Abstract
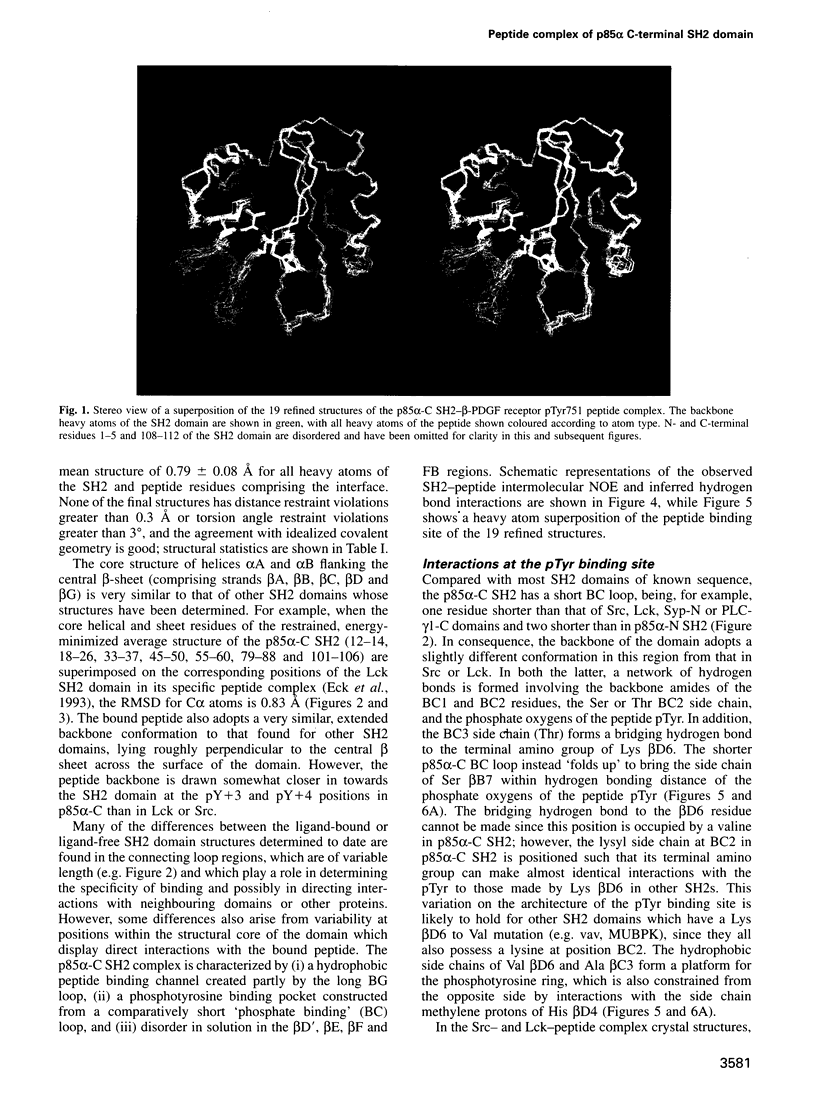
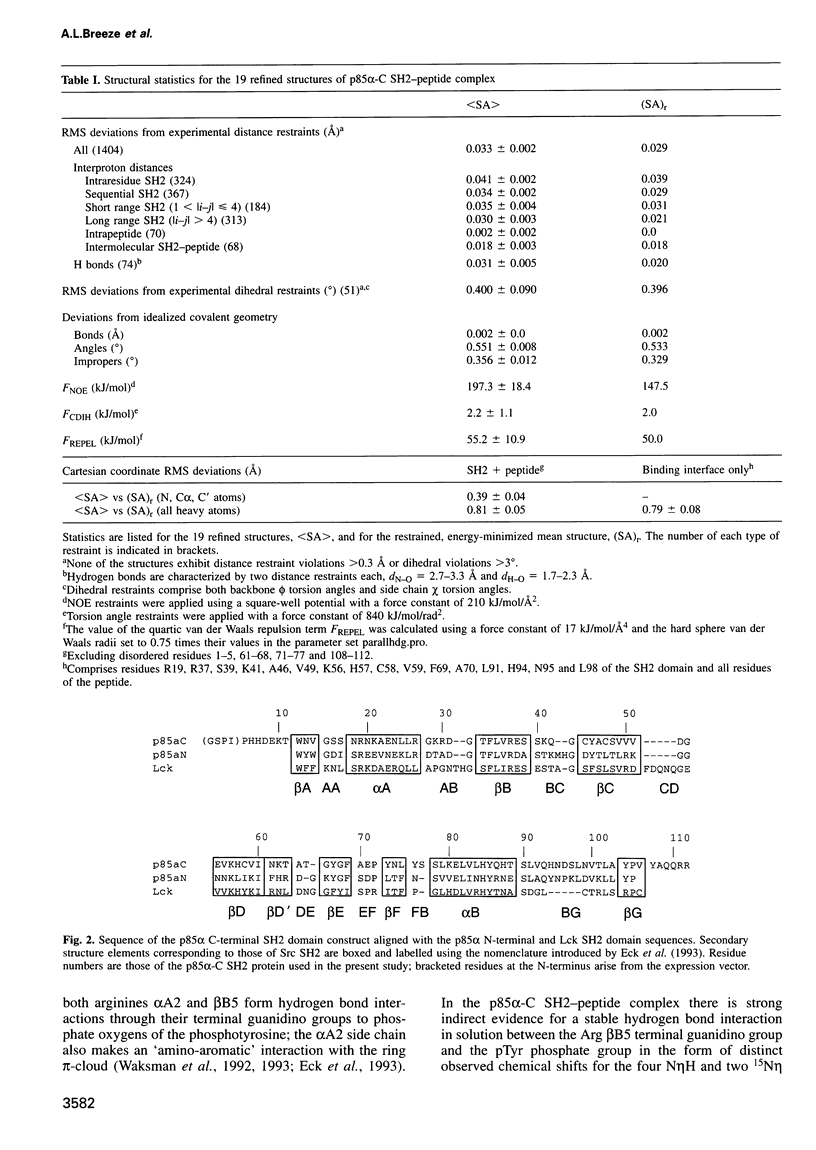
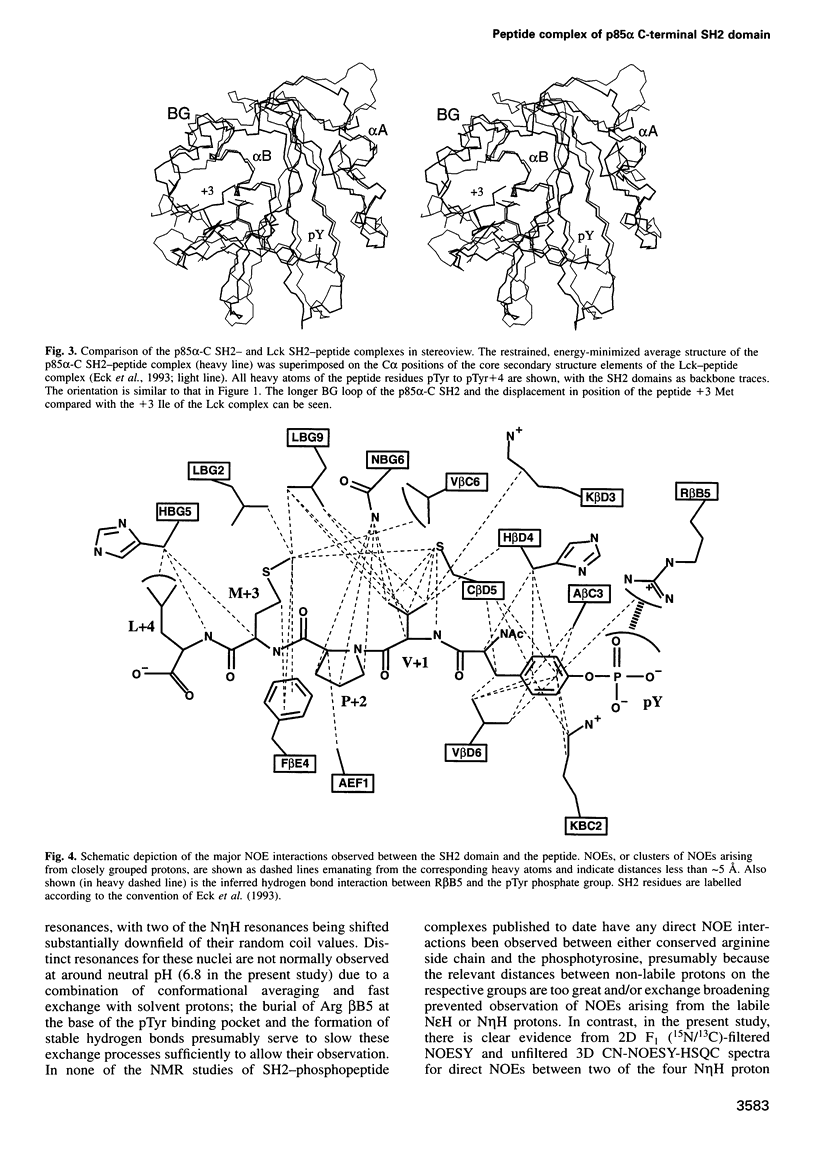
We have determined the solution structure of the C-terminal SH2 domain of the p85 alpha subunit of human phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase (EC 2.7.1.137) in complex with a phosphorylated tyrosine pentapeptide sequence from the platelet-derived growth factor receptor using heteronuclear nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Overall, the structure is similar to other SH2 domain complexes, but displays different detail interactions within the phosphotyrosine binding site and in the recognition site for the +3 methionine residue of the peptide, the side chain of which inserts into a particularly deep and narrow pocket which is displaced relative to that of other SH2 domains. The contacts made within this +3 pocket provide the structural basis for the strong selection for methionine at this position which characterizes the SH2 domains of PI3-kinase. Comparison with spectral and structural features of the uncomplexed domain shows that the long BG loop becomes less mobile in the presence of the bound peptide. In contrast, extreme resonance broadening encountered for most residues in the beta D', beta E and beta F strands and associated connecting loops of the domain in the absence of peptide persists in the complex, implying conformational averaging in this part of the molecule on a microsecond-to-millisecond time scale.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booker G. W., Breeze A. L., Downing A. K., Panayotou G., Gout I., Waterfield M. D., Campbell I. D. Structure of an SH2 domain of the p85 alpha subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):684–687. doi: 10.1038/358684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham S. A., Waxham M. N., Arrate P. M., Brock T. A. Interaction of the Flt-1 tyrosine kinase receptor with the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mapping of a novel site involved in binding. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20254–20257. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing A. K., Driscoll P. C., Harvey T. S., Dudgeon T. J., Smith B. O., Baron M., Campbell I. D. Solution structure of the fibrin binding finger domain of tissue-type plasminogen activator determined by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):821–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eck M. J., Shoelson S. E., Harrison S. C. Recognition of a high-affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide by the Src homology-2 domain of p56lck. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):87–91. doi: 10.1038/362087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Kaplan D. R., Kavanaugh W. M., Turck C. W., Williams L. T. A phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase binds to platelet-derived growth factor receptors through a specific receptor sequence containing phosphotyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzesiek S., Bax A. Amino acid type determination in the sequential assignment procedure of uniformly 13C/15N-enriched proteins. J Biomol NMR. 1993 Mar;3(2):185–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00178261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatada M. H., Lu X., Laird E. R., Green J., Morgenstern J. P., Lou M., Marr C. S., Phillips T. B., Ram M. K., Theriault K. Molecular basis for interaction of the protein tyrosine kinase ZAP-70 with the T-cell receptor. Nature. 1995 Sep 7;377(6544):32–38. doi: 10.1038/377032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensmann M., Booker G. W., Panayotou G., Boyd J., Linacre J., Waterfield M., Campbell I. D. Phosphopeptide binding to the N-terminal SH2 domain of the p85 alpha subunit of PI 3'-kinase: a heteronuclear NMR study. Protein Sci. 1994 Jul;3(7):1020–1030. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiles I. D., Otsu M., Volinia S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Dhand R., Panayotou G., Ruiz-Larrea F., Thompson A., Totty N. F. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: structure and expression of the 110 kd catalytic subunit. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90166-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel U., Harvey T. S., Driscoll P. C., Campbell I. D. Human epidermal growth factor. High resolution solution structure and comparison with human transforming growth factor alpha. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 5;227(1):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90697-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapeller R., Cantley L. C. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Bioessays. 1994 Aug;16(8):565–576. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashishian A., Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Phosphorylation sites in the PDGF receptor with different specificities for binding GAP and PI3 kinase in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1373–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Fantl W. J., Williams L. T. The C-terminal SH2 domain of p85 accounts for the high affinity and specificity of the binding of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1451–1459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Hu Q., Williams L. T. A region of the 85-kilodalton (kDa) subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binds the 110-kDa catalytic subunit in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5560–5566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Kominos D., Jacques S., Margolis B., Schlessinger J., Shoelson S. E., Kuriyan J. Crystal structures of peptide complexes of the amino-terminal SH2 domain of the Syp tyrosine phosphatase. Structure. 