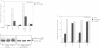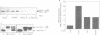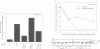Abstract
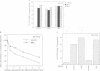
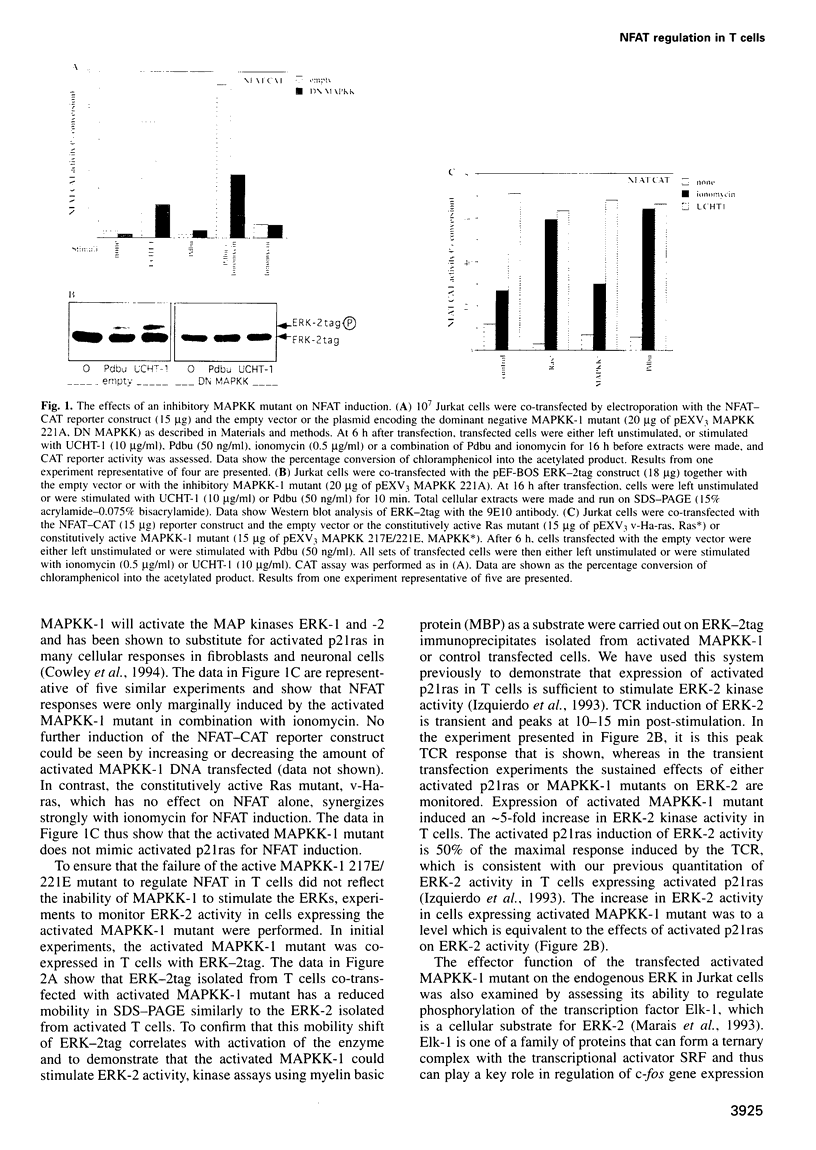
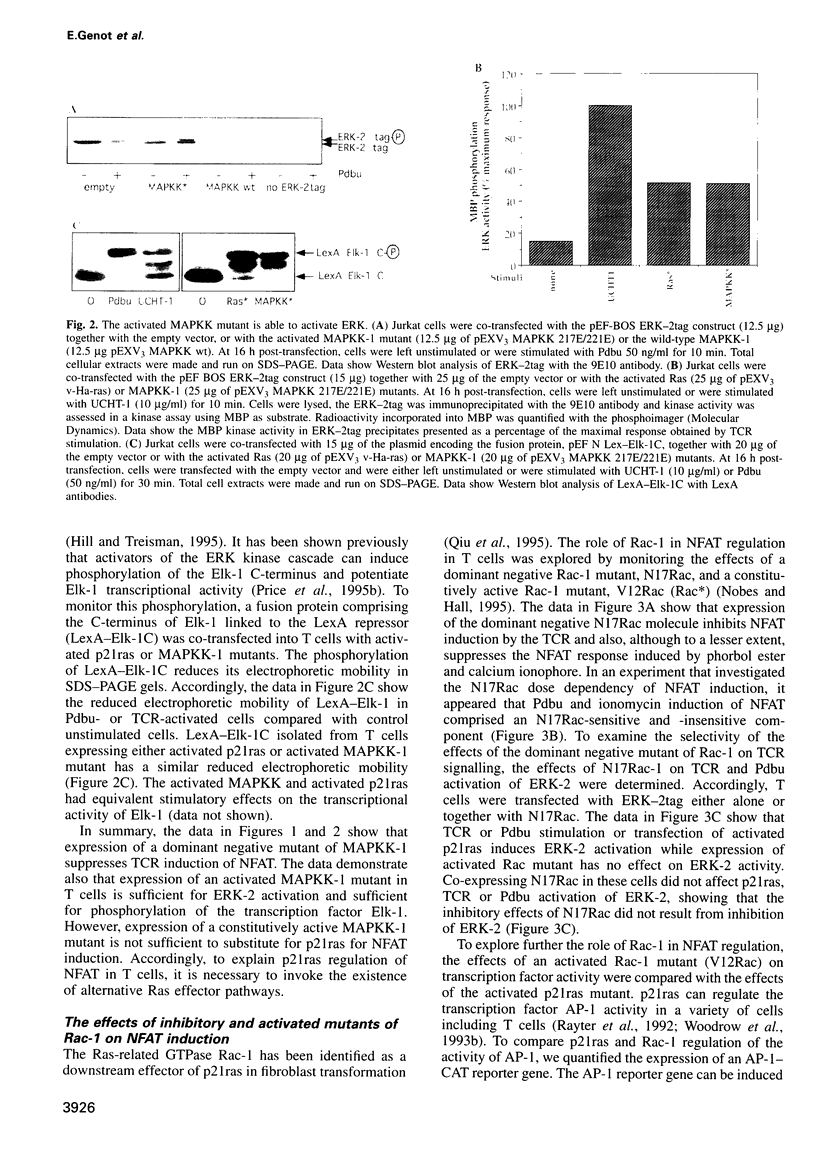
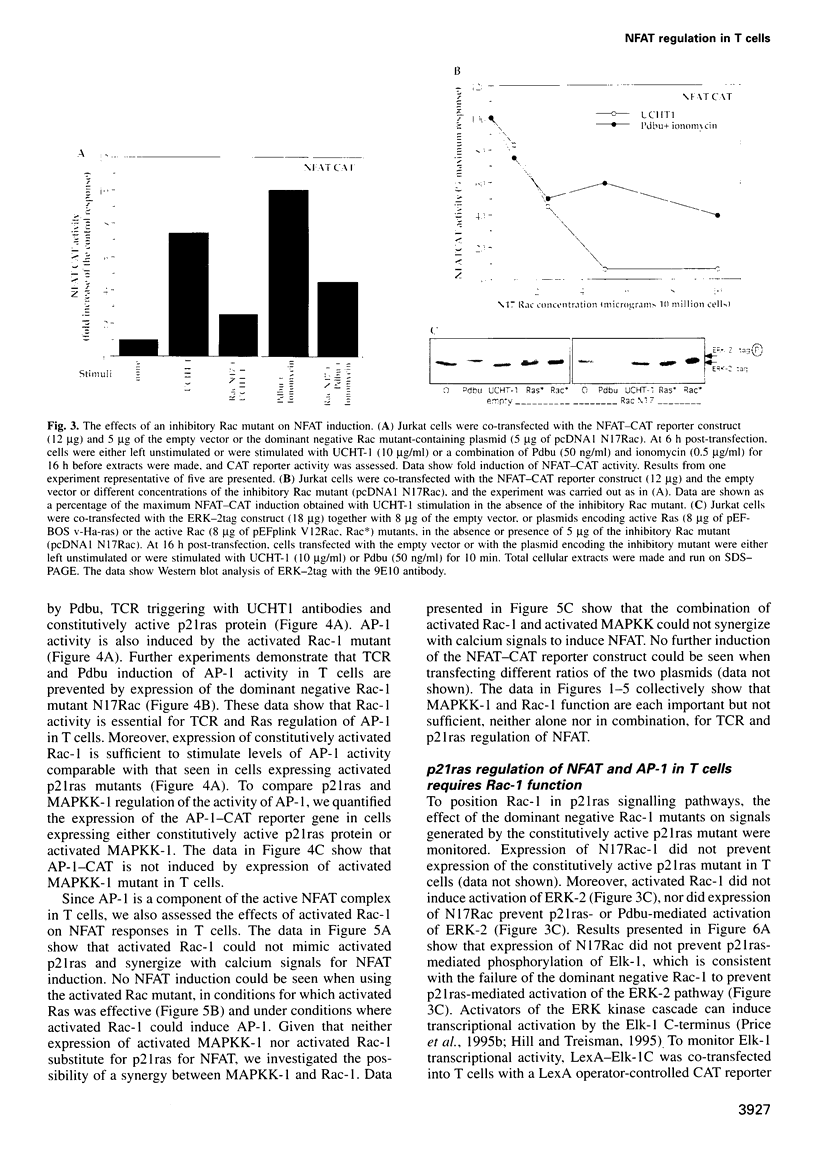
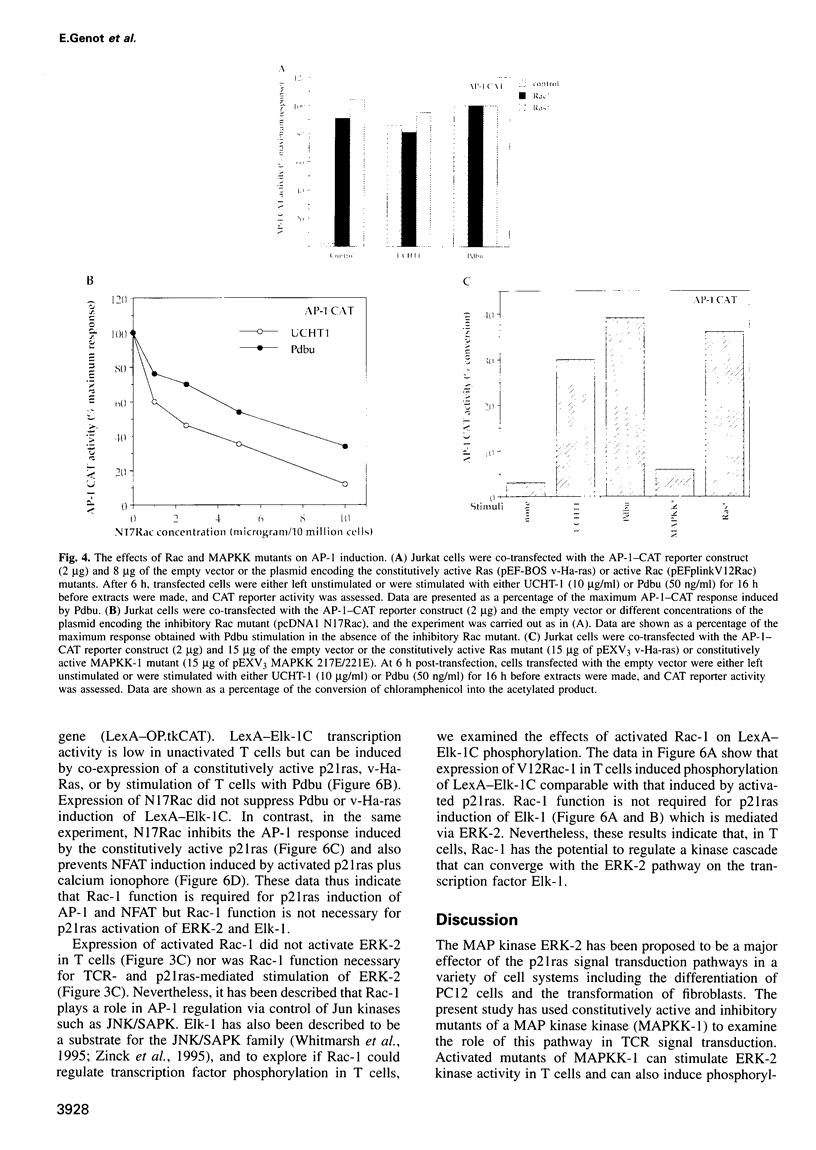
