaryotic mRNA stability. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B., Fried M. The structure of the human intron-containing S8 ribosomal protein gene and determination of its chromosomal location at 1p32-p34.1. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):68–75. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré B., Leffers H., Madsen P., Rasmussen H. H., Vandekerckhove J., Celis J. E. Molecular cloning and expression of a transformation-sensitive human protein containing the TPR motif and sharing identity to the stress-inducible yeast protein STI1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8485–8491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez F., Campos-Ortega J. A. A region of the Drosophila genome necessary for CNS development. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):310–312. doi: 10.1038/282310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpinski B. A., Morle G. D., Huggenvik J., Uhler M. D., Leiden J. M. Molecular cloning of human CREB-2: an ATF/CREB transcription factor that can negatively regulate transcription from the cAMP response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4820–4824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Tsai D. E., Keene J. D. Exploring molecular diversity with combinatorial shape libraries. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. J., Baker B. S. The Drosophila gene rbp9 encodes a protein that is a member of a conserved group of putative RNA binding proteins that are nervous system-specific in both flies and humans. J Neurosci. 1993 Mar;13(3):1045–1056. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-01045.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King P. H., Levine T. D., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Keene J. D. Mammalian homologs of Drosophila ELAV localized to a neuronal subset can bind in vitro to the 3' UTR of mRNA encoding the Id transcriptional repressor. J Neurosci. 1994 Apr;14(4):1943–1952. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-04-01943.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike K., Urata Y., Goto S. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the cDNA encoding human 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (lipoamide). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1963–1967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine T. D., Gao F., King P. H., Andrews L. G., Keene J. D. Hel-N1: an autoimmune RNA-binding protein with specificity for 3' uridylate-rich untranslated regions of growth factor mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3494–3504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser E., Leung T., Salihuddin H., Tan L., Lim L. A non-receptor tyrosine kinase that inhibits the GTPase activity of p21cdc42. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):364–367. doi: 10.1038/363364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marusich M. F., Weston J. A. Identification of early neurogenic cells in the neural crest lineage. Dev Biol. 1992 Feb;149(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90285-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzawa Y., Miyauchi T., Hamanoue M., Ando S., Yoshida J., Takao S., Shimazu H., Adachi M., Muramatsu T. A novel core protein as well as polymorphic epithelial mucin carry peanut agglutinin binding sites in human gastric carcinoma cells: sequence analysis and examination of gene expression. J Biochem. 1992 Nov;112(5):609–615. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattheakis L., Vu L., Sor F., Nomura M. Retroregulation of the synthesis of ribosomal proteins L14 and L24 by feedback repressor S8 in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):448–452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. T., Schiller D. L., Franke W. W. Sequence analysis of cytoplasmic mRNA-binding proteins of Xenopus oocytes identifies a family of RNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogue-Geile K., Geiser J. R., Shu M., Miller C., Wool I. G., Meisler A. I., Pipas J. M. Ribosomal protein genes are overexpressed in colorectal cancer: isolation of a cDNA clone encoding the human S3 ribosomal protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3842–3849. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Blau H. M. Genetic complementation reveals a novel regulatory role for 3' untranslated regions in growth and differentiation. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):903–917. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90579-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Conboy M. J., Rando T. A., Blau H. M. Tumor suppression by RNA from the 3' untranslated region of alpha-tropomyosin. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1107–1117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90320-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. D., Roufa D. J. A cloned human ribosomal protein gene functions in rodent cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3767–3774. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinow S., Campos A. R., Yao K. M., White K. The elav gene product of Drosophila, required in neurons, has three RNP consensus motifs. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1570–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.3144044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shay J. W., Baba T., Zhan Q. M., Kamimura N., Cuthbert J. A. HeLaTG cells have mitochondrial DNA inserted into the c-myc oncogene. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1869–1874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C., Hille A., Seidel J., Rijnbout S., Waheed A., Schmidt B., Geuze H., von Figura K. Cloning and expression of human steroid-sulfatase. Membrane topology, glycosylation, and subcellular distribution in BHK-21 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13865–13872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokoe D., Engel K., Campbell D. G., Cohen P., Gaestel M. Identification of MAPKAP kinase 2 as a major enzyme responsible for the phosphorylation of the small mammalian heat shock proteins. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 30;313(3):307–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian Q., Streuli M., Saito H., Schlossman S. F., Anderson P. A polyadenylate binding protein localized to the granules of cytolytic lymphocytes induces DNA fragmentation in target cells. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):629–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai D. E., Harper D. S., Keene J. D. U1-snRNP-A protein selects a ten nucleotide consensus sequence from a degenerate RNA pool presented in various structural contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4931–4936. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton R. P., Struhl G. RNA regulatory elements mediate control of Drosophila body pattern by the posterior morphogen nanos. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):955–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90368-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Friedlander P., Lamoureux C., Zannis-Hadjopoulos M., Price G. B. cDNA clones contain autonomous replication activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 23;1174(3):241–257. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90193-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Allen E., Marsh B., Mohandas T., Wang N., Taggart R. T., Shapiro L. J. Cloning and expression of steroid sulfatase cDNA and the frequent occurrence of deletions in STS deficiency: implications for X-Y interchange. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90447-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