1994 May 15;2(5):423–438. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Givol D., Yarden Y. Interkinase domain of kit contains the binding site for phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):678–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Driscoll P. C., Kay L. E., Wingfield P. T., Bax A., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Overcoming the overlap problem in the assignment of 1H NMR spectra of larger proteins by use of three-dimensional heteronuclear 1H-15N Hartmann-Hahn-multiple quantum coherence and nuclear Overhauser-multiple quantum coherence spectroscopy: application to interleukin 1 beta. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6150–6156. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narula S. S., Yuan R. W., Adams S. E., Green O. M., Green J., Philips T. B., Zydowsky L. D., Botfield M. C., Hatada M., Laird E. R. Solution structure of the C-terminal SH2 domain of the human tyrosine kinase Syk complexed with a phosphotyrosine pentapeptide. Structure. 1995 Oct 15;3(10):1061–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00242-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A., Sharp K. A., Honig B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins. 1991;11(4):281–296. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilges M., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M. Determination of three-dimensional structures of proteins from interproton distance data by hybrid distance geometry-dynamical simulated annealing calculations. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 14;229(2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overduin M., Rios C. B., Mayer B. J., Baltimore D., Cowburn D. Three-dimensional solution structure of the src homology 2 domain of c-abl. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90437-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotou G., Gish G., End P., Truong O., Gout I., Dhand R., Fry M. J., Hiles I., Pawson T., Waterfield M. D. Interactions between SH2 domains and tyrosine-phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor sequences: analysis of kinetic parameters by a novel biosensor-based approach. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3567–3576. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascal S. M., Singer A. U., Gish G., Yamazaki T., Shoelson S. E., Pawson T., Kay L. E., Forman-Kay J. D. Nuclear magnetic resonance structure of an SH2 domain of phospholipase C-gamma 1 complexed with a high affinity binding peptide. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petros A. M., Kawai M., Luly J. R., Fesik S. W. Conformation of two non-immunosuppressive FK506 analogs when bound to FKBP by isotope-filtered NMR. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 24;308(3):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81300-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccione E., Case R. D., Domchek S. M., Hu P., Chaudhuri M., Backer J. M., Schlessinger J., Shoelson S. E. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p85 SH2 domain specificity defined by direct phosphopeptide/SH2 domain binding. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3197–3202. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piotto M., Saudek V., Sklenár V. Gradient-tailored excitation for single-quantum NMR spectroscopy of aqueous solutions. J Biomol NMR. 1992 Nov;2(6):661–665. doi: 10.1007/BF02192855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Bardelli A., Maina F., Longati P., Panayotou G., Dhand R., Waterfield M. D., Comoglio P. M. A novel recognition motif for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding mediates its association with the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4600–4608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedijk M., Liu X., van der Geer P., Letwin K., Waterfield M. D., Hunter T., Pawson T. Tyr721 regulates specific binding of the CSF-1 receptor kinase insert to PI 3'-kinase SH2 domains: a model for SH2-mediated receptor-target interactions. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1365–1372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Kominos D., Robertson S. C., Pant N., Baltimore D., Birge R. B., Cowburn D., Hanafusa H., Mayer B. J., Overduin M. Crystal structure of the phosphotyrosine recognition domain SH2 of v-src complexed with tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):646–653. doi: 10.1038/358646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Shoelson S. E., Pant N., Cowburn D., Kuriyan J. Binding of a high affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide to the Src SH2 domain: crystal structures of the complexed and peptide-free forms. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):779–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90405-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu R. X., Word J. M., Davis D. G., Rink M. J., Willard D. H., Jr, Gampe R. T., Jr Solution structure of the human pp60c-src SH2 domain complexed with a phosphorylated tyrosine pentapeptide. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 21;34(7):2107–2121. doi: 10.1021/bi00007a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]