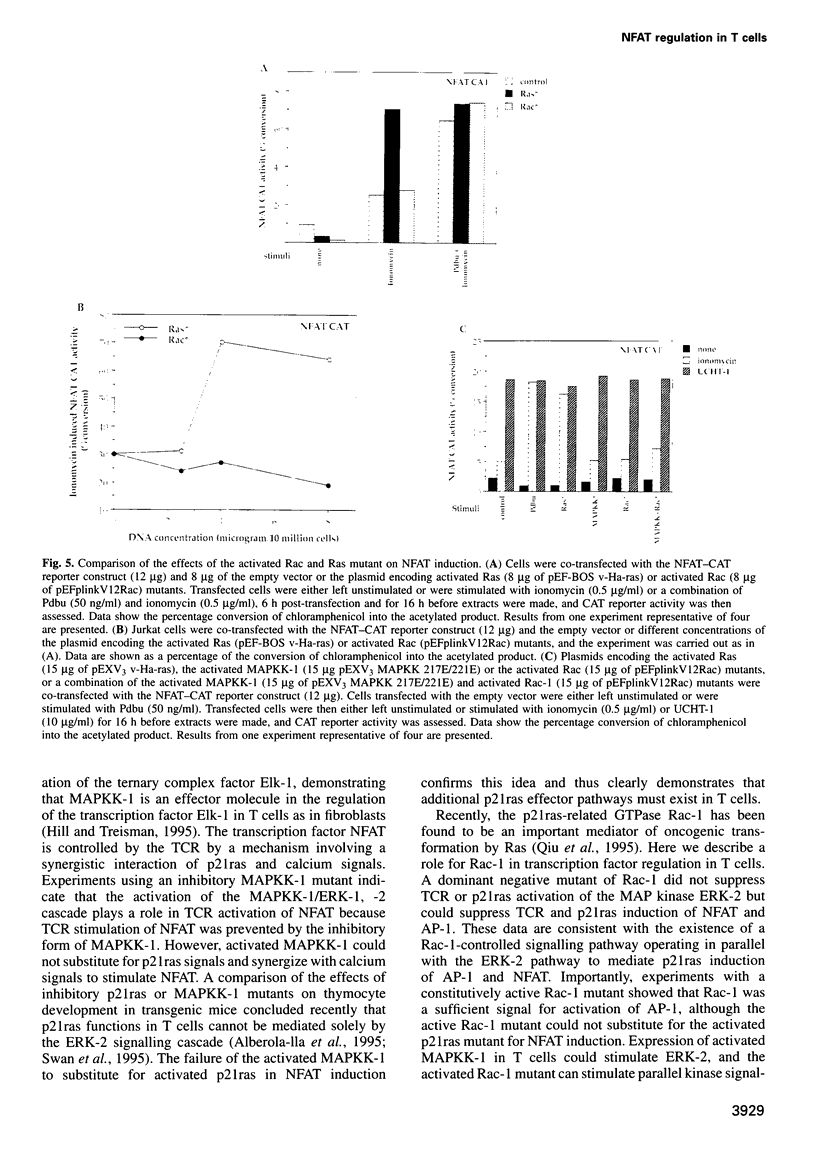
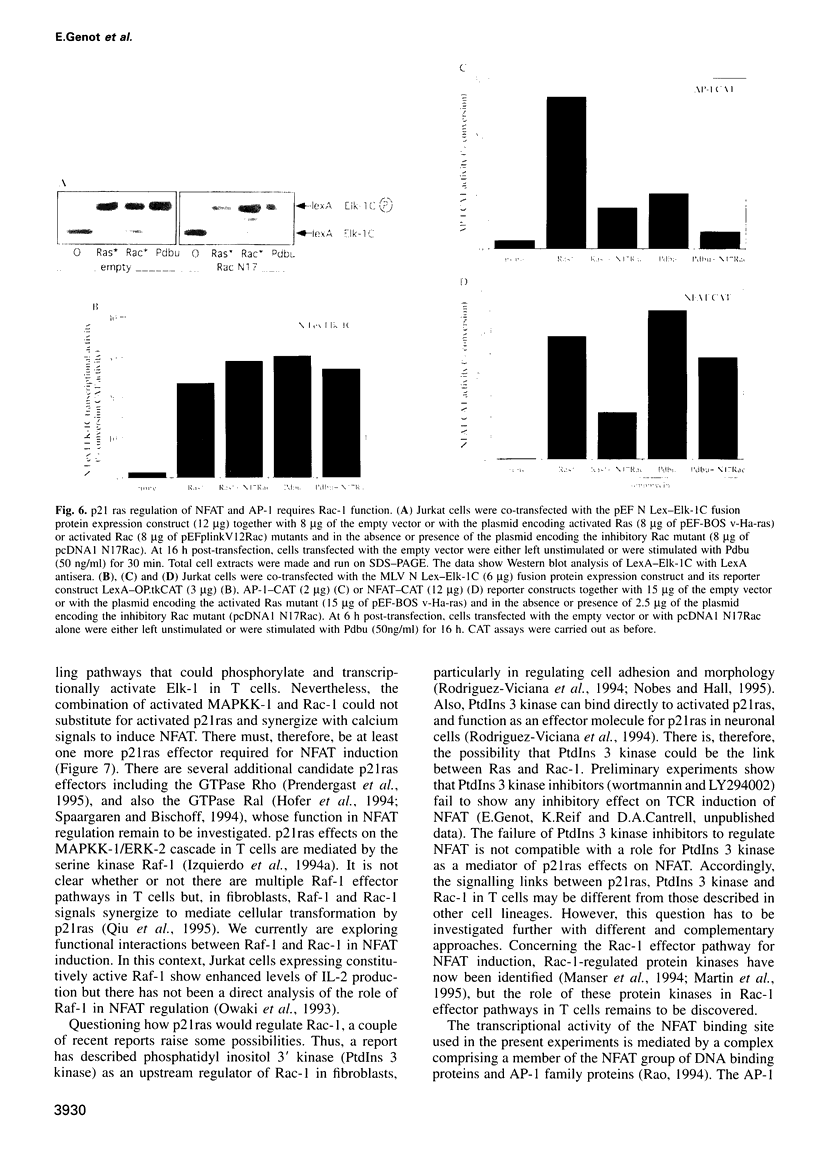
The transcription factor, Nuclear Factor of Activated T cells (NFAT) is a major target for p21ras and calcium signalling pathways in the IL-2 gene and is induced by p21ras signals acting in synergy with calcium/calcineurin signals. One p21ras effector pathway involves the MAP kinase ERK-2, and we have examined its role in NFAT regulation. Expression of dominant negative MAPKK-1 prevents NFAT induction. Constitutively active MAPKK-1 fully activates ERK-2 and the transcription factor Elk-1, but does not substitute for activated p21ras and synergize with calcium/calcineurin signals to induce NFAT. Expression of dominant negative N17Rac also prevents TCR and p21ras activation of NFAT, but without interfering with the ERK-2 pathway. The transcriptional activity of the NFAT binding site is mediated by a complex comprising a member of the NFAT group and AP-1 family proteins. The induction of AP-1 by p21ras also requires Rac-1 function. Activated Rac-1 could mimic activated p21ras to induce AP-1 but not to induce NFAT. Moreover, the combination of activated MAPKK-1 and Rac-1 could not substitute for activated p21ras and synergize with calcium signals to induce NFAT. Thus, p21ras regulation of NFAT in T cells requires the activity of multiple effector pathways including those regulated by MAPKK-1/ERK-2 and Rac-1.
