Abstract
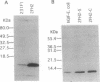
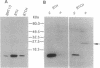
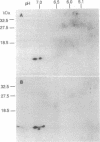
Secretion of bioactive glycosylation-inhibiting factor (GIF) appears to be restricted to suppressor T (Ts) cells, although various human and murine cell line cells secrete the 13-kDa peptide that reacts with anti-GIF. Nucleotide sequences of GIF cDNA from the Ts and non-Ts cells are identical, indicating that bioactive GIF and inactive GIF have an identical amino acid sequence. A stable transfectant of human GIF (hGIF) cDNA in BMT10 cells secretes inactive GIF peptide, whereas transfection of a chimeric cDNA encoding a fusion protein consisting of the N-terminal region of procalcitonin precursor and hGIF into the same cells results in secretion of bioactive GIF. Evidence was obtained that the fusion protein goes into the endoplasmic reticulum and is cleaved for the secretion of mature GIF peptide, whereas the inactive 13-kDa peptide synthesized by the former transfectant does not go through the endoplasmic reticulum. However, a stable transfectant of hGIF cDNA in mouse Ts hybridoma contains inactive GIF in the cytosol and secretes bioactive hGIF without participation of the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi system. Heterogeneity of the 13-kDa hGIF from the transfectant was detected in two-dimensional electrophoresis. The results suggested that Ts cells have a machinery that converts a portion of inactive cytosolic GIF peptide to bioactive GIF during secretion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akasaki M., Jardieu P., Ishizaka K. Immunosuppressive effects of glycosylation inhibiting factor on the IgE and IgG antibody response. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3172–3179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhagen J., Calandra T., Mitchell R. A., Martin S. B., Tracey K. J., Voelter W., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Bucala R. MIF is a pituitary-derived cytokine that potentiates lethal endotoxaemia. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):756–759. doi: 10.1038/365756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. E., Pan K. M., Huang Z., Baldwin M., Fletterick R. J., Prusiner S. B. Structural clues to prion replication. Science. 1994 Apr 22;264(5158):530–531. doi: 10.1126/science.7909169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M., Kuchroo V. K., Whitters M. J., O'Hara R. M., Jr, Kelleher K., Kubo R. T., Dorf M. E. Expression of functional alpha beta T cell receptor gene rearrangements in suppressor T cell hybridomas correlates with antigen binding, but not with suppressor cell function. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2809–2819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomi H., Tagaya Y., Nakano T., Mikayama T., Ishizaka K. Antigen-binding glycosylation inhibiting factor from a human T-cell hybridoma specific for bee venom phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K. Regulation of IgE synthesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:159–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Adachi M., Ishizaka K. Antigen-specific T cells that form IgE-potentiating factor, IgG-potentiating factor, and antigen-specific glycosylation-enhancing factor on antigenic stimulation. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2534–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Ishizaka K. Construction of antigen-specific suppressor T cell hybridomas from spleen cells of mice primed for the persistent IgE antibody formation. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3270–3277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardieu P., Akasaki M., Ishizaka K. Carrier-specific suppression of antibody responses by antigen-specific glycosylation-inhibiting factors. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1494–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel J., Bossy-Wetzel E., Radvanyi F., Klagsbrun M., Folkman J., Hanahan D. Neovascularization is associated with a switch to the export of bFGF in the multistep development of fibrosarcoma. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1095–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90033-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanahan A., Williams J. B., Sanders L. K., Nathans D. Growth factor-induced delayed early response genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3919–3929. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. C., Kawagishi M., Mikayama T., Inagaki Y., Takeuchi T., Ohashi H. Processing of a fusion protein by endoprotease in COS-1 cells for secretion of mature peptide by using a chimeric expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8957–8961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikayama T., Nakano T., Gomi H., Nakagawa Y., Liu Y. C., Sato M., Iwamatsu A., Ishii Y., Weiser W. Y., Ishizaka K. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding glycosylation-inhibiting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10056–10060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nagata S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5322–5322. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesch A., Hartmann E., Rohde K., Rubartelli A., Sitia R., Rapoport T. A. A novel pathway for secretory proteins? Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):86–88. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90186-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paralkar V., Wistow G. Cloning the human gene for macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Genomics. 1994 Jan 1;19(1):48–51. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubartelli A., Cozzolino F., Talio M., Sitia R. A novel secretory pathway for interleukin-1 beta, a protein lacking a signal sequence. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1503–1510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08268.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. K., Kuchroo V. K., Kawasaki H., Jayaraman S., Iwata M., Ishizaka K., Dorf M. E. A monoclonal antibody raised to lipomodulin recognizes T suppressor factors in two independent hapten-specific suppressor networks. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2213–2220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagaya Y., Mori A., Ishizaka K. Biochemical characterization of murine glycosylation-inhibiting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9117–9121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P., Gomi H., Takeuchi T., Carini C., Tagaya Y., Ishizaka K. Glycosylation-inhibiting factor from human T cell hybridomas constructed from peripheral blood lymphocytes of a bee venom-sensitive allergic patient. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):729–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser W. Y., Temple P. A., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Remold H. G., Clark S. C., David J. R. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding a human macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7522–7526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C. The prion connection: now in yeast? Science. 1994 Apr 22;264(5158):528–530. doi: 10.1126/science.7909168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]