Abstract
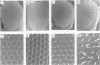
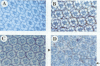
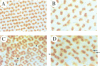
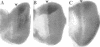
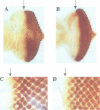
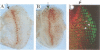
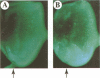
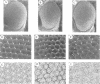
The deregulation of E2F activity is thought to contribute to the uncontrolled proliferation of many tumor cells. While the effects of overexpressing E2F genes have been studied extensively in tissue culture, the consequences of elevating E2F activity in vivo are unknown. To address this issue, transgenic lines of Drosophila were studied in which ectopic expression of dE2F and dDP was targeted to the developing eye. The co-expression of dDP or dE2F disrupted normal eye development, resulting in abnormal patterns of bristles, cone cells and photoreceptors. dE2F/dDP expression caused ectopic S phases in post-mitotic cells of the eye imaginal disc but did not disrupt the onset of neuronal differentiation. Most S phases were seen in uncommitted cells, although some cells that had initiated photo-receptor differentiation were also driven into the cell cycle. Elevated expression of dE2F and dDP caused apoptosis in the eye disc. The co-expression of baculovirus p35 protein, an inhibitor of cell death, strongly enhanced the dE2F/dDP-dependent phenotype. These results show that, in this in vivo system, the elevation of E2F activity caused post-mitotic cells to enter the cell cycle. However, these cells failed to proliferate unless rescued from apoptosis.
Full text
PDF
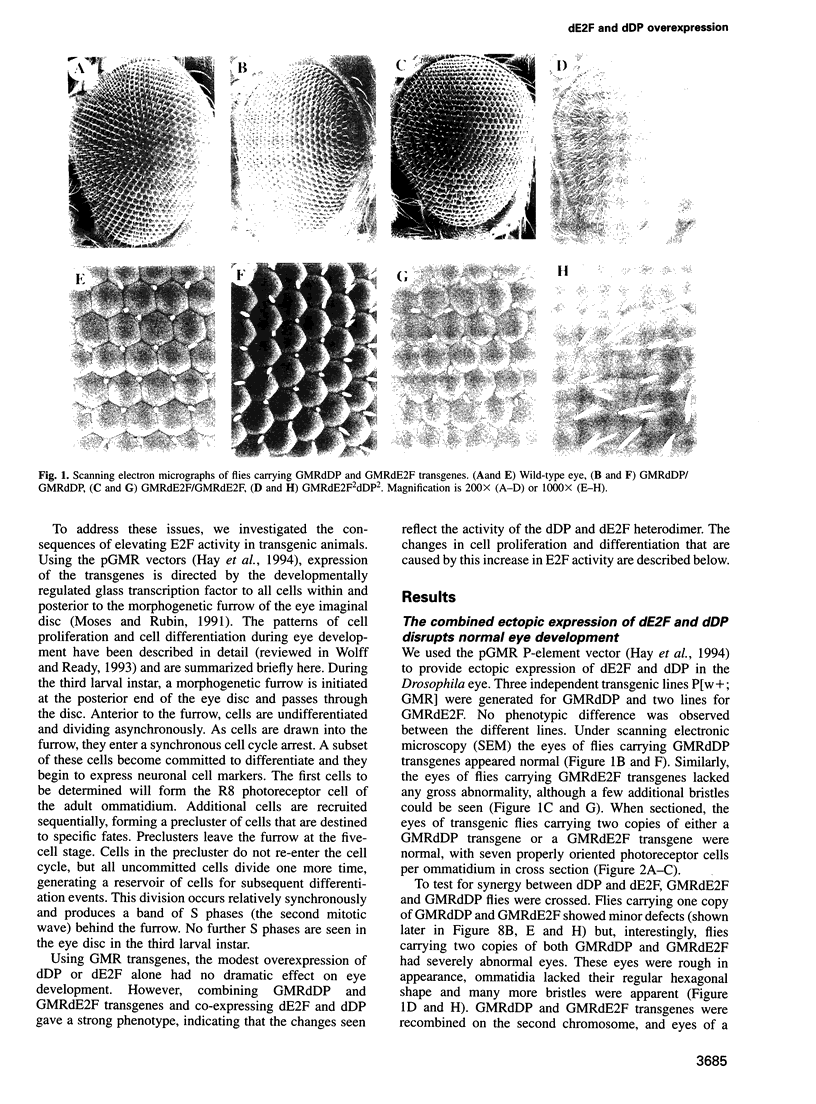

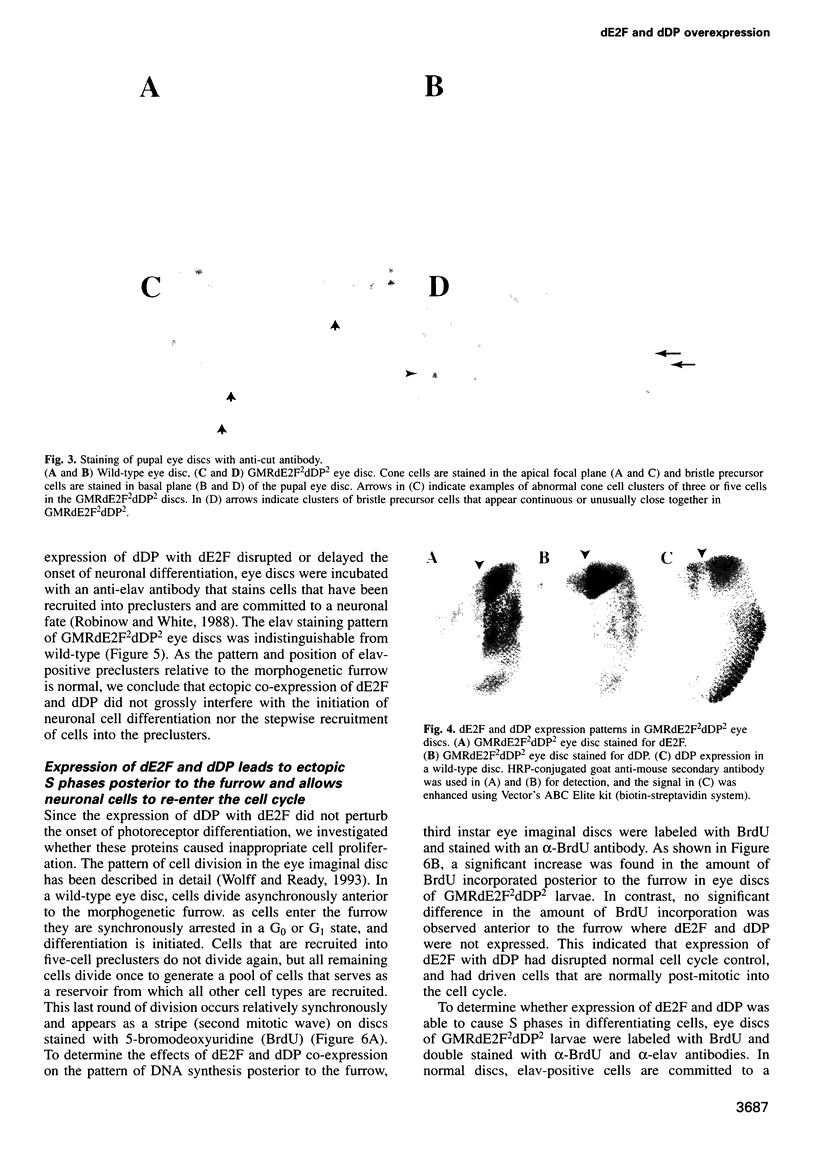
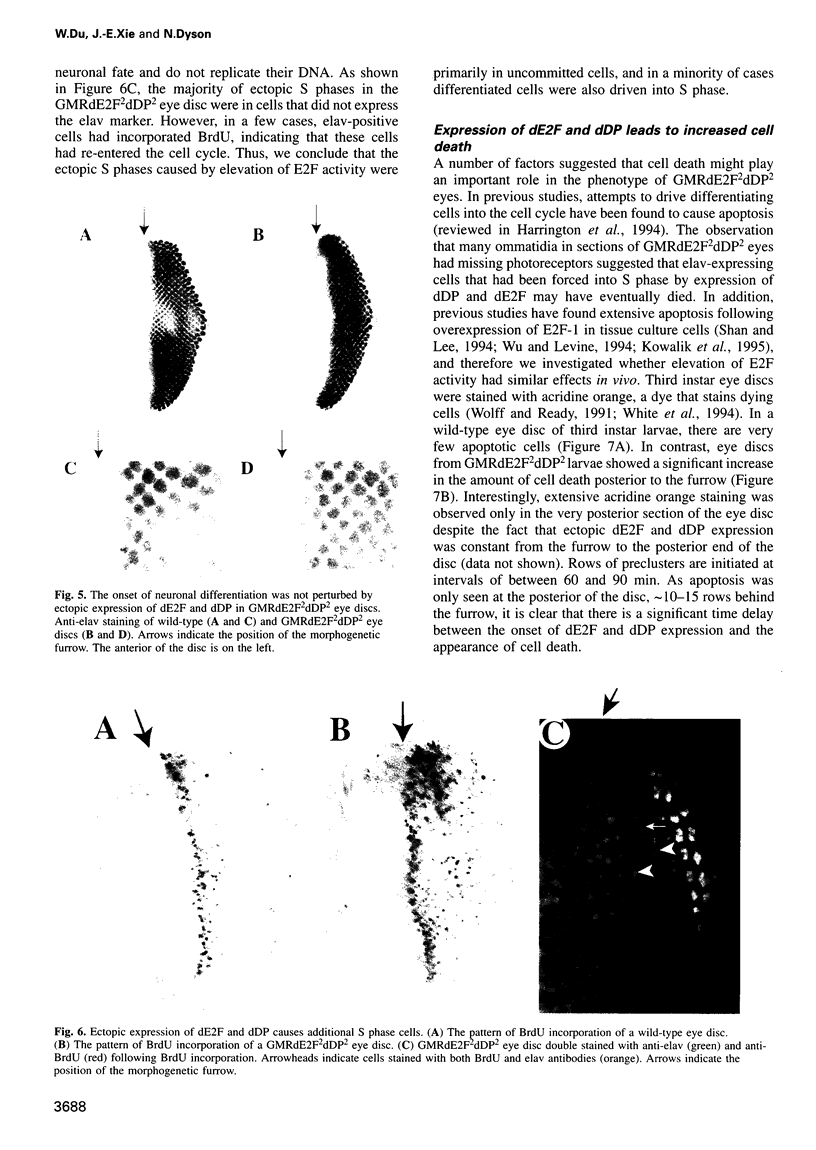
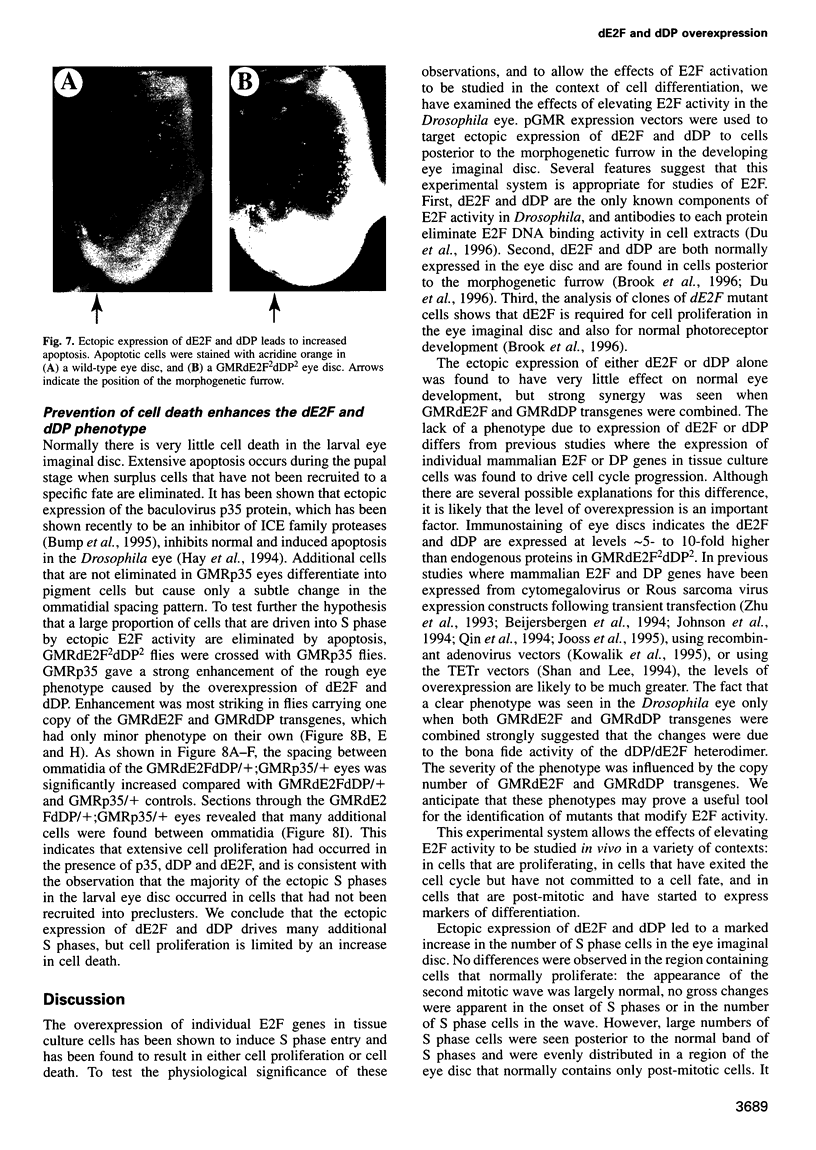


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beijersbergen R. L., Kerkhoven R. M., Zhu L., Carlée L., Voorhoeve P. M., Bernards R. E2F-4, a new member of the E2F gene family, has oncogenic activity and associates with p107 in vivo. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 15;8(22):2680–2690. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.22.2680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Postembryonic patterns of expression of cut, a locus regulating sensory organ identity in Drosophila. Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):441–450. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook A., Xie J. E., Du W., Dyson N. Requirements for dE2F function in proliferating cells and in post-mitotic differentiating cells. EMBO J. 1996 Jul 15;15(14):3676–3683. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bump N. J., Hackett M., Hugunin M., Seshagiri S., Brady K., Chen P., Ferenz C., Franklin S., Ghayur T., Li P. Inhibition of ICE family proteases by baculovirus antiapoptotic protein p35. Science. 