Full text
PDF

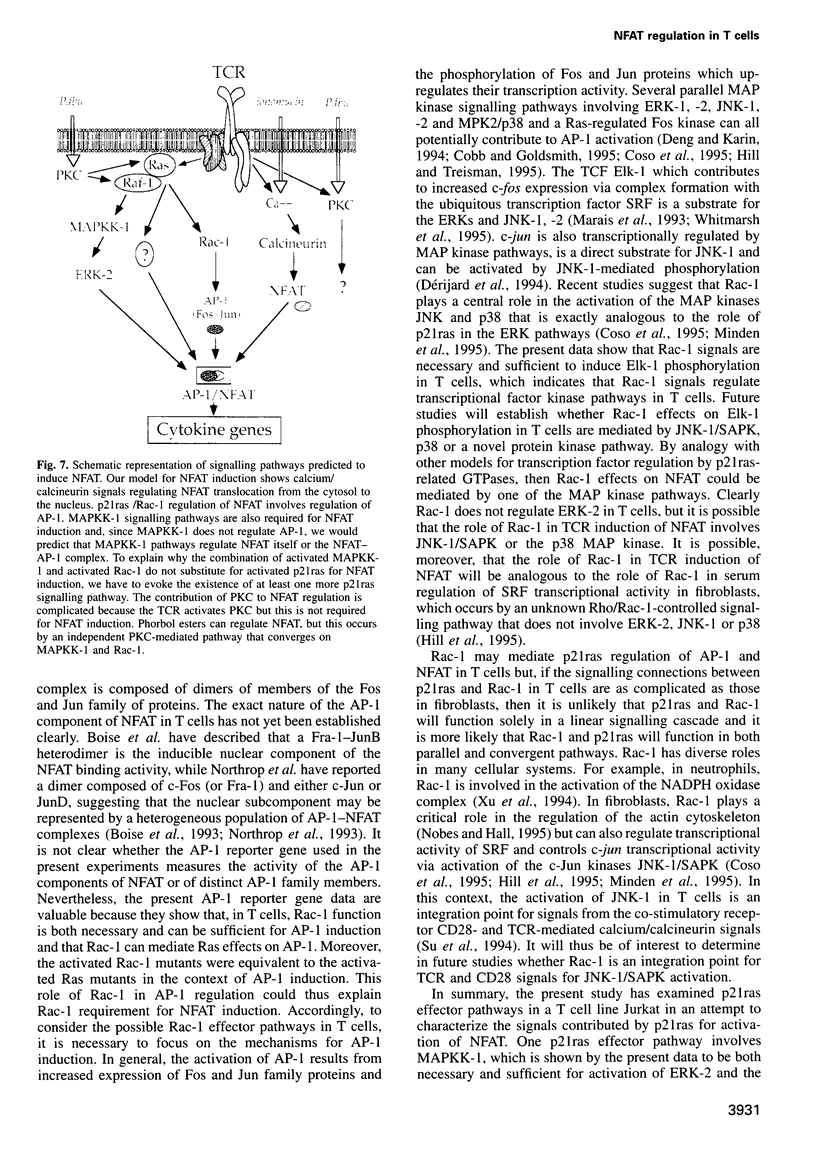


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberola-Ila J., Forbush K. A., Seger R., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Selective requirement for MAP kinase activation in thymocyte differentiation. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):620–623. doi: 10.1038/373620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldari C. T., Macchia G., Telford J. L. Interleukin-2 promoter activation in T-cells expressing activated Ha-ras. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4289–4291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boise L. H., Petryniak B., Mao X., June C. H., Wang C. Y., Lindsten T., Bravo R., Kovary K., Leiden J. M., Thompson C. B. The NFAT-1 DNA binding complex in activated T cells contains Fra-1 and JunB. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1911–1919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Goldsmith E. J. How MAP kinases are regulated. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 23;270(25):14843–14846. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.25.14843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coso O. A., Chiariello M., Yu J. C., Teramoto H., Crespo P., Xu N., Miki T., Gutkind J. S. The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley S., Paterson H., Kemp P., Marshall C. J. Activation of MAP kinase kinase is necessary and sufficient for PC12 differentiation and for transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):841–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng T., Karin M. c-Fos transcriptional activity stimulated by H-Ras-activated protein kinase distinct from JNK and ERK. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):171–175. doi: 10.1038/371171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Corthésy B., Bram R. J., Crabtree G. R. Nuclear association of a T-cell transcription factor blocked by FK-506 and cyclosporin A. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):803–807. doi: 10.1038/352803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genot E. M., Parker P. J., Cantrell D. A. Analysis of the role of protein kinase C-alpha, -epsilon, and -zeta in T cell activation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 28;270(17):9833–9839. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.17.9833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Treisman R. Transcriptional regulation by extracellular signals: mechanisms and specificity. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Wynne J., Treisman R. The Rho family GTPases RhoA, Rac1, and CDC42Hs regulate transcriptional activation by SRF. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1159–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Sun Y. L., Williamson K., Xu X. Isolation of two new members of the NF-AT gene family and functional characterization of the NF-AT proteins. Immunity. 1995 May;2(5):461–472. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer F., Fields S., Schneider C., Martin G. S. Activated Ras interacts with the Ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11089–11093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo Pastor M., Reif K., Cantrell D. The regulation and function of p21ras during T-cell activation and growth. Immunol Today. 1995 Mar;16(3):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo M., Bowden S., Cantrell D. The role of Raf-1 in the regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 by the T cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):401–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo M., Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J., Cantrell D. p21ras couples the T cell antigen receptor to extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 in T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1993 Oct 1;178(4):1199–1208. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.4.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser E., Leung T., Salihuddin H., Zhao Z. S., Lim L. A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):40–46. doi: 10.1038/367040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. MAP kinase kinase kinase, MAP kinase kinase and MAP kinase. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Bollag G., McCormick F., Abo A. A novel serine kinase activated by rac1/CDC42Hs-dependent autophosphorylation is related to PAK65 and STE20. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):1970–1978. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medema R. H., Wubbolts R., Bos J. L. Two dominant inhibitory mutants of p21ras interfere with insulin-induced gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5963–5967. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., Claret F. X., Abo A., Karin M. Selective activation of the JNK signaling cascade and c-Jun transcriptional activity by the small GTPases Rac and Cdc42Hs. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1147–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobes C. D., Hall A. Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrop J. P., Ho S. N., Chen L., Thomas D. J., Timmerman L. A., Nolan G. P., Admon A., Crabtree G. R. NF-AT components define a family of transcription factors targeted in T-cell activation. Nature. 1994 Jun 9;369(6480):497–502. doi: 10.1038/369497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price L. S., Norman J. C., Ridley A. J., Koffer A. The small GTPases Rac and Rho as regulators of secretion in mast cells. Curr Biol. 1995 Jan 1;5(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price M. A., Rogers A. E., Treisman R. Comparative analysis of the ternary complex factors Elk-1, SAP-1a and SAP-2 (ERP/NET). EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2589–2601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu R. G., Chen J., Kirn D., McCormick F., Symons M. An essential role for Rac in Ras transformation. Nature. 1995 Mar 30;374(6521):457–459. doi: 10.1038/374457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao A. NF-ATp: a transcription factor required for the co-ordinate induction of several cytokine genes. Immunol Today. 1994 Jun;15(6):274–281. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayter S. I., Woodrow M., Lucas S. C., Cantrell D. A., Downward J. p21ras mediates control of IL-2 gene promoter function in T cell activation. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4549–4556. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Viciana P., Warne P. H., Dhand R., Vanhaesebroeck B., Gout I., Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D., Downward J. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase as a direct target of Ras. Nature. 1994 Aug 18;370(6490):527–532. doi: 10.1038/370527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J. A nonchromatographic assay for expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in eucaryotic cells. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaargaren M., Bischoff J. R. Identification of the guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator for Ral as a putative effector molecule of R-ras, H-ras, K-ras, and Rap. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12609–12613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su B., Jacinto E., Hibi M., Kallunki T., Karin M., Ben-Neriah Y. JNK is involved in signal integration during costimulation of T lymphocytes. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):727–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan K. A., Alberola-Ila J., Gross J. A., Appleby M. W., Forbush K. A., Thomas J. F., Perlmutter R. M. Involvement of p21ras distinguishes positive and negative selection in thymocytes. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):276–285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij C. L., Guidos C., Crabtree G. R. Cell type specificity and activation requirements for NFAT-1 (nuclear factor of activated T-cells) transcriptional activity determined by a new method using transgenic mice to assay transcriptional activity of an individual nuclear factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15788–15795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warne P. H., Viciana P. R., Downward J. Direct interaction of Ras and the amino-terminal region of Raf-1 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):352–355. doi: 10.1038/364352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Littman D. R. Signal transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmarsh A. J., Shore P., Sharrocks A. D., Davis R. J. Integration of MAP kinase signal transduction pathways at the serum response element. Science. 1995 Jul 21;269(5222):403–407. doi: 10.1126/science.7618106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. H., Woodrow M., Cantrell D. A., Murray E. J. Protein kinase C is not a downstream effector of p21ras in activated T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jan;25(1):42–47. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Barry D. C., Settleman J., Schwartz M. A., Bokoch G. M. Differing structural requirements for GTPase-activating protein responsiveness and NADPH oxidase activation by Rac. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23569–23574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinck R., Cahill M. A., Kracht M., Sachsenmaier C., Hipskind R. A., Nordheim A. Protein synthesis inhibitors reveal differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and stress-activated protein kinase pathways that converge on Elk-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;15(9):4930–4938. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.9.4930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]