Abstract
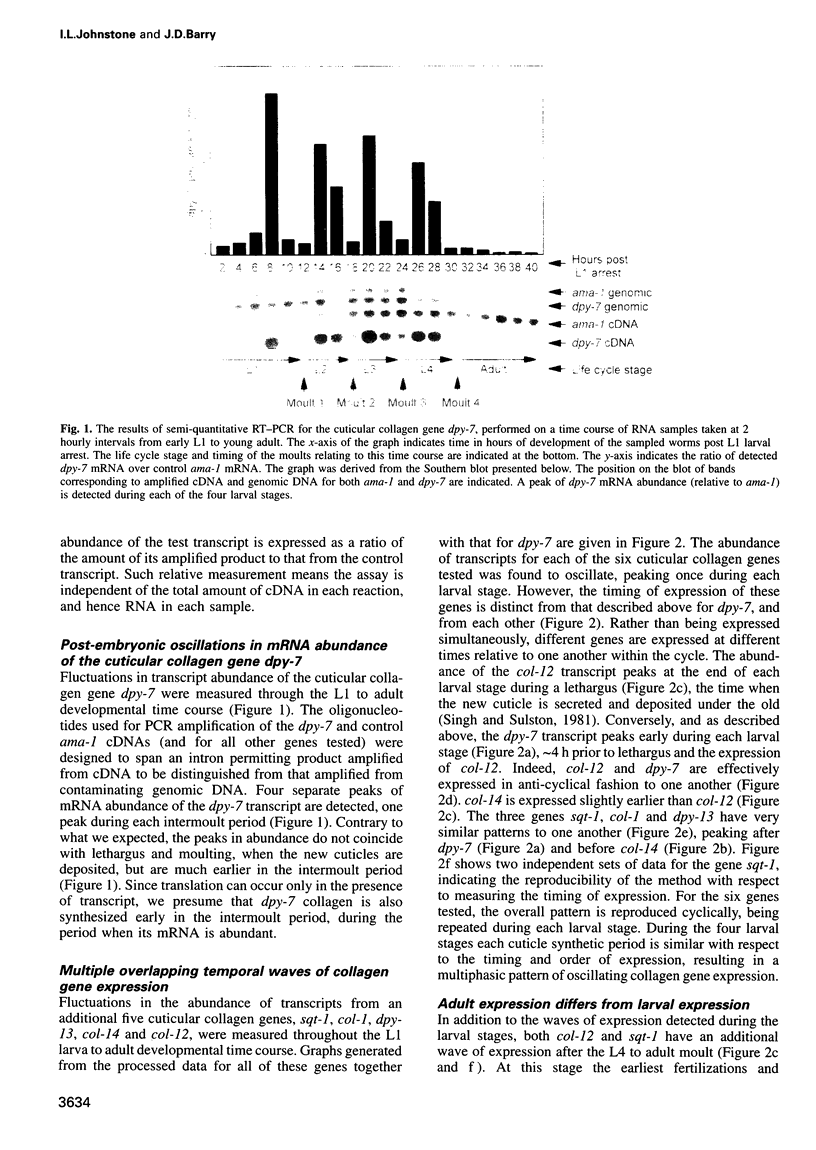
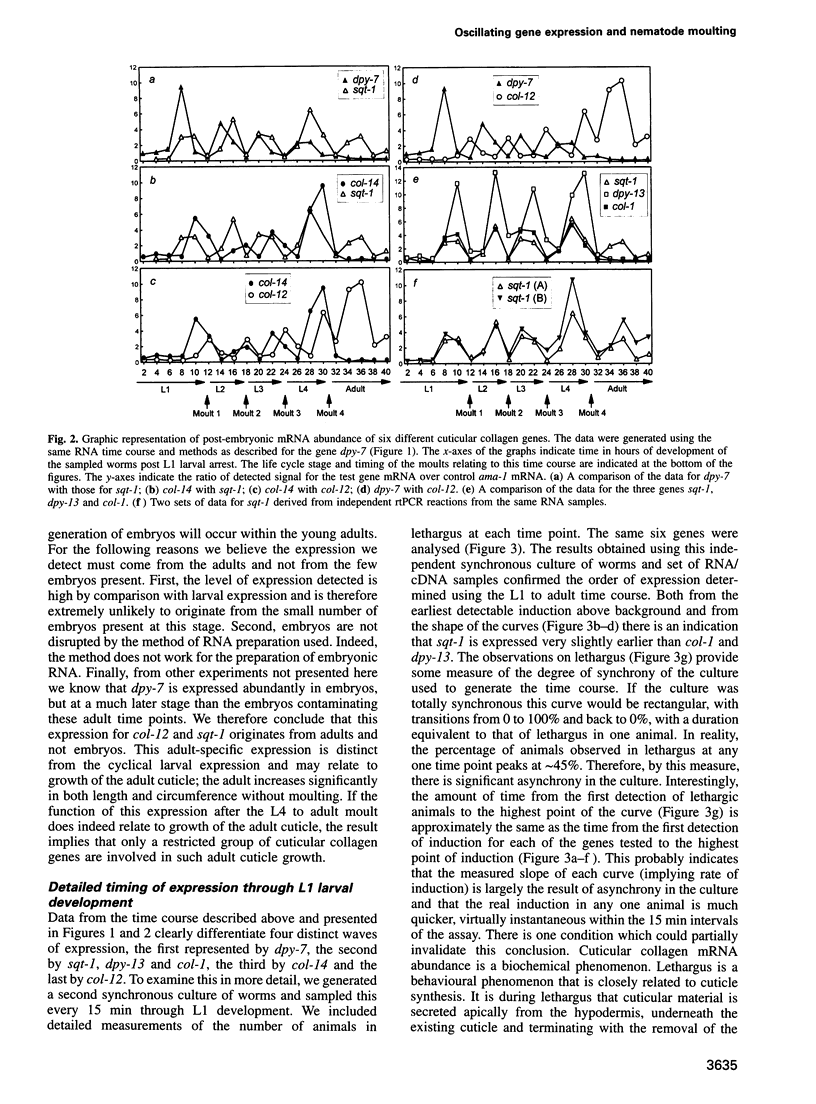
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is contained within a multifunctional exoskeleton, the cuticle, that contains a large number of distinct collagens. As the nematode proceeds from the egg through four larval stages to the adult, transition between larval stages is marked by synthesis of a new cuticle and subsequent moulting of the old one. This is a cyclically repeated developmental event, frequently described as the moulting cycle. We have examined the temporal expression of a group of six genes encoding distinct cuticular collagens. As expected, mRNA abundance for each of the six genes tested is found to oscillate, peaking once during each larval stage. Unexpectedly, the periods of abundance for each gene do not coincide, different genes being expressed at different times relative to one another within the moulting cycle. We detect a programme of temporally distinct waves of collagen gene expression, the precise pattern of which is repeated during each of the four larval stages. This multiphasic pattern of oscillating cuticular collagen gene expression indicates an unexpected complexity of temporal control during the nematode moulting cycle and has implications for collagen trimerization and cuticle synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akam M. The molecular basis for metameric pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1987 Sep;101(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V. A hierarchy of regulatory genes controls a larva-to-adult developmental switch in C. elegans. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V., Horvitz H. R. Heterochronic mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1984 Oct 26;226(4673):409–416. doi: 10.1126/science.6494891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V., Moss E. G. Heterochronic genes and the temporal control of C. elegans development. Trends Genet. 1994 Apr;10(4):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird D. M., Riddle D. L. Molecular cloning and sequencing of ama-1, the gene encoding the largest subunit of Caenorhabditis elegans RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4119–4130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. N., Fields C., Kramer J. M., Rosenzweig B., Hirsh D. Sequence comparisons of developmentally regulated collagen genes of Caenorhabditis elegans. Gene. 1989;76(2):331–344. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. N., Kramer J. M., Hirsh D. Number and organization of collagen genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2389–2395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. N., Kusch M., Edgar R. S. Cuticle of Caenorhabditis elegans: its isolation and partial characterization. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):7–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. N., Staprans S., Edgar R. S. The cuticle of Caenorhabditis elegans. II. Stage-specific changes in ultrastructure and protein composition during postembryonic development. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):456–470. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90204-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W., Martinez Arias A. Boundaries and fields in early embryos. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90467-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone I. L., Shafi Y., Barry J. D. Molecular analysis of mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans collagen gene dpy-7. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3857–3863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone I. L. The cuticle of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: a complex collagen structure. Bioessays. 1994 Mar;16(3):171–178. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M., Cox G. N., Hirsh D. Comparisons of the complete sequences of two collagen genes from Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):599–606. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M., French R. P., Park E. C., Johnson J. J. The Caenorhabditis elegans rol-6 gene, which interacts with the sqt-1 collagen gene to determine organismal morphology, encodes a collagen. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2081–2089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M. Genetic analysis of extracellular matrix in C. elegans. Annu Rev Genet. 1994;28:95–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.28.120194.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M., Johnson J. J., Edgar R. S., Basch C., Roberts S. The sqt-1 gene of C. elegans encodes a collagen critical for organismal morphogenesis. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M. Structures and functions of collagens in Caenorhabditis elegans. FASEB J. 1994 Mar 1;8(3):329–336. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.3.8143939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R. Hox genes in vertebrate development. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larminie C. G., Johnstone I. L. Isolation and characterization of four developmentally regulated cathepsin B-like cysteine protease genes from the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. DNA Cell Biol. 1996 Jan;15(1):75–82. doi: 10.1089/dna.1996.15.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mello C. C., Kramer J. M., Stinchcomb D., Ambros V. Efficient gene transfer in C.elegans: extrachromosomal maintenance and integration of transforming sequences. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3959–3970. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04966.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouazana R., Herbage D. Biochemical characterization of the cuticle collagen of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 28;669(2):236–243. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park Y. S., Kramer J. M. Tandemly duplicated Caenorhabditis elegans collagen genes differ in their modes of splicing. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90360-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politz J. C., Edgar R. S. Overlapping stage-specific sets of numerous small collagenous polypeptides are translated in vitro from Caenorhabditis elegans RNA. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):853–860. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J. E., Horvitz H. R. Post-embryonic cell lineages of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1977 Mar;56(1):110–156. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Meyerowitz E. M. The ABCs of floral homeotic genes. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90291-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Mende N., Bird D. M., Albert P. S., Riddle D. L. dpy-13: a nematode collagen gene that affects body shape. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):567–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90215-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]