1995 Sep 29;269(5232):1885–1888. doi: 10.1126/science.7569933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cagan R. L., Ready D. F. Notch is required for successive cell decisions in the developing Drosophila retina. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1099–1112. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W., Vidal M., Xie J. E., Dyson N. RBF, a novel RB-related gene that regulates E2F activity and interacts with cyclin E in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1996 May 15;10(10):1206–1218. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.10.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio R. J., O'Farrell P. H. Developmental control of a G1-S transcriptional program in Drosophila. Development. 1994 Jun;120(6):1503–1515. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.6.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio R. J., O'Farrell P. H., Xie J. E., Brook A., Dyson N. The transcription factor E2F is required for S phase during Drosophila embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1995 Jun 15;9(12):1445–1455. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.12.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Brook A., Dembski M., Yenush L., Dyson N. DNA-binding and trans-activation properties of Drosophila E2F and DP proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6359–6363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E. K., Speck S. H., Kaelin W. G., Jr E2F-1-mediated transactivation is inhibited by complex formation with the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6914–6918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Vairo G., Chittenden T., Xiao Z. X., Xu G., Wydner K. L., DeCaprio J. A., Lawrence J. B., Livingston D. M. E2F-4, a new member of the E2F transcription factor family, interacts with p107. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 15;8(22):2665–2679. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.22.2665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girling R., Partridge J. F., Bandara L. R., Burden N., Totty N. F., Hsuan J. J., La Thangue N. B. A new component of the transcription factor DRTF1/E2F. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):83–87. doi: 10.1038/362083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan I. K., Hu K. Q., Asha H., Quintanilla A., Ezzell R. M., Settleman J. Characterization of rho GTPase family homologues in Drosophila melanogaster: overexpressing Rho1 in retinal cells causes a late developmental defect. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):292–302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington E. A., Fanidi A., Evan G. I. Oncogenes and cell death. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):120–129. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay B. A., Wolff T., Rubin G. M. Expression of baculovirus P35 prevents cell death in Drosophila. Development. 1994 Aug;120(8):2121–2129. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.8.2121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He J., Allen J. R., Collins V. P., Allalunis-Turner M. J., Godbout R., Day R. S., 3rd, James C. D. CDK4 amplification is an alternative mechanism to p16 gene homozygous deletion in glioma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 15;54(22):5804–5807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Ed H. The retinoblastoma protein as a transcriptional repressor. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;3(2):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90150-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Harlow E., Fattaey A. Inhibition of E2F-1 transactivation by direct binding of the retinoblastoma protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6501–6508. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Lees J. A., Vidal M., Dyson N., Harlow E., Fattaey A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90107-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey-Hoyle M., Conroy R., Huber H. E., Goodhart P. J., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Cloning and characterization of E2F-2, a novel protein with the biochemical properties of transcription factor E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7802–7812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Cress W. D., Jakoi L., Nevins J. R. Oncogenic capacity of the E2F1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12823–12827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Schwarz J. K., Cress W. D., Nevins J. R. Expression of transcription factor E2F1 induces quiescent cells to enter S phase. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):349–352. doi: 10.1038/365349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jooss K., Lam E. W., Bybee A., Girling R., Müller R., La Thangue N. B. Proto-oncogenic properties of the DP family of proteins. Oncogene. 1995 Apr 20;10(8):1529–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamb A. Cell-cycle regulators and cancer. Trends Genet. 1995 Apr;11(4):136–140. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., Heberlein U., Rubin G. M. The homeo domain protein rough is expressed in a subset of cells in the developing Drosophila eye where it can specify photoreceptor cell subtype. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):712–727. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalik T. F., DeGregori J., Schwarz J. K., Nevins J. R. E2F1 overexpression in quiescent fibroblasts leads to induction of cellular DNA synthesis and apoptosis. J Virol. 