Abstract
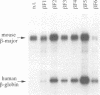
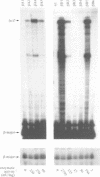
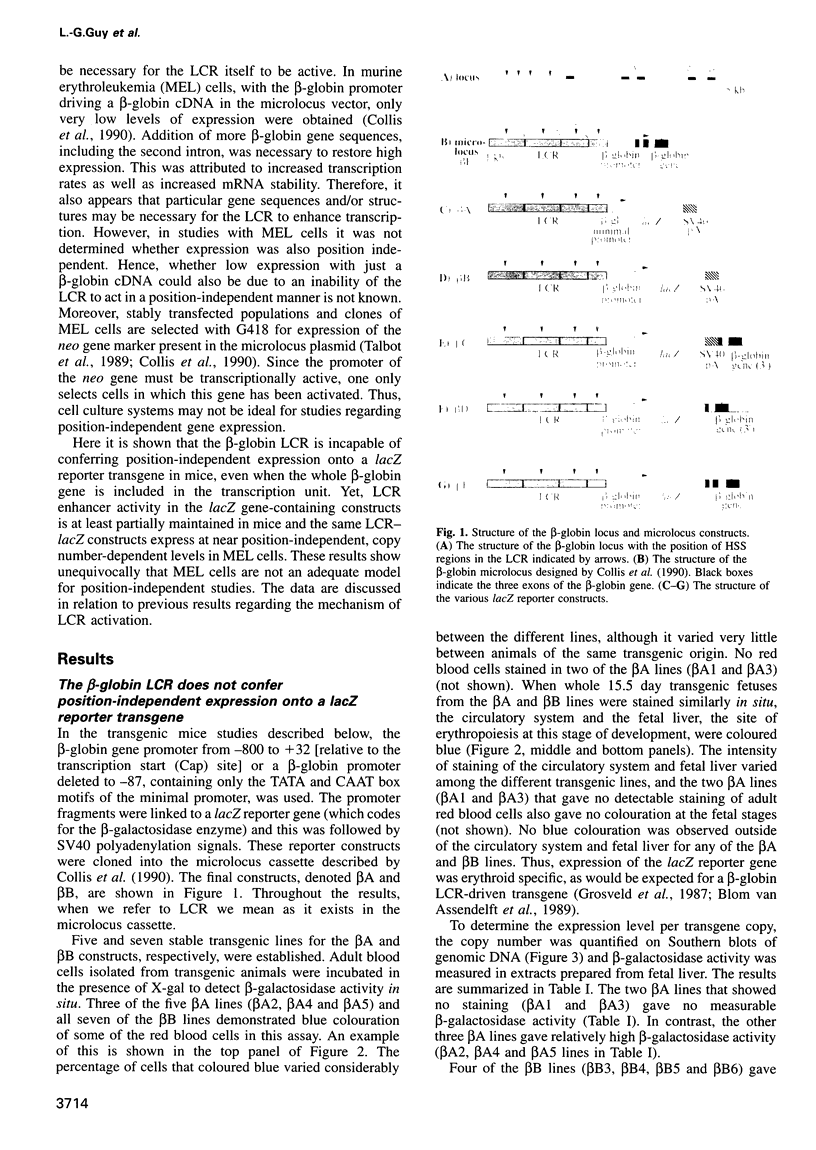
The beta-globin locus control region (LCR) confers high levels of position-independent, copy number-dependent expression onto globin transgenes. Here > 40 independent transgenic mouse lines and founders that carried the LCR in cis with the beta-globin gene promoter driving a lacZ reporter gene were studied. Expression of the lacZ transgene was assayed by measuring beta-galactosidase enzyme activity in fetal liver extracts, the levels of which correlated with the quantity of lacZ mRNA determined using RNase protection assays. Unexpectedly, expression of the lacZ transgene was found to show strong position effects, varying as much as 700-fold per transgene copy. These position effects occurred even if the whole beta-globin gene was incorporated as part of the lacZ reporter gene. Moreover, DNase I-hypersensitive sites appeared in the transgene LCR in high expressing but not in low expressing lines, suggesting that the LCR itself was position dependent. In contrast, MEL cell clones, in which transcriptionally active integration sites were selected for, gave < 13-fold variation in expression per copy of an LCR-lacZ construct. These results show that the lacZ reporter affects the ability of the LCR to activate chromatin in mice and that culture cells are not an adequate model for position-independent gene expression studies.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behringer R. R., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D., Townes T. M. Two 3' sequences direct adult erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7056–7060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom van Assendelft G., Hanscombe O., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. The beta-globin dominant control region activates homologous and heterologous promoters in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90630-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifer C., Yannoutsos N., Krüger G., Grosveld F., Sippel A. E. Dissection of the locus control function located on the chicken lysozyme gene domain in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 11;22(20):4202–4210. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.20.4202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulikas T. Relation between carcinogenesis, chromatin structure and poly(ADP-ribosylation) (review). Anticancer Res. 1991 Mar-Apr;11(2):489–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Bernier G., Mathieu M., Rossant J., Kothary R. The mouse dystonia musculorum gene is a neural isoform of bullous pemphigoid antigen 1. Nat Genet. 1995 Jul;10(3):301–306. doi: 10.1038/ng0795-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bérard J., Gaboury L., Landers M., De Repentigny Y., Houle B., Kothary R., Bradley W. E. Hyperplasia and tumours in lung, breast and other tissues in mice carrying a RAR beta 4-like transgene. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5570–5580. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chada K., Magram J., Costantini F. An embryonic pattern of expression of a human fetal globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):685–689. doi: 10.1038/319685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis P., Antoniou M., Grosveld F. Definition of the minimal requirements within the human beta-globin gene and the dominant control region for high level expression. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):233–240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini F., Radice G., Magram J., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Papayannopoulou T., Chada K. Developmental regulation of human globin genes in transgenic mice. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:361–370. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delvoye N. L., Destroismaisons N. M., Wall L. A. Activation of the beta-globin promoter by the locus control region correlates with binding of a novel factor to the CAAT box in murine erythroleukemia cells but not in K562 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6969–6983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon N., Grosveld F. Transcriptional regulation of multigene loci: multilevel control. Trends Genet. 1993 Apr;9(4):134–137. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90208-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J., Talbot D., Dillon N., Grosveld F. Synthetic human beta-globin 5'HS2 constructs function as locus control regions only in multicopy transgene concatamers. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):127–134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05638.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J., Tan-Un K. C., Harper A., Michalovich D., Yannoutsos N., Philipsen S., Grosveld F. A dominant chromatin-opening activity in 5' hypersensitive site 3 of the human beta-globin locus control region. EMBO J. 1996 Feb 1;15(3):562–568. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epner E., Kim C. G., Groudine M. What does the locus control region control? Curr Biol. 1992 May;2(5):262–264. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90379-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiering S., Epner E., Robinson K., Zhuang Y., Telling A., Hu M., Martin D. I., Enver T., Ley T. J., Groudine M. Targeted deletion of 5'HS2 of the murine beta-globin LCR reveals that it is not essential for proper regulation of the beta-globin locus. Genes Dev. 1995 Sep 15;9(18):2203–2213. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.18.2203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Epner E., Driscoll M. C., Enver T., Brice M., Papayannopoulou T., Groudine M. A deletion of the human beta-globin locus activation region causes a major alteration in chromatin structure and replication across the entire beta-globin locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1637–1649. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Thompson C., Elder J. T., Groudine M. A developmentally stable chromatin structure in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1359–1363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Wilson F. D., Lang G., Kioussis D. Human CD2 3'-flanking sequences confer high-level, T cell-specific, position-independent gene expression in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90631-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanscombe O., Whyatt D., Fraser P., Yannoutsos N., Greaves D., Dillon N., Grosveld F. Importance of globin gene order for correct developmental expression. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1387–1394. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht A., Laroche T., Strahl-Bolsinger S., Gasser S. M., Grunstein M. Histone H3 and H4 N-termini interact with SIR3 and SIR4 proteins: a molecular model for the formation of heterochromatin in yeast. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):583–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90512-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber M. C., Bosch F. X., Sippel A. E., Bonifer C. Chromosomal position effects in chicken lysozyme gene transgenic mice are correlated with suppression of DNase I hypersensitive site formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 11;22(20):4195–4201. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.20.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez G., Griffiths S. D., Ford A. M., Greaves M. F., Enver T. Activation of the beta-globin locus control region precedes commitment to the erythroid lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10618–10622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. G., Epner E. M., Forrester W. C., Groudine M. Inactivation of the human beta-globin gene by targeted insertion into the beta-globin locus control region. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):928–938. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollias G., Hurst J., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene contains a downstream developmental specific enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5739–5747. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Stamatoyannopoulos J. A. Position independence and proper developmental control of gamma-globin gene expression require both a 5' locus control region and a downstream sequence element. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):6087–6096. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.6087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madisen L., Groudine M. Identification of a locus control region in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus that deregulates c-myc expression in plasmacytoma and Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Genes Dev. 1994 Sep 15;8(18):2212–2226. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.18.2212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Enver T. Targeting gene expression to haemopoietic stem cells: a chromatin-dependent upstream element mediates cell type-specific expression of the stem cell antigen CD34. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 1;14(3):564–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R. X-chromosome inactivation: molecular mechanisms and genetic consequences. Trends Genet. 1994 Jul;10(7):230–235. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Sandgren E. P., Koeller D. M., Brinster R. L. Distal regulatory elements from the mouse metallothionein locus stimulate gene expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5266–5275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipsen S., Talbot D., Fraser P., Grosveld F. The beta-globin dominant control region: hypersensitive site 2. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2159–2167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzina S., Hanscombe O., Whyatt D., Grosveld F., Philipsen S. Hypersensitive site 4 of the human beta globin locus control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1413–1419. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Lee E., Westphal H., Felsenfeld G. An enhancer/locus control region is not sufficient to open chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3990–3998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Lee E., Westphal H., Felsenfeld G. Site-independent expression of the chicken beta A-globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):749–752. doi: 10.1038/348749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Lee E., Westphal H. Function of the upstream hypersensitive sites of the chicken beta-globin gene cluster in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 May 25;23(10):1790–1794. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.10.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G., Garrick D., Wu W., Kearns M., Martin D., Whitelaw E. Position-dependent variegation of globin transgene expression in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5371–5375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatoyannopoulos J. A., Goodwin A., Joyce T., Lowrey C. H. NF-E2 and GATA binding motifs are required for the formation of DNase I hypersensitive site 4 of the human beta-globin locus control region. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 3;14(1):106–116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Collis P., Antoniou M., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring integration site-independent gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):352–355. doi: 10.1038/338352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Philipsen S., Fraser P., Grosveld F. Detailed analysis of the site 3 region of the human beta-globin dominant control region. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2169–2177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Behringer R. R. Human globin locus activation region (LAR): role in temporal control. Trends Genet. 1990 Jul;6(7):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Lingrel J. B., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1715–1723. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudel M., Costantini F. A 3' enhancer contributes to the stage-specific expression of the human beta-globin gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):954–961. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K., Legouy E., Stewart V., Depinho R., Alt F. W. Differential regulation of the N-myc gene in transfected cells and transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2096–2103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlatanova J. S., van Holde K. E. Chromatin loops and transcriptional regulation. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1992;2(3):211–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]