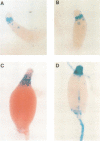
Abstract
A mutant which failed to complete development was isolated from a population of cells that had been subjected to insertional mutagenesis using restriction enzyme-mediated integration. The disrupted gene, dhkA, encodes the conserved motifs of a histidine kinase as well as the response regulator domain. It is likely that the histidine in DhkA is autophosphorylated and the phosphate passed to one or more response regulators. Such two-component systems function in a variety of bacterial signal transduction pathways and have been characterized recently in yeast and Arabidopsis. In Dictyostelium, we found that DhkA functions both in the regulation of prestalk gene expression and in the control of the terminal differentiation of prespore cells.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alex L. A., Simon M. I. Protein histidine kinases and signal transduction in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1994 Apr;10(4):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourret R. B., Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crovello C. S., Furie B. C., Furie B. Histidine phosphorylation of P-selectin upon stimulation of human platelets: a novel pathway for activation-dependent signal transduction. Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):279–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90315-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N. G protein-linked signaling pathways control the developmental program of Dictyostelium. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early A. E., Gaskell M. J., Traynor D., Williams J. G. Two distinct populations of prestalk cells within the tip of the migratory Dictyostelium slug with differing fates at culmination. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):353–362. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante R., Loomis W. F. Whole-mount in situ hybridization of cell-type-specific mRNAs in Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1995 Sep;171(1):262–266. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A. Integration of signaling information in controlling cell-fate decisions in Dictyostelium. Genes Dev. 1995 Jun 15;9(12):1427–1444. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.12.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosnaugh K. L., Loomis W. F. Enhancer regions responsible for temporal and cell-type-specific expression of a spore coat gene in Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1993 May;157(1):38–48. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosnaugh K. L., Loomis W. F. Spore coat genes SP60 and SP70 of Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5215–5218. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskins C., Clark A. M., Aubry L., Segall J. E., Firtel R. A. The Dictyostelium MAP kinase ERK2 regulates multiple, independent developmental pathways. Genes Dev. 1996 Jan 1;10(1):118–128. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskins C., Maeda M., Firtel R. A. Identification and functional analysis of a developmentally regulated extracellular signal-regulated kinase gene in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6996–7012. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Histidine phosphorylation and phosphoryl group transfer in bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):139–143. doi: 10.1038/336139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua J., Chang C., Sun Q., Meyerowitz E. M. Ethylene insensitivity conferred by Arabidopsis ERS gene. Science. 1995 Sep 22;269(5231):1712–1714. doi: 10.1126/science.7569898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jermyn K. A., Duffy K. T., Williams J. G. A new anatomy of the prestalk zone in Dictyostelium. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):144–146. doi: 10.1038/340144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jermyn K. A., Williams J. G. An analysis of culmination in Dictyostelium using prestalk and stalk-specific cell autonomous markers. Development. 1991 Mar;111(3):779–787. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.3.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieber J. J., Rothenberg M., Roman G., Feldmann K. A., Ecker J. R. CTR1, a negative regulator of the ethylene response pathway in Arabidopsis, encodes a member of the raf family of protein kinases. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):427–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90119-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Loomis W. F. Tagging developmental genes in Dictyostelium by restriction enzyme-mediated integration of plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8803–8807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F. Lateral inhibition and pattern formation in Dictyostelium. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1993;28:1–46. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F. The number of developmental genes in Dictyostelium. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1978;14(2):497–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Takekawa M., Saito H. Activation of yeast PBS2 MAPKK by MAPKKKs or by binding of an SH3-containing osmosensor. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.7624781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Wurgler-Murphy S. M., Saito H. A two-component system that regulates an osmosensing MAP kinase cascade in yeast. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):242–245. doi: 10.1038/369242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. K., Richardson D. L., Lee S., Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. Expression of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in prespore cells is sufficient to induce spore cell differentiation in Dictyostelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10561–10565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Magasanik B. Covalent modification of the glnG product, NRI, by the glnL product, NRII, regulates the transcription of the glnALG operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5909–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill J. W., Bier E. Double-label in situ hybridization using biotin and digoxigenin-tagged RNA probes. Biotechniques. 1994 Nov;17(5):870, 874-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota I. M., Varshavsky A. A yeast protein similar to bacterial two-component regulators. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):566–569. doi: 10.1126/science.8211183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Signal transduction schemes of bacteria. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):857–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90267-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. L., Hong C. B., Loomis W. F. A prespore gene, Dd31, expressed during culmination of Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1991 Apr;144(2):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90421-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. L., Loomis W. F., Kimmel A. R. Progression of an inductive signal activates sporulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Development. 1994 Oct;120(10):2891–2900. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.10.2891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster S. C., Noegel A. A., Oehme F., Gerisch G., Simon M. I. The hybrid histidine kinase DokA is part of the osmotic response system of Dictyostelium. EMBO J. 1996 Aug 1;15(15):3880–3889. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Kuspa A., Shaulsky G., Ecke M., Maeda M., Gaskins C., Firtel R. A., Loomis W. F. A MAP kinase necessary for receptor-mediated activation of adenylyl cyclase in Dictyostelium. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(3):405–413. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.3.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Loomis W. F. Cell type regulation in response to expression of ricin A in Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1993 Nov;160(1):85–98. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Loomis W. F. Initial cell type divergence in Dictyostelium is independent of DIF-1. Dev Biol. 1996 Mar 15;174(2):214–220. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout V., Gottesman S. RcsB and RcsC: a two-component regulator of capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):659–669. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.659-669.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Duffy K. T., Lane D. P., McRobbie S. J., Harwood A. J., Traynor D., Kay R. R., Jermyn K. A. Origins of the prestalk-prespore pattern in Dictyostelium development. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1157–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90771-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]