1995 Apr;69(4):2491–2500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.4.2491-2500.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Thangue N. B. DRTF1/E2F: an expanding family of heterodimeric transcription factors implicated in cell-cycle control. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Mar;19(3):108–114. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Saito M., Vidal M., Valentine M., Look T., Harlow E., Dyson N., Helin K. The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7813–7825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses K., Rubin G. M. Glass encodes a site-specific DNA-binding protein that is regulated in response to positional signals in the developing Drosophila eye. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):583–593. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani K., Nevins J. R. Functional properties of a Drosophila homolog of the E2F1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1603–1612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otterson G. A., Kratzke R. A., Coxon A., Kim Y. W., Kaye F. J. Absence of p16INK4 protein is restricted to the subset of lung cancer lines that retains wildtype RB. Oncogene. 1994 Nov;9(11):3375–3378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin X. Q., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr, Adams P. D. Deregulated transcription factor E2F-1 expression leads to S-phase entry and p53-mediated apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10918–10922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H., O'Keefe L. V., Marty T., Saint R. Ectopic cyclin E expression induces premature entry into S phase and disrupts pattern formation in the Drosophila eye imaginal disc. Development. 1995 Oct;121(10):3371–3379. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.10.3371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinow S., White K. The locus elav of Drosophila melanogaster is expressed in neurons at all developmental stages. Dev Biol. 1988 Apr;126(2):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Vidal M., Cobrinik D., Geng Y., Onufryk C., Chen A., Weinberg R. A. E2F-4 and E2F-5, two members of the E2F family, are expressed in the early phases of the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2403–2407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. E., Ichimura K., Reifenberger G., Collins V. P. CDKN2 (p16/MTS1) gene deletion or CDK4 amplification occurs in the majority of glioblastomas. Cancer Res. 1994 Dec 15;54(24):6321–6324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shan B., Lee W. H. Deregulated expression of E2F-1 induces S-phase entry and leads to apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8166–8173. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shan B., Zhu X., Chen P. L., Durfee T., Yang Y., Sharp D., Lee W. H. Molecular cloning of cellular genes encoding retinoblastoma-associated proteins: identification of a gene with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5620–5631. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro G. I., Edwards C. D., Kobzik L., Godleski J., Richards W., Sugarbaker D. J., Rollins B. J. Reciprocal Rb inactivation and p16INK4 expression in primary lung cancers and cell lines. Cancer Res. 1995 Feb 1;55(3):505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P., Wong S. H., Hong W. Overexpression of E2F-1 in rat embryo fibroblasts leads to neoplastic transformation. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3329–3338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Gunning D. A., Cho J., Zipursky L. Cell cycle progression in the developing Drosophila eye: roughex encodes a novel protein required for the establishment of G1. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):1003–1014. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90440-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Ready D. F. Cell fate in the Drosophila ommatidium. Dev Biol. 1987 Sep;123(1):264–275. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K., Grether M. E., Abrams J. M., Young L., Farrell K., Steller H. Genetic control of programmed cell death in Drosophila. Science. 1994 Apr 29;264(5159):677–683. doi: 10.1126/science.8171319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff T., Ready D. F. Cell death in normal and rough eye mutants of Drosophila. Development. 1991 Nov;113(3):825–839. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.3.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. L., Zukerberg L. R., Ngwu C., Harlow E., Lees J. A. In vivo association of E2F and DP family proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2536–2546. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Levine A. J. p53 and E2F-1 cooperate to mediate apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3602–3606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wölfel T., Hauer M., Schneider J., Serrano M., Wölfel C., Klehmann-Hieb E., De Plaen E., Hankeln T., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Beach D. A p16INK4a-insensitive CDK4 mutant targeted by cytolytic T lymphocytes in a human melanoma. Science. 1995 Sep 1;269(5228):1281–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.7652577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., van den Heuvel S., Helin K., Fattaey A., Ewen M., Livingston D., Dyson N., Harlow E. Inhibition of cell proliferation by p107, a relative of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1111–1